Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
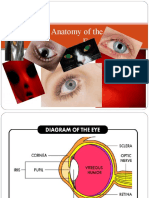
3800lecture 1 - Eye Anatomy
Загружено:
Akshay DhawanОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
3800lecture 1 - Eye Anatomy
Загружено:
Akshay DhawanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EYE ANATOMY
http://everlastingelephants.blogspot.com/2009/08/what-is-eye-cataract.html
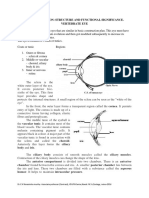
EYE ANATOMY
The orbital bone
The
eye socket
Formed
by:
Cheekbone
Forehead
Temple
Side of nose
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Eye_orbit_anatomy_anterior2.jpg
Eye
is cushioned within orbit by
pads of fat
Lacrimal gland
Produces
tears
Tears
drain through the
nasolacrimal duct
http://mwsu-bio101.ning.com/forum/topics/distinct-human-celltypes-1?commentId=2263214%3AComment%3A10331
EYE ANATOMY
Eyelids (L):
Protection:
Protects eye from foreign matter
(dust, dirt, debris)
Protects against bright light that
might damage the eye
Help
spread tears over surface of
eye- moist & comfort
Eyelashes (L):
Filter
out foreign matter
prevent it from getting into eye
http://www.medical-look.com/human_anatomy/organs/Eyelids_and_eyelashes.html
EYE ANATOMY
Conjunctiva (Conj):
Thin,
clear layer of skin
Covering of the front of eye
Covers the sclera and the
inside of the eyelids
Function:
Keeps bacteria and foreign
material from getting behind eye
http://www.images.missionforvisionusa.org/anatomy/2005/11/conjunctiva-answers.html
EYE ANATOMY
Sclera (S):
White
of the eye
Tough, opaque tissue that
extends around the eye
Surrounds the eye and gives
the eye its shape
The sclera is attached to the
extraocular muscles
http://www.thirdeyehealth.com/sclera.html
EYE ANATOMY
Extraocular Muscles
6
extraocular muscles that are
attached to each eye
Help move the eye left, right,
up, down and diagonally
These 6 muscles are:
Superior rectus
Inferior rectus
Medial rectus
Lateral rectus
Inferior oblique
Superior oblique
http://media.photobucket.com/image/introduction%20to%20eye%20anatomy/trimurtulu/Eye.jpg
EYE ANATOMY
Cornea (K):
Clear
layer at the front &
center of eye
Located in front of the iris
(colored part of eye)
Function:
Focus light as it enters eye
Avascular
Only organ that has no blood
vessels
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cornea.jpg
EYE ANATOMY
Anterior Chamber (AC):
Fluid-filled
space
Behind the cornea & in
front of the iris
Fluid = Aqueous humor
(AH)
AH helps nourish the cornea
& the lens
http://www.djo.harvard.edu/files/2528_310.jpg
http://www.goodhope.org.uk/departments/eyedept/angleclosureetc.htm
EYE ANATOMY
Pupil (P):
Iris (I):
Central opening of iris
Ring shaped tissue
Colored part of eye
Controls the amount of light
that enters the eye
Two muscle fibers:
Contraction
http://www.bioconsulting.com/Bio_Tech_Assessment.html
Constricts pupil in bright light
Dilation
Dilates pupil in dark
http://www.goodhope.org.uk/departments/eyedept/angleclosureetc.htm
EYE ANATOMY
Anterior Chamber Angle
Located
where the cornea meets
the iris
Trabecular Meshwork
Site where aqueous humor drains
out of eye
If AH cannot properly drain out
Pressure build up inside eye
Causes optic nerve damage &
evetually vision loss = glaucoma
http://seniorhealth.about.com/library/conditions/blglaucoma2.htm
EYE ANATOMY
Posterior Chamber (PC):
Fluid-filled
space
Aqueous Humor!
Immediately
behind the iris but
infront of the lens
http://seniorhealth.about.com/library/conditions/blglaucoma2.htm
EYE ANATOMY
Crystalline Lens:
Clear,
flexible structure
Behind the iris & pupil
Surrounded by a ring of
muscular tissue ciliary
body
The lens & ciliary body
help control fine focusing of
light as it passes through
the eye
http://www.smartplanet.com/business/blog/smart-takes/artificial-lens-implant-to-givepatients-high-definition-vision-better-than-2020/2558/
EYE ANATOMY
Vitreous Chamber:
Located
behind the lens &
in front of the retina
Filled with a gel-like fluid
called the vitreous humor
The vitreous help maintain
the shape of the eye
http://www.ophthobook.com/questions/question-how-many-chambers-are-there-in-the-eye
EYE ANATOMY
Retina:
Acts
like the film in a camera to
create an image
Consists of a specialized layer of cells
Converts light signals into nerve
signal then send these signals to the
optic nerve
hhttp://www1.appstate.edu/~kms/classes/psy3203/EyePhysio/human_retina.htm
Optic nerve carries the signals to the
brain
The brain helps process the image
Rods-
low light situations
Cones- allows you to see color
http://www.answersingenesis.org/tj/v13/i1/retina.asp
EYE ANATOMY
Macula
Located in the central part of
the retina
Responsible for giving sharp
central vision
Used for reading, recognizing
faces, and watching TV
Any disease that affects the
macula will cause a change &
impairment in the central
vision
http://www.dukehealth.org/eye_center/specialties/macular_degeneration/care_guides/macular_degen
eration_frequently_asked_questions
EYE ANATOMY
Choroid
A
layer of tissue that is:
Located under the retina
Separates retina & sclera
Mostly
made up of blood vessels
Helps nourish the retina by
carrying the blood supply to the
eyes internal structures
http://www.cnib.ca/en/your-eyes/eye-conditions/amd/the-eye/basics/Default.aspx
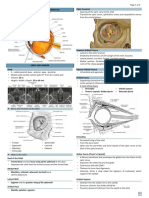
EYE ANATOMY
Optic Nerve
A
bundle of 1 million nerve
fibers
Responsible for transmitting
nerve signals from the eye to
the brain
The optic disc is the front
surface of the optic nerve
http://cssd.us/body.cfm?id=802
The optic disc is visible on the
retina
http://www.wollongong.youronlinecommunity.com.au/wollongong-online/2008/50/walkthrulife/eyehealth.html
Вам также может понравиться
- Lowe Syndrome (Oculocerebrorenal syndrome) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandLowe Syndrome (Oculocerebrorenal syndrome) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The EyeДокумент30 страницAnatomy of The Eyesukhi20mil100% (1)
- Eye Anatomy Lecture OverviewДокумент20 страницEye Anatomy Lecture OverviewJennifer Dixon100% (1)
- Organs of VisionДокумент3 страницыOrgans of VisionNarasimha Murthy100% (1)
- EYE Anatomy FactsДокумент6 страницEYE Anatomy FactsEdgar Betancourt VeraОценок пока нет
- L 01 Ocular AnatomyДокумент13 страницL 01 Ocular Anatomydoni anandaОценок пока нет
- Oculomotor NerveДокумент4 страницыOculomotor NerveHuzaifah IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesДокумент3 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglОценок пока нет
- Gross Eye AnatomyДокумент48 страницGross Eye AnatomyAzizan Hanny100% (1)
- Myopia by NamanДокумент19 страницMyopia by NamanAkshit ChitkaraОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of the Eye: Key Parts and FunctionsДокумент12 страницAnatomy of the Eye: Key Parts and Functionsfathul rahman100% (2)
- Anatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahДокумент36 страницAnatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahRida ShahОценок пока нет
- Ocular InjuryДокумент46 страницOcular InjurysnyОценок пока нет
- Sclera AnatomyДокумент21 страницаSclera AnatomyMiriam Mwangi100% (1)
- (Ophtha) 1.1 Anatomy of The EyeДокумент4 страницы(Ophtha) 1.1 Anatomy of The EyePatrick BautistaОценок пока нет
- Visual and Lacrimal AppratusДокумент45 страницVisual and Lacrimal AppratusAzman Bin KadirОценок пока нет
- Eyes AnatomyДокумент2 страницыEyes AnatomyAurea Jasmine DacuycuyОценок пока нет
- Glaucoma and CataractДокумент30 страницGlaucoma and CataractJayselle ArvieОценок пока нет
- CraniumДокумент20 страницCraniumDifa ZafiraОценок пока нет
- Si Kodhil - Lens AnatomyДокумент26 страницSi Kodhil - Lens AnatomyAndriati Nadhila100% (1)
- Cogan Syndrome Surger 4, AnkitДокумент18 страницCogan Syndrome Surger 4, AnkitAnkit Tonger AnkyОценок пока нет
- HyperopiaДокумент6 страницHyperopiaTesfsh MekonenОценок пока нет
- Ocular AnatomyДокумент39 страницOcular AnatomyShilvi ShahОценок пока нет
- Diseases of The Spinal CordДокумент89 страницDiseases of The Spinal CordLolla SinwarОценок пока нет
- FIU - Eye AnatomyДокумент23 страницыFIU - Eye AnatomyKira23406Оценок пока нет
- General Diagnosis Board Review NotesДокумент16 страницGeneral Diagnosis Board Review NotesmaeydakhalidОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound of Eye and OrbitДокумент90 страницUltrasound of Eye and OrbitManish Kumar100% (1)
- ORBITДокумент46 страницORBITdr yati gothwalОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of EarДокумент92 страницыAnatomy of EarGaurav KatariaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi PherwaniДокумент43 страницыAnatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi Pherwanisafasayed100% (1)
- Ophthalmology Revision LectureДокумент80 страницOphthalmology Revision LectureCarla LaniganОценок пока нет
- DYSPHAGIA FINALgДокумент48 страницDYSPHAGIA FINALgSurbhi BhartiОценок пока нет
- 734 Visual Pathway LesionsДокумент25 страниц734 Visual Pathway LesionsNarendra N NaruОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of the EyeДокумент3 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of the EyecarminaduriasОценок пока нет
- NSAIDs: Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory DrugsДокумент45 страницNSAIDs: Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory DrugsArvi KhanОценок пока нет
- Ptosis Types & Clinical Features: Made By:-Amritansh PandeyДокумент14 страницPtosis Types & Clinical Features: Made By:-Amritansh PandeyalexОценок пока нет
- Scalp & Skull AnatomyДокумент3 страницыScalp & Skull AnatomyAngel Kim100% (1)
- Cranial Nerves and Its ExaminationДокумент136 страницCranial Nerves and Its ExaminationNileshОценок пока нет
- Ophthalmic EmergencyДокумент17 страницOphthalmic EmergencyMohammad HelalОценок пока нет
- OCULAR TRAUMA: SIGNS, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENTДокумент50 страницOCULAR TRAUMA: SIGNS, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENTfatimaОценок пока нет
- Head to Toe Assessment Guide < 40 charsДокумент22 страницыHead to Toe Assessment Guide < 40 charsNessa Layos MorilloОценок пока нет
- Ocular EmergenciesДокумент4 страницыOcular EmergenciesJim Jose AntonyОценок пока нет
- TBL 1 - Refractive Error SlidesДокумент66 страницTBL 1 - Refractive Error SlidesAmirah Azman100% (4)
- Scoliosis PPT B IngДокумент11 страницScoliosis PPT B IngSyifa Anindya100% (1)
- Cranial Nerve Exam in DetailДокумент36 страницCranial Nerve Exam in DetailANIE100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesДокумент20 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesLaidy Aizahlyn Indoc Angod100% (1)
- Ocular EmergenciesДокумент38 страницOcular EmergenciesHaania KhanОценок пока нет
- Congenital-Torticollis (Wry Neck)Документ57 страницCongenital-Torticollis (Wry Neck)Shafiq Mohd NorОценок пока нет
- Eye Anatomy and Exam EssentialsДокумент35 страницEye Anatomy and Exam EssentialsJoyeeta Das100% (1)
- Cranial NervesДокумент67 страницCranial NervesBahaa ShaabanОценок пока нет
- 1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesДокумент124 страницы1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesSMEY204100% (1)
- Bell's PalsyДокумент1 страницаBell's PalsyAdrian MallarОценок пока нет
- DR - Rieva Kuliah 7 November - 2018Документ38 страницDR - Rieva Kuliah 7 November - 2018Nisrina100% (1)
- Lens and CataractДокумент55 страницLens and CataractRold Brio Sos100% (1)
- 3.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye - Nov. 3 - Dr. CastilloДокумент13 страниц3.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye - Nov. 3 - Dr. CastilloHanako Sasaki AranillaОценок пока нет
- 13 Subjective RefractionДокумент19 страниц13 Subjective Refractionmuhammad farizОценок пока нет
- Dandy-Walker SyndromeДокумент12 страницDandy-Walker SyndromeHarshita bansalОценок пока нет
- Trigeminal Nerve: Presented by DR Harees Shabir JR I Departmant of PedodonticsДокумент77 страницTrigeminal Nerve: Presented by DR Harees Shabir JR I Departmant of PedodonticsHarees ShabirОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Eye: Shabnum Naseem Lecturer Surgical TechnologyДокумент18 страницAnatomy of Eye: Shabnum Naseem Lecturer Surgical TechnologyShimmering MoonОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The EyeДокумент3 страницыAnatomy of The EyeManish SharafОценок пока нет
- Supreme Court AOR Examination - Leading Cases - D.K. Basu v. State of W.BДокумент3 страницыSupreme Court AOR Examination - Leading Cases - D.K. Basu v. State of W.BAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Case Summary Suresh Kumar Koushal and Another V NAZ Foundation and OthersДокумент6 страницCase Summary Suresh Kumar Koushal and Another V NAZ Foundation and OthersAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- NOW SSL Installation Instructions PDFДокумент1 страницаNOW SSL Installation Instructions PDFAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- American Legal Realism MovementДокумент5 страницAmerican Legal Realism MovementAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Sant Lal V Kamla PrasadДокумент6 страницSant Lal V Kamla PrasadAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- MRTP Vs CLДокумент28 страницMRTP Vs CLJyotsnaОценок пока нет
- The Delhi Rent Control Act 1958Документ19 страницThe Delhi Rent Control Act 1958Akshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- The Delhi Rent Control Act 1958Документ19 страницThe Delhi Rent Control Act 1958Akshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Private International Law 2012 Pril 20.11.2015Документ4 страницыPrivate International Law 2012 Pril 20.11.2015Akshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- OmbudsmanДокумент2 страницыOmbudsmanAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- General Drafting5w46tyyДокумент28 страницGeneral Drafting5w46tyyAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Transfer of PropertyДокумент44 страницыTransfer of PropertyAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- The Transfer of Property Act 1882Документ48 страницThe Transfer of Property Act 1882Iqra FarooqОценок пока нет
- CRLP (A) 17169 2014Документ51 страницаCRLP (A) 17169 2014Akshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Pil ProjectДокумент12 страницPil ProjectAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Philosophies of EducationДокумент47 страницPhilosophies of EducationAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- FIR Alleging Rape Can Be Quashed Where Accused and Victim Compromise and Are Happily Married: Punjab and Haryana High CourtДокумент4 страницыFIR Alleging Rape Can Be Quashed Where Accused and Victim Compromise and Are Happily Married: Punjab and Haryana High CourtLive LawОценок пока нет
- Title of The Topic. Title of The ProcedureДокумент3 страницыTitle of The Topic. Title of The ProcedureAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Gujarat High Court (Amoagh)Документ11 страницGujarat High Court (Amoagh)ushutupОценок пока нет
- Private International LawДокумент4 страницыPrivate International LawAsha Anbalagan0% (1)
- Suggested Reforms To The Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003Документ11 страницSuggested Reforms To The Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003Akshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Criminal AttemptДокумент7 страницCriminal AttemptAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Syllabus of Banking & Insurance LawДокумент4 страницыSyllabus of Banking & Insurance LawAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Bank NationalisationДокумент4 страницыBank NationalisationAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Criminal Law Rape DefinitionДокумент3 страницыCriminal Law Rape DefinitionAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- Enforcement of International Legal Obligations in A National JurisdictionДокумент24 страницыEnforcement of International Legal Obligations in A National JurisdictionAkshay DhawanОценок пока нет
- SarfaesiДокумент4 страницыSarfaesiSa DuaОценок пока нет
- Plant morphology anatomy tissues cellsДокумент23 страницыPlant morphology anatomy tissues cellsmka8208650% (2)
- Panchanga - The 5 Key Components of the Hindu CalendarДокумент19 страницPanchanga - The 5 Key Components of the Hindu CalendarRishi KumarОценок пока нет
- Ali Al-Qushji and His Contributions To Mathematics and AstronomyДокумент10 страницAli Al-Qushji and His Contributions To Mathematics and Astronomyiwanipis06112104Оценок пока нет
- Personal Statement of Mohammed Imad Eddine Alliouche PDFДокумент2 страницыPersonal Statement of Mohammed Imad Eddine Alliouche PDFImad AllioucheОценок пока нет
- Stream Sediment Geochemical Mapping of The Mount Pinatubo-Dizon Mine Area, The Philippines Implications For Mineral Exploration and Environmental RiskДокумент18 страницStream Sediment Geochemical Mapping of The Mount Pinatubo-Dizon Mine Area, The Philippines Implications For Mineral Exploration and Environmental RiskKristopanus Patiung LantemonaОценок пока нет
- The Variety of LifeДокумент2 страницыThe Variety of LifeGeorge JonesОценок пока нет
- For The Beauty of The EarthДокумент4 страницыFor The Beauty of The EarthGi67% (3)
- Prediction of end-bearing capacity of rock-socketed shafts considering RQDДокумент14 страницPrediction of end-bearing capacity of rock-socketed shafts considering RQDN.D.Jiji100% (1)
- Planetary Dignities and RelationshipsДокумент9 страницPlanetary Dignities and RelationshipsSaurav ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Moon Declination-1990-2020Документ192 страницыMoon Declination-1990-2020sind badОценок пока нет
- High-Sulphidation Epithermal Quartz-Alunite Gold Silver DepositsДокумент10 страницHigh-Sulphidation Epithermal Quartz-Alunite Gold Silver DepositsMohammad Wildan ArifinОценок пока нет
- Cosmic Wheel and TetrahedronДокумент2 страницыCosmic Wheel and TetrahedronAtazothnashaas100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницDetailed Lesson PlanNikki Angelie TerrenalОценок пока нет
- ENVS 337 Basins: Formation, Filling & Resources DR Rob DullerДокумент30 страницENVS 337 Basins: Formation, Filling & Resources DR Rob DullerbobecaweОценок пока нет
- Phytoplankton and EquilibriumДокумент403 страницыPhytoplankton and EquilibriumMohdDanishОценок пока нет
- The Wiltshire Lamb, Gosport, HampshireДокумент15 страницThe Wiltshire Lamb, Gosport, HampshireWessex ArchaeologyОценок пока нет
- DR Krishna Kumar PDFДокумент2 страницыDR Krishna Kumar PDFravenathy0% (1)
- The Boneyard Project Year 2 2013 2Документ3 страницыThe Boneyard Project Year 2 2013 2api-258990534Оценок пока нет
- Science 6 - 3nd Qrt. ExamДокумент4 страницыScience 6 - 3nd Qrt. ExamM'Grace Sagrado Tagailo LptОценок пока нет
- 5e Flower Dissection Investigation - Spring 2016Документ3 страницы5e Flower Dissection Investigation - Spring 2016api-309653899Оценок пока нет
- Popular Astronomy Simon NewcombДокумент584 страницыPopular Astronomy Simon NewcombSivason100% (1)
- Arudha PadaДокумент39 страницArudha PadaKhoo Hock Leong Khoo100% (2)
- Practice Test: B C D B C Caused Cancer in Laboratory Rats. DДокумент5 страницPractice Test: B C D B C Caused Cancer in Laboratory Rats. DNguyen CuongОценок пока нет
- Past Exam Questions: Geol 101: Physical GeologyДокумент2 страницыPast Exam Questions: Geol 101: Physical GeologyKishan MadhooОценок пока нет
- 01 Motions of Earth and SeasonsДокумент37 страниц01 Motions of Earth and SeasonsDivya Nayaka50% (2)
- Handouts For Ancient ScienceДокумент9 страницHandouts For Ancient ScienceGen ArnistoОценок пока нет
- Lucia 1995 Rock-FabricPetrophysical Classification of Carbonate Pore SpaceДокумент26 страницLucia 1995 Rock-FabricPetrophysical Classification of Carbonate Pore SpaceMarcos Antonio Romero Arteaga100% (1)
- (Episteme 7) Roberto Torretti (Auth.) - Philosophy of Geometry From Riemann To Poincaré-Springer Netherlands (1978)Документ472 страницы(Episteme 7) Roberto Torretti (Auth.) - Philosophy of Geometry From Riemann To Poincaré-Springer Netherlands (1978)Mário Raia NetoОценок пока нет
- Filipino ChemistДокумент10 страницFilipino ChemistNevely98% (109)
- Formation Evaluation EssentialsДокумент38 страницFormation Evaluation EssentialsAban Robert100% (2)