Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Atopic Dermatitis
Загружено:
Annisa Sasa0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
61 просмотров26 страницAtopic dermatitis (AD) can be divided into three stages: infantile, childhood, and adolescent/adult. Infantile AD typically appears before 1 year of age and presents as itchy erythema on the cheeks and other areas. Childhood AD presents as less acute, drier lesions on the antecubitals, wrists, eyelids and around the neck. Adolescent and adult AD presents as localized, scaly plaques in areas like the antecubitals and neck. Pruritus is a hallmark of AD and is worsened by humidity, sweating, allergens and irritants. Treatment involves identification and avoidance of triggers, topical emollients and anti
Исходное описание:
penyakit kulit
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документAtopic dermatitis (AD) can be divided into three stages: infantile, childhood, and adolescent/adult. Infantile AD typically appears before 1 year of age and presents as itchy erythema on the cheeks and other areas. Childhood AD presents as less acute, drier lesions on the antecubitals, wrists, eyelids and around the neck. Adolescent and adult AD presents as localized, scaly plaques in areas like the antecubitals and neck. Pruritus is a hallmark of AD and is worsened by humidity, sweating, allergens and irritants. Treatment involves identification and avoidance of triggers, topical emollients and anti
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
61 просмотров26 страницAtopic Dermatitis
Загружено:
Annisa SasaAtopic dermatitis (AD) can be divided into three stages: infantile, childhood, and adolescent/adult. Infantile AD typically appears before 1 year of age and presents as itchy erythema on the cheeks and other areas. Childhood AD presents as less acute, drier lesions on the antecubitals, wrists, eyelids and around the neck. Adolescent and adult AD presents as localized, scaly plaques in areas like the antecubitals and neck. Pruritus is a hallmark of AD and is worsened by humidity, sweating, allergens and irritants. Treatment involves identification and avoidance of triggers, topical emollients and anti
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 26
Atopic Dermatitis
AD can be divided into three stages:
1. Infantile atopic dermatitis:
2 months-2 years of age
2.Childhood atopic dermatitis:
2 years-10 years
3. Adolescent and adult atopic dermatitis
Infantile Atopic Dermatitis
60 % In the first year of life
Usually . 2 month of age
Clinic: Itchy erythema of the cheeks
Intraepidermal vesiclesrupture
moist, crusted areas extend to
other part of the body (scalp, neck,
forehead, wrist, extensor extremities
buttocks and diaper area spared
Chidhood Atopic Dermatitis
Childhood
Clinic: less acute lesions
Lesions less exudative, drier,
>papular
Locations: antecubital, popliteal
fossae, flexor wrist, eyelids, face,
around the neck
lichenified, slightly scaly/ infiltrated
plaques
Adolescents and adult AD
Older patients
Clinic: Localized erythematous, scaly, papular/
vesicular plaques
Pruritic, lichenified plaques
Location: antecubital and popliteal fossae, front
and sides of neck, forehead, area about the
eyes
Eruptions generalized more severe in
flexures lichenified
Plaques often erythematous/ hyperpigmented
Major Clinical features of AD (base on
Hanifin and Rajka)
- Intense pruritus & excoriation
- Typical morphology and distribution of skin
lesions:-facial and extensor involvement in
infant and early childhood
-flexural lichenification in adult
- Chronic or chronically relapsing dermatitis
(>6 weeks)
- Personal and family history of atopic disease
Minor features
-Dryness of the skin (xerosis)
-Ichthyosis, keratosis pilaris, hyperlinear
palms
-Non specific hand/foot dermatitis
-Scalp dermatitis e.g. cradle cap
-Allergic shiners
-Recurrent conjunctivitis and keratoconus
- IgE reactivity
-Dennie-Morgan infraorbital fold
-Orbital darkening
-Pityriasis alba
-Food hypersensitivity
Intense pruritus
Itching, Scratching the day worse at
night sleep disruption
Pat AD threshold of itching decreased
Humidity
Excessive sweating
Exposure to allergens, irritants (soap,
detergent acrylic, wool) itch
Whats the etiology of pruritus in
AD ?
- Not well understood
- Local release of proinflammatory mediators &
cytokines
Rukwied and Heyer (1999)
Pruritus:
- Histamine
- Cytokines
- leukotrienes
- neuropeptide
- proteases
Morphological characteristic of AD
-Acute lesions are papules, vesicles on
erythematous background with sign of erosion,
bleeding and serous exudate
-Sub acute lesions are erythematous and scaly
papules on dry background
-Chronic lesions are fibrotic papules on lichenified
(thickened) back ground
-Excoriation due to scratching in a all stage
-Infection may alter the appearance with the presence of
oozing or local abscess
-Even uninvolved skin is often dry and scaly
Investigation
Total Ig E > not helpful diagnosis
Skin prick test (SPT)
Specific Ig E (RAST) more helpful
SPT/RAST
Most children AD sensitized to food
(milk, egg, peanut, soy, wheat, fish)
SPT/RAST (+) 90% useful screening
-If SPT(+) confirm food elimination
Atopy patch test
-With food, aero allergen specificity &
clinical relevant
-Patch test to detect delayed type skin
hypersensitivity
-40% PAT ad CD to metal, fragance:
lanolin, emollients
Basic Treatment
Skin care
Emollients
Avoidance of irritants, sudden
changes of temperature, humidity
Identification of
specific
Exacerbating factors
Anti inflammatory
Treatment
TREATMENT OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS
Allergens
Microbes
Emotional factors
Avoidance of trigger factors
1. Irritants detergents
soap
2. Allergens: Food allergen
Airborne allergens
Child < 5 years : Usually allergy to 1 or > food
cows milk, egg, wheat, bean
3. House dust mite: older children
young adult
4. Emotional stress
TOPICAL EMOLLIENT
BASIS TOPICAL TREATMENT :
2 3 X / DAY
WATER LOSS
ITCHING
Topical treatment
CREAM / LOTION : EARLY PHASE
OINTMENT : LICHENI FIED SKIN
SEVERE CASE :
AFTER OINTMENT WETWRAP DRESSING
EPIDERMAL WATER LOSS
TOPICAL CROMOLYN IN WATER SOLUBLE
EMOLLIENT VEHICLE ANTI INFLAMATORY
EFFECT
ANTIBIOTIC
FUSIDIC ACID
GRAM (+)
TETRA CYCLINE
SKIN CLEANSER 10% POVIDONE
IODINE
GENERALIZED INFECTION : ANTI
MICROBIAL BATH (CHLORHEXIDIN 0,005%)
SISTEMIC ANTIBIOTIC : FLUCLOCXACILLIN :
MUPIROCIN
OTHER TREATMENT
STRATEGIES
UVA PHOTOTERAPY
CICLOSPORIN
IF
Chemical and Functional Classification
H1-antihistamine
Chemical 1
st
generation 2
nd
generation
Alkylamine Chlorpheniramine Acrivastine
Piperazine Hydroxyzine Cetirizine,
levocetetirizine
Piperidine Cyproheptadine Astemizol
Desloratadine
Fexofenadine
Loratadine
Ethanolamines Diphenhidramine
Ethylenediamines Pyrilamine
Phenothiazine Promethazine
Anti inflammatory effects of AH
Expression of cell adhesion molecules
Chemotaxis of eosinophilia & others cells
Proinflammatory cytokines
Adhesion protein
Antiallergic activities
Release of mediator from mast cell and
basophil
(Direct inhibitory effect on calcium-ion
channels inward calcium)
Anti-inflammation effect
Atopic Dermatitis in Child
Atopic Dermatitis in Infant and Child
Atopic Dermatitis in Child
Вам также может понравиться
- Atopic DermatitisДокумент22 страницыAtopic DermatitisBonitavanyОценок пока нет
- Dermatitis DR Citra 260907Документ56 страницDermatitis DR Citra 260907Adam AriwibawaОценок пока нет
- Eczematous EruptionsДокумент27 страницEczematous EruptionsSmartcool SoОценок пока нет
- Atopic DermatitisДокумент9 страницAtopic DermatitisJorge De VeraОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Dermatitis AtopicДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Dermatitis AtopicBanni Aprilita PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Algorithm PDFДокумент1 страницаAtopic Dermatitis Treatment Algorithm PDFkhuzaimahОценок пока нет
- Dermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof - Harijono)Документ38 страницDermatitis Atopic Presentation (Prof - Harijono)Yovan PrakosaОценок пока нет
- Approach To Patient With Allergic Diseases: Jovilia M. Abong, M.D. FPCP, Fpsaai, MSCДокумент65 страницApproach To Patient With Allergic Diseases: Jovilia M. Abong, M.D. FPCP, Fpsaai, MSCCristinaConcepcionОценок пока нет
- HI Classmates!!!Документ36 страницHI Classmates!!!Alex SilvanoОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Disorders StudentsДокумент46 страницCardiovascular Disorders StudentsPye Antwan DelvaОценок пока нет
- Skin Infections and InfestationsДокумент37 страницSkin Infections and InfestationsAremu OlatayoОценок пока нет
- Atopic Eczema 11Документ71 страницаAtopic Eczema 11khola aijazОценок пока нет
- Erythema MultiformeДокумент29 страницErythema MultiformeSurabhi Sharma100% (1)
- Bacterial InfectionДокумент41 страницаBacterial InfectionUmmi Rinandari100% (1)
- Pyloric StenosisДокумент11 страницPyloric StenosisJustin CharlesОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Skin Infections - Course VIIIДокумент37 страницBacterial Skin Infections - Course VIIIAngelie PedregosaОценок пока нет
- DddsДокумент50 страницDddsOsama AlhaseОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Skin Infection Power PointДокумент138 страницBacterial Skin Infection Power PointArwi WijayaОценок пока нет
- Dermatitis101 Diagnosis Treatment EczemaДокумент45 страницDermatitis101 Diagnosis Treatment EczemaUkhti NounaniarnurseОценок пока нет
- Final Examination: Polytechnic University of The Philippines Open Universitysysten4Документ1 страницаFinal Examination: Polytechnic University of The Philippines Open Universitysysten4Leigh LynОценок пока нет
- Croup SyndromeДокумент3 страницыCroup SyndromeMabesОценок пока нет
- Erythema NodosumДокумент42 страницыErythema Nodosummedpedshospitalist100% (1)
- ILA - Hirschsprungs DiseaseДокумент48 страницILA - Hirschsprungs DiseaseSoleh Ramly100% (1)
- 1 Principles of First Aid and Its PracticeДокумент118 страниц1 Principles of First Aid and Its PracticeMohamed SamyОценок пока нет
- Interface Dermatitis: Rajendra Singh, MDДокумент97 страницInterface Dermatitis: Rajendra Singh, MDsatkriti100% (2)
- Phylum RhizopodaДокумент2 страницыPhylum RhizopodaLiborMyslivecek100% (1)
- Anti Fungal DrugsДокумент6 страницAnti Fungal Drugsbilal ahmadОценок пока нет
- Lupus EritematousДокумент27 страницLupus EritematousNazwa Warda Amalia100% (2)
- Short Notes On Public Speaking MaterialsДокумент2 страницыShort Notes On Public Speaking Materialsstrawberry_89Оценок пока нет
- SyphilisДокумент89 страницSyphilisAnuZ13thОценок пока нет
- Classic Childhood ExanthemsДокумент66 страницClassic Childhood ExanthemsBorzoo Tajdin100% (1)
- UrticariaДокумент12 страницUrticarialilyrbrtОценок пока нет
- DermatomycosesДокумент73 страницыDermatomycosessnylstlОценок пока нет
- Quiz 9Документ189 страницQuiz 9Joshua PayneОценок пока нет
- PsoriasisДокумент27 страницPsoriasisMishaОценок пока нет
- Derma Report Contact DermatitisДокумент25 страницDerma Report Contact DermatitisYusnida RahmawatiОценок пока нет
- Hypersensitivity: by Yundzir FurqanДокумент18 страницHypersensitivity: by Yundzir FurqanFuЯqanFriesОценок пока нет
- Bataan vs. Dy PacДокумент2 страницыBataan vs. Dy Pacanalyn100% (1)
- Allergic Disorder: Dadan Surysaputra 20710031Документ22 страницыAllergic Disorder: Dadan Surysaputra 20710031Dadan SuryasaputraОценок пока нет
- Skin Tumor 1Документ30 страницSkin Tumor 1Vicky Ilda Viantini100% (1)
- Superficial and Deep Perivascular DermatitisДокумент55 страницSuperficial and Deep Perivascular DermatitisMarnie RoviraОценок пока нет
- Central Nervous System Infections: Gonzalo B. Roman JR.,MD.,FPSPДокумент72 страницыCentral Nervous System Infections: Gonzalo B. Roman JR.,MD.,FPSPBenjamin PrabhuОценок пока нет
- Dermatitis HerpetiformisДокумент16 страницDermatitis HerpetiformisTriasnidaОценок пока нет
- LeprosyДокумент6 страницLeprosyMaricel Y. LizadaОценок пока нет
- Coriolis EffectДокумент18 страницCoriolis Effectletter_ashish4444Оценок пока нет
- Salas v. First Finance Leasing CorporationДокумент2 страницыSalas v. First Finance Leasing CorporationKatrina PerezОценок пока нет
- Eczema 1Документ122 страницыEczema 1sahithiОценок пока нет
- SinusitisДокумент14 страницSinusitispraywinОценок пока нет
- Miliaria SVДокумент26 страницMiliaria SVTaufiq Ramadhan100% (1)
- VERUCCA VULGARIS PresentationДокумент28 страницVERUCCA VULGARIS PresentationBrilliantIbnuSina100% (2)
- Insect Bite ReactionДокумент21 страницаInsect Bite ReactionSiska TeurupunОценок пока нет
- Approach To A Patient With Jaundice: Group A9 Cho, Chua Family, Co Family, CofrerosДокумент115 страницApproach To A Patient With Jaundice: Group A9 Cho, Chua Family, Co Family, CofrerosEunice Co100% (1)
- HistoplasmosisДокумент12 страницHistoplasmosis사이맄 진Оценок пока нет
- ImpetigoДокумент13 страницImpetigoTasya SyafhiraОценок пока нет
- Function of The SkinДокумент69 страницFunction of The SkinapermatagamaОценок пока нет
- Nanda Nursing Diagnosis Examples:: Vague Uneasy Feeling ofДокумент3 страницыNanda Nursing Diagnosis Examples:: Vague Uneasy Feeling ofYOLANDA P. DELCASTILLOОценок пока нет
- Dms146 Slide DermatitisДокумент65 страницDms146 Slide DermatitisAdhitya Rama Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Atopic DermatitisДокумент26 страницAtopic DermatitissetiabudiОценок пока нет
- Dermatitis Eksematosa - Dr. Kristo A. Nababan, Sp. KKДокумент91 страницаDermatitis Eksematosa - Dr. Kristo A. Nababan, Sp. KKJhost Clinton PurbaОценок пока нет
- Dr. R. Sekhon - Dermatology Telehealth Jan 27 MRДокумент45 страницDr. R. Sekhon - Dermatology Telehealth Jan 27 MRAnissa ADОценок пока нет
- Data SampelДокумент4 страницыData SampelAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- 2009 Pediatric Spine and PND Imaging GuidelinesДокумент18 страниц2009 Pediatric Spine and PND Imaging GuidelinesAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Tuberculous Pleural Effusion in ChildrenДокумент5 страницTuberculous Pleural Effusion in ChildrenAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Tuberculous Pleural Effusion in ChildrenДокумент5 страницTuberculous Pleural Effusion in ChildrenAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Expression Patterns of Nociceptin in Rats Following Experimental Tooth MovementДокумент5 страницExpression Patterns of Nociceptin in Rats Following Experimental Tooth MovementAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Hypertension: Clinical Management of Primary Hypertension in AdultsДокумент38 страницHypertension: Clinical Management of Primary Hypertension in AdultsAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Hypertension: Clinical Management of Primary Hypertension in AdultsДокумент38 страницHypertension: Clinical Management of Primary Hypertension in AdultsAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Pleural Tuberculosis PDFДокумент6 страницPleural Tuberculosis PDFFyan FiradyОценок пока нет
- Update On Tuberculous Pleural EffusionДокумент8 страницUpdate On Tuberculous Pleural EffusionChristian TabarezОценок пока нет
- Approach To Pleural EffusionДокумент10 страницApproach To Pleural EffusionMatin Ahmad KhanОценок пока нет
- Pleural Tuberculosis PDFДокумент6 страницPleural Tuberculosis PDFFyan FiradyОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Pleural EffusionДокумент24 страницыDiagnosis and Treatment of Pleural EffusionAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- The Sma Parrot R TestДокумент1 страницаThe Sma Parrot R TestAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Lamp IranДокумент1 страницаLamp IranAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Update On Tuberculous Pleural EffusionДокумент8 страницUpdate On Tuberculous Pleural EffusionChristian TabarezОценок пока нет
- 1317 Trajman ERJ 2008 Pleural TB DiagnosisДокумент9 страниц1317 Trajman ERJ 2008 Pleural TB DiagnosisAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Belajar Efektif Dalam Proses PembelajaranДокумент21 страницаBelajar Efektif Dalam Proses PembelajaranAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Monday 17 Muharram 1412 A.HДокумент1 страницаMonday 17 Muharram 1412 A.HAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Belajar Efektif Dalam Proses PembelajaranДокумент21 страницаBelajar Efektif Dalam Proses PembelajaranAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Pleural EffusionДокумент24 страницыDiagnosis and Treatment of Pleural EffusionAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Tetanus Bacterial ToxinsДокумент35 страницTetanus Bacterial ToxinsAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Atopic DermatitisДокумент26 страницAtopic DermatitisAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Myelitis: Dr. Kiking Ritarwan, MKT, SpsДокумент15 страницMyelitis: Dr. Kiking Ritarwan, MKT, SpsAnnisa Sasa100% (1)
- Diseases of The Spinal Cord: Dr. Khairul P Surbakti, SpsДокумент35 страницDiseases of The Spinal Cord: Dr. Khairul P Surbakti, SpsAnnisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightДокумент593 страницыHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Bms166 Slide NeuropathyДокумент47 страницBms166 Slide NeuropathycrossdressОценок пока нет
- Infections of The Central Nervous System08Документ47 страницInfections of The Central Nervous System08Annisa SasaОценок пока нет
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightДокумент593 страницыHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Unrar SRCДокумент1 страницаUnrar SRCMax SuvilianОценок пока нет
- Report in Per Dev CorrectedДокумент34 страницыReport in Per Dev CorrectedJosh lyan RiveraОценок пока нет
- Transfer and Business Taxation SyllabusДокумент5 страницTransfer and Business Taxation SyllabusamqqndeahdgeОценок пока нет
- Dri InternshipДокумент38 страницDri InternshipGuruprasad Sanga100% (3)
- Dungeon World ConversionДокумент5 страницDungeon World ConversionJosephLouisNadeauОценок пока нет
- Ventricular Septal DefectДокумент8 страницVentricular Septal DefectWidelmark FarrelОценок пока нет
- NG Teng Fong Discharge DocumentsДокумент14 страницNG Teng Fong Discharge DocumentsAnonymous yGwMIPJRawОценок пока нет
- FINAL PAPER Marketing Plan For Rainbow Air PurifierДокумент12 страницFINAL PAPER Marketing Plan For Rainbow Air PurifierMohola Tebello Griffith100% (1)
- Rooftop Rain Water Harvesting in An Educational CampusДокумент9 страницRooftop Rain Water Harvesting in An Educational CampusAkshay BoratiОценок пока нет
- Covid-19 Mitigation PlanДокумент8 страницCovid-19 Mitigation PlanEkum EdunghuОценок пока нет
- Data Sheet No. 01.12.01 - PR6 - 7 Inductive Pulse ModuleДокумент1 страницаData Sheet No. 01.12.01 - PR6 - 7 Inductive Pulse ModuleThaynar BarbosaОценок пока нет
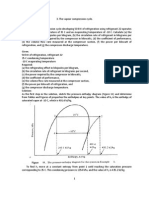
- The Vapour Compression Cycle (Sample Problems)Документ3 страницыThe Vapour Compression Cycle (Sample Problems)allovid33% (3)
- READING 4 UNIT 8 Crime-Nurse Jorge MonarДокумент3 страницыREADING 4 UNIT 8 Crime-Nurse Jorge MonarJORGE ALEXANDER MONAR BARRAGANОценок пока нет
- A Project Report On A Study On Amul Taste of India: Vikash Degree College Sambalpur University, OdishaДокумент32 страницыA Project Report On A Study On Amul Taste of India: Vikash Degree College Sambalpur University, OdishaSonu PradhanОценок пока нет
- Quality Factor of Inductor and CapacitorДокумент4 страницыQuality Factor of Inductor and CapacitoradimeghaОценок пока нет
- Soalan 9 LainДокумент15 страницSoalan 9 LainMelor DihatiОценок пока нет
- Goals in LifeДокумент4 страницыGoals in LifeNessa Layos MorilloОценок пока нет
- How McDonald'sДокумент2 страницыHow McDonald'spratik khandualОценок пока нет
- Xi 3 1Документ1 страницаXi 3 1Krishnan KozhumamОценок пока нет
- Adsorbents and Adsorption Processes For Pollution ControlДокумент30 страницAdsorbents and Adsorption Processes For Pollution ControlJoao MinhoОценок пока нет
- Those With MoonДокумент1 страницаThose With MoonRosee AldamaОценок пока нет
- A Critical Appreciation of Ode To NightingaleДокумент3 страницыA Critical Appreciation of Ode To NightingaleBaloch Karawan100% (2)
- AtelectasisДокумент37 страницAtelectasisSandara ParkОценок пока нет
- United States v. Victor Vallin-Jauregui, 4th Cir. (2013)Документ4 страницыUnited States v. Victor Vallin-Jauregui, 4th Cir. (2013)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Inducement of Rapid Analysis For Determination of Reactive Silica and Available Alumina in BauxiteДокумент11 страницInducement of Rapid Analysis For Determination of Reactive Silica and Available Alumina in BauxiteJAFAR MUHAMMADОценок пока нет
- Starkville Dispatch Eedition 9-10-20Документ12 страницStarkville Dispatch Eedition 9-10-20The DispatchОценок пока нет
- ACF5950 - Assignment # 7 Semester 2 2015: The Business Has The Following Opening Balances: Additional InformationДокумент2 страницыACF5950 - Assignment # 7 Semester 2 2015: The Business Has The Following Opening Balances: Additional InformationkietОценок пока нет
- Introduction and Vapour Compression CycleДокумент29 страницIntroduction and Vapour Compression Cycleمحسن الراشدОценок пока нет
- SGT PDFДокумент383 страницыSGT PDFDushyanthkumar DasariОценок пока нет
- Neuro M Summary NotesДокумент4 страницыNeuro M Summary NotesNishikaОценок пока нет
- ATI Respiratory PowerpointДокумент90 страницATI Respiratory PowerpointAnn KelseaОценок пока нет