Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Data Communication and Networking
Загружено:
Unwritten Story0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
17 просмотров4 страницыBasic
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документBasic
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
17 просмотров4 страницыData Communication and Networking
Загружено:
Unwritten StoryBasic
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
Domain Name System (Chapter-25,Page-795)
There are several applications in the application layer of the
internet model that follows client/server paradigm.
These client/server applications can be classified into two
categories.
1. Applications which is directly used by the user. ExampleGmail
2. Application which support those application programs.
. Domain Name System (DNS) client/server application
sends a request to the DNS server to map the
website/email address to corresponding internet protocol
(IP) address. IP address looks like 172.27.27.83,which is
very tough to remember.
Domain Name System (Chapter-25,Page-795)
Protocols:
SMTP : Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (e-mail)
DNS : Domain Name System
To identify an entity , TCP/IP protocols use the IP address ,
which uniquely identifies the connection of a host to the
Internet.
We need a system that can map a name to an
address or an address to a name.
When the Internet was small , mapping was done by using
a host file. The host file had only two columns: name and
address.
Every host could store the host file on its disk and update it
periodically from a master host file.
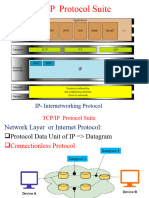
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is the basic
communication language or protocol of the Internet. It can also
be used as a communications protocol in a private network (either
anintranetor anextranet). When you are set up with direct access to
the Internet, your computer is provided with a copy of the TCP/IP
program just as every other computer that you may send messages
to or get information from also has a copy of TCP/IP.
TCP/IP is a two-layer program. The higher layer, Transmission Control
Protocol, manages the assembling of a message or file into smaller
packets that are transmitted over the Internet and received by a TCP
layer that reassembles the packets into the original message. The
lower layer,Internet Protocol, handles theaddresspart of each packet
so that it gets to the right destination. Eachgatewaycomputer on the
network checks this address to see where to forward the message.
Even though some packets from the same message are routed
differently than others, they'll be reassembled at the destination.
What is host?
The term "host" is used in several contexts, in each of
which it has a slightly different meaning:
1. In Internet protocol specifications, the term "host" means
any computer that has full two-way access to other
computers on the Internet. A host has a specific "local or
host number" that, together with the network
number, forms its uniqueIP address. If you use
Point-to-Point Protocolto get access to your access
provider, you have a unique IP address for the duration of
any connection you make to the Internet and your
computer is a host for that period. In this context, a "host"
is anodein a network.
Вам также может понравиться
- DCN - 5 - Four Types of AddressingДокумент62 страницыDCN - 5 - Four Types of AddressingShiza SahooОценок пока нет
- Traditional Applications - Electronic Mail (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, MIME) - HTTP - Web Services - DNS-SNMPДокумент39 страницTraditional Applications - Electronic Mail (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, MIME) - HTTP - Web Services - DNS-SNMPanish.t.pОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Data CommunicationsДокумент47 страницChapter 1: Introduction: Data CommunicationsYihune NegesseОценок пока нет
- D. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolДокумент7 страницD. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolEcho greenОценок пока нет
- Notes e CommerceДокумент83 страницыNotes e CommerceSawmya ShanmuganathanОценок пока нет
- ECE541 Data Networks 1: Application Layer Functionality and ProtocolsДокумент27 страницECE541 Data Networks 1: Application Layer Functionality and ProtocolsUnicorn54Оценок пока нет
- Cs8591 Computer Networks 1103969345 CN NotesДокумент240 страницCs8591 Computer Networks 1103969345 CN Notesfirstandlastname1100Оценок пока нет
- Batrisyia-C-WDD-Research - Server Technologies and Management ServicesДокумент3 страницыBatrisyia-C-WDD-Research - Server Technologies and Management ServicesBatrisyia SainiОценок пока нет
- 1 StudyДокумент7 страниц1 StudyAman GoyalОценок пока нет
- Software Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 ApprovedДокумент25 страницSoftware Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 ApprovedUday SinghОценок пока нет
- TCP/IP Protocol Stack ExplainedДокумент24 страницыTCP/IP Protocol Stack ExplainedToni-ann WillisОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Web ApplicationsДокумент11 страницLecture 1 Introduction To Web ApplicationsTalha RiazОценок пока нет
- CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals OSI and TCP/IP Models Application LayerДокумент28 страницCCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals OSI and TCP/IP Models Application LayerPernikDessiYustiza100% (1)
- TCP IP & AddressesДокумент18 страницTCP IP & Addresses366VEDANTI BACHCHUWARОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of the World Wide WebДокумент27 страницA Brief History of the World Wide WebsagarmethaОценок пока нет
- Application LayerДокумент24 страницыApplication LayerJI TENОценок пока нет
- TCP-Ip - W3 TutorialsДокумент7 страницTCP-Ip - W3 TutorialsSeba S JustinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ41 страницаChapter 7Muqeemuddin SyedОценок пока нет
- Comptia-Network Study GuideДокумент36 страницComptia-Network Study GuideJonathan Velez Velazquez100% (3)
- N+ Study MaterailДокумент59 страницN+ Study MaterailasimalampОценок пока нет
- TCP IpДокумент5 страницTCP Ipapi-3798412Оценок пока нет
- I SetupДокумент4 страницыI SetupRitik JayswalОценок пока нет
- Unit VIIДокумент8 страницUnit VIIabdul jawadОценок пока нет
- TCP/IP Communication ProcessДокумент42 страницыTCP/IP Communication ProcessHassan allaОценок пока нет
- Chapter PresentationДокумент114 страницChapter Presentationbalu51Оценок пока нет
- NetworkingДокумент2 страницыNetworkingbubu nakiОценок пока нет
- 3 .TCPДокумент13 страниц3 .TCPazazelaveyОценок пока нет
- Mc5303-Web-Programming-Essentials-All UnitsДокумент75 страницMc5303-Web-Programming-Essentials-All UnitsrathinadeviОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ14 страницChapter 2Eyosias BelachewОценок пока нет
- LABSHEET-2 Introduction To Network Programming and Writing A Simple Daytime Client-ServerДокумент15 страницLABSHEET-2 Introduction To Network Programming and Writing A Simple Daytime Client-ServerAnupama InturiОценок пока нет
- Tcp/Ip: Computer Communication ProtocolДокумент8 страницTcp/Ip: Computer Communication Protocolrosyprincess18Оценок пока нет
- TCP/IP TutorialДокумент8 страницTCP/IP Tutorialapi-3721578100% (2)
- Applications of TCP/IPДокумент3 страницыApplications of TCP/IPUsama JavedОценок пока нет
- Application Layer Protocols and Services ExplainedДокумент32 страницыApplication Layer Protocols and Services ExplainedYayan Prasetya100% (1)
- Network+ Study GuideДокумент51 страницаNetwork+ Study Guiderseara1127Оценок пока нет
- Lecture12 Application LayerДокумент33 страницыLecture12 Application Layernguyenquanglinh01121999Оценок пока нет
- Network CompTIAДокумент38 страницNetwork CompTIApedrazini18100% (1)
- TCP Ip OverviewДокумент10 страницTCP Ip OverviewWasef AnwarОценок пока нет
- 7 Internet ProtocolsДокумент47 страниц7 Internet Protocolsmiamor07Оценок пока нет
- Free Comptia Network+ Study Guide by MC McseДокумент48 страницFree Comptia Network+ Study Guide by MC McseMalluОценок пока нет
- Tcp/Ip Model: Physical Layer Data Link Layer Network Layer Transport Layer Application LayerДокумент4 страницыTcp/Ip Model: Physical Layer Data Link Layer Network Layer Transport Layer Application LayerIjlalMujtabaОценок пока нет
- THD - (TCP-IP Network Study)Документ15 страницTHD - (TCP-IP Network Study)Ceh DjamelОценок пока нет
- Unit V: Introduction To: Session, Presentation and APPLICATION LayersДокумент47 страницUnit V: Introduction To: Session, Presentation and APPLICATION LayersNiranjan AcharyaОценок пока нет
- CCNA1-CH15-Application LayerДокумент68 страницCCNA1-CH15-Application Layerkaramn3matОценок пока нет
- What Is The InternetДокумент10 страницWhat Is The InternetPrincess Prinks GulatiОценок пока нет
- The Reference Model Part 2Документ6 страницThe Reference Model Part 2roysayanccp05Оценок пока нет
- 1-4 TCP-IP ModelДокумент4 страницы1-4 TCP-IP ModelDragan StančevОценок пока нет
- Application Layer ProtocolsДокумент33 страницыApplication Layer ProtocolsSarah AliОценок пока нет
- Questions and Answers - ProtocolsДокумент4 страницыQuestions and Answers - ProtocolsVishal PaupiahОценок пока нет
- UNIT 3 CNДокумент17 страницUNIT 3 CNniharikaОценок пока нет
- Physical Layer Data Link Layer: Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)Документ44 страницыPhysical Layer Data Link Layer: Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)GauravОценок пока нет
- 00 NetworkReviewДокумент26 страниц00 NetworkReviewZee ZaboutОценок пока нет
- CN UNIT-1 Application Layer ProtocolsДокумент39 страницCN UNIT-1 Application Layer ProtocolsKowsalya GОценок пока нет
- CH 5Документ91 страницаCH 5avantikabakshiОценок пока нет
- The OSI Network Model StandardДокумент10 страницThe OSI Network Model Standardcheal_che2Оценок пока нет
- The Internet Protocol SuiteДокумент5 страницThe Internet Protocol SuiteErwinMacaraigОценок пока нет
- Building Socket ApplicationsДокумент13 страницBuilding Socket Applicationsjitugoua13122018Оценок пока нет
- WT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebДокумент20 страницWT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebSACHIDANAND CHATURVEDIОценок пока нет
- TCP IpДокумент6 страницTCP Ipkannanperu123Оценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsОт EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsОценок пока нет
- Temporal Coherence: Interference of Object and ReferenceДокумент5 страницTemporal Coherence: Interference of Object and ReferenceUnwritten StoryОценок пока нет
- Temporal Coherence: Interference of Object and ReferenceДокумент5 страницTemporal Coherence: Interference of Object and ReferenceUnwritten StoryОценок пока нет
- Maxwell's EquationsДокумент9 страницMaxwell's EquationsUnwritten StoryОценок пока нет
- Laplace Transform Solves Diff Eq EfficientlyДокумент13 страницLaplace Transform Solves Diff Eq EfficientlyUnwritten StoryОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationДокумент1 страницаNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationUnwritten StoryОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Physical Electronics Bill WilsonДокумент263 страницыIntroduction To Physical Electronics Bill WilsonUnwritten StoryОценок пока нет
- ODWEK BasicsAndBeyondДокумент314 страницODWEK BasicsAndBeyondcursocmodОценок пока нет
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Computer Science 2210/13 October/November 2019Документ14 страницCambridge Assessment International Education: Computer Science 2210/13 October/November 2019Sarim JavedОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент214 страницPDFKumari YehwaОценок пока нет
- Waltonchain White Paper 2.0 - ENДокумент72 страницыWaltonchain White Paper 2.0 - ENrlarapscribdОценок пока нет
- Modern Statistics GuideДокумент4 страницыModern Statistics GuideErille Julianne (Rielianne)100% (1)
- Boq ElcДокумент12 страницBoq ElcRicardo JuliusОценок пока нет
- Epow KS10H KS20HДокумент6 страницEpow KS10H KS20HstrahinjaОценок пока нет
- JSP 2 Struts Eclipse 3 DAO ANSI SQL DB and More With ExamplesДокумент250 страницJSP 2 Struts Eclipse 3 DAO ANSI SQL DB and More With Examplesapi-3696230Оценок пока нет
- 19CBS1003 - Usability Design of Software Applications - LabДокумент10 страниц19CBS1003 - Usability Design of Software Applications - LabYala yoloОценок пока нет
- 1020-Amdocs Placement Paper - 2Документ1 страница1020-Amdocs Placement Paper - 2AdityakshkОценок пока нет
- AR Research PaperДокумент18 страницAR Research PaperShresh KumarОценок пока нет
- Training Devices and Addressing ......................................................................... 1-2Документ12 страницTraining Devices and Addressing ......................................................................... 1-2Julian David Arevalo GarciaОценок пока нет
- Revelprog Is: User ManualДокумент41 страницаRevelprog Is: User ManualRoger Chavez PachasОценок пока нет
- GEM Premier 3500 - Interface ProtocolДокумент136 страницGEM Premier 3500 - Interface ProtocolJoão VictorОценок пока нет
- Archanadhaygude - 2yoe - SoftwaredeveloperДокумент2 страницыArchanadhaygude - 2yoe - SoftwaredeveloperPRESALES C2LBIZОценок пока нет
- 1.modicon M580 - PresentationДокумент24 страницы1.modicon M580 - PresentationAhmed SamiОценок пока нет
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak Pre-TranscriptДокумент2 страницыUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak Pre-Transcriptsalhin bin bolkeriОценок пока нет
- SynopsisДокумент12 страницSynopsisTony HobbsОценок пока нет
- Kern-Ew220-3nm Manual Ba Ew Eg-N GBДокумент55 страницKern-Ew220-3nm Manual Ba Ew Eg-N GBConstantinus MagnusОценок пока нет
- Himanshu Goyal (Resume)Документ3 страницыHimanshu Goyal (Resume)Himanshu GoyalОценок пока нет
- SAP MM ErrorsДокумент4 страницыSAP MM ErrorsRakesh Kumar Behera100% (4)
- Data Extraction From Hand-Filled Form Using Form TemplateДокумент7 страницData Extraction From Hand-Filled Form Using Form TemplateEditor IJRITCCОценок пока нет
- BC10 WebДокумент576 страницBC10 Webjiezhao080406Оценок пока нет
- Skyscanner Tone of VoiceДокумент32 страницыSkyscanner Tone of VoiceJefferson Bobby OrtegaОценок пока нет
- CTRPF AR Cheat Code DatabaseДокумент180 страницCTRPF AR Cheat Code DatabaseIndraSwacharyaОценок пока нет
- U2 Activity1 A-BДокумент2 страницыU2 Activity1 A-BFELIX ROBERT VALENZUELAОценок пока нет
- Full Stack Java Developer ResumeДокумент7 страницFull Stack Java Developer Resumevitig2Оценок пока нет
- Miran Sapphire 205B ManualДокумент216 страницMiran Sapphire 205B ManualrobertsmithingОценок пока нет
- Fujitsu Desktop Esprimo Q956: Data SheetДокумент9 страницFujitsu Desktop Esprimo Q956: Data SheetFederico SanchezОценок пока нет
- Pre-Calculus 11 WorkbookДокумент44 страницыPre-Calculus 11 Workbooklogicalbase3498Оценок пока нет