Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Revisedelectronicsppt 120423011815 Phpapp01
Загружено:
aizienursyafiqahОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Revisedelectronicsppt 120423011815 Phpapp01
Загружено:
aizienursyafiqahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
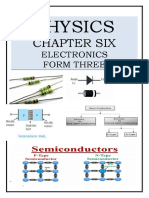
Basic Electrical
&
Electronics
Parameters
Basic elements of electricity
o Conductors - keep loose grip on their
electrons and allow electrons to move freely.
Metals are usually good conductors.
o Insulators - keep close hold of their electrons
and do not allow free movement of electrons.
Glass, wood, plastic, mica, fiberglass and air
are good insulators
Current & Resistance
CURRENT
The flow of electrons
within an electronic
circuit.
Measured in Amperes
Electronic symbol I
Also known as amps.
RESISTANCE
Opposition to the flow of
electrons in an electronic
circuit.
Measured in Ohms
Electronic symbol R
Also represented by Omega
Voltage & Power
VOLTAGE
The potential, or
pushing power, of
electricity available to
a circuit.
Measured in Volts
Electronic symbol E
Also symbolized as V
POWER
The measure of the ability
of an electronic circuit to
accomplish a task.
Measured in Watts
Electronic symbol P
Also symbolized as W
Ohms Law
Ohms Law relates Current (I),
Voltage (E) and Resistance (R)
The relationship can be written three
ways:
E = I x R
I = E / R
R = E/I
Introduction to Passive components
Def: Which does not have any internal
capacity to change energy format from
one form to another .
Resistor Capacitor Inductor
RESISTANCE : OPPOSITION TO THE
FLOW OF ELECTRONS THROUGH A
CONDUCTOR
All materials exhibit some resistance, even
the best of conductors
UNIT OF RESISTANCE IS OHM(S)
TWO PARAMETERS ASSOCIATED WITH
RESISTORS -RESISTANCE VALUE IN
OHMS
POWER HANDLING CAPABILITIES IN
WATTS
Resistor & Definition
Resistor Family Tree
RESISTORS
LEADED
CARBON
FILM
METAL
FILM
THICK FILM
THIN FILM
SMT
Metal Oxide
Film
WIREWOUND
+/-5%
GENERAL
PURPOSE
+/-1%
HIGHER
PERFORMANCE
HIGH POWER
>2W
HIGH POWER
+/-1%
+/-5%
GENERAL
PURPOSE
<+/-1%
SPECIAL
8
1/8, 1/4, , 1 , 2 , 20 WATTS
Types of Resistor
FIXED : THE FIXED RESISTANCES ARE THOSE
WHOSE VALUES CANNOT BE CHANGED
VARIABLE: VALUE OF THE RESISTANCE CAN
BE CHANGED WITHIN SPECIFIC RANGE
Types of Resistor
Fixed types of resistor
Colour Code Resistor
Wire Wound Resistor
Fusable Resistor
Applications & Availability
Area of Application: Voltage divider
Circuit, Feed back Circuit, Phase shift
circuit, Biasing Circuits, timer circuit,
Attenuators, Power supply section.
Available Std: E6,e12,e24,e48 E96,e192
Industrial std: e24, e96.
Types of variable resistor
Trimpot
Preset
Rotary
Potentiometer
Sliding
Potentiometer
Cermat
Rheostat
Application of variable Resistor
Introduction
to
Capacitors
Definition & Symbol
A device that stores energy in
electric field.
Two conductive plates
separated by a non conductive
material.
Electrons accumulate on one
plate forcing electrons away
from the other plate leaving a
net positive charge.
Think of a capacitor as very
small, temporary storage
battery.
Properties & Types
A capacitor blocks the passage of DC current.
A capacitor passes AC current.
Unit of Capacitance is Faradays.
Value of the capacitance is given by its value
and the max voltage which can be safely applied
to it which is know as working voltage ( WVDC)
Symbol for FIXED :
Symbol for Variable :
Capacitor Family Tree
CAPACITORS
ELECTROSTATIC
CERAMIC FILM ALUMINUM TANTALUM
ELECTROLYTIC
Non polarized
AC or DC operation
Lower Capacitance
Polarized
DC operation
Higher Capacitance
18
Markets
CAPACITORS
ELECTROSTATIC
CERAMIC FILM ALUMINUM TANTALUM
ELECTROLYTIC
Biggest market
Lowest Cost
1206 Long LT
0603 & 0402 good choices
Better performance at higher cost
SMT longer LT
Large Cap in Small Sizes
Long LT
Price Increases on C/ D/ E sizes
Large Cap at low cost
SMT increasing LT
Price flat on TH
19
Polarized Capacitor
One lead is positive and other is
negative marked
Basic Types of polarized Capacitor :
Electrolytic Capacitor
Tantalum Capacitor
Can Capacitor
Types of Electrolytic Capacitor
Radial
Axial
AVAILABLE RANGE & APPLICATION
FOR ELECTROLYTIC CAP: 1 TO 68,000 F
FOR TANTALUM ELECTROLYTIC
CAPACITOR : 1 TO 470 F
AREA OF APPLICATION: TIMER CKT,
DECOUPLING CAPS, FEED BACK CIRCUITS,
PHASE SHIFT CIRCUITS
Non Polarized
Ceramic
disk
Monolithic
ceramic
Dipped
silver-mica
Mylar
Mylar
Styroflex
Common capacitance ranges are:
Micro - - 10
-6
Nano - - 10
-9
Pico - - 10
-12
n
p
Types of Dielectric used :
Paper, Ceramic, Glass, Mica, Polyester, Mylar
Ceramic Disc Capacitor (Radial)
Cap Value
102 = 1000pF
Dielectric
Y5F
Voltage
1KV = 1000VDC
Cap Tolerance
C = +/-.25pF
D = +/-.5pF
F = +/-1%
G = +/-2%
J = +/-5%
K = +/-10%
M = +/-20%
Z = +80%/-20%
Example shown
P/N: NCD103K1KVY5PTR
Dielectric
Y5P
Cap Value
103 = 0.01uF
Voltage
1KV = 1000VDC
Example shown
P/N: NCD102K1KVY5F
23
Conversion Tables :
101 = 0.0001 f
102 = 0.001f
103 = 0.01f
104 = 0.1f
105 = 1 f
106 = 10 f
APPLICATION
DE-COUPLING
NOISE FILTER
POWER CONDITIONING
RESONANCE
TIMER
SNUBBER
MOTOR STARTERS
SENSORS
TOUCH SWITCH
SIGNAL PROCESSING
VARIABLE CAPACITOR
is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and
repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically.
Types of variable capacitor :
Trimmer
Gang Capacitor
Used in: Impedance Matching for Antenna
RF Tuning Circuits
Radios
High Powered Transmitter
Inductors
&
Transformer
Inductors
Def: An inductor is a coil of wire
through which electrons move, and
energy is stored in the resulting
magnetic field.
Inductors store energy in a magnetic
field, not an electric field.
When the source of electrons is
removed, the magnetic field collapses
immediately.
Inductance is Measured in Henry
Core types
Types of Inductor
Molded inductor & air-wound
inductor
Ferrite core Toroidal
transformer
Air wound inductor
Adjustable air-wound inductor
Iron powder Toroidal inductor
Encapsulated Torroid coil Variable
Variable Inductor
Factors influencing inductance
The amount of
inductance is
influenced by a
number of
factors :
Number of coil turns.
Diameter of coil.
Spacing between
turns.
Size of the wire used.
Type of material inside
the coil.
Applications
Resonant Circuits
Tuned Circuits in Radio Reception & Broadcasting
Antenna
Electric Transmission
Filter in Power supplies
Energy storage devices in SMPS
Audio Frequencies
Transformers
Definition
A static device which transfer the electrical energy from primary
winding to secondary winding, works on the principle of mutual
Induction.
Based on the formula :
Where : V
s
is induced voltage in secondary winding
: V
p
is induced voltage in primary winding
: N
s
is number turns in Secondary winding
:
N
p
is number turns in Primary winding
Thus transformer allows only Alternating current.
Basic Type of transformer are : Step Down, Step Up
Step Down: When Secondary winding will be less than Primary
winding,
Step Up: When Secondary winding will be more than Primary
Winding.
Identification & Testing
Types Testing Procedure for transformer are: Cold Check & Hot check
Cold Check: Without applying voltage to transformer and measuring
the resistance of each winding , then determining the Primary &
Secondary Winding.
Hot Check : With applying voltage transformer & measuring the
output voltage at each windings and then determining the Primary &
Secondary windings.
Transformers Losses : Eddy current Losses,
Hysteresis Losses,
Mechanical Losses,
Stray Losses
Types of transformers
Auto transformers
Audio transformers
Leakage Transformers
Resonant Transformers, IFT
Isolation transformers or Instruments Transformers
Pulse Transformers
Current Transformer
Voltage Transformer
Active Components
Def : which have internal capacity to change energy format from one
form to another, hence require a external source, whose operation
can be controlled.
Dis Advantages of Vacuum Tubes :
Large Space Consumption
Large amount Heat dissipation
Power consumption is high
Introduction to semiconductors
Def : material whose conductivity lies in between conductor &
insulator.
Commonly used to Semiconductor: Silicon, Germanium, Gallium
Arsenide, Boron, Antimony.
Advantage of Semiconductor material :
Less space consumption
Power consumed is less
Heat dissipated is less
Low Cost
Diode
&
Transistor
Diode & Types
A semiconductor diode is
formed with pieces of N & P-
type SC material are joined
The P material is called the anode.
The N material is called the
cathode.
The resulting structure is
called a PN junction.
A PN junction (or diode)
is a switch or component
through which electrons will
flow easily in one direction but
not in the opposite direction.
In P-type semiconductor Holes
are Majority Charge Carriers
In N-Type semiconductor
Electron are Majority Charge
Carriers
Common Symbol of Diode :
Rectifier Diode :
Signal / Switching Diode :
Zener Diode :
Light
Emitting
Diode :
Testing Procedure for Diode
FIGURE 1431 To check a diode, select
diode check on a digital Multiimeter.
The display will indicate the voltage drop
(difference) between the meter leads. The
meter itself applies a low-voltage
signal(usually about 3 volts) and displays
the difference on the display.
(a) When the diode is forward biased, the
meter should display a voltage between
0.500 and 0.700 V (500 to 700 mV).
(b) When the meter leads are reversed, the
meter should read OL (over limit) because
the diode is reverse biased and blocking
current flow.
Different types of Moulded
Bridge Rectifier
Practical Testing of Zener Diode
BZX55 Zener Diode Power Rating 500mW
2.4V 2.7V 3.0V 3.3V 3.6V 3.9V 4.3V 4.7V
5.1V 5.6V 6.2V 6.8V 7.5V 8.2V 9.1V 10V
11V 12V 13V 15V 16V 18V 20V 22V
24V 27V 30V 33V 36V 39V 43V 47V
BZX85 Zener Diode Power Rating 1.3W
3.3V 3.6V 3.9V 4.3V 4.7V 5.1V 5.6 6.2V
6.8V 7.5V 8.2V 9.1V 10V 11V 12V 13V
15V 16V 18V 20V 22V 24V 27V 30V
33V 36V 39V 43V 47V 51V 56V 62V
Transistor & Its types
Def : Its three terminal & Two Junction Devices, transfer the signal
from low resistance region to high resistance region
Emitter
Base
Collector
Transistor & Types
Low Power
Medium Power
High -Power
Transistor Nos.
Low Power : BC 182, BC 182c,BC 546, BC 547b, BC 548,
NC 549, BC 549b, BC 639m, BF 194, BC 167.
Medium Power : BC 107, BC 108, BC 108C, BC 549B,
2N3053, BFY51, BC177, BC 178, BC 179, BC 477, BC 478,
HC 100, BD 115, BEL 100N, CD100, 2N2955,2N2907
2N2222,2N2905, SK100.2N4403, 2N4125, 2N3906,
High Power : TIP 29, TIP 31, Tip 31, TIP 41, 2N3055,
TIP 32A, TIP 32C, BUX 84, TIP 122, TIP 127, 2N3055,
KSE 13007, 13008, MJE 13007, BD246, C4313, TIP 42
Testing Procedure using Multimeter
Application
Switching
Amplifier
Oscillator
Comparator
Series Voltage Regulator
Sensors
Field Effect Transistor
It Contains Four leads: the Drain, Source, Two Gates or Shield
The area between the source and drain terminals is called the channel.
N- Channel FET P- Channel FET
Basic Advantage of FET : High Input Impedance (Z
in
)
Testing Procedure
Turn Offs: Connect ve lead of MM to Gate & +ve lead to
Source of the FET.
Turn On Condition: Connect ve lead of MM to source &
+ve lead to gate. MM should show 0L.
Verifying On: connect +ve lead to drain & -ve lead to
source. MM should show .000
Turn OFF: Connect ve lead of MM to Gate & +ve lead to
Source of the FET. MM show 0L.
Verifying OFF: Connect to ve lead to source & +ve lead to
drain. MM should OL
Area Of Application
Small Signal Amplifier
Voltage Controlled Rsistor
Switch
In Op-Amps
Uni-Junction Transistor
Testing Procedure
Select High Resistance range in Ohmmeter;
Connect -ve lead of OM to emitter & +ve lead B1 ,
B2 one after other. OM should show Approx. High
resistance on both sides.
Connect +ve lead of OM to emitter & -ve lead B1 ,
B2 one after another. OM should show Approx.
Low resistance on both sides.
Applications
In Triggering Circuit
In relaxation oscillator
In transducer
Switching Circuits
IC Regulator
A higher end voltage regulator whose output
voltage remains constant with irrespective of any
Input Voltage variation.
Types of Voltage regulator :
1. Fixed +ve Regulator
2. Fixed -ve Regulator
3. Variable Regulator
Adv: Inexpensive, versatile,
Thermal shutdown, provides
Current/Voltage boosting
Configuration
For +ve regulator;78XX family
Pin: 1= Input
2= Ground
3= Output
Ex: 7805, 06, 08, 09, 12, 15, 18, 24
For ve regulator;79XX Family
Pin: 1= Ground
2= Input
3= Output
Ex: 7905, 06,08,09, 12, 15, 18, 24
Variable Regulator
Def: are those who voltage can be varied and
utilized.
Advantages of adjustable voltage regulators:
* improved system performance
* improved overload protection
*improved system reliability
Example: LM317, LM337
Types of Variable regulator: Positive, Negative
Configuration & Types
The LM 317,117,338,350 is a three terminal
positive voltage regulator, which can be operated with the
output voltage regulated at any setting over the
range of 1.2 V to 57 V.
The LM 337,137 series of voltage regulators are a
negative adjustable voltage regulators
The three terminals are Vin, Vout
and ADJUSTMENT(ADJ).
Application: Variable power supply ,
Switching Circuits
Integrated Circuits
An integrated circuit (IC) is a miniature ,low cost
electronic circuit consisting of active and passive
components fabricated together on a single crystal
of silicon.
The active components are transistors and diodes
and passive components are resistors and
capacitors.
There are two major kinds of ICs:
Analog (linear) which are used as amplifiers, timers
and oscillators
Digital (logic) which are used in Gates, Flip-Flop,
Counters, Shift Registers, Microprocessors,
Microcontrollers and Memories, DSP
Advantage of IC
Miniaturization and hence increased equipment density.
Cost reduction due to batch processing.
Increased system reliability due to the elimination of
soldered joints.
Improved functional performance.
Matched devices.
Increased operating speeds.
Reduction in power consumption
Integrated Circuits
IC CAN
SIP PACKAGES
Integrated Circuits
DIP PACKAGE
QUAD FLAT PACKAGE
Integrated Circuits
PLASTIC LEADED CHIP CARRIERS
Integrated Circuits
EPROM
MICROPROCESSOR
Вам также может понравиться
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- NID in Computer Hardware Engineering Technology CurriculumДокумент78 страницNID in Computer Hardware Engineering Technology Curriculumtezom techeОценок пока нет
- SSC2001S Application NoteДокумент18 страницSSC2001S Application NoteGerardo Mendez CamarilloОценок пока нет
- Question NoДокумент3 страницыQuestion NoHasham SohailОценок пока нет
- An 6076Документ13 страницAn 6076Kannabhiran Arumugam100% (1)
- Physics Higher Secondary Second YearДокумент237 страницPhysics Higher Secondary Second YearDhanalakshmi DhanalakshmiОценок пока нет
- CPE-231 Lab #4 Diode Clipper CircuitsДокумент5 страницCPE-231 Lab #4 Diode Clipper CircuitsaneesОценок пока нет
- Emergency Coin Operated Mobile Battery Charger Project OverviewДокумент122 страницыEmergency Coin Operated Mobile Battery Charger Project OverviewtriloksawantОценок пока нет
- Phase Controlled Rectifier Circuit TypesДокумент107 страницPhase Controlled Rectifier Circuit TypesVarun Singh IndaОценок пока нет
- Microwave Lab Manual BIT MesraДокумент66 страницMicrowave Lab Manual BIT Mesrahjdvghws bhdhusОценок пока нет
- Automatic pump control and level indicator circuitДокумент43 страницыAutomatic pump control and level indicator circuitvasu thakurОценок пока нет
- DVP SS2 ManualДокумент19 страницDVP SS2 ManualMUIFTIKHARОценок пока нет
- Chapter Six: PhysicsДокумент8 страницChapter Six: Physicssaed cabdiОценок пока нет
- Electronic Materials: Chapter 4: Semiconductor DevicesДокумент25 страницElectronic Materials: Chapter 4: Semiconductor Deviceschinh buiОценок пока нет
- D3SBA60 600V 4A Rectifier Spec SheetДокумент6 страницD3SBA60 600V 4A Rectifier Spec SheetRkarlithoz ZeRooОценок пока нет
- BE ECE Scheme & Syllabus 2017Документ152 страницыBE ECE Scheme & Syllabus 2017Kenny SОценок пока нет
- Amprobe ACD-50 Series - ManualДокумент164 страницыAmprobe ACD-50 Series - ManualcostelchelariuОценок пока нет
- PebookletДокумент53 страницыPebookletAdriana SerbanОценок пока нет
- Edc Unit Wise QuestionsДокумент2 страницыEdc Unit Wise QuestionsMuppala Chiranjeevi0% (1)
- STK0380P: PreliminaryДокумент4 страницыSTK0380P: PreliminaryHaider AliОценок пока нет
- Teaching Plan For Basic of Electronics and Communication EngineeringДокумент3 страницыTeaching Plan For Basic of Electronics and Communication Engineeringsanjay kumarОценок пока нет
- 8-Channel Digital Input Module For Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCS)Документ26 страниц8-Channel Digital Input Module For Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCS)adaptive4u4527Оценок пока нет
- A Guide To Digital & Analogue Multimeters - Ian PooleДокумент68 страницA Guide To Digital & Analogue Multimeters - Ian Poolequick_bad0% (1)
- Faults in Phantom Powered Microphone PreamplifiersДокумент17 страницFaults in Phantom Powered Microphone PreamplifierskirillОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronic Lab Manual Bit 231Документ89 страницBasic Electronic Lab Manual Bit 231Sumanta BhattacharyyaОценок пока нет
- Service Manual Minarctig Evo 200: Kemppi OyДокумент27 страницService Manual Minarctig Evo 200: Kemppi OyLucyan IonescuОценок пока нет
- EDC Practical 1Документ6 страницEDC Practical 1nandkishor joshiОценок пока нет
- Syllabus B.Tech. First Yr Biotechnology Effective From 2022 23 RДокумент44 страницыSyllabus B.Tech. First Yr Biotechnology Effective From 2022 23 RDipika SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- A Multi-Input Bridgeless Resonant AC-DC Converter ForДокумент4 страницыA Multi-Input Bridgeless Resonant AC-DC Converter ForshaliniОценок пока нет
- Full Wave Rectifier Using Bridge CircuitДокумент4 страницыFull Wave Rectifier Using Bridge CircuitZbОценок пока нет
- Sample Problem For Quiz 1Документ3 страницыSample Problem For Quiz 1Christelle Cha LotaОценок пока нет