Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
P02 4e
Загружено:
KseiFoseiUsuОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
P02 4e
Загружено:
KseiFoseiUsuАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter Two
Implementing Strategy: The
Balanced Scorecard and the
Value Chain
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Learning Objectives
Explain how to implement a competitive strategy by
using Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities-Threats
(SWOT) Analysis
Explain how to implement a competitive strategy by
focusing on the execution of goals
Explain how to implement a competitive strategy
using value-chain analysis
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Learning Objectives
(continued)
Explain how to implement a competitive strategy
using the Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
Explain how to expand a conventional Balanced
Scorecard (BSC) by integrating sustainability
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Implementing a Strategy
There are two main competitive strategies:
cost leadership
differentiation
Once a firm chooses which strategy to follow,
there are various means of implementation:
SWOT Analysis
Focus on execution
Value-chain analysis
Balanced scorecard (BSC)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
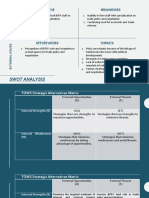
SWOT Analysis
Identification of critical success factors (CSFs)
tied to strategyfor example:
Product innovation
Quality
Skill development
Identification of quantitative measures for the
specified CSFsfor example:
Number of design changes or new patents
Number of defects or number of returns
Number of training hours or amount of skill
performance improvement
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
SWOT Analysis
(continued)
The SWOT analysis has four areas:
S strengths/internal
W weaknesses/internal
O opportunities/external
T threats/external
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
Look at product lines,
management, R&D,
manufacturing, marketing,
and strategy
Look at barriers to entry,
intensity of rivalry among
competitors, substitute
goods, and
customer/supplier
bargaining power
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Execution
The CSFs a manager executes depend on the
chosen strategy
Cost leadership: operational performance and
quality
Differentiation: customer satisfaction and innovation
Differentiated firms must pay close attention to
marketing and product development
Management accountants assist by gathering,
analyzing, and reporting on relevant information
Can be improved through benchmarking and total
quality improvement (e.g., Malcolm Baldrige Quality
Award)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen,
Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Value-Chain Analysis
Means to reach the detail-level of analysis
CSFs must be implemented in each and every phase of
operations
Helps a firm better understand its competitive
advantage by analyzing what processes add value
(processes that do not add value can be deleted or
outsourced)
Design to manufacturing to service after sale
Not all areas will get the same attention (identification of
areas most important to the customer will determine the
firms focus)
Goal = the most value at the lowest possible cost
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Value-Chain Analysis
Value-chain analysis has two steps:
Identify the value-chain activities at the smallest level
possible
Develop a competitive advantage by reducing cost
or adding value
To develop a competitive advantage, a firm
must consider the following:
What is our competitive advantage (strategy)?
Where can we add value for the customer?
Where can we reduce costs?
Are any of our processes linked (linkages exploited)?
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
10
Example: Value-Chain Analysis
in Computer Manufacturing
Computer Intelligence Company (CIC)
manufactures computers for small businesses
The company has an excellent reputation for
service and reliability as well as a growing
customer list
Is there any way to add value for the customer
while reducing costs?
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
11
Example: Value-Chain Analysis in
Computer Manufacturing (continued)
The company is considering two options:
Option One is to continue functioning as is
Option Two includes two separate outsourcing
decisions: (a) the purchase or manufacture of
parts, and (b) providing service internally or
outsourcing it
It is important to consider company strategy
in outsourcing decisions
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
12
Value-Chain Analysis in Computer
Manufacturing (continued)
Value Activity
Option One Current
Option Two Potential
Acquiring raw
materials
CIC is not involved at
this step
CIC is not involved at
this step
Manufacturing
computer chips and
other parts
CIC is not involved at
this step; cost is $200
CIC is not involved at
this step; cost is $200
Manufacturing
components, some of
which CIC can make
CIC purchases $300 of
parts for each unit
CIC manufactures these
units for $190 per unit
plus $55,000 monthly
Assembling
CICs costs are $250
CICs costs are $250
Marketing, distributing, CICs costs are
and servicing
$175,000 per month
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
CIC contracts out these
services for $130 per
month
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
13
Results of
Value-Chain Analysis
Manufacturing
Option One
Option Two
Savings with
Option Two
600 x $300 =
$180,000
Marketing,
distributing, and
servicing
$175,000 per month
600 x 190 +
$55,000 =
$169,000
$78,000 per month
$11,000
$97,000 per month
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
14
Results of Value-Chain Analysis
(continued)
CIC can save $108,000 ($11,000 + $97,000) per
month by manufacturing the parts and contracting
out marketing, distributing, and servicing
The main factor driving the decision is company
strategy, which in this case is quality and customer
service
For a firm pursuing a differentiation strategy, the best
option is not necessarily the one which provides the
most savings (savings is a secondary consideration)
From a strategic viewpoint, Option One is preferred over
Option Two
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
15
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
A performance report based on a broad set of
financial and nonfinancial measures that is crucial
to understanding and implementing a strategy
This report groups a firms CSFs into four areas:
Financial perspective (financial measures)
Customer perspective (customer satisfaction)
Internal business process perspective (e.g., productivity
and speed)
Learning and innovation (e.g., training and number of
new patents or products)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
16
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) (continued)
Benefits
Means for implementing strategy
Means to achieve a desired organizational change in
strategy
Can be used to determine managements
compensation and rewards
Coordinates efforts within the firm to achieve CSFs
Limitations
Nonfinancial information is subjective
Confidentiality must be insured for certain information
Must be adaptable and frequently updated
Costly and time-consuming to implement
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
17
The Balanced Scorecard
(BSC) (continued)
A properly constructed BSC can be used to infer a
companys strategy
BSC Strategy, rather than Strategy BSC
The emphasis placed on each performance
perspective reflects the strategy of the firm
For a cost leader, the operations perspective might be the
most important; for a differentiator, the customer
perspective
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
18
Strategy Map
A strategy map is a cause-and-effect diagram of
the relationships embodied in a BSC:
Shows how the achievement of CSFs in one perspective
should affect the achievement of goals in another
perspective
The financial perspective is the target in the strategy map
because financial performance is the ultimate goal for
most profit-seeking organizations
Success in the other perspectives leads directly to
improved financial performance and shareholder value
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
19
Sustainability
The fifth perspective for many organizations
The balancing of short-term and long-term goals in
all three dimensions of the companys
performanceeconomic, social, and environmental:
Environmental reports use environmental performance
indicators (EPIs) to measure sustainability
These indicators are in three areas:
Operational (measure stresses to the environment/regulatory
compliance issues)
Management (try to reduce environmental effects)
Environmental condition (measure environmental quality)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
The BSC and Not-For-Profit
(NFP) Organizations
Competitive strategy is different:
Must satisfy funding authorities, political leaders, and the
general public
The BSC can still be used to monitor CSFs related
to internal processes, customer satisfaction,
financial measures, and human resources
measures
Value-chain analysis can still be used to determine
at what points costs can be reduced or value added
on the value chain
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
20
21
The Role of Accounting
Three cost-management resources for implementing
strategy are discussed in this chapter:
SWOT analysis provides a system and structure to
identify CSFs
Value-chain analysis builds on the CSFs by breaking
them down into detailed activities
The BSC provides a way to implement the detailed
strategy developed through the previous two analyses; it
provides the processes for evaluating the organizations
achievement of CSFs
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
22
Chapter Summary
Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities-Threats (SWOT)
Analysis provides a system and structure in which to
identify a firms critical success factors (CSFs)
Execution of goals is important in implementing a
strategy
Execution depends on the competitive strategy a firm is
pursuing
Management accountants assist management by
gathering, analyzing, and reporting on relevant
information
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
23
Chapter Summary (continued)
Value-chain analysis builds on the CSFs identified in
SWOT analysis by breaking them into detailed activities
The balanced scorecard (BSC) provides the processes
for evaluating a firms achievement of CSFs
Sustainability builds on the conventional BSC by
balancing short-term and long-term goals
Sustainability focuses on economic, social, and
environmental issues
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Strategic Management Bba 6 SemesterДокумент46 страницStrategic Management Bba 6 Semestermahika bishtОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Strategic Management..Ppt (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)Документ95 страницUnit 2 Strategic Management..Ppt (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)vasudevprasad100% (1)
- Mba 301Документ26 страницMba 301Akash skillsОценок пока нет
- Bullet-3 StratmanДокумент5 страницBullet-3 StratmankksasdjcОценок пока нет
- Session 3: Environment and The Firm, PEST & Scenario PlanningДокумент35 страницSession 3: Environment and The Firm, PEST & Scenario PlanningRahul DhabhaiОценок пока нет
- MGT680 IntellipathДокумент342 страницыMGT680 IntellipathDonna De JesusОценок пока нет
- Swot Analysis: Strengths WeaknessesДокумент3 страницыSwot Analysis: Strengths WeaknessesOna DlanorОценок пока нет
- Business Analysi1Документ2 страницыBusiness Analysi1zurehanОценок пока нет
- BCK LMS - Dec 23 - MVSIRДокумент35 страницBCK LMS - Dec 23 - MVSIRnasiransar26Оценок пока нет
- University of West London The Claude Littner Business SchoolДокумент18 страницUniversity of West London The Claude Littner Business SchoolNishani PoornimaОценок пока нет
- Pakola Strategic ReportДокумент15 страницPakola Strategic Reportsabah100% (4)
- Marketing Plan Inihaw Ni KuyaДокумент13 страницMarketing Plan Inihaw Ni KuyaFatima Tawasil100% (1)
- Stress Management Plan Exemplar 3Документ3 страницыStress Management Plan Exemplar 3api-247024656Оценок пока нет
- NURS FPX 6216 Assessment 1 Instructions - Mentor InterviewДокумент5 страницNURS FPX 6216 Assessment 1 Instructions - Mentor Interviewfarwaamjad771Оценок пока нет
- Event ManagementДокумент11 страницEvent ManagementPooja Singh100% (2)
- Internship Report: General BankingДокумент30 страницInternship Report: General Bankingasif khanОценок пока нет
- Muhit Al Faisal PDFДокумент17 страницMuhit Al Faisal PDFbarshanОценок пока нет
- Congress Tourism in Turkey: SWOT Analysis and Related StrategiesДокумент7 страницCongress Tourism in Turkey: SWOT Analysis and Related StrategiesAdnan AlajoreОценок пока нет
- AUTONCIILM10V3Документ289 страницAUTONCIILM10V3Jenny NervezaОценок пока нет
- ParaphrasingДокумент3 страницыParaphrasingRommel YabisОценок пока нет
- Pepsico: A ReportДокумент23 страницыPepsico: A ReportĐức Anh LeoОценок пока нет
- Universiti Utara MalaysiaДокумент16 страницUniversiti Utara MalaysiaGilang FirjatullahОценок пока нет
- Personal Entrepreneurial Competencies - SUMMARY GRD. 10Документ36 страницPersonal Entrepreneurial Competencies - SUMMARY GRD. 10Sanjai AlopОценок пока нет
- Catholic University of Mozambique School of Education and Comnication Individual English Work Theme: Business PlanДокумент9 страницCatholic University of Mozambique School of Education and Comnication Individual English Work Theme: Business PlanAna da GlóriaОценок пока нет
- AcknowledgementДокумент32 страницыAcknowledgementNeha Kapur0% (1)
- Summers Final PPT LimeroadДокумент43 страницыSummers Final PPT LimeroadPeeyush Modi50% (4)
- Chapter 4Документ6 страницChapter 4Ervin AawitinОценок пока нет
- Technical Writing: Process and Product / Sharon J. Gerson, Steven M. GersonДокумент1 страницаTechnical Writing: Process and Product / Sharon J. Gerson, Steven M. GersonChristopher MsowoyaОценок пока нет
- Case StudiesДокумент7 страницCase StudiesmouseОценок пока нет
- SWOT Analysis AssignmentДокумент3 страницыSWOT Analysis AssignmentCrisDBОценок пока нет