Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Two Port Networks
Загружено:
Chris AielloАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Two Port Networks
Загружено:
Chris AielloАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
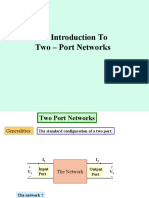
An Introduction To
Two Port Networks
The University of Tennessee
Electrical and Computer Engineering
Knoxville, TN
wlg
Two Port Networks
Generalities:
The standard configuration of a two port:
I1
+
V1
_
Input
Port
I2
The Network
The network ?
The voltage and current convention ?
* notes
Output
Port
+
V2
_
Two Port Networks
Network Equations:
Impedance
Z parameters
Admittance
Y parameters
Transmission
A, B, C, D
parameters
* notes
V1 = z11I1 + z12I2
V2 = b11V1 - b12I1
V2 = z21I1 + z22I2
I2 = b21V1 b22I1
I1 = y11V1 + y12V2
V1 = h11I1 + h12V2
I2 = y21V1 + y22V2
Hybrid
H parameters
I2 = h21I1 + h22V2
V1 = AV2 - BI2
I1 = g11V1 + g12I2
I1 = CV2 - DI2
V2 = g21V1 + g22I2
Two Port Networks
Z parameters:
V
z 1
11 I
1
V
z 1
12 I
2
I 0
1
V
z 2
21 I
1
I 0
2
V
2
22 I
2
I 0
1
* notes
I 0
2
z11 is the impedance seen looking into port 1
when port 2 is open.
z12 is a transfer impedance. It is the ratio of the
voltage at port 1 to the current at port 2 when
port 1 is open.
z21 is a transfer impedance. It is the ratio of the
voltage at port 2 to the current at port 1 when
port 2 is open.
z22 is the impedance seen looking into port 2
when port 1 is open.
Two Port Networks
Y parameters:
I
y 1
11 V
1
I
y 1
12 V
2
* notes
V 0
2
V 0
1
I
y 2
21 V
1
V 0
2
I
y 2
22 V
2
V 0
1
y11 is the admittance seen looking into port 1
when port 2 is shorted.
y12 is a transfer admittance. It is the ratio of the
current at port 1 to the voltage at port 2 when
port 1 is shorted.
y21 is a transfer impedance. It is the ratio of the
current at port 2 to the voltage at port 1 when
port 2 is shorted.
y22 is the admittance seen looking into port 2
when port 1 is shorted.
Two Port Networks
Z parameters:
Example 1
Given the following circuit. Determine the Z parameters.
I1
I2
10
+
V1
_
+
20
20
V2
_
Find the Z parameters for the above network.
Two Port Networks
Z parameters:
Example 1 (cont 1)
For z11:
For z22:
Z11 = 8 + 20||30 = 20
Z22 = 20||30 = 12
I1
For z12:
+
20
V1
V
z 1
12 I
2
I2
10
I 0
1
20 xI 2 x 20
V1
8 xI 2
20 30
20
V2
_
Therefore:
z 12
8 xI 2
8
I2
z 21
Two Port Networks
Z parameters:
Example 1 (cont 2)
The Z parameter equations can be expressed in
matrix form as follows.
V1 z11
V z
2 21
z12 I 1
z 22 I 2
V1 20 8 I 1
V
I
2 8 12 2
Two Port Networks
Z parameters:
Example 2 (problem 18.7 Alexander & Sadiku)
You are given the following circuit. Find the Z parameters.
I1
I2
V1
_
+
Vx
V2
2Vx
Two Port Networks
Z parameters:
V
z 1
11 I
1
Example 2 (continue p2)
I1
I 0
2
V
V 2V x
6V x V x 2V x
I1 x x
1
6
6
3V x
I1
2
V1
+
Vx
V2
2Vx
but V x V1 I 1
Other Answers
Z21 = -0.667
Substituting gives;
3V1 I 1
I1
2
I2
V1
5
z 11
or
I1
3
Z12 = 0.222
Z22 = 1.111
Two Port Networks
Transmission parameters (A,B,C,D):
The defining equations are:
V1 A B V2
I
I
1 C D 2
V1
A
V2
I1
C
V2
I2 = 0
V1
B
I2
V2 = 0
I2 = 0
I1
D
I2
V2 = 0
Two Port Networks
Transmission parameters (A,B,C,D):
Example
Given the network below with assumed voltage polarities and
Current directions compatible with the A,B,C,D parameters.
I1
+
-I2
+
R1
V1
R2
V2
_
We can write the following equations.
V1 = (R1 + R2)I1 + R2I2
V2 = R2I1 + R2I2
It is not always possible to write 2 equations in terms of the Vs and Is
Of the parameter set.
Two Port Networks
Transmission parameters (A,B,C,D):
Example (cont.)
V1 = (R1 + R2)I1 + R2I2
V2 = R2I1 + R2I2
From these equations we can directly evaluate the A,B,C,D parameters.
V1
A
V2
I1
V2
I2 = 0
I2 = 0
R1 R 2
R2
1
R2
V1
=
B
V
=
0
I2
2
I1
I2
V2 = 0
R1
Later we will see how to interconnect two of these networks together for a final answer
* notes
Two Port Networks
Hybrid Parameters:
V1 h11
I h
2 21
V1
h11
I1
I2
h21
I1
* notes
The equations for the hybrid parameters are:
h12 I 1
h22 V2
V2 = 0
V1
h12
V2
V2 = 0
I2
h22
V2
I1 = 0
I1 = 0
Two Port Networks
The following is a popular model used to represent
a particular variety of transistors.
Hybrid Parameters:
I1
I2
K1
V1
K2V2
_
K3V1
V2
_
We can write the following equations:
V1 AI 1 BV 2
V2
I 2 CI 1
D
* notes
K4
Two Port Networks
Hybrid Parameters:
V1 AI 1 BV 2
V2
I 2 CI 1
D
We want to evaluate the H parameters from the above set of equations.
V1
h11
I1
I2
h21
I1
K1
V2 = 0
=
V2 = 0
K3
V1
h12
V2
I2
h22
V2
K2
I1 = 0
=
I1 = 0
1
K
4
Two Port Networks
Another example with hybrid parameters.
Hybrid Parameters:
Given the circuit below.
I1
-I2
The equations for the circuit are:
+
R1
V1
R2
V2
V1 = (R1 + R2)I1 + R2I2
V2 = R2I1 + R2I2
The H parameters are as follows.
h11
h21
V1
I1
I2
I1
V2=0
=
V2=0
R1
-1
h12
V1
V2
h22
I2
V2
I1=0
I1=0
1
R2
Two Port Networks
Modifying the two port network:
Earlier we found the z parameters of the following network.
I1
I2
10
+
V1
+
20
V1 20 8 I 1
V 8 12 I
2
2
* notes
20
V2
_
Two Port Networks
Modifying the two port network:
We modify the network as shown be adding elements outside the two ports
6
+
10 v
_
I1
I2
10
+
V1
+
20
20
V2
_
We now have:
V1 = 10 - 6I1
V2 = - 4I2
Two Port Networks
Modifying the two port network:
We take a look at the original equations and the equations describing
the new port conditions.
V1 20 8 I 1
V 8 12 I
2
2
So we have,
10 6I1 = 20I1 + 8I2
-4I2 = 8I1 + 12I2
* notes
V1 = 10 - 6I1
V2 = - 4I2
Two Port Networks
Modifying the two port network:
Rearranging the equations gives,
I 1 26
I 8
2
16
10
0
I1
0.4545
I -0.2273
2
Two Port Networks
Y Parameters and Beyond:
Given the following network.
I1
+
V1
I2
+
1
s
V2
_
(a) Find the Y parameters for the network.
(b) From the Y parameters find the z parameters
Two Port Networks
Y Parameter Example
I
y 1
11 V
1
I1 = y11V1 + y12V2
I
y 1
12 V
2
V 0
2
V 0
1
I2 = y21V1 + y22V2
I1
I2
+
V1
I
y 2
21 V
1
I
y 2
22 V
2
V 0
2
+
1
s
V2
_
short
To find y11
V1 I 1 (
s ) I 2
1
21 s
2 s 1
so
We use the above equations to
evaluate the parameters from the
network.
I
y 1
11 V
1
V 0
2
s + 0.5
V 0
1
Two Port Networks
Y Parameter Example
I1
I
y 2
21 V
1
V 0
2
+
V1
I2
+
1
s
_
1
We see
V1 2I 2
I
y 2
21 V
1
= 0.5 S
V2
_
Two Port Networks
Y Parameter Example
I1
To find y12 and y21 we reverse
things and short V1
I
y 1
12 V
2
+
V1
short
I2
+
1
s
V2
_
V 0
1
I
y 2
22 V
2
We have
V 0
1
We have
V2 2I1
I
y 1
12 V 2
= 0.5 S
2s
V2 I 2
( s 2)
1
y22 0.5
s
Two Port Networks
Y Parameter Example
Summary:
y11
y
21
y12 s 0.5
0.5
y22 0.5 0.5 1 s
Now suppose you want the Z parameters for the same network.
Two Port Networks
Going From Y to Z Parameters
For the Y parameters we have:
For the Z parameters we have:
V Z I
I Y V
From above;
V Y
I Z I
Therefore
Z Y
z
z
11
12
z
z
21 22
y
y
22
12
Y
Y
y
y
11
21
Y
Y
where
Y det Y
Two Port Parameter Conversions:
Two Port Parameter Conversions:
To go from one set of parameters to another, locate the set of parameters
you are in, move along the vertical until you are in the row that contains
the parameters you want to convert to then compare element for element
H
z11
h22
Interconnection Of Two Port Networks
Three ways that two ports are interconnected:
Y parameters
ya
* Parallel
y ya
yb
Z parameters
z za
za
Series
yb
zb
zb
ABCD parameters
* Cascade
Ta
Tb
T Ta Tb
Interconnection Of Two Port Networks
Consider the following network:
I1
Find
V2
V1
R1
I2
R1
+
V1
_
T1
R2
T2
R2
V2
_
Referring to slide 13 we have;
R1 R2
V1 R
2
I
1 1
R2
R R
2
R1 1
R2
1
1
R2
R1 V
2
1 2
Interconnection Of Two Port Networks
R1 R2
V1 R
2
I
1 1
R2
R R
2
R1 1
R2
1
1
R2
R1 V
2
I
1 2
Multiply out the first row:
R R 2 R
R R
2 1 V 1
2 R R ( I )
V1 1
1
2
R
R
1
2
R
2
2
2
Set I2 = 0 ( as in the diagram)
V2
V1
R2 2
R1 3 R1 R2 R2 2
2
Can be verified directly
by solving the circuit
Basic Laws of Circuits
End of Lesson
Two-Port Networks
Вам также может понравиться
- ch19 Two-Port Networks PDFДокумент19 страницch19 Two-Port Networks PDFRohit Gandhi0% (1)
- Devices & Circuits RLC CircuitsДокумент28 страницDevices & Circuits RLC CircuitsANJALI DEOREОценок пока нет
- Application of ABCDДокумент15 страницApplication of ABCDSantanu Nath50% (4)
- Multistage AmplifierДокумент22 страницыMultistage AmplifierVijay AnandhОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics: Single Phase AC-AC ConvertersДокумент18 страницPower Electronics: Single Phase AC-AC ConvertersMaruti MohiteОценок пока нет
- Unijunction TransistorДокумент12 страницUnijunction TransistorGogoi LeftoverОценок пока нет
- Lab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterДокумент5 страницLab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterHemanth GedelaОценок пока нет
- Voltage Multipliers: Half-Wave Voltage DoublerДокумент5 страницVoltage Multipliers: Half-Wave Voltage DoublerKade Ben100% (1)
- Common Emitter UnbypassedДокумент38 страницCommon Emitter Unbypassedaliffuden 123Оценок пока нет
- Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersДокумент15 страницThree Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersAnonymous 78iAn6100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-77-Đã Chuyển ĐổiДокумент9 страницElectrical and Electronics Measurements and Instrumentation-77-Đã Chuyển ĐổiNguyên Nguyễn SơnОценок пока нет
- Unijunction Transistor: By: Smridhi ChawlaДокумент27 страницUnijunction Transistor: By: Smridhi Chawlasmridhi chawla100% (1)
- Power Semiconductor DevicesДокумент11 страницPower Semiconductor DevicesBhavesh Kaushal100% (1)
- EM-I Lab Viva Questions Updated OnДокумент6 страницEM-I Lab Viva Questions Updated OnNagamohan BilluОценок пока нет
- UNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEEДокумент12 страницUNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEESomesh Singh RathoreОценок пока нет
- EDC-II Unit-4 Part 1 SCR, Diac, Triac, SCS, GTO, & LASCRДокумент39 страницEDC-II Unit-4 Part 1 SCR, Diac, Triac, SCS, GTO, & LASCRsamarthОценок пока нет
- ELECTRON DEVICES AND CIRCUITS: 2 Marks Q & AДокумент28 страницELECTRON DEVICES AND CIRCUITS: 2 Marks Q & Ag jagadeesan83% (6)
- Merz Price Differential Protection For TransformerДокумент2 страницыMerz Price Differential Protection For TransformerapjbalamuruganОценок пока нет
- S6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFДокумент27 страницS6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFhariОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics - 2 MARKSДокумент30 страницPower Electronics - 2 MARKSkarthik kumar50% (4)
- Power Electronics Lab ManualДокумент47 страницPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Unit-3 3. Bipolar Junction TransistorДокумент31 страницаUnit-3 3. Bipolar Junction TransistorshivaniОценок пока нет
- Clippers and ClamersДокумент15 страницClippers and ClamersThilaga MohanОценок пока нет
- Experiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA MethodДокумент6 страницExperiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA Method61EEPrabhat Pal100% (1)
- Chap 1 Single PhaseTransformerДокумент37 страницChap 1 Single PhaseTransformerKritika MehtaОценок пока нет
- Experiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveДокумент13 страницExperiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveskmrajkumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 - Three Phase TransformerДокумент30 страницChapter 10 - Three Phase TransformerWarez Ali0% (1)
- LabSheet Experiments - Giatutinhyeu14 - 2Документ176 страницLabSheet Experiments - Giatutinhyeu14 - 2Nhi OtОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFДокумент8 страницElectronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFVenkata SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ13 страницChapter 6aregawi weleabezgiОценок пока нет
- Ec8261 Lab ManualДокумент94 страницыEc8261 Lab ManualJayamani Krishnan0% (1)
- Magnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateДокумент60 страницMagnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateSuyash SinghОценок пока нет
- Single Phase Series and Parallel Inverter FinalДокумент19 страницSingle Phase Series and Parallel Inverter Finalmazza23467% (3)
- 3 ChopperДокумент63 страницы3 ChopperFaida HamidОценок пока нет
- Ac DrivesДокумент36 страницAc Drivesaswardi50% (2)
- Lecture 1 - Mesh and Nodal AnalysisДокумент50 страницLecture 1 - Mesh and Nodal AnalysisCindy KoechОценок пока нет
- Chapter ThreeДокумент67 страницChapter Threeetayhailu80% (5)
- EEET 205 Lab - 102Документ53 страницыEEET 205 Lab - 102Franch Maverick Arellano LorillaОценок пока нет
- BJT Biasing (DC Analysis)Документ10 страницBJT Biasing (DC Analysis)Mozibor RahmanОценок пока нет
- Buet Eee 08Документ15 страницBuet Eee 08kalamhassan33% (3)
- Power Electronics Lab Manual With LogoДокумент69 страницPower Electronics Lab Manual With LogoPunith Gowda M BОценок пока нет
- Half Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryДокумент10 страницHalf Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryLakshayОценок пока нет
- Transformer Lab ManualДокумент68 страницTransformer Lab ManualRolando Cruz100% (1)
- Power Electronics (Ques - Ch2 - Rectifiers) PDFДокумент44 страницыPower Electronics (Ques - Ch2 - Rectifiers) PDFmadivala nagaraja0% (1)
- Em Lab-II ManualДокумент45 страницEm Lab-II Manualrkadiraj701150% (4)
- Lecture 7 Three-Phase TransformersДокумент4 страницыLecture 7 Three-Phase TransformersShahrim MohdОценок пока нет
- Circuitrix EventДокумент6 страницCircuitrix EventNikhil KumarОценок пока нет
- Op Amp IntegratorДокумент14 страницOp Amp IntegratorMuhammad Haroon50% (2)
- Power BJTДокумент14 страницPower BJTJahangeer SoomroОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Lab Manual1Документ72 страницыPower Electronics Lab Manual1Harish SvОценок пока нет
- Two Port NetworksДокумент34 страницыTwo Port Networksvijayalakshmiv VEMURIОценок пока нет
- NA Unit-IVДокумент33 страницыNA Unit-IVvijayalakshmiv VEMURIОценок пока нет
- Two Port NetworksДокумент33 страницыTwo Port Networkskumiko580Оценок пока нет
- Two Port Networks PPT 1 B TECH 3RDДокумент32 страницыTwo Port Networks PPT 1 B TECH 3RDEuthecas KipkiruiОценок пока нет
- Two Port networks-NEOДокумент30 страницTwo Port networks-NEOAntaredja KartasasmitaОценок пока нет
- Ec2 Chpter 1Документ54 страницыEc2 Chpter 1Leet CyberwormОценок пока нет
- Elena Jaringan 2 PortДокумент15 страницElena Jaringan 2 PortFarid AlhasanОценок пока нет
- Andersen CH 19 Final R1Документ19 страницAndersen CH 19 Final R1utpОценок пока нет
- LMH Chapter5Документ58 страницLMH Chapter5Nguyen Son N NguyenОценок пока нет
- Two Port 2021Документ34 страницыTwo Port 2021Paidamoyo MuzvidziwaОценок пока нет
- ELEN 127 - Lab 4Документ1 страницаELEN 127 - Lab 4ajaypalОценок пока нет
- Document 2Документ1 страницаDocument 2ajaypalОценок пока нет
- Elen 104 - HW 3Документ2 страницыElen 104 - HW 3ajaypalОценок пока нет
- Linear Voltage Regulator ProjectДокумент14 страницLinear Voltage Regulator ProjectajaypalОценок пока нет
- IEEE Branch Leadership Training P G: Rahim Khoie, PH.DДокумент56 страницIEEE Branch Leadership Training P G: Rahim Khoie, PH.DajaypalОценок пока нет
- Katha June 1984Документ8 страницKatha June 1984tempsabyОценок пока нет
- Prelab 4Документ3 страницыPrelab 4ajaypalОценок пока нет
- Gopalsingh Resume2Документ1 страницаGopalsingh Resume2ajaypalОценок пока нет
- Eng1 - Annotated Analytical BibliographyДокумент3 страницыEng1 - Annotated Analytical BibliographyajaypalОценок пока нет
- SCTR 19 - Annotated BibДокумент2 страницыSCTR 19 - Annotated BibajaypalОценок пока нет
- Working Hard or Hardly WorkingДокумент2 страницыWorking Hard or Hardly WorkingajaypalОценок пока нет
- Eng1 - Writing Assingment 2nd DraftДокумент5 страницEng1 - Writing Assingment 2nd DraftajaypalОценок пока нет
- Heart of ChocolateДокумент5 страницHeart of ChocolateajaypalОценок пока нет
- G CH 16Документ5 страницG CH 16ajaypalОценок пока нет
- G CH 10Документ4 страницыG CH 10ajaypalОценок пока нет
- Undergraduate Bulletin Class 2008Документ229 страницUndergraduate Bulletin Class 2008ajaypalОценок пока нет
- Gill 1Документ4 страницыGill 1ajaypalОценок пока нет
- G CH 13Документ4 страницыG CH 13ajaypalОценок пока нет
- G CH 4Документ3 страницыG CH 4ajaypalОценок пока нет
- Gill 1Документ3 страницыGill 1ajaypalОценок пока нет
- G CH 11Документ4 страницыG CH 11ajaypalОценок пока нет
- G CH 8Документ4 страницыG CH 8ajaypalОценок пока нет
- G CH 5Документ4 страницыG CH 5ajaypalОценок пока нет
- We Are DarkДокумент4 страницыWe Are DarkajaypalОценок пока нет
- PygmalionДокумент10 страницPygmalionajaypal100% (4)
- Examples S-Convex FunctionsДокумент7 страницExamples S-Convex Functionstradutora100% (2)
- Mongo DB Basic CommandsДокумент15 страницMongo DB Basic CommandsgauriОценок пока нет
- Anachem NotesДокумент1 страницаAnachem NoteshОценок пока нет
- Cool Fire Manual 45M620N2UK-01Документ198 страницCool Fire Manual 45M620N2UK-01prejby91% (11)
- B8 em WavesДокумент1 страницаB8 em Wavesbalikisyakubu64Оценок пока нет
- Iconnect v3.1 User ManualДокумент105 страницIconnect v3.1 User Manualcjamiz2006Оценок пока нет
- REVIEW TASK 1 - Capitalization, Punctuation, Fragments, Run-On Sentences and Subject & Verb Agreement Review (-1Документ2 страницыREVIEW TASK 1 - Capitalization, Punctuation, Fragments, Run-On Sentences and Subject & Verb Agreement Review (-1Johao DoradoОценок пока нет
- IISER Aptitude Test 17th Sept 2021Документ22 страницыIISER Aptitude Test 17th Sept 2021Muskaan KathuriaОценок пока нет
- SeepageДокумент25 страницSeepagesheikh jamilОценок пока нет
- Running Concurrent WorkflowsДокумент10 страницRunning Concurrent WorkflowsyprajuОценок пока нет
- HW 2 SolДокумент5 страницHW 2 SoltechutechuОценок пока нет
- Drawing Free-Body DiagramsДокумент5 страницDrawing Free-Body DiagramsMahamadali DesaiОценок пока нет
- Elementary Data Organisation-1Документ15 страницElementary Data Organisation-1zidhi bachaОценок пока нет
- Applied Statistics For Bioinformatics Using RДокумент279 страницApplied Statistics For Bioinformatics Using RArdhi ShihabОценок пока нет
- Fasteners For Use With PC BoardsДокумент25 страницFasteners For Use With PC BoardsJustin PhanОценок пока нет
- The Comparison of Two Activation Techniques To Prepare Activated Carbon From Corn CobДокумент7 страницThe Comparison of Two Activation Techniques To Prepare Activated Carbon From Corn CobRafaelaMarinhoFonsecaОценок пока нет
- Video Display DevicesДокумент66 страницVideo Display DevicesshabanaОценок пока нет
- Module01 - AHPДокумент18 страницModule01 - AHPmia100% (1)
- Ict SS 1Документ37 страницIct SS 1angus ogwucheОценок пока нет
- U Center UserGuide (UBX 13005250)Документ94 страницыU Center UserGuide (UBX 13005250)Phi Ra Uch100% (1)
- Face Mask DetectionДокумент34 страницыFace Mask DetectionAmarjeet AmratОценок пока нет
- R1218x SERIES: Step-Up DC/DC Converter For White LED BacklightДокумент21 страницаR1218x SERIES: Step-Up DC/DC Converter For White LED Backlight666667Оценок пока нет
- Exploring Linux Build Systems - Buildroot Lab ManualДокумент38 страницExploring Linux Build Systems - Buildroot Lab Manualhamzamehboob103Оценок пока нет
- Multilevel Converters - Dual Two-Level Inverter SchemeДокумент226 страницMultilevel Converters - Dual Two-Level Inverter Schemejuancho2222Оценок пока нет
- LiftCell User ManualДокумент4 страницыLiftCell User ManualEdini ZenaОценок пока нет
- Application Note: Vishay General SemiconductorДокумент4 страницыApplication Note: Vishay General SemiconductorMamoon AlrimawiОценок пока нет
- Windows Forms in VBNET Tutorial With Example CodeДокумент12 страницWindows Forms in VBNET Tutorial With Example CodeLubadri LmОценок пока нет
- Surgical Sutures: Suture SizeДокумент7 страницSurgical Sutures: Suture SizeMei PayumoОценок пока нет
- AmdДокумент14 страницAmdObed Andalis100% (1)
- Qap For Steam TurbineДокумент3 страницыQap For Steam TurbinedgmprabhakarОценок пока нет