Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (Part 2) (Ch:20 P.O.M.E)
Загружено:
KaziRafi0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров9 страницEco 104
Оригинальное название
Lecture 10_ECO 104
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документEco 104
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров9 страницECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (Part 2) (Ch:20 P.O.M.E)
Загружено:
KaziRafiEco 104
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 9
Lecture 10
Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply
(Part 2)
(Ch:20; P.O.M.E)
ECO 104
Faculty: Asif Chowdhury
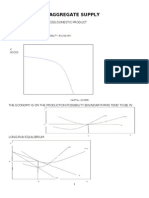
The distinction between long run & short
run phases in an economy is defined by
the behavior of Aggregate Supply (AS).
As we have seen previously, the long run
AS doesnt respond to price changes,
however the short run AS is responsive to
price & there is a direct relationship
between price & quantity of goods &
services supplied. They move in the
same direction. Hence the short run AS is
upward sloping.
Why is AS curve upward
sloping:
Macroeconomist
have
formed
three
theories to explain why the AS curve is
upward sloping in the short run All these
three
theories
share
one
common
implication; whenever price deviates from
expected level ( the level that the people
expected the general price to be at),
quantity supply of output deviates from its
long run natural rate level. Higher than
expected price implies higher than natural
rate of output, lower than expected price
implies lower than natural rate of output.
The three theories explaining
why AS is upward sloping:
o The Sticky Wage Theory: Nominal wage being set based on
expected price level-actual price level may be higher or lowercost of production varying accordingly-employment & output
varying accordingly in the short run.
o The Sticky Price Theory: due to presence of Menu Cost not all
firms change price simultaneously towards the general price
level. Some firms can lag behind & depending on whether the
price level is higher or lower than the long run trend will
accordingly induce more quantity supplied, or less quantity
supplied of goods & services.
o The Misperception Theory: When general price level is rising/
falling supplier may be under the misperception that their
relative prices has risen/fallen, they will then adjust quantity
supply of output accordingly. It also applies in case of nominal
wage, when nominal wage is falling worker might not perceive
that the overall price level is also falling, hence react by
increasing/decreasing labor supply.
Summing up the theories:
Quantity of Output Supplied: Natural Rate of
Output+ a( Actual Price Level-Expected Price
Level)
As mentioned previously, we are seeing a
deviation in output from its long run natural rate,
when actual price level is different from expected
level.
Its important to note that all the theories present
a temporary scenario, hence the short run, in the
long run wages, prices & misperceptions are all
adjusted according to the long run trend.
Factors that can shift the short
run AS curve:
All the factors that can shift the long run AS
can also shift the short run AS. E.g. capital,
labor are factors which shifts both the long
run & short run AS. However, in addition to
these factors, the expected price level is
the additional factor which can shift the
short run AS. The three theories which tries
to explain why the short run AS is upward
sloping, are all based on the expected price
level. So when expectation of people
regarding price level changes, the short
run AS shifts.
Taking the case of Sticky Wage Theory
again; when expected price level is high,
nominal wage level also tends to be high,
cost of production rise, output level falls &
AS curve shifts to the left & vice versa.
During short run the expectations of price
level by people are fixed, in the long run
these expectations adjust & this in turn
causes the AS curve to shift & it shifts
towards the long run AS level.
Effects of shift in Aggregate
Demand (AD):
Output level falls-Employment level
falls-Price level falls- recession &
unemployment happens- due to
lower price, expected price level is
low, so short run AS curve shifts upthe economy moves back to its
natural rate of output at a lower
price level.
Effects of shift in Aggregate
Supply (AS):
Output level falls & price rises-leads to Stagflation.
o Stagflation: falling output (recession) & rising
prices ( Inflation)
Rising prices leads to rising nominal wage-this in
turn leads to wage-price spiral-however eventually
falling output & lower level of employment leads
to lower nominal wage level-again short run AS
curve shifts up to the long run level of output at a
lower price level.
The government can push up Aggregate Demand
to counter the effect of falling Aggregate Supply,
this will restore the economy to its natural rate &
avoid falling output & employment, but the price
will be at a permanently higher level.
Вам также может понравиться
- Aggregate Supply AnswersДокумент10 страницAggregate Supply AnswersMomoОценок пока нет
- BSECO - 12 (Aggregate Supply Curve)Документ15 страницBSECO - 12 (Aggregate Supply Curve)Paris AliОценок пока нет
- Aggregate SupplyДокумент9 страницAggregate SupplyMomoОценок пока нет
- Worksheet For Chapter 15 (2023)Документ27 страницWorksheet For Chapter 15 (2023)Ncebakazi DawedeОценок пока нет
- Ch4 Aggregate SSДокумент13 страницCh4 Aggregate SSProveedor Iptv EspañaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Macro SolutionДокумент11 страницChapter 2 Macro Solutionsaurabhsaurs100% (1)
- Chapter 5Документ11 страницChapter 5HayamnotОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand and Supply AnalysisДокумент44 страницыAggregate Demand and Supply AnalysisTinotenda DubeОценок пока нет
- Essay Test ECO 121 Nguyễn Hồ Phan Hiển MKT1604Документ3 страницыEssay Test ECO 121 Nguyễn Hồ Phan Hiển MKT1604Nguyễn Lê DươngОценок пока нет
- Economics of Compensation-Note4Документ16 страницEconomics of Compensation-Note4Shanthu BiswasОценок пока нет
- Ad AsДокумент24 страницыAd AsoggyОценок пока нет
- Ecn 341 Lecture Note 7-Classical Macroeconomics and Keynesian General Equilibrium of The As-Ad ModelДокумент26 страницEcn 341 Lecture Note 7-Classical Macroeconomics and Keynesian General Equilibrium of The As-Ad ModelZayyОценок пока нет
- CH3 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyДокумент40 страницCH3 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyTiviyaОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Supply & Aggregate DemandДокумент51 страницаAggregate Supply & Aggregate DemandRahul ShakyaОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics 1 - Chapter FiveДокумент38 страницMacroeconomics 1 - Chapter FiveBiruk YidnekachewОценок пока нет
- Session 18Документ15 страницSession 18Sid Tushaar SiddharthОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Supply: Economy at Potential Gross Domestic Product Microeconomic ViewДокумент6 страницAggregate Supply: Economy at Potential Gross Domestic Product Microeconomic ViewMAk KhanОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply EconomicsДокумент38 страницAggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply EconomicsEsha ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Course9 - Introduction To Economic FluctuationsДокумент12 страницCourse9 - Introduction To Economic FluctuationsAngga ArsitekОценок пока нет
- Ch. 22 & 23 - As-AD Analysis - PostedДокумент35 страницCh. 22 & 23 - As-AD Analysis - PostedEslam HendawiОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand and Supply: Factors That Change The Price Level and Real GDPДокумент53 страницыAggregate Demand and Supply: Factors That Change The Price Level and Real GDPCunanan, Malakhai JeuОценок пока нет
- 2.3 Demand and Supply in A Labour MarketДокумент6 страниц2.3 Demand and Supply in A Labour MarketFoisal Mahmud RownakОценок пока нет
- Questions For Review p772: Q2, Q4, Q5Документ5 страницQuestions For Review p772: Q2, Q4, Q5Rashid AyubiОценок пока нет
- FINALSДокумент16 страницFINALSJes DonadilloОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics Lecture :)Документ14 страницMacroeconomics Lecture :)John WoodОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Supply PowerPoint PresentationДокумент24 страницыAggregate Supply PowerPoint PresentationRatna VadraОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics Encapsulated in Three Models (Recovered)Документ33 страницыMacroeconomics Encapsulated in Three Models (Recovered)Katherine Asis NatinoОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Economic Fluctuations:: "Macroeconomics by Mankiw"Документ23 страницыIntroduction To Economic Fluctuations:: "Macroeconomics by Mankiw"rabia liaqatОценок пока нет
- FINAL Econ ReportДокумент13 страницFINAL Econ ReportTsum Lok TungОценок пока нет
- MacroEconomics AssignmentДокумент13 страницMacroEconomics AssignmentMayankОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand Aggregate SupplyДокумент32 страницыAggregate Demand Aggregate SupplySandesh Lokhande100% (1)
- Session 8 Aggregate Demand and SupplyДокумент42 страницыSession 8 Aggregate Demand and SupplyJustin Gil NojaОценок пока нет
- Review PPT MakroekonomiДокумент13 страницReview PPT MakroekonomiSiti HumairahОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Supply & Aggregate Demand:: (Y C + I + G + NX) (GDP Consumption + Investment + Gov + Export - Import)Документ5 страницAggregate Supply & Aggregate Demand:: (Y C + I + G + NX) (GDP Consumption + Investment + Gov + Export - Import)Blake AskewОценок пока нет
- 3 2 2 Long Run Aggregate SupplyДокумент34 страницы3 2 2 Long Run Aggregate SupplyMohammad Farhan NewazОценок пока нет
- ECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (Part 1) (Ch:20 P.O.M.E)Документ16 страницECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (Part 1) (Ch:20 P.O.M.E)KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- As Study NotesДокумент3 страницыAs Study NotesKrish MonparaОценок пока нет
- Eea Mid 1Документ13 страницEea Mid 1Pavan ParthikОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Supply Classicals and KeynesianДокумент10 страницAggregate Supply Classicals and KeynesianTooba FarooqОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4: The Full Macroeconomic Model ObjectivesДокумент26 страницLesson 4: The Full Macroeconomic Model ObjectivesAChristensen1299Оценок пока нет
- Instructor: Shruti Sharma PGP I, 2015: Microeconomics Session 1: The Basics of Demand and SupplyДокумент43 страницыInstructor: Shruti Sharma PGP I, 2015: Microeconomics Session 1: The Basics of Demand and SupplyAnonymous H8AZMsОценок пока нет
- ECO2x 2018 55 Aggregate Supply R0-EnДокумент2 страницыECO2x 2018 55 Aggregate Supply R0-EnElsa PucciniОценок пока нет
- 33 - HomeworkДокумент7 страниц33 - HomeworkChâu TrầnОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyДокумент34 страницыAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyGazal ReyazОценок пока нет
- Macro Presentation 8 Top 5 RevisedДокумент37 страницMacro Presentation 8 Top 5 RevisedMosОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand and SupplyДокумент21 страницаAggregate Demand and SupplyJestoni VillareizОценок пока нет
- Theories of WagesДокумент14 страницTheories of WagesGracy RengarajОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8: Keynesian System (Iv) : Aggregate Supply and DemandДокумент11 страницChapter 8: Keynesian System (Iv) : Aggregate Supply and Demandstanely ndlovuОценок пока нет
- Macro-1 Handout Chapter 4, 5 and 6Документ47 страницMacro-1 Handout Chapter 4, 5 and 6S Tariku GarseОценок пока нет
- More On The As-Ad Model: (Supplementary Notes For Chapter 7)Документ24 страницыMore On The As-Ad Model: (Supplementary Notes For Chapter 7)Chen YuyingОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Supply & Business Cycles: Unit HighlightsДокумент14 страницAggregate Supply & Business Cycles: Unit HighlightsprabodhОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics Theories and Policies 10th Edition Froyen Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент27 страницMacroeconomics Theories and Policies 10th Edition Froyen Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFStevenCookexjrp100% (10)
- Prayoga Dwi N - Summary CH 27Документ4 страницыPrayoga Dwi N - Summary CH 27Prayoga Dwi NugrahaОценок пока нет
- Aggregate DemandДокумент50 страницAggregate DemandKishan PatelОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyДокумент26 страницAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyYashik SahniОценок пока нет
- Marshallian & Walrasian Equilibrium AnalysisДокумент29 страницMarshallian & Walrasian Equilibrium AnalysisPalak100% (1)
- Krug2e Macro Ps Ch12Документ14 страницKrug2e Macro Ps Ch12Stephen Michael Palmer100% (3)
- Classical Model 1Документ6 страницClassical Model 1blipbruceОценок пока нет
- Oferta AgregadaДокумент30 страницOferta AgregadaFederico LopezОценок пока нет
- MKT 470 RajuДокумент66 страницMKT 470 RajuKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Dessler Ch5Документ47 страницDessler Ch5KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- HR NSU - ContentsДокумент1 страницаHR NSU - ContentsKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- HR NSU - ContentsДокумент1 страницаHR NSU - ContentsKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Intervention MethodsДокумент15 страницIntervention MethodsKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Dessler Ch1Документ31 страницаDessler Ch1KaziRafi100% (1)
- হুমায়ূন আহমেদ-কৃষ্ণপক্ষДокумент89 страницহুমায়ূন আহমেদ-কৃষ্ণপক্ষতারিক মোর্শেদОценок пока нет
- TLC Quicktip ExcelДокумент12 страницTLC Quicktip ExcelRajas GuruОценок пока нет
- HRM Dessler 11e Chapter 3Документ27 страницHRM Dessler 11e Chapter 3texpectationsОценок пока нет
- Dessler Ch2Документ34 страницыDessler Ch2KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Dessler Ch4Документ40 страницDessler Ch4KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Waitingline 130208111052 Phpapp01Документ28 страницWaitingline 130208111052 Phpapp01KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: The Evolution of Management ThoughtДокумент16 страницChapter 2: The Evolution of Management ThoughtKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- CH 05Документ36 страницCH 05Jayson Villena Malimata100% (2)
- The Epidemiological Triad Is Basically The Traditional Concept of DiseaseДокумент1 страницаThe Epidemiological Triad Is Basically The Traditional Concept of DiseaseKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Conjugation in SpirogyraДокумент3 страницыConjugation in SpirogyraKaziRafi100% (1)
- 4 Inch 2 Column Front / Back PageДокумент1 страница4 Inch 2 Column Front / Back PageKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: The Changing Environment of Management: MGT 210 Section17&18Документ24 страницыChapter 3: The Changing Environment of Management: MGT 210 Section17&18KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Children Preventive & Community DentistryДокумент2 страницыChildren Preventive & Community DentistryKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- 10 Top Tips: Access Cavities and Canal LocationДокумент8 страниц10 Top Tips: Access Cavities and Canal LocationKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Chap 05Документ58 страницChap 05KaziRafi0% (1)
- Children Preventive & Community DentistryДокумент2 страницыChildren Preventive & Community DentistryKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- 10 Top Tips: Access Cavities and Canal LocationДокумент8 страниц10 Top Tips: Access Cavities and Canal LocationKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- CH 4 Summer 2013Документ26 страницCH 4 Summer 2013KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Fin 254 Time Value of Money ProblemsДокумент1 страницаFin 254 Time Value of Money ProblemsKaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Chap 07Документ50 страницChap 07KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Argumentative Paper FormatДокумент3 страницыArgumentative Paper FormatJanJan ClarosОценок пока нет
- Bus173 Chap03Документ42 страницыBus173 Chap03KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Mid 2Документ109 страницMid 2KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 04Документ41 страницаChapter 04KaziRafiОценок пока нет
- Elliott Wave SummarizedДокумент1 страницаElliott Wave SummarizedNd Reyes100% (7)
- Edusure School: Macro - EconomicsДокумент7 страницEdusure School: Macro - EconomicsbhaskkarОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - The Demand For MoneyДокумент31 страницаUnit 2 - The Demand For Moneyrichard kapimpaОценок пока нет
- Parkinmacro12 1300Документ18 страницParkinmacro12 1300Mr. JahirОценок пока нет
- Goods Market Equilibrium: Derivation of The IS CurveДокумент20 страницGoods Market Equilibrium: Derivation of The IS CurvehomayunОценок пока нет
- SS10-11-Money Demand and SupplyДокумент26 страницSS10-11-Money Demand and SupplySiddharth100% (1)
- Executive SummaryДокумент5 страницExecutive SummarySyed AliОценок пока нет
- Gases Ideales Problemas Resueltos 2017-1. TermodinamicaДокумент37 страницGases Ideales Problemas Resueltos 2017-1. TermodinamicaCarla CalixtroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 & 10 - : Solutions To Problem Set # 8Документ11 страницChapter 9 & 10 - : Solutions To Problem Set # 8rashiОценок пока нет
- Principles of Macroeconomics, 9e - TB1 (Case/Fair/Oster) : Diff: 1 TopicДокумент135 страницPrinciples of Macroeconomics, 9e - TB1 (Case/Fair/Oster) : Diff: 1 TopicNathalie NassarОценок пока нет
- The Birth of MacroeconomicsДокумент6 страницThe Birth of MacroeconomicsNoreen CatapangОценок пока нет
- FIN350 - Solutions Slides 9Документ4 страницыFIN350 - Solutions Slides 9David NguyenОценок пока нет
- Market Economy Permanent Contract Capacity Boom Bottom Out Run Up STH Exceed Excess of STH Endogenous Exogenous Demographic RadicalДокумент5 страницMarket Economy Permanent Contract Capacity Boom Bottom Out Run Up STH Exceed Excess of STH Endogenous Exogenous Demographic RadicalHannah KhuongОценок пока нет
- Basic Concept of Macro Economics: Dr.S.BalasubramaniamДокумент31 страницаBasic Concept of Macro Economics: Dr.S.Balasubramaniamexams_sbsОценок пока нет
- Introduction To MacroeconomicsДокумент58 страницIntroduction To MacroeconomicsDivyankar VarmaОценок пока нет
- 2 1 The Level of Overall Economic ActivityДокумент3 страницы2 1 The Level of Overall Economic ActivityjohnssОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Economics - Monetary Policy - Handout PDFДокумент7 страницIGCSE Economics - Monetary Policy - Handout PDFdenny_sitorusОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Measuring The National Income AccountsДокумент14 страницChapter 2 Measuring The National Income AccountsAlthea Faye RabanalОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Macroeconomics (Lecture 1)Документ21 страницаIntroduction To Macroeconomics (Lecture 1)Salman HaiderОценок пока нет
- TermodinâmicaДокумент3 страницыTermodinâmicathiagopoetarnОценок пока нет
- Bm111 (Unit3) NotesДокумент14 страницBm111 (Unit3) NotesMohd asimОценок пока нет
- 2.1 The Level of Overall Economic Activity (HL)Документ56 страниц2.1 The Level of Overall Economic Activity (HL)Shuchun YangОценок пока нет
- DevEcon Part AДокумент7 страницDevEcon Part ABugs BunnyОценок пока нет
- Research Proposal Presentation 2Документ14 страницResearch Proposal Presentation 2Václav FrančeОценок пока нет
- Limitations of Harrod DomarДокумент3 страницыLimitations of Harrod DomarprabindraОценок пока нет
- Final Reaserch-3Документ52 страницыFinal Reaserch-3Dereje BelayОценок пока нет
- 7Документ12 страниц7Mohammed EL HabibОценок пока нет
- Macro Economics NotesДокумент18 страницMacro Economics NotesKhalid AzizОценок пока нет
- Eco104 - Assignment 2Документ4 страницыEco104 - Assignment 2zilani ahmedОценок пока нет
- Monetary Policy and The Federal Reserve: Current Policy and ConditionsДокумент25 страницMonetary Policy and The Federal Reserve: Current Policy and ConditionsJithinОценок пока нет