Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Age of Exploration and Trade PP
Загружено:
btcherryАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Age of Exploration and Trade PP
Загружено:
btcherryАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AGE OF EXPLORATION
AND TRADE
Unit 15
1. circumnavigate
9. scientific method
2. allies
10. Age of Enlightenment
3. plantation
11. social contract
4. cash crops
12. separation of powers
5. mercantilism
6. geocentric
7. Scientific Revolution
8. heliocentric
KEY TERMS
13. popular sovereignty
14. bourgeoisie
15. coup d'tat
16. abolitionism
In the 1400s and 1500s, countries in Western Europe began
exploring the world. They wanted spices, silk, and other goods
from Asia.
A Greek geographer named Claudius Ptolemy had drawn maps
of the world. Europeans began studying his maps.
EUROPE GETS READY TO EXPLORE
By the 1400s, four kingdoms were looking for a sea route to
Asia. All of them had ports on the Atlantic Ocean.
The race was on between England, Portugal, Spain, and
France.
In the early 1400s, England and France were still fighting each
other, and Spain was battling the Muslims.
Portugal was free to lead the way to explore new trade routes
to Asia.
EARLY VOYAGES OF DISCOVERY
In 1488 Bartolomeu Dias reached the southern tip of Africa.
Nine years later, Vasco da Gama rounded the tip of Africa.
An Italian navigator then came up with a different plan to get
to Asia. His name was Christopher Columbus.
He decided to sail west, not easy, across the Atlantic Ocean.
Columbus had three ships: the Santa Maria, the Nina, and the
Pinta. They left Spain in 1492 and headed west.
After many weeks, they finally saw land. Columbus thought he
was in Asia. He did not realize he was in the Americas.
Europeans eventually realized they had found a new
continent.
In 1520 Ferdinand Magellan sailed south along the coast of
South America. He found a way around the continent. He then
went west. His sailors almost starved.
After four months at sea, they reached the present-day
Philippines. There, Magellan died in a battle between local
groups.
His crew then went west across the Indian Ocean. They went
around Africa and back to Spain.
They were the first known people to circumnavigate, or sail
around, the world.
By 1519 Hernan Cortes was in Mexico and hoping to find gold.
He defeated the Aztecs by using guns and horses; creating
allies with other Native Americans; attacking first; and,
disease weakened the Aztec.
THE SPANISH CONQUER MEXICO
Spanish explorer Francisco Pizarro conquered the Inca people,
eventually becoming governor of Peru and appointing a new
Inca emperor who had to obey him.
Even after Pizarro died, Inca rebels continued to fight the
Spanish.
However, the conquest of Peru allowed Spanish rule to move
into much of South America.
SPAIN CONQUERS PERU
By the 1600s, Spanish settlers were growing sugarcane on
large farms called plantations.
At first, Native Americans did all the work. Then disease and
mistreatment caused most of them to die.
Spain brought enslaved Africans to work on the plantations
and in the gold and silver mines.
The Portuguese also used enslaved Africans to do their hard
work in Brazil.
SETTLING THE AMERICAS
The French came to North America to set up fur trading posts.
During the 1600s, the English came to North America for many
reasons. Some people wanted to make money. Others wanted
religious freedom.
Tobacco became the first cash crop of the English colonies. A
cash crop is grown in large amounts to sell and make money.
Europeans came up with the idea of mercantilism. This is a
theory that a countrys power depends on its wealth.
Countries can increase their wealth by owning more gold and
silver.
WORLD TRADE CHANGES
Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas changed through
trading.
The world traded people, goods, tools, ideas, and even
diseases.
This is called the Columbian Exchange, after Christopher
Columbus.
The Americas would send corn, potatoes, squash, beans,
tomatoes, chocolate, chili peppers, and peanuts to Europe.
Europe would send wheat, oats, barley, rye, rice, horses,
cattle, pigs, sheep, chickens, and coffee to the Americas.
A GLOBAL EXCHANGE
Not everything that passed between Europe and America was
good. Europeans gave germs to the Native Americans.
Some diseases were deadly and killed millions of people.
In the 1400s, people started to explore the world. Because of
this, Europeans were able to make better maps. These maps
helped explorers reach far-away lands. They brought back new
information about oceans, continents, animals, plants, and
diseases.
Scientists organized it all.
EARLY SCIENCE
In the 1500s, scientists in Europe began to experiment and
started the Scientific Revolution.
Nicolaus Copernicus stated that the Earth and other planets
move around the sun.
Johannes Kepler stated that planets move in ellipses.
Galileo Galilei used the telescope to support the heliocentric
view of the universe.
NEW IDEAS ABOUT THE UNIVERSE
Isaac Newton came up with the law of gravity.
Andreas Vesalius studied how the human body works by
dissecting, or cutting open, dead bodies.
Robert Hooke began to use a microscope.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek improved the microscope by adding
more powerful lenses.
Robert Boyle proved that matter is made up of elements.
NEW SCIENTIFIC ADVANCES
Francis Bacon came up with the scientific method. This
method is an orderly way to collect and study facts.
During the 1700s, educated Europeans saw reason as a light
that could reveal truth. As a result, this time period became
known as the Age of Enlightenment.
Thomas Hobbes argued that people were naturally violent and
selfish. He believed that natural law meant people needed
strong rulers to tell them what to do.
John Locke believed that natural law gave all people basic
rights from birth. These included the right to life, liberty, and
to own property.
REASON AND POLITICS
The English settled thirteen colonies in North America.
The southern colonies had large plantations. They used
enslaved Africans to work the land.
The northern colonies had smaller farms because of the cooler
climate and rocky soil.
BRITAINS AMERICAN COLONIES
The American colonies provided raw materials to Britain but
they also bought manufactured goods such as clothing and
furniture from the country.
Britain tried to control this trade using the Navigation Acts
(required the colonies to sell goods only to members of the
British Empire).
ROAD TO REVOLT
The war with France to control North America had left Britain
deeply in debt. The British government then decided to add
taxes to items sent to the colonists.
Britain needed the money to pay back its debts.
The colonists were angry and began to boycott British goods.
Tension in the colonies led to a battle at Lexington,
Massachusetts, between the British soldiers and the colonists.
On July 4, 1776, Congress issued the Declaration of
Independence (all men are created equal, people have rights
that no one can take away, governments must protect
peoples rights, and people can overthrow governments that
do not protect their rights).
The U.S. would win their independence.
A WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE
Вам также может понравиться
- Age of ExplorationДокумент10 страницAge of ExplorationJuli ZannelliОценок пока нет
- Industrila RevolutionДокумент26 страницIndustrila RevolutionAjay Pratap SinghОценок пока нет
- Period 2 Multiple Choice TestДокумент7 страницPeriod 2 Multiple Choice TestAvОценок пока нет
- Protestant Reformation15Документ23 страницыProtestant Reformation15Julius BaldivinoОценок пока нет
- Industrial Revolution Textbook PagesДокумент5 страницIndustrial Revolution Textbook Pagesapi-306956814Оценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Imperialism WeeblyДокумент17 страницUnit 5 Imperialism Weeblyapi-224598013Оценок пока нет
- Neoclassicism II: Culture and Society in The Eighteenth CenturyДокумент3 страницыNeoclassicism II: Culture and Society in The Eighteenth CenturySara PattersonОценок пока нет
- Carlsonrichard III PaperДокумент35 страницCarlsonrichard III Paperapi-272615928Оценок пока нет
- Extract AnalysisДокумент3 страницыExtract AnalysisThảo huỳnhОценок пока нет
- The Crucible IntroductionДокумент36 страницThe Crucible Introductionapi-254108669Оценок пока нет
- The Odyssey Background Notes TextbookДокумент3 страницыThe Odyssey Background Notes Textbookapi-332060185Оценок пока нет
- Do Computers DreamДокумент6 страницDo Computers Dream2501motokoОценок пока нет
- T T W H H: Rchaeology and THEДокумент61 страницаT T W H H: Rchaeology and THEJoshua Grant100% (1)
- CH 25 Sec 1 - The Beginnings of IndustrializationДокумент6 страницCH 25 Sec 1 - The Beginnings of IndustrializationMrEHsiehОценок пока нет
- Industrial RevolutionДокумент6 страницIndustrial RevolutionSanjana GaneshОценок пока нет
- A Very Old Man With Enormous WingsДокумент4 страницыA Very Old Man With Enormous WingsRimshaОценок пока нет
- The Film That I Watched Is Entitled : Name: Pan's Labyrinth Date: 8/4/2015Документ3 страницыThe Film That I Watched Is Entitled : Name: Pan's Labyrinth Date: 8/4/2015MSMОценок пока нет
- Chapter 19 & 20 Notes Industrial RevolutionДокумент40 страницChapter 19 & 20 Notes Industrial RevolutionDavid DuezОценок пока нет
- Study Questions For Books Previously Taught in Young Adult Literature and in ChildrenДокумент49 страницStudy Questions For Books Previously Taught in Young Adult Literature and in Childrenapi-3695470100% (1)
- Paradise Engineering ? A Reality or Nightmare ?Документ40 страницParadise Engineering ? A Reality or Nightmare ?Lisa ClancyОценок пока нет
- The French Revolution UnfoldsДокумент32 страницыThe French Revolution UnfoldsMisha MunickОценок пока нет
- A Very Old Man With Enormous Wings Tale by Gabriel García Márquez PaperДокумент3 страницыA Very Old Man With Enormous Wings Tale by Gabriel García Márquez PaperMartinОценок пока нет
- Readers Response NotesДокумент9 страницReaders Response Notesapi-235184247Оценок пока нет
- Pans Labyrinth & DystopiaДокумент22 страницыPans Labyrinth & DystopiaBea BrabanteОценок пока нет
- A Very Old Man With Enormous Wings - TextДокумент6 страницA Very Old Man With Enormous Wings - TextAlex yangОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1Документ32 страницыLesson 1John DarwinОценок пока нет
- 9 ASP LitchartДокумент10 страниц9 ASP Litchartvenkata.krishnanОценок пока нет
- Magna Carta BriefingДокумент11 страницMagna Carta BriefingunlockdemocracyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Study GuideДокумент8 страницChapter 2 Study GuideMichael VanDenburghОценок пока нет
- Animal Farm WS1Документ2 страницыAnimal Farm WS1Stentel MicaelaОценок пока нет
- Guide To Asking Questions in LiteratureДокумент6 страницGuide To Asking Questions in LiteratureReizel GarciaОценок пока нет
- The Hours CompatibilityДокумент11 страницThe Hours Compatibilityalz66Оценок пока нет
- Jonathan Swift Gullivers TravelsДокумент17 страницJonathan Swift Gullivers TravelsMartaCampilloОценок пока нет
- Pastoral, Satire, and Ecology in The Modern Memorial Park: Evelyn Waugh's The Loved One and Forest LawnДокумент61 страницаPastoral, Satire, and Ecology in The Modern Memorial Park: Evelyn Waugh's The Loved One and Forest LawnbeepyouОценок пока нет
- Ind RevolutionДокумент22 страницыInd RevolutionDaniela SolísОценок пока нет
- Eng Ext1 - Pans Labyrinth Quotes and AnalysisДокумент22 страницыEng Ext1 - Pans Labyrinth Quotes and Analysiskat100% (1)
- CH 23 Sec 2 - The Revolution Brings Reform and TerrorДокумент6 страницCH 23 Sec 2 - The Revolution Brings Reform and TerrorMrEHsieh100% (1)
- The American Revolution: Mr. MccaskillДокумент16 страницThe American Revolution: Mr. MccaskillT. McCaskill100% (1)
- Industrial RevolutionДокумент2 страницыIndustrial RevolutionDiana MariaОценок пока нет
- Absolutism and Constitutionalism Thesis StatementsДокумент3 страницыAbsolutism and Constitutionalism Thesis Statementsapi-282463341Оценок пока нет
- European History AP Review 1Документ12 страницEuropean History AP Review 1John BarhamОценок пока нет
- Ap Eh CH 13 NotesДокумент10 страницAp Eh CH 13 NotestykiaОценок пока нет
- AP European History: Chapter 14 Reading GuideДокумент3 страницыAP European History: Chapter 14 Reading GuideJason NeifferОценок пока нет
- Main Beat LiteratureДокумент23 страницыMain Beat LiteratureСундет КадирбаевОценок пока нет
- Absolutism & Enlightenment 2Документ41 страницаAbsolutism & Enlightenment 2IsabellaОценок пока нет
- AP Euro Ch. 15 NotesДокумент2 страницыAP Euro Ch. 15 NotesJSun YiОценок пока нет
- AP World History SyllabusДокумент13 страницAP World History SyllabusghhhhhhjОценок пока нет
- American RevolutionДокумент34 страницыAmerican RevolutionChris KellerОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes of Sept 19Документ6 страницLecture Notes of Sept 19Greg LoncaricОценок пока нет
- Sciensctist ChartДокумент4 страницыSciensctist ChartWillSmithОценок пока нет
- Cuba Missile Crisisjs2Документ15 страницCuba Missile Crisisjs2api-223701495Оценок пока нет
- Age of AbsolutismДокумент6 страницAge of Absolutismlyzlie CañedoОценок пока нет
- 0 - From Enlightment To RomanticismДокумент11 страниц0 - From Enlightment To RomanticismSarha FiorenzaОценок пока нет
- Igcse Depth Study D - Usa, 1919-41Документ19 страницIgcse Depth Study D - Usa, 1919-41GracefulVanshika Sharma100% (1)
- Unit 3nДокумент7 страницUnit 3nMichael VanDenburghОценок пока нет
- Imperialism in AfricaДокумент13 страницImperialism in Africaapi-294843376Оценок пока нет
- Ap Euro SyllabusДокумент4 страницыAp Euro Syllabusapi-293084040Оценок пока нет
- Unit 6-European ExplorationДокумент33 страницыUnit 6-European ExplorationIgor Radulovic100% (1)
- AP* U.S. History Review and Study Guide Aligned With American Pageant 15th EditionОт EverandAP* U.S. History Review and Study Guide Aligned With American Pageant 15th EditionОценок пока нет
- Class VI Bangladesh and Global Studies Colonization of The Americas IE Sheet #5: Colonization of The Americas The New WorldДокумент4 страницыClass VI Bangladesh and Global Studies Colonization of The Americas IE Sheet #5: Colonization of The Americas The New WorldTanzina ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Primary Source FeudalismДокумент3 страницыPrimary Source Feudalismbtcherry0% (1)
- Lat Long Japan ReviewДокумент2 страницыLat Long Japan ReviewbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Medieval Europe PPДокумент28 страницMedieval Europe PPbtcherryОценок пока нет
- GR Mongols in ChinaДокумент3 страницыGR Mongols in ChinabtcherryОценок пока нет
- Yalu River Geo and HistДокумент3 страницыYalu River Geo and HistbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Geo and History Capital Cities in Ancient ChinaДокумент3 страницыGeo and History Capital Cities in Ancient ChinabtcherryОценок пока нет
- Imperial China and Asia PPДокумент30 страницImperial China and Asia PPbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Eco of Hist Gold in AfricaДокумент2 страницыEco of Hist Gold in AfricabtcherryОценок пока нет
- Guided Reading CH 15 Sec 2Документ2 страницыGuided Reading CH 15 Sec 2btcherryОценок пока нет
- Eco of Hist CurrencyДокумент2 страницыEco of Hist CurrencybtcherryОценок пока нет
- On Your Map of Ancient Asia Identify...Документ1 страницаOn Your Map of Ancient Asia Identify...btcherryОценок пока нет
- Unit 9 Assessment by TCДокумент3 страницыUnit 9 Assessment by TCbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Rome and The Byzantine Empire PPДокумент33 страницыRome and The Byzantine Empire PPbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Five Paragraph Essay OrganizerДокумент1 страницаFive Paragraph Essay OrganizerbtcherryОценок пока нет
- GR Ch14L2 The Spread of IslamДокумент4 страницыGR Ch14L2 The Spread of IslambtcherryОценок пока нет
- Eco of Hist Credit in The Islamic EmpireДокумент3 страницыEco of Hist Credit in The Islamic Empirebtcherry50% (2)
- Eco of Hist Christian MonasteriesДокумент2 страницыEco of Hist Christian MonasteriesbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Unit 8 Assessment by TCДокумент2 страницыUnit 8 Assessment by TCbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Primary Source Jesus and The Jewish ReligionДокумент3 страницыPrimary Source Jesus and The Jewish ReligionbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Eco of Hist Inflation and The Fall of RomeДокумент2 страницыEco of Hist Inflation and The Fall of RomebtcherryОценок пока нет
- Becoming A Republic Gov Rome GRДокумент3 страницыBecoming A Republic Gov Rome GRbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Unit 7 Assessment by TCДокумент3 страницыUnit 7 Assessment by TCbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Would You Rather Questions For KidsДокумент3 страницыWould You Rather Questions For Kidsbtcherry100% (1)
- Unit 7 PPДокумент34 страницыUnit 7 PPbtcherryОценок пока нет
- Promotion Presentation 2013Документ26 страницPromotion Presentation 2013Skycop OnallagОценок пока нет
- UA21 Linking Relief, Rehabilitation and Development - Role of Urban AgricultureДокумент48 страницUA21 Linking Relief, Rehabilitation and Development - Role of Urban AgricultureDaisy100% (1)
- Flawed Giant ReviewДокумент6 страницFlawed Giant ReviewMatt CarpenterОценок пока нет
- Warfighting 1Документ26 страницWarfighting 1condorblack2001100% (2)
- ĐỀ THI ANH CHUYÊN KHXH NHÂN VĂN - 2022Документ11 страницĐỀ THI ANH CHUYÊN KHXH NHÂN VĂN - 2022Tú BíОценок пока нет
- Odyssey 5-8 CharCapДокумент2 страницыOdyssey 5-8 CharCapibateamposeidonОценок пока нет
- Abrahamian - The Structural Causes of The Revolution (1980)Документ7 страницAbrahamian - The Structural Causes of The Revolution (1980)Hassan as-SabbaghОценок пока нет
- The Ten Promised ParadiseДокумент5 страницThe Ten Promised ParadiseBlack Pearl Of SunnahОценок пока нет
- Arie de Geus-Living Company Growth, Learning and Longevity in Business (1999)Документ260 страницArie de Geus-Living Company Growth, Learning and Longevity in Business (1999)Alwan NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Class Xii - English Unit 1 Prose - The Two Gentlemen of VeronaДокумент9 страницClass Xii - English Unit 1 Prose - The Two Gentlemen of VeronaRamkumar Suresh N VОценок пока нет
- Edinburgh Military Tattoo Program 2012Документ31 страницаEdinburgh Military Tattoo Program 2012john_crawford_1Оценок пока нет
- Today's Fallen Heroes Saturday 12 October 1918 (1416)Документ29 страницToday's Fallen Heroes Saturday 12 October 1918 (1416)MickTierneyОценок пока нет
- The Great Depression EssayДокумент7 страницThe Great Depression Essayapi-463452419Оценок пока нет
- 10th Social Science Eng Medium Question Bank-2016 KolarДокумент8 страниц10th Social Science Eng Medium Question Bank-2016 Kolarsgshekar30100% (1)
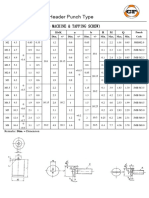
- Header Punch Standards (JIS-2nd Punch)Документ9 страницHeader Punch Standards (JIS-2nd Punch)nikesh singhОценок пока нет
- Roman Dmowski Understood': Ethnic Cleansing As Permanent RevolutionДокумент24 страницыRoman Dmowski Understood': Ethnic Cleansing As Permanent RevolutionAndrej ShpirtОценок пока нет
- ODB - Soc Sci (Gov History)Документ2 страницыODB - Soc Sci (Gov History)aloevera1994Оценок пока нет
- Military Geography PDFДокумент6 страницMilitary Geography PDF4521852100% (1)
- Medieval CastlesДокумент251 страницаMedieval CastlesRenata Šućurović97% (38)
- Compilation of 10 Famous Photographers and Their PhotographsДокумент13 страницCompilation of 10 Famous Photographers and Their PhotographsRegine G. ChiongОценок пока нет
- U. S. Naval Forces Vietnam Monthly Historical Summary Oct 1970Документ81 страницаU. S. Naval Forces Vietnam Monthly Historical Summary Oct 1970Robert ValeОценок пока нет
- Cuba Past and PresentДокумент20 страницCuba Past and Presentapi-278201617Оценок пока нет
- Pringle & Arkin - Single Integrated Operational Plan (SIOP) - The Secret US Plan For Nuclear War (1983)Документ269 страницPringle & Arkin - Single Integrated Operational Plan (SIOP) - The Secret US Plan For Nuclear War (1983)Charles Henry Norville83% (6)
- Royal Navy LeadershipДокумент13 страницRoyal Navy Leadershipjoethompson007Оценок пока нет
- Containment Structured Academic Controversy-NoДокумент6 страницContainment Structured Academic Controversy-Noapi-526098972Оценок пока нет
- Brief History of The Philippine National PoliceДокумент36 страницBrief History of The Philippine National Policejetlee estacion100% (1)
- Russian ArmsДокумент211 страницRussian Armsmortimerov100% (4)
- Philippine Secession IsmДокумент110 страницPhilippine Secession IsmDaniella ReyesОценок пока нет
- Wound BallisticsДокумент897 страницWound Ballisticsintense4dislike100% (3)
- Advanced Warforged 3.5 RaceДокумент14 страницAdvanced Warforged 3.5 Racejlewis_4Оценок пока нет