Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Business Mathematics
Загружено:
Girjesh Chouhan100%(1)100% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
777 просмотров14 страницRATIO "in the ratio a / b which is written as a : b, is a mathematical operations" PERCENTAGE "the word percent consist of two words 'per' and 'cent', per means each and cent means hundred" simultaneous equations "have two variables, e.g:4 x + y = 2"
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документRATIO "in the ratio a / b which is written as a : b, is a mathematical operations" PERCENTAGE "the word percent consist of two words 'per' and 'cent', per means each and cent means hundred" simultaneous equations "have two variables, e.g:4 x + y = 2"
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(1)100% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
777 просмотров14 страницBusiness Mathematics
Загружено:
Girjesh ChouhanRATIO "in the ratio a / b which is written as a : b, is a mathematical operations" PERCENTAGE "the word percent consist of two words 'per' and 'cent', per means each and cent means hundred" simultaneous equations "have two variables, e.g:4 x + y = 2"
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 14
RATIO
“In the ratio a / b which is written as a : b, is a
mathematical operations ratio and fraction are written
in the same manner but in fact, their meanings are
different”
Formula:
ax + bx = n for two parts
ax + bx + cx = n for three parts
Proportion:
A statement which represents that the two ratio are
equal is called proportion, eg: let the two ratios a/b
and c/d be equal than equation a / b = c / d is a
proportion or a / b :: c / d or a:b::c:d
Percentage: the word percent consist of two words ‘per’
and ‘cent’, per means each and cent means hundred
Commission: Amount of commission = Rate of
commission x Amount of sales / 100
Rate of commission = Amount of commission x 100 /
Amount of sales
Amount of sales = Amount of commission x 100 /
Rate of commissio
Amount of del – creder commission = Credit sales x
Rate commission / 100
Profit and loss: Profit percent = Profit x 100 / cost
price, Cost price = profit x 100 / profit %.
SIMULATANEOUS EQUATIONS
“simultaneous equations have two variables, e.g:4 x + y
= 2”
METHODS:
Graphical method: to solve two simultaneous
equations in two variables by graphic method
Substitutions method: this method consists of
expressing one variable in term of other in any one
equation and substituting this value in other equation
by solving this equation so formed
Comparison method: keeping one variable at one
end and all other values at other end, do the same
with other equation also and put these equation in
front of each other by putting “=” sign in between,
only one variable would be remaining to be found
Elimination method: “2X +Y = 8” – “2X - Y = 4”,
answer is 2Y = 4, so Y = 2 and thereby X = 3.
ELEMENTARY MATRIX
“Matrix gives a systematic method to write a system of
equations. Whatever be the size of that system of
equations”
TYPES:
Horizontal Matrix: more columns and less rows
Vertical Matrix: less columns and more rows
Row Matrix: more than one columns and one row
Column Matrix: one column and more than one rows
Vector Matrix: one column and one row
Square Matrix: equal amount of columns and rows
THEORY OF LOGARITHM
“if ax = n (a > 0, a ≠ 1) then the index x is called the
logarithms of the number n with respect to the base a
and is expressed as Logan = x read as the logarithm
of n to the base a is x”
Definition:
The logarithm of a number to a given base is the index
or power to which the base must be raised to produce
the number i.e. to make it equal to the given number
for eg: 32 = 9 will be written as Log39 = 2
Anti-Logarithm:
The antilogarithm function antilogb(y) is the
inverse function of the logarithm function logb(x); it
can be written in closed form as by. The antilog
notation was common before the advent of modern
calculators and computers: tables of antilogarithms to
the base 10 were useful in carrying out computations
by hand
Differential calculus:
The study of the definition, properties, and
applications of the derivative of a function. The
process of finding the derivative is
called differentiation. Given a function and a point in
the domain, the derivative at that point is a way of
encoding the small-scale behavior of the function near
that point. By finding the derivative of a function at
every point in its domain, it is possible to produce a
new function, called the derivative function or just
the derivative of the original function.
SIMPLE INTEREST
“The consideration of sum of money to be paid for the
borrowed money”
Calculation: Principal x rate x months / (100 x 12)
Compound Interest: When the simple interest is
added to the principal so that the amount become the
principal for next period
Linear Programming:
Linear programming (LP) is a mathematical method
for determining a way to achieve the best outcome
(such as maximum profit or lowest cost) in a given
mathematical model for some list of requirements
represented as linear equations. More formally, linear
programming is a technique for the optimization of
a linear objective function, subject to linear
equality and linear inequality constraints.
APT Contact
Landline No. 4082444 /
2445 / 2453
Mobile No. 9755557307
Website :
www.aptinfoservices.co
m
E-mail :
info@aptinfoservices.com
Вам также может понравиться
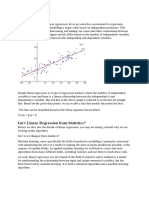
- Isn't Linear Regression From Statistics?Документ4 страницыIsn't Linear Regression From Statistics?umang rajanОценок пока нет
- Linear Regression For BeginnersДокумент4 страницыLinear Regression For BeginnersrajatОценок пока нет
- LINEAR PROGRAMMING OVERVIEWДокумент9 страницLINEAR PROGRAMMING OVERVIEWjonty777Оценок пока нет
- MGMT ScienceДокумент35 страницMGMT ScienceraghevjindalОценок пока нет
- Maths ProjectДокумент20 страницMaths ProjectChirag JoshiОценок пока нет
- A3 110006223Документ7 страницA3 110006223Samuel DharmaОценок пока нет
- Curve Fitting With MatlabДокумент38 страницCurve Fitting With Matlabtanushrisharma100% (1)
- UNIt-3 TYДокумент67 страницUNIt-3 TYPrathmesh Mane DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Maximizing Profits with Linear ProgrammingДокумент23 страницыMaximizing Profits with Linear ProgrammingAjay Vernekar100% (1)
- ME 17 - Homework #5 Solving Partial Differential Equations Poisson's EquationДокумент10 страницME 17 - Homework #5 Solving Partial Differential Equations Poisson's EquationRichardBehielОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra NotesДокумент29 страницLinear Algebra NotesArun P MadhavОценок пока нет
- Linear Regression: What Is Regression Analysis?Документ21 страницаLinear Regression: What Is Regression Analysis?sailusha100% (1)
- INTRODUCTION TO STATISTICS USING RДокумент20 страницINTRODUCTION TO STATISTICS USING REduard MarsОценок пока нет
- Project On Linear Programming ProblemsДокумент29 страницProject On Linear Programming ProblemsVinod Bhaskar67% (129)
- Linear RegressionДокумент83 страницыLinear RegressionRajaОценок пока нет
- Quick and Dirty Regression TutorialДокумент6 страницQuick and Dirty Regression TutorialStefan Pius DsouzaОценок пока нет
- calculausДокумент8 страницcalculausezrachupaza151Оценок пока нет
- Linear ProgrammingДокумент54 страницыLinear ProgrammingkatsandeОценок пока нет
- Notes On Linear ProgrammingДокумент13 страницNotes On Linear Programmingdrseema659Оценок пока нет
- Condition NumberДокумент4 страницыCondition NumberDeep JoshiОценок пока нет
- RegressionДокумент9 страницRegressionRaghavendra SwamyОценок пока нет
- Integration and DifferentiationДокумент27 страницIntegration and DifferentiationJane-Josanin ElizanОценок пока нет
- Assign#5 CorrelationДокумент2 страницыAssign#5 Correlationjax328Оценок пока нет
- Vijay Maths ProjectДокумент54 страницыVijay Maths ProjectVijay MОценок пока нет
- Calculate change, assessments, sums, largest number, leap yearsДокумент6 страницCalculate change, assessments, sums, largest number, leap yearsAyesha KhanОценок пока нет
- Implementation of Linear Regression With PythonДокумент5 страницImplementation of Linear Regression With PythonMaisha MashiataОценок пока нет
- Linear Programming Techniques for Resource AllocationДокумент23 страницыLinear Programming Techniques for Resource AllocationAlain BernabeОценок пока нет
- 7 - Programming With MATLABДокумент22 страницы7 - Programming With MATLABErtan AkçayОценок пока нет
- Sales and AdvertisingДокумент14 страницSales and AdvertisingShaheen ZafarОценок пока нет
- LP Chapter 1Документ65 страницLP Chapter 1trixie eustaquioОценок пока нет
- How To Use MATLABДокумент5 страницHow To Use MATLABapi-3857351Оценок пока нет
- Notes On MATLABДокумент26 страницNotes On MATLABSVR07Оценок пока нет
- Graphing Rational FunctionsДокумент7 страницGraphing Rational FunctionsSam PiehlОценок пока нет
- Least Square MethodДокумент2 страницыLeast Square MethodgknindrasenanОценок пока нет
- Plotting Experimental Data in Graphs and Error AnalysisДокумент35 страницPlotting Experimental Data in Graphs and Error AnalysisSURESH SURAGANIОценок пока нет
- Linear Regression - Jupyter NotebookДокумент56 страницLinear Regression - Jupyter NotebookUjwal Vajranabhaiah100% (2)
- Business Mathematics and Statistics E-Sample PDFДокумент36 страницBusiness Mathematics and Statistics E-Sample PDFCaroline NdiranguОценок пока нет
- Lab 04 Eigen Value Partial Pivoting and Elimination PDFДокумент12 страницLab 04 Eigen Value Partial Pivoting and Elimination PDFUmair Ali ShahОценок пока нет
- Matlab Tutorial: Introduction to the FundamentalsДокумент10 страницMatlab Tutorial: Introduction to the Fundamentalsmysteriosan454Оценок пока нет
- Expressions and FunctionsДокумент42 страницыExpressions and FunctionsBrian FreemanОценок пока нет
- Simplex Method For Standard Maximization ProblemДокумент6 страницSimplex Method For Standard Maximization ProblemyyyОценок пока нет
- 5.6 - Linear Programming: DefinitionsДокумент11 страниц5.6 - Linear Programming: DefinitionsRamon VillarealОценок пока нет
- Arithmetic OperationsДокумент3 страницыArithmetic OperationskhumisoОценок пока нет
- AptitudeДокумент11 страницAptitudeVineeth ReddyОценок пока нет
- MidtermreviewprojectpptxДокумент37 страницMidtermreviewprojectpptxapi-553954607Оценок пока нет
- Linear Regression StatsДокумент2 страницыLinear Regression StatsytnateОценок пока нет
- LINEAR PROGRAMMING: OPTIMIZING WITH CONSTRAINTSДокумент19 страницLINEAR PROGRAMMING: OPTIMIZING WITH CONSTRAINTSChristian paul ArnaizОценок пока нет
- Unit 3.1 Gradient Descent in Linear RegressionДокумент6 страницUnit 3.1 Gradient Descent in Linear Regressiontruptiratho5Оценок пока нет
- Project On Linear Programming ProblemsДокумент32 страницыProject On Linear Programming ProblemsJeeban BaralОценок пока нет
- Mba or Unit-Iii NotesДокумент12 страницMba or Unit-Iii NotesAmruta PeriОценок пока нет
- Ten ProblemsДокумент31 страницаTen ProblemsCH. Kranthi RekhaОценок пока нет
- Programming ReportДокумент46 страницProgramming ReportKauths AnudinОценок пока нет
- Anti Derivative of CSCДокумент4 страницыAnti Derivative of CSCnishagoyalОценок пока нет
- Lecture2 NotesДокумент17 страницLecture2 NotesQamar SultanaОценок пока нет
- Sympoly Toolbox IssuesДокумент7 страницSympoly Toolbox IssuesAli FahemОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1Документ20 страницLesson 1Cares OlotrabОценок пока нет
- Matlab Training Session Iii Numerical Methods: Solutions To Systems of Linear EquationsДокумент14 страницMatlab Training Session Iii Numerical Methods: Solutions To Systems of Linear EquationsAli AhmadОценок пока нет
- MATLAB Environment & Basic Math OperationsДокумент25 страницMATLAB Environment & Basic Math OperationsBurak IşıkОценок пока нет
- Be Familiar With The Chartered Accountancy CourseДокумент31 страницаBe Familiar With The Chartered Accountancy CourseGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Indian Contract ActДокумент30 страницIndian Contract ActGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Word ProcessingДокумент13 страницWord ProcessingGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Principles of AccountsДокумент23 страницыPrinciples of AccountsGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Development of EnterpreneurshipДокумент33 страницыDevelopment of EnterpreneurshipGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Micro EconomicsДокумент37 страницMicro EconomicsGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Operating System BasicsДокумент12 страницOperating System BasicsGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Computer BasicsДокумент24 страницыComputer BasicsGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Business OrganisationДокумент33 страницыBusiness OrganisationGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Business EnvironmentДокумент30 страницBusiness EnvironmentGirjesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- WMA01 01 Rms 20180308Документ28 страницWMA01 01 Rms 20180308Omar HashemОценок пока нет
- Sardar Patel College Engineering Academic Book 2015-16Документ53 страницыSardar Patel College Engineering Academic Book 2015-16AdvaitОценок пока нет
- 10 Non-Exact EquationsДокумент20 страниц10 Non-Exact EquationsKaye EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- Functions of Several Variables ExplainedДокумент92 страницыFunctions of Several Variables ExplainedSwapnil SahuОценок пока нет
- 9th Class 2nd TestДокумент1 страница9th Class 2nd TestNabeel HussainОценок пока нет
- B.E. EEE SyllabusДокумент196 страницB.E. EEE Syllabusrkar-7Оценок пока нет
- Cprogramming TutorialДокумент371 страницаCprogramming Tutorialdheeraj ShahОценок пока нет
- Guidelines for Late Arrivals During Licensure ExamsДокумент9 страницGuidelines for Late Arrivals During Licensure ExamsJessie Radaza TutorОценок пока нет
- Syllabus 1st Year B1.tech - PDFДокумент52 страницыSyllabus 1st Year B1.tech - PDFSudip GhimireОценок пока нет
- Math (Grade 1, Semester 1) : Right Triangle TrigonometryДокумент51 страницаMath (Grade 1, Semester 1) : Right Triangle TrigonometryhenryОценок пока нет
- Printable Week 1 SlidesДокумент16 страницPrintable Week 1 SlidesSpencer gamingОценок пока нет
- Signature Assignment Related RatesДокумент4 страницыSignature Assignment Related Ratesapi-306799768Оценок пока нет
- Batch Process Control StrategiesДокумент12 страницBatch Process Control StrategiesSunny SunОценок пока нет
- Maths (041) Xii PB 1 QP Set CДокумент7 страницMaths (041) Xii PB 1 QP Set Cup14604Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics n5 - Study Guide 2021 (Damelin)Документ60 страницMathematics n5 - Study Guide 2021 (Damelin)ondellakereОценок пока нет
- Program: Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence: Section 1. Linear Algebra and Analytic GeometryДокумент49 страницProgram: Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence: Section 1. Linear Algebra and Analytic GeometryTameneОценок пока нет
- Convolutional neural networks for text classification: Implementing forward, backward and gradient checkingДокумент3 страницыConvolutional neural networks for text classification: Implementing forward, backward and gradient checkingYvonne Yifan ZhouОценок пока нет
- Chapter1: Numerical Differentiation: 1.1 Finite Difference Approximation of The DerivativeДокумент51 страницаChapter1: Numerical Differentiation: 1.1 Finite Difference Approximation of The DerivativeHassan allaОценок пока нет
- Elements of Complex AnalysisДокумент62 страницыElements of Complex AnalysisNaledi xuluОценок пока нет
- Calculus 1 Module Aguilar Joanne - 2020Документ115 страницCalculus 1 Module Aguilar Joanne - 2020Bert AguilarОценок пока нет
- Discovering Equations From Data: Melissa R. McguirlДокумент29 страницDiscovering Equations From Data: Melissa R. McguirlsaidОценок пока нет
- Multivariable Calculus Review SheetДокумент2 страницыMultivariable Calculus Review SheetSteven Walker100% (1)
- The Boundary Value Problem For Second Order Ordinary Linear Differential Equation With Variable CoefficientДокумент44 страницыThe Boundary Value Problem For Second Order Ordinary Linear Differential Equation With Variable CoefficientGMAILОценок пока нет
- MATHДокумент28 страницMATHBarry ChenОценок пока нет
- B. Tech. Revised Scheme Syllabus CSE BДокумент147 страницB. Tech. Revised Scheme Syllabus CSE BmtechОценок пока нет
- BBA-BBIS PROGRAM-SYLLABUS-June 2013 (Latest) PDFДокумент123 страницыBBA-BBIS PROGRAM-SYLLABUS-June 2013 (Latest) PDFMargaretisaОценок пока нет
- Spe 131787Документ15 страницSpe 131787downloader1983Оценок пока нет
- Calculus - II - Paul DawkinsДокумент379 страницCalculus - II - Paul Dawkinssumeet1417100% (3)
- Differentiation and Integration FormulasДокумент3 страницыDifferentiation and Integration FormulasAbell AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- HW 3 SolДокумент3 страницыHW 3 Solmasfenix1Оценок пока нет