Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Customer Perceptions of Service: Mcgraw-Hill © 2000 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies
Загружено:
shakilarathnasiri0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров21 страницаcustomer perception
Оригинальное название
Chap04
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документcustomer perception
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров21 страницаCustomer Perceptions of Service: Mcgraw-Hill © 2000 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies
Загружено:
shakilarathnasiricustomer perception
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 21
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
1
S
M
S
M
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
Chapter 4
CUSTOMER
PERCEPTI ONS OF
SERVI CE
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
2
S
M
Objectives for Chapter 4:
Customer Perceptions of
Service
Provide you with definitions and
understanding of customer satisfaction and
service quality
Show that service encounters or the
moments of truth are the building blocks of
customer perceptions
Highlight strategies for managing customer
perceptions of service
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
3
S
M
Figure 4-1
Customer Perceptions of
Service Quality and
Customer Satisfaction
Service
Quality
Reliability
Responsiveness
Assurance
Empathy
Tangibles
Product
Quality
Price
Personal
Factors
Customer
Satisfaction
Situational
Factors
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
4
S
M
Factors Influencing
Customer Satisfaction
Product/service quality
Product/service attributes or features
Consumer Emotions
Attributions for product/service success or
failure
Equity or fairness evaluations
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
5
S
M
Outcomes of
Customer Satisfaction
Increased customer retention
Positive word-of-mouth communications
Increased revenues
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
6
S
M
Figure 4-3
Relationship between Customer
Satisfaction and Loyalty in
Competitive Industries
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
Very
dissatisfied
Dissatisfied Neither
satisfied nor
dissatisfied
Satisfied Very
satisfied
Satisfaction measure
L
o
y
a
l
t
y
(
r
e
t
e
n
t
i
o
n
)
Source: James L. Heskett, W. Earl Sasser, Jr., and Leonard A. Schlesinger, The Service Profit Chain, (New York, NY: The Free Press, 1997), p. 83.
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
7
S
M
Service Quality
The customers judgment of overall
excellence of the service provided in
relation to the quality that was expected.
Process and outcome quality are both
important.
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
8
S
M
The Five Dimensions of
Service Quality
Ability to perform the promised
service dependably and accurately.
Knowledge and courtesy of
employees and their ability to
convey trust and confidence.
Physical facilities, equipment, and
appearance of personnel.
Caring, individualized attention the
firm provides its customers.
Willingness to help customers and
provide prompt service.
Tangibles
Reliability
Responsiveness
Assurance
Empathy
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
9
S
M
Exercise to
Identify Service Attributes
In groups of five, choose a services industry and spend 10 minutes
brainstorming specific requirements of customers in each of the five
service quality dimensions. Be certain the requirements reflect the
customers point of view.
Reliability:
Assurance:
Tangibles:
Empathy:
Responsiveness:
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
10
S
M
SERVQUAL Attributes
Providing service as promised
Dependability in handling customers
service problems
Performing services right the first time
Providing services at the promised time
Maintaining error-free records
Keeping customers informed as to
when services will be performed
Prompt service to customers
Willingness to help customers
Readiness to respond to customers
requests
RELIABILITY
RESPONSIVENESS
Employees who instill confidence in
customers
Making customers feel safe in their
transactions
Employees who are consistently courteous
Employees who have the knowledge to
answer customer questions
ASSURANCE
Giving customers individual attention
Employees who deal with customers in a
caring fashion
Having the customers best interest at heart
Employees who understand the needs of
their customers
Convenient business hours
EMPATHY
Modern equipment
Visually appealing facilities
Employees who have a neat,
professional appearance
Visually appealing materials
associated with the service
TANGIBLES
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
11
S
M
The Service Encounter
is the moment of truth
occurs any time the customer interacts with the firm
can potentially be critical in determining customer satisfaction and
loyalty
types of encounters:
remote encounters
phone encounters
face-to-face encounters
is an opportunity to:
build trust
reinforce quality
build brand identity
increase loyalty
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
12
S
M
Check-In
Request Wake-Up Call
Checkout
Bellboy Takes to Room
Restaurant Meal
Figure 4-4
A Service Encounter
Cascade for a Hotel Visit
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
13
S
M
Sales Call
Ordering Supplies
Billing
Delivery and Installation
Servicing
Figure 4-5
A Service Encounter
Cascade for an Industrial
Purchase
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
14
S
M
Critical Service Encounters
Research
GOAL - understanding actual events and
behaviors that cause customer dis/satisfaction
in service encounters
METHOD - Critical Incident Technique
DATA - stories from customers and employees
OUTPUT - identification of themes underlying
satisfaction and dissatisfaction with service
encounters
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
15
S
M
Sample Questions for Critical
Incidents Technique Study
Think of a time when, as a customer, you had a
particularly satisfying (dissatisfying) interaction
with an employee of .
When did the incident happen?
What specific circumstances led up to this
situation?
Exactly what was said and done?
What resulted that made you feel the interaction
was satisfying (dissatisfying)?
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
16
S
M
Common Themes in Critical
Service Encounters Research
Recovery: Adaptability:
Spontaneity: Coping:
Employee Response
to Service Delivery
System Failure
Employee Response
to Customer Needs
and Requests
Employee Response
to Problem Customers
Unprompted and
Unsolicited Employee
Actions and Attitudes
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
17
S
M
Recovery
Acknowledge
problem
Explain causes
Apologize
Compensate/upgrade
Lay out options
Take responsibility
Ignore customer
Blame customer
Leave customer to
fend for him/herself
Downgrade
Act as if nothing is
wrong
DO
DONT
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
18
S
M
Adaptability
Recognize the
seriousness of the need
Acknowledge
Anticipate
Attempt to
accommodate
Explain rules/policies
Take responsibility
Exert effort to
accommodate
Promise, then fail to
follow through
Ignore
Show unwillingness to
try
Embarrass the customer
Laugh at the customer
Avoid responsibility
DO DONT
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
19
S
M
Spontaneity
Take time
Be attentive
Anticipate needs
Listen
Provide information
(even if not asked)
Treat customers fairly
Show empathy
Acknowledge by name
Exhibit impatience
Ignore
Yell/laugh/swear
Steal from or cheat a
customer
Discriminate
Treat impersonally
DO
DONT
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
20
S
M
Coping
Listen
Try to accommodate
Explain
Let go of the
customer
Take customers
dissatisfaction
personally
Let customers
dissatisfaction affect
others
DO
DONT
McGraw-Hill
2000 The McGraw-Hill Companies
21
S
M
Figure 4-6
Evidence of Service from the
Customers Point of View
People
Process
Physical
Evidence
Contact employees
Customer him/herself
Other customers Operational flow of
activities
Steps in process
Flexibility vs.
standard
Technology vs.
human
Tangible
communication
Servicescape
Guarantees
Technology
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Sample Ravens SPM Online ReportДокумент5 страницSample Ravens SPM Online ReportAyaw Jud Ko LabdaОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- 34630.Seneca-Resume Writing Guide PDFДокумент8 страниц34630.Seneca-Resume Writing Guide PDFfiq_hugo319Оценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент764 страницыPDFDe JavuОценок пока нет
- Project Risk ManagementДокумент104 страницыProject Risk Managementtsrinivasan5083Оценок пока нет
- Ladd CC 1964 - Stress-Strain Behavior of Saturated Clay and Basic Strength Principles PDFДокумент125 страницLadd CC 1964 - Stress-Strain Behavior of Saturated Clay and Basic Strength Principles PDFSaraswati NoorОценок пока нет
- PL010 PUPI Technical Information REV01.2016 PDFДокумент16 страницPL010 PUPI Technical Information REV01.2016 PDFAhmed TahaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 (Marketing Updated)Документ9 страницChapter 1 (Marketing Updated)i211416 Shizza KianiОценок пока нет
- Discovery LearningДокумент14 страницDiscovery LearningYuki JudaiОценок пока нет
- Tabaq With Tang Band 4Документ4 страницыTabaq With Tang Band 4Lmute MedioliОценок пока нет
- Raghad Kamel's ResumeДокумент7 страницRaghad Kamel's ResumeMostafa Mohamed GamalОценок пока нет
- Aravindhan PT CV CSWIP TrainerДокумент4 страницыAravindhan PT CV CSWIP TrainerGanesan RamamoorthyОценок пока нет
- 839-4816 (Office) or (770) 301-8648 (Cell) : Corporate Finance: A Focused Approach, by Michael C. Ehrhardt / Eugene FДокумент1 страница839-4816 (Office) or (770) 301-8648 (Cell) : Corporate Finance: A Focused Approach, by Michael C. Ehrhardt / Eugene FlilbouyinОценок пока нет
- Data 6005AДокумент1 страницаData 6005AErick De La RoSaОценок пока нет
- Structure 1Документ5 страницStructure 1Thunder AnimeОценок пока нет
- Canon Ts5000 (Impressora) MANUALДокумент441 страницаCanon Ts5000 (Impressora) MANUALMiguel DinisОценок пока нет
- Exploration and Implementation of Commonality ValuДокумент19 страницExploration and Implementation of Commonality ValuJoaocatalo cataloОценок пока нет
- Sec D CH 12 Regression Part 2Документ66 страницSec D CH 12 Regression Part 2Ranga SriОценок пока нет
- Easyworship Documentation ManualДокумент34 страницыEasyworship Documentation ManualAragorn100% (2)
- 2 HSE Kumar KushДокумент3 страницы2 HSE Kumar KushankitОценок пока нет
- A словаДокумент297 страницA словаailisha libraОценок пока нет
- Reading 1 - Science - BIOL105 - Disease - ResponseДокумент9 страницReading 1 - Science - BIOL105 - Disease - ResponsemykrohОценок пока нет
- Aster 30 Sampt PDFДокумент2 страницыAster 30 Sampt PDFmig29Оценок пока нет
- Fundamental Neuroscience For Basic and Clinical Applications 5Th Edition Duane E Haines Full ChapterДокумент67 страницFundamental Neuroscience For Basic and Clinical Applications 5Th Edition Duane E Haines Full Chaptermaxine.ferrell318100% (8)
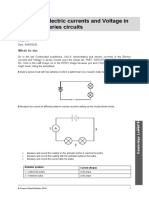
- Circuits Virtual LabДокумент2 страницыCircuits Virtual LabPaula GómezОценок пока нет
- Wmwbqi J Cix Vi Cökœ de "Qvwi 2015-Avm÷ 2022Документ17 страницWmwbqi J Cix Vi Cökœ de "Qvwi 2015-Avm÷ 2022JuwelОценок пока нет
- Safety PledgeДокумент3 страницыSafety Pledgeapi-268778235100% (1)
- Project Mana Session 1 (With Practice)Документ59 страницProject Mana Session 1 (With Practice)Harper LamОценок пока нет
- Administrative Guide Cambridge Professional Development Qualifications PDQ 2022 2023Документ25 страницAdministrative Guide Cambridge Professional Development Qualifications PDQ 2022 2023Ali FetohОценок пока нет
- Sixth Sense TechnologyДокумент36 страницSixth Sense TechnologyMahtab AОценок пока нет
- Application For Petitioned Class: College of Engineering and ArchitectureДокумент2 страницыApplication For Petitioned Class: College of Engineering and ArchitectureJohn A. CenizaОценок пока нет