Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
GSM Report
Загружено:
Danilyn Padillo Lucio0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
141 просмотров10 страницThe document summarizes the architecture and major components of a GSM network. It is divided into three systems: the switching system (SS), the base station system (BSS), and the operation and support system (OSS). The SS includes databases like the HLR and VLR that store subscriber information and the MSC that controls calls. The BSS consists of BTSs that handle radio interfaces and BSCs that control multiple BTSs. The OSS monitors and maintains the network through an operations and maintenance center.
Исходное описание:
gsm
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document summarizes the architecture and major components of a GSM network. It is divided into three systems: the switching system (SS), the base station system (BSS), and the operation and support system (OSS). The SS includes databases like the HLR and VLR that store subscriber information and the MSC that controls calls. The BSS consists of BTSs that handle radio interfaces and BSCs that control multiple BTSs. The OSS monitors and maintains the network through an operations and maintenance center.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
141 просмотров10 страницGSM Report
Загружено:
Danilyn Padillo LucioThe document summarizes the architecture and major components of a GSM network. It is divided into three systems: the switching system (SS), the base station system (BSS), and the operation and support system (OSS). The SS includes databases like the HLR and VLR that store subscriber information and the MSC that controls calls. The BSS consists of BTSs that handle radio interfaces and BSCs that control multiple BTSs. The OSS monitors and maintains the network through an operations and maintenance center.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 10
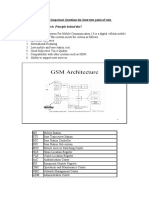
GSM ARCHITECTURE
AND CALL FLOW
GSM (Global System for Mobile
Communications)
The GSM system is a frequency- and time-division
system.
Each physical channel is characterized by a carrier
frequency and a time slot number.
GSM system frequencies include two bands at 900 MHz
and 1800 MHz commonly referred to as the GSM-900
and DCS-1800 systems.
GSM offers users good voice quality, call privacy, and
network security. SIM cards provide the security
mechanism for GSM. SIM cards are like credit cards and
identify the user to the GSM network. They can be used
with any GSM handset, providing phone access,
ensuring delivery of appropriate services to that user
and automatically billing the subscribers network usage
back to the home network.
GSM provides recommendations, not requirements
The GSM network is divided into three major systems:
The switching system (SS)
The base station system (BSS)
The operation and support system (OSS).
The Switching System (SS)
The switching system (SS) is responsible for performing call processing and subscriber-related
functions. The switching system includes the following
functional units:
home location register (HLR)The HLR is a database used for storage and management
of subscriptions. The HLR
is considered the most important database, as it stores permanent
data about subscribers, including a subscriber's service profile, location information, and
activity status. When an individual buys a
subscription from one of the PCS operators, he or
she is registered in the HLR of that operator.
mobile services switching center (MSC)The MSC performs the telephony switching
functions of the system. It controls calls to and from other telephone and data systems. It
also performs such functions as toll
signaling, and others.
ticketing, network interfacing, common channel
Visitor location register (VLR)The VLR is a database that contains temporary
information about subscribers that is needed by the MSC in order to service visiting
subscribers. The VLR is always integrated with the MSC. When a mobile station roams into a
new MSC area, the VLR connected to that MSC will request data about the mobile station
from the HLR. Later, if the mobile station makes a call, the VLR will have the information
needed for call setup without having to interrogate the HLR each time.
Authentication center (AUC)A unit called the AUC provides authentication and
encryption parameters that verify the user's identity and ensure the confidentiality of each
call. The AUC protects network operators from different types of fraud found in today's cellular
world.
Equipment identity register (EIR)The EIR is a database that contains information about
the identity of mobile equipment that prevents calls from stolen, unauthorized, or defective
mobile stations. The AUC and EIR are implemented as stand-alone nodes or as a combined
AUC/EIR node.
The Base Station System (BSS)
All radio-related functions are performed in the BSS, which consists of base station
controllers (BSCs) and the base transceiver stations (BTSs).
BSCThe BSC provides all the control functions and physical links between the MSC
and BTS. It is a high-
capacity switch that provides functions such as handover, cell
configuration data, and control of radio frequency (RF) power levels in base transceiver
stations. A number of BSCs are served by an MSC.
BTSThe BTS handles the radio interface to the mobile station. The BTS is the radio
equipment (transceivers
and antennas) needed to service each cell in the network.
A group of BTSs are controlled by a BSC.
The Operation and Support System
The operations and maintenance center (OMC) is connected to all equipment in the
switching system and to the BSC. The implementation of OMC is called the operation and
support system (OSS). The OSS is the functional entity from which the network operator
monitors and controls the system. The purpose of OSS is to
offer the customer cost-effective support for centralized, regional, and local operational
and maintenance activities that are required for a GSM network. An important function of
OSS is to provide a network overview and support the maintenance activities of different
operation and maintenance organizations.
Вам также может понравиться
- History of PhilosophyДокумент50 страницHistory of PhilosophyDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Manual CAT 345C LДокумент20 страницManual CAT 345C LRicardo SotoОценок пока нет
- Maria Clara 3Документ5 страницMaria Clara 3Danilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- GTAG-14 Edited With Ad 05-20-20101 PDFДокумент32 страницыGTAG-14 Edited With Ad 05-20-20101 PDFpiornelОценок пока нет
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesОт EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- NUR 104 Nursing Process MY NOTESДокумент77 страницNUR 104 Nursing Process MY NOTESmeanne073100% (1)
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationОт EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- GSM Network ComponentsДокумент23 страницыGSM Network ComponentsShakeel AminОценок пока нет
- Welcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Документ29 страницWelcome All Trainees: Course No. 270 by Rajesh Suwalka Engineer (WMTDC)Rajesh Suwalka100% (1)
- CS Core NetworkДокумент19 страницCS Core NetworkPedro YlliaОценок пока нет
- GSM, GPRS and UMTS OverviewДокумент56 страницGSM, GPRS and UMTS Overviewambika_sОценок пока нет
- GSM System Architecture: Mobile-Services Switching CenterДокумент20 страницGSM System Architecture: Mobile-Services Switching Centerpg5555Оценок пока нет
- GSM Architecture and InterfacesДокумент25 страницGSM Architecture and InterfacesTelebeansОценок пока нет
- World Wide Wireless StandardsДокумент67 страницWorld Wide Wireless Standardspalak goyalОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Документ6 страницGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)RobertoОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationsДокумент23 страницыGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationsiamravieОценок пока нет
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)Документ15 страницTime Division Multiple Access (TDMA)Swapnarekha NarravulaОценок пока нет
- Basics Communication Theory & Antenna TheoryДокумент29 страницBasics Communication Theory & Antenna TheoryRajesh SuwalkaОценок пока нет
- GSM RF Quick Reference GuideДокумент5 страницGSM RF Quick Reference Guidesantoshkumar2711Оценок пока нет
- Global System MobileДокумент55 страницGlobal System Mobilekaran ThakurОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM) : DefinitionДокумент9 страницGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM) : DefinitionAnfal AslamОценок пока нет
- GSM SystemДокумент13 страницGSM Systemiamhridoy74Оценок пока нет
- Mobile Wireless CommunicationДокумент8 страницMobile Wireless CommunicationTran Bao DuongОценок пока нет
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Документ11 страницGSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Teja MylavarapuОценок пока нет
- Lec 8 - GSM ArchitectureДокумент45 страницLec 8 - GSM ArchitectureMirza Adil ferozОценок пока нет
- 1.GSM OverviewДокумент46 страниц1.GSM OverviewAmit ThakurОценок пока нет
- Cellular Radio SystemsДокумент21 страницаCellular Radio SystemsYemuraiОценок пока нет
- GSM OverviewДокумент6 страницGSM OverviewSudeepta SahaОценок пока нет
- GSM Architecture: Project ReportДокумент40 страницGSM Architecture: Project ReportaadafullОценок пока нет
- MC R20 - Unit-2Документ43 страницыMC R20 - Unit-2Yadavilli VinayОценок пока нет
- Chapter # 1Документ51 страницаChapter # 1Chea SovongОценок пока нет
- GSM Network ArchitectureДокумент5 страницGSM Network Architecturenarayanan07Оценок пока нет
- Wireless WANs, GSM and Wi - MAXДокумент18 страницWireless WANs, GSM and Wi - MAXNewОценок пока нет
- MCN Unit 4.1Документ18 страницMCN Unit 4.1venkatОценок пока нет
- Module 3 Wireless Systems and Standards - AMPS GSMДокумент28 страницModule 3 Wireless Systems and Standards - AMPS GSMagh22623Оценок пока нет
- GSMДокумент14 страницGSMNewОценок пока нет
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS) Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS) Operation Support Subsystem (OSS)Документ3 страницыBase Station Subsystem (BSS) Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS) Operation Support Subsystem (OSS)api-19624645Оценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliДокумент66 страницGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile Communication Shabana Majeed 2009-MS-CE-03Документ15 страницGlobal System For Mobile Communication Shabana Majeed 2009-MS-CE-03mirzamwaqarОценок пока нет
- GSM ArchitectureДокумент10 страницGSM ArchitectureRucha GhareОценок пока нет
- GSM Global System For Mobile CommunicationsДокумент26 страницGSM Global System For Mobile CommunicationsKaushik AhmedОценок пока нет
- GSM: System Architecture: Prepared by Mehrin MeherДокумент28 страницGSM: System Architecture: Prepared by Mehrin MeherRajib MistryОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationДокумент5 страницGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationNaveen JhaОценок пока нет
- 2 Mobile NetworksДокумент42 страницы2 Mobile NetworksS t a r D u s tОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Документ30 страницGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Prakash PatilОценок пока нет
- Mobile Networking Assignment: Harem Masroor Syed D/o. Syed Masroor AlamДокумент34 страницыMobile Networking Assignment: Harem Masroor Syed D/o. Syed Masroor AlamHarem MasroorОценок пока нет
- An Introductory Presentation On GSM System: Presented ByДокумент43 страницыAn Introductory Presentation On GSM System: Presented ByLet's Go TlmОценок пока нет
- Very Good Advanced Slides of GSMДокумент77 страницVery Good Advanced Slides of GSMZaka KayaniОценок пока нет
- Basic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0oДокумент34 страницыBasic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0ovilaphong vongphachithОценок пока нет
- GSM Full InitialДокумент22 страницыGSM Full Initialvishwajeet1986100% (1)
- CD MaДокумент2 страницыCD MaRauniyar EsperantozzОценок пока нет
- Architecture of GSMДокумент7 страницArchitecture of GSMhuzaif zahoorОценок пока нет
- GSM Data CompleteДокумент12 страницGSM Data CompleteAdeel TajОценок пока нет
- Operation and Maintenance CenterДокумент3 страницыOperation and Maintenance CenterRabia RindОценок пока нет
- Ericsson CA638 CF688 Introduction To GSM DCS PCS SystemsДокумент27 страницEricsson CA638 CF688 Introduction To GSM DCS PCS SystemsDr MohammedОценок пока нет
- Mobile Communication EE-451: by DR Mir Yasir Umair Assistant Professor, MCS, NUSTДокумент20 страницMobile Communication EE-451: by DR Mir Yasir Umair Assistant Professor, MCS, NUSTFaheem SulehriОценок пока нет
- Architecture of The GSM NetworkДокумент17 страницArchitecture of The GSM NetworkOmFaОценок пока нет
- Global System For Mobile (GSM)Документ17 страницGlobal System For Mobile (GSM)Barhav SarbastОценок пока нет
- Network Access Technology Security FinДокумент140 страницNetwork Access Technology Security FinPARASPKKATHURIAОценок пока нет
- GSM SMS and Call FlowДокумент21 страницаGSM SMS and Call FlowLendry NormanОценок пока нет
- Some Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1Документ23 страницыSome Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1nileshОценок пока нет
- Ik1330lab2 (KTH)Документ7 страницIk1330lab2 (KTH)Mehdi RabbaniОценок пока нет
- Fiber OpticsДокумент7 страницFiber OpticsDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- 4GДокумент103 страницы4GDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Acknowledgement ReceptДокумент1 страницаAcknowledgement ReceptDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Activity 1 Phase Shifter: Belza, Robeto R. Engr. Eugene Dy Lucio, Danilyn P. Organis, Zenaida DДокумент2 страницыActivity 1 Phase Shifter: Belza, Robeto R. Engr. Eugene Dy Lucio, Danilyn P. Organis, Zenaida DDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Activity 7 Bipolar Junction Transistor FundamentalsДокумент4 страницыActivity 7 Bipolar Junction Transistor FundamentalsDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Electronics Lab ReportsДокумент46 страницElectronics Lab ReportsDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Circuits 2 Lab 2Документ5 страницCircuits 2 Lab 2Danilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Lab ResultДокумент1 страницаLab ResultDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Experiment 8.1: LabДокумент8 страницExperiment 8.1: LabDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- E-Cosplay: General GuidelinesДокумент3 страницыE-Cosplay: General GuidelinesDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Tribute Concept PaperДокумент7 страницTribute Concept PaperDanilyn Padillo LucioОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics Practice ProblemsДокумент4 страницыElectrostatics Practice ProblemsMohammed Aftab AhmedОценок пока нет
- Store Docket - Wood PeckerДокумент89 страницStore Docket - Wood PeckerRakesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Peter Brandt InterviewДокумент38 страницPeter Brandt InterviewNishant P Kalaskar100% (1)
- How To Connect To iSCSI Targets On QNAP NAS Using MPIO On Windows 2008Документ30 страницHow To Connect To iSCSI Targets On QNAP NAS Using MPIO On Windows 2008Jazz OberoiОценок пока нет
- Factsheet AMRT 2023 01Документ4 страницыFactsheet AMRT 2023 01arsyil1453Оценок пока нет
- Device InfoДокумент3 страницыDevice InfoGrig TeoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 34 Esip For FinalДокумент35 страницChapter 34 Esip For FinalJeaniel BorlingОценок пока нет
- Self Regulated StudyДокумент6 страницSelf Regulated StudyAdelheyde HeleneОценок пока нет
- Ip TunnelingДокумент15 страницIp TunnelingBon Tran HongОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 AДокумент10 страницUnit 4 AChetan p ShirahattiОценок пока нет
- Math Habits of MindДокумент12 страницMath Habits of MindAzmi SallehОценок пока нет
- Cyanocobalamin Injection Clinical Pharmacology Drug MonographДокумент36 страницCyanocobalamin Injection Clinical Pharmacology Drug MonographLaureyОценок пока нет
- TuberkulosisДокумент285 страницTuberkulosisTeuku M. FebriansyahОценок пока нет
- The English We SpeakДокумент2 страницыThe English We Speakcaeronmustai100% (1)
- Croda Smarter Polymers Guide Sep 2019Документ20 страницCroda Smarter Polymers Guide Sep 2019Keith Tamura100% (1)
- Marshall Mix Design (Nptel - ceTEI - L26 (1) )Документ7 страницMarshall Mix Design (Nptel - ceTEI - L26 (1) )andrewcwng0% (1)
- Pavlishchuck Addison - 2000 - Electrochemical PotentialsДокумент6 страницPavlishchuck Addison - 2000 - Electrochemical PotentialscomsianОценок пока нет
- Stability TestДокумент28 страницStability TestjobertОценок пока нет
- CompTIAN10 004Документ169 страницCompTIAN10 004Ian RegoОценок пока нет
- 56257375851Документ3 страницы56257375851Anneliese FernandesОценок пока нет
- Philips fwt9200Документ37 страницPhilips fwt9200Alex BrazОценок пока нет
- Lecture Planner - Chemistry - MANZIL For JEE 2024Документ1 страницаLecture Planner - Chemistry - MANZIL For JEE 2024Rishi NairОценок пока нет
- Bachelors of Engineering: Action Research Project - 1Документ18 страницBachelors of Engineering: Action Research Project - 1manasi rathiОценок пока нет
- Federal Public Service CommissionДокумент2 страницыFederal Public Service CommissionNasir LatifОценок пока нет
- Reforms of Parvez MusharifДокумент8 страницReforms of Parvez MusharifTalha AslamОценок пока нет
- CIT 811 TMA 4 Quiz QuestionДокумент3 страницыCIT 811 TMA 4 Quiz QuestionjohnОценок пока нет
- REM630 Broch 756825 LRENdДокумент6 страницREM630 Broch 756825 LRENdsihamuОценок пока нет