Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Aldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)
Загружено:
Irianto Rizaldi Faturrahman0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
116 просмотров29 страницaldehida
Оригинальное название
6. Aldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документaldehida
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
116 просмотров29 страницAldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)
Загружено:
Irianto Rizaldi Faturrahmanaldehida
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 29
Learning Goals
1 Draw the structures and discuss the physical
properties of aldehydes and ketones.
2 From the structures, write the common and
I.U.P.A.C. names of aldehydes and ketones.
3 Write equations for the preparation of
aldehydes and ketones.
4 Write equations representing the oxidation of
carbonyl compounds.
5 Write equations representing the reduction of
carbonyl compounds.
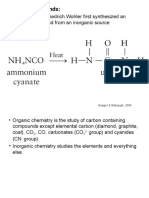
Introduction
Carbonyl compound: Any
compound that contains a
carbonyl group (C=O).
Carbonyl groups are strongly
polarized, with a partial
positive charge on carbon
and partial negative charge
on oxygen.
Carbonyl compound
Polarity of carbonyl group contributes to its reactivity.
C=O bond is shorter, stronger, and more polar than C=C bond
in alkenes.
Carbonyl compounds are broadly divided into two groups:
aldehydes and ketones are in one group and the second group
contains carboxylic acids, esters, acid chlorides and amides.
Nomenclature
Properties
Preparation reactions of Aldehydes and
Ketones
Characteristic reactions of Aldehydes and
Ketones
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Both aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group C=O
- The difference between aldehyde and ketone was found to be:
In aldehyde C=O attach with H and R i.e
In ketone C=O attach with two R
C O
R
R
I.U.P.A.C. Nomenclature and Common Names
1. Determine the parent compound, that is, the longest
continuous carbon chain containing the carbonyl group.
2. Replace the final -e of the parent alkane with -al.
3. Number the chain beginning with the carbonyl carbon
(or aldehyde group) as carbon-1.
4. Number and name all substituents as usual.
Naming Aldehydes
Examples
CH
3
CH
2
CH
CH
3
CH
2
C H
O
CHO
3-methylpentanal
1-cyclopentenemethanal
=>
9
Nomenclature Aldehyde Common Names
The simplest aldehydes are known by their
common names:
formaldehyde, HCHO
acetaldehyde, CH3CHO
benzaldehyde, C6H5CHO
Use the I.U.P.A.C. and common nomenclature systems to name
each of the following compounds.
Common Aldehydes
Formaldehyde, HCHO: Toxic but useful. It kills viruses, fungi
and bacteria. It is used in disinfecting and sterilizing
equipment. The polymerization property of formaldehyde is
utilized in adhesives and for binding plywood.
Acetaldehyde (CH
3
CHO): Sweet smelling. Present in ripe
fruits, especially in apples. It is less toxic than formaldehyde.
Benzaldehyde, C
6
H
5
CHO, is commonly known as almond oil.
It is used in cooking.
Formaldehyde
Gas at room temperature.
Formalin is a 40% aqueous solution.
O
C
O
C
O
C
H
H
H
H
H
H
heat
H C
O
H
H
2
O
H C
H
OH
HO
trioxane, m.p. 62C
formaldehyde,
b.p. -21C
formalin
=>
Naming Ketones
1. The -e ending of the parent alkane is replaced with
the -one suffix of the ketone family.
2. The location of the carbonyl carbon is indicated with a
number.
Examples
CH
3
C
O
CH
CH
3
CH
3
O
Br
CH
3
C
O
CH
CH
3
CH
2
OH
3-methyl-2-butanone
3-bromocyclohexanone
4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butanone
=>
Ketone Common Names
Some ketones are also known by their
common names. These are the names of the
two alkyl groups (usually alphabetized)
bonded to the carbonyl group followed by the
word ketone.
methyl ethyl ketone (MEK)
CH
3
CH
2
COCH
3
acetone CH
3
COCH
3
Use the I.U.P.A.C. and common nomenclature systems to name
each of the following compounds.
Acetone (CH
3
COCH
3
): It is one of the most
widely used solvents. It can dissolve most
organic compounds and is also miscible with
water. Acetone is highly volatile and highly
flammable.
Common Ketones
Boiling Points
More polar, so higher boiling point than
comparable alkane or ether.
Cannot H-bond to each other, so lower
boiling point than comparable alcohol.
=>
Examples
Arrange the following in order of increasing
boiling point.
pentanal
2-pentanol
ethyl isopropyl ether
pentane
Solubility
Good solvent for alcohols.
Lone pair of electrons on oxygen of
carbonyl can accept a hydrogen bond from
O-H or N-H.
Acetone and acetaldehyde are miscible in
water.
=>
Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
Summary of reactions disscussed in earlier chapter that
yield of ketones and aldehydes.
a. Ozonolysis of alkenes
b.Hydration of alkynes
c.Friedel-Crafts acylation of aromatic
d.Oxidaton of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones
e.Other useful methods
Вам также может понравиться
- Chapter 16 - Test Bank Chem 200Документ110 страницChapter 16 - Test Bank Chem 200Jan Chester Chan80% (5)
- P - Aldehydes and Ketones PDFДокумент32 страницыP - Aldehydes and Ketones PDFAyush Srivastava78% (23)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionОт EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Organic Review Study GuideДокумент11 страницOrganic Review Study Guideapi-299996815Оценок пока нет
- Hyrocarbons OwnДокумент22 страницыHyrocarbons OwnRia PerezОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry CurrentДокумент48 страницOrganic Chemistry CurrentBierzo JomarОценок пока нет
- Ketones and Aldehydes2022 Copy 1Документ56 страницKetones and Aldehydes2022 Copy 1Camille SolanaОценок пока нет
- Topic 14. Organic ChemistryДокумент24 страницыTopic 14. Organic ChemistryBashar Abu HijlehОценок пока нет
- Gen - Chem Module 3 PDFДокумент8 страницGen - Chem Module 3 PDFWendellОценок пока нет
- Brady Ch25-Organic Biochem PDFДокумент55 страницBrady Ch25-Organic Biochem PDFAlams Rizan FirdausОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Addition To The Carbonyl GroupДокумент55 страницAldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Addition To The Carbonyl GroupPaul Jhon EugenioОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry ImprovedДокумент47 страницOrganic Chemistry ImprovedRachel Kieda100% (14)
- Module 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydeДокумент62 страницыModule 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydePrincess NavarroОценок пока нет
- Functional GroupsДокумент41 страницаFunctional Groupsapi-239855791Оценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry PPT - Ch. 22 - 11th Grade - II TERM - DeC'23Документ138 страницOrganic Chemistry PPT - Ch. 22 - 11th Grade - II TERM - DeC'23Ana Pamela MejiaОценок пока нет
- Nota Kimia Carbon Compoun Form 5Документ16 страницNota Kimia Carbon Compoun Form 5akusabrina2012Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Aldehydes and KetonesДокумент34 страницыLecture 1 Introduction To Aldehydes and KetonesKoki King100% (1)
- NotesДокумент7 страницNotesAmahОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and Ketones-DSVOLДокумент107 страницAldehydes and Ketones-DSVOLMERCY ATUYAОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3.1-ALKENE PDFДокумент51 страницаChapter 3.1-ALKENE PDFYasserAbyОценок пока нет
- Alkanes: Alkane Homologous Series. The Alkanes Form A Homologous Series. A HydrocarbonДокумент9 страницAlkanes: Alkane Homologous Series. The Alkanes Form A Homologous Series. A HydrocarbonVannah RomasantaОценок пока нет
- Chap 1Документ105 страницChap 1Irfan AzaharОценок пока нет
- Final PPT Aldehydes and KetonesДокумент14 страницFinal PPT Aldehydes and KetonesShireen BatoolОценок пока нет
- Synthesis of Drug - 2Документ44 страницыSynthesis of Drug - 2'Nurirjawati ElRuri KawangОценок пока нет
- HydrocarbonsДокумент11 страницHydrocarbonsCornellius KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Functional GroupДокумент45 страницFunctional Groupmonasteriomatthew7Оценок пока нет
- CH - 8 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsДокумент32 страницыCH - 8 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acidspinkykuku12Оценок пока нет
- Alkanes SlideДокумент14 страницAlkanes Slidevictoryayapaye147Оценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbons 1Документ32 страницыHydrocarbons 1Jocelyn MatigaОценок пока нет
- Aldehyde and Ketones FДокумент70 страницAldehyde and Ketones Fmichelmanirakiza591Оценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Alkanes Alkanes & & Alkanes Alkanes & & Cycloalkanes CycloalkanesДокумент61 страницаOrganic Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Alkanes Alkanes & & Alkanes Alkanes & & Cycloalkanes CycloalkanesRSLОценок пока нет
- Carbon CompoundДокумент61 страницаCarbon CompoundhaslimiОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Organic ChemsitryДокумент36 страницIntroduction To Organic ChemsitryRyanОценок пока нет
- Organic Compounds:: - Alkanes 1828: Friedrich Wohler First Synthesized An Organic Compound From An Inorganic SourceДокумент30 страницOrganic Compounds:: - Alkanes 1828: Friedrich Wohler First Synthesized An Organic Compound From An Inorganic SourcePermana PakpahanОценок пока нет
- Alkenes and AlkynesДокумент46 страницAlkenes and AlkynesshyroneruttoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsДокумент25 страницChemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsSharmini RajagopalОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemistryДокумент59 страницOrganic ChemistryUsmanAntizionistОценок пока нет
- Learner q2 Week 67 Gen - ChemДокумент82 страницыLearner q2 Week 67 Gen - ChemrikrikОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Carbon CompoundДокумент35 страницIntroduction To Carbon CompoundMohd NorihwanОценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbons: Learning OutcomesДокумент32 страницыHydrocarbons: Learning Outcomestrenyce alexanderОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Note Form 5Документ9 страницChemistry Note Form 5SofiyyahOpieОценок пока нет
- Carbon Atom and Organic CompoundsДокумент40 страницCarbon Atom and Organic CompoundsceeОценок пока нет
- Ncert LessonДокумент32 страницыNcert LessonBhagwatОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry 1Документ110 страницOrganic Chemistry 1Mahmoud RslanОценок пока нет
- Final Exam 40% Exams 45% Report 5% Homework 10%Документ74 страницыFinal Exam 40% Exams 45% Report 5% Homework 10%kaleijaОценок пока нет
- Aldehyde PDFДокумент32 страницыAldehyde PDFMalti GuptaОценок пока нет
- Organic Chem 10 SL2023Документ111 страницOrganic Chem 10 SL2023Fadilatu Abdoul ZakouОценок пока нет
- C15 HydrocarbonsДокумент31 страницаC15 HydrocarbonsKris DookharanОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and KetonesДокумент25 страницAldehydes and KetonesPauline Grace CadusaleОценок пока нет
- Week 3 Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesДокумент67 страницWeek 3 Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesNikol BaltazarОценок пока нет
- 2021 1.5 - 1.7 Double Bonded Functional GroupsДокумент27 страниц2021 1.5 - 1.7 Double Bonded Functional GroupsMia PereiraОценок пока нет
- Week 2 - Organic CompoundsДокумент56 страницWeek 2 - Organic CompoundsMorissette GarciaОценок пока нет
- NSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.1 - TsumebДокумент91 страницаNSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.1 - Tsumebsikereteromanus9Оценок пока нет
- Chem 3Документ14 страницChem 3Rhea MandatoОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry - Pertemuan KeduapptДокумент60 страницOrganic Chemistry - Pertemuan Keduapptnadhilah shabrinaОценок пока нет
- Alcoholes 3Документ47 страницAlcoholes 3Дана ЧилибаеваОценок пока нет
- Unit 14 - Organic ChemistryДокумент56 страницUnit 14 - Organic ChemistryRey GoldОценок пока нет
- Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryДокумент40 страницNomenclature of Organic ChemistrySeema YadavОценок пока нет
- Nanay Organic ReviewДокумент45 страницNanay Organic ReviewAimee MangubatОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersОценок пока нет
- Chemical and Physical Properties of Oil and FatsДокумент40 страницChemical and Physical Properties of Oil and FatsAzrin RahmanОценок пока нет
- EJMCM - Volume 7 - Issue 7 - Pages 3481-349Документ11 страницEJMCM - Volume 7 - Issue 7 - Pages 3481-349Wassim LounissiОценок пока нет
- Reagen Penampak Noda KLT PDFДокумент3 страницыReagen Penampak Noda KLT PDFDhani KenОценок пока нет
- Research Progress On Chemical Constituents of ZingДокумент22 страницыResearch Progress On Chemical Constituents of ZingAnisah Rahmah YulianiОценок пока нет
- Special Features of Organoboron Chemistry: Boron Is Electrophilic Because of Its Empty P OrbitalДокумент15 страницSpecial Features of Organoboron Chemistry: Boron Is Electrophilic Because of Its Empty P Orbitalevsgoud_goud100% (2)
- 6 12 Polymers1Документ13 страниц6 12 Polymers1Pedro Moreno de SouzaОценок пока нет
- R315 AbenojaJL HYDROCARBONSДокумент8 страницR315 AbenojaJL HYDROCARBONSJL AbenojaОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction-1 (13Документ1 страницаOxidation and Reduction-1 (13Aditya ChudasamaОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Part 1Документ29 страницCarbohydrate Part 1Des LumabanОценок пока нет
- DGT Organic Compounds C NitrogenДокумент15 страницDGT Organic Compounds C Nitrogensc5753972Оценок пока нет
- InteresterificationДокумент35 страницInteresterificationTram VuОценок пока нет
- Dryer DesignДокумент88 страницDryer DesignRADHESHYAMОценок пока нет
- Table of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature - Master Organic ChemistryДокумент23 страницыTable of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature - Master Organic ChemistryKanika SinghОценок пока нет
- Al KynesДокумент26 страницAl KynesS JОценок пока нет
- Free Materials Form Pharma VisionДокумент10 страницFree Materials Form Pharma VisionRPh Krishna Chandra JagritОценок пока нет
- 11.alcohol, Phenol & Ethers Colour BookletДокумент84 страницы11.alcohol, Phenol & Ethers Colour BookletVishal Malik100% (1)
- Bonding in Carbonyl CompoundsДокумент11 страницBonding in Carbonyl CompoundsRohini SelvarajahОценок пока нет
- Nomanclature Type 1Документ20 страницNomanclature Type 1Vinod Kumar100% (1)
- Substances Listed in EU Directives On Plastics in Contact With FoodДокумент38 страницSubstances Listed in EU Directives On Plastics in Contact With FoodVictor CastrejonОценок пока нет
- 2013 01 20 Le Hong Phong ProfileДокумент10 страниц2013 01 20 Le Hong Phong ProfileQuyen HoangОценок пока нет
- Track2 Full 1Документ86 страницTrack2 Full 1KathyPazmiñoViteriОценок пока нет
- ECДокумент4 страницыECabhishekОценок пока нет
- Syllabus P.G PDFДокумент80 страницSyllabus P.G PDFNancy WaliaОценок пока нет
- Problem 26 Chemical Structure and Absolute Stereochemistry of ConiineДокумент6 страницProblem 26 Chemical Structure and Absolute Stereochemistry of ConiineLê Hoàng MinhОценок пока нет
- Macromolecules 1Документ31 страницаMacromolecules 1api-267079239Оценок пока нет
- Hoccoh H H H: Paper 2 - Structured Questions A) I)Документ7 страницHoccoh H H H: Paper 2 - Structured Questions A) I)Ying LiangОценок пока нет
- Mock Test-Solutions & Halogen DerivativesДокумент3 страницыMock Test-Solutions & Halogen Derivativesshreyaraghuwanshi16Оценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith, ch3Документ29 страницOrganic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith, ch3sungyeon heoОценок пока нет
- Sulfonation Lec 6Документ54 страницыSulfonation Lec 6Zain Ul AbideenОценок пока нет