Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fundamentals Exam Review - Thermodynamics
Загружено:
Anonymous 2QaKT3S8RАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fundamentals Exam Review - Thermodynamics
Загружено:
Anonymous 2QaKT3S8RАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
+
FE
Thermodynamic
s
Review
Dr. Omar Meza
Assistant Professor
Department of Mechanical
Engineering
Topics covered
Thermodynamics Law
1st and 2nd law
Energy , heat and work
Availability and reversibility
Cycles
Ideal gases
Mixture of gases
Phase change
Heat Transfer
Properties of:
enthalpy
entropy
Tips for taking exam
Use the reference handbook
Know what it contains
Know what types of problems you can use it for
Know how to use it to solve problems
Refer to it frequently
Work backwards when possible
FE exam is multiple choice with single correct answer
Plug answers into problem when it is convenient to do so
Try to work backwards to confirm your solution as often as
possible
Progress from easiest to hardest problem
Same number of points per problem
Calculator tips
Check the NCEES website to confirm your model is allowed
Avoid using it to save time!
Many answers do not require a calculator (fractions vs. decimals)
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
For a simple substance,
specification of any two
intensive,
independent
properties is sufficient to
fix all the rest.
Handbook page:
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
A substance that has a
fixed
chemical
composition throughout
is called a pure substance.
Handbook page:
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
A substance whose properties are uniform throughout is
referred to as
A.A solid
B.An ideal substance
C.A pure substance
D.A standard substance
A substance whose properties are uniform throughout is
referred to as
A.A solid
B.An ideal substance
C.A pure substance
D.A standard substance
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
Given: Steam at 2.0 kPa is saturated at 17.5 oC. In what
state will the steam be at 40 oC if the pressure is 2.0 kPa?
T= 40oC
Tsat= 17.5oC
Analysis:
@ P = 2.0 kPa, Tsat = 17.5oC
Tsat < T superheated vapor
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
Find the volume occupied by 20 kg of steam at 0.4 MPa,
400oC
At 0.4 MPa the Tsat=142oC approximately. It means that the
steam is in the superheated region
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
Real gases exhibit idealgas behavior at relatively
low pressures and high
temperatures.
Handbook page:
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
All real gases deviate somewhat from ideal gas behavior: PV=
mRT. For which of the following conditions is the deviation
the smallest?
A.High temperature and low volume
B.High temperature and low pressures
C.High pressures and low volumes
D.High pressure and low temperatures
When the volume of an ideal gas is doubled while the
temperature is halved, what happens to the pressure?
A.Pressure is doubled
Pv X(2v) 4Xv
B.Pressure is halved
=
=
T
( T / 2)
T
C.Pressure is quartered
D.Pressure is quadrupled
P
X=
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
Handbook page:
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
Properties of Single-Component
Systems
First Law of Thermodynamics
Handbook page:
First Law of Thermodynamics
( Qin- Qout
) +( Win- Wout
) = U + KE + PE
Formal sign convention: Heat transfer to a
system and work done by a system are
positive; heat transfer from a system and work
done on a system are negative.
Wb is positive for expansion
Wb is negative for compression
Handbook page:
First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics
During a process, 30J of work are done by a closed
stationary system on its surroundings. The internal energy
of the system decreases by 40 j. What is the heat transfer?
Qin - Qout + Win - Wout U KE PE
Qnet - Wout U
Qnet U Wout
Qnet 40 J 30 J 10 J
First Law of Thermodynamics
Handbook page:
First Law of Thermodynamics
Calculate the work done by a piston contained within a
cylinder with air if 2m3 is tripled while the temperature is
maintained at a constant T = 30oC. The initial pressure is
P1=400 kPa absolute.
First Law of Thermodynamics
Polytropic process in a closed system
First Law of Thermodynamics
Handbook page:
First Law of Thermodynamics
Handbook page:
First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics
Handbook page:
First Law of Thermodynamics
Handbook page:
First Law of Thermodynamics
Handbook page:
First Law of Thermodynamics
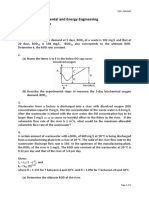
A steam coil operating at steady state receives 30 kg/min of
steam with an enthalpy of 2900 kJ/kg. if the steam leaves
with an enthalpy of 1600 kJ/min, what is the rate of heat
transfer from the coil?
First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Handbook page:
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Basic Cycles
Ideal Gas Mixture
Handbook page:
Ideal Gas Mixture
Ideal Gas Mixture
Ideal Gas Mixture
Psychrometrics
Handbook page:
Psychrometrics
Mollier Diagram
Handbook page:
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics
Combustion Processes
Combustion Processes
Combustion Processes
Combustion Processes
Combustion Processes
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Handbook page:
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Part of the heat received by a heat
engine is converted to work, while the
rest is rejected to a sink.
This is a law.
1.It is always observed in real heat engines.
2.One cannot derive it from first principles.
3.No exceptions are known.
It is not just that we havent looked hard
enough and that future discoveries will make
it possible to convert heat completely to work.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The efficiency of a refrigerator is
expressed in terms of the
coefficient of performance (COP).
The objective of a refrigerator is to
remove heat (QL) from the
refrigerated space.
Can the value of COPR
be greater than unity?
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The work
supplied to a
heat pump is
used to
extract energy
from the cold
outdoors and
carry it into
the warm
indoors.
for fixed values of QL and QH
Second Law of Thermodynamics
A)
B)
C)
D)
1500-MW
600-MW
900-MW
2100-MW
Second Law of Thermodynamics
A)
B)
C)
D)
Yes
No
Not clear
NA
Entropy
Entropy
A)
B)
C)
D)
2.82 kJ/K
6.86 kJ/K
-8.10 kJ/K
8.10 kJ/K
Preguntas?
Comentarios?
Muchas
Gracias !
Вам также может понравиться
- Angela Foudray's Thermodynamics SlidesДокумент597 страницAngela Foudray's Thermodynamics SlidesNickMeyer0% (1)
- Penguapan Pengembunan 5 2Документ18 страницPenguapan Pengembunan 5 2Dhiyaul IhsantiОценок пока нет
- Gravimetric Analysis (PDFDrive)Документ167 страницGravimetric Analysis (PDFDrive)ChilaОценок пока нет
- Basic Formulas in Chemical ENgineering ThermodynamicsДокумент2 страницыBasic Formulas in Chemical ENgineering ThermodynamicsJeffrey RoblesОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Hipolito Sta Maria Solution Manual Chapter 3Документ4 страницыThermodynamics Hipolito Sta Maria Solution Manual Chapter 3Norisa Jaimie Del Mundo100% (1)
- Tutorial One Heat Conduction: 5 2. A P M º N 0Документ7 страницTutorial One Heat Conduction: 5 2. A P M º N 0kookoОценок пока нет
- Power Plant Load DesignДокумент24 страницыPower Plant Load DesignJohn Raymond LumanlanОценок пока нет
- HW Solutions Chapter 4-5Документ17 страницHW Solutions Chapter 4-5Guyz WongthongsriОценок пока нет
- Question Paper Code:: Nitro PDF Software 100 Portable Document Lane WonderlandДокумент3 страницыQuestion Paper Code:: Nitro PDF Software 100 Portable Document Lane WonderlandBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANОценок пока нет
- Fire Alarm SystemДокумент15 страницFire Alarm SystemnОценок пока нет
- Review of Fluid MechanicsДокумент51 страницаReview of Fluid MechanicsMikko Arvin ChuaОценок пока нет
- Student Book PDFДокумент286 страницStudent Book PDFgeorgedragosОценок пока нет
- Refrigeration FormulasДокумент8 страницRefrigeration FormulasAshfaq Ali KhanОценок пока нет
- Lab Report #1Документ5 страницLab Report #1Jorge GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Calculus ManipulationsДокумент5 страницThermodynamic Calculus ManipulationsAnshu Kumar GuptaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 - Part 1Документ63 страницыChapter 9 - Part 1muhammad izzul100% (1)
- Mass & Energy Balance - Introduction To Process VariablesДокумент75 страницMass & Energy Balance - Introduction To Process VariablesMhmd RobertoОценок пока нет
- Si UnitsДокумент92 страницыSi UnitsRAVI2296Оценок пока нет
- Partial Fractions PDFДокумент4 страницыPartial Fractions PDFmadsalimiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 GeneralitiesДокумент24 страницыChapter 1 GeneralitiesPuwa CalvinОценок пока нет
- PhyChem Lab Problem Set No 1Документ9 страницPhyChem Lab Problem Set No 1Mark Ryan TripoleОценок пока нет
- Exam3 Practice ExamДокумент4 страницыExam3 Practice ExamMatthew FernandezОценок пока нет
- The Working SubstanceДокумент10 страницThe Working SubstanceBryan YuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsДокумент62 страницыChapter 1 - Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsAzrul NizarОценок пока нет
- Instructors Supplement PDFДокумент295 страницInstructors Supplement PDFchemggОценок пока нет
- Me ThermodynamicsДокумент63 страницыMe ThermodynamicsGlenn Ray ErasmoОценок пока нет
- Mae 320 HW 04 SolДокумент7 страницMae 320 HW 04 SolEvan DurstОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Glossary: Ab Initio (Lat., "From First Principles")Документ74 страницыChemistry Glossary: Ab Initio (Lat., "From First Principles")IWantToBelieve8728100% (2)
- Inorganic Special Examination 2015 20161Документ2 страницыInorganic Special Examination 2015 20161Rodriguez RommelОценок пока нет
- Exam Weekly Exam5Документ4 страницыExam Weekly Exam5Gab LibetarioОценок пока нет
- CCN2252 Environmental and Energy Engineering T08 Water PollutionДокумент3 страницыCCN2252 Environmental and Energy Engineering T08 Water PollutionfelixОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент165 страницThermodynamicssukande100% (1)
- Phychem ProblemsДокумент1 919 страницPhychem ProblemsAubrey VelasquezОценок пока нет
- Sample Problem ThermoДокумент25 страницSample Problem ThermoJonnah Faye Mojares0% (1)
- 2 Reversed Carnot Engine HP & Ref MachДокумент10 страниц2 Reversed Carnot Engine HP & Ref MachJustin MercadoОценок пока нет
- CoulsonДокумент5 страницCoulsonStefani Ann CabalzaОценок пока нет
- Loop Mesh AnalysisДокумент29 страницLoop Mesh AnalysisOmkar Kumar JhaОценок пока нет
- Me 6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Short Questions and Answers - Unit 2Документ7 страницMe 6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Short Questions and Answers - Unit 2BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics GlossaryДокумент1 страницаThermodynamics GlossaryzugoelfinitoОценок пока нет
- Units ConversionДокумент17 страницUnits Conversiondiasm1970Оценок пока нет
- GX Operating Manual v0.4 EДокумент38 страницGX Operating Manual v0.4 EBadmaarag JlssОценок пока нет
- Steam Table SI Units PDFДокумент256 страницSteam Table SI Units PDFAlex SeguidaОценок пока нет
- CHE 312 Lecture 2Документ17 страницCHE 312 Lecture 2Muhammad Hamza EjazОценок пока нет
- Momentum TransferДокумент47 страницMomentum TransferVishwath RamОценок пока нет
- Humidification and Drying ProblemsДокумент2 страницыHumidification and Drying ProblemsKuo SarongОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент60 страницThermodynamicsMahender ThotakuriОценок пока нет
- Electric Power Generation: Fossil Fuel: JA Nos M. Bee RДокумент12 страницElectric Power Generation: Fossil Fuel: JA Nos M. Bee RJesús Paz GonzálezОценок пока нет
- Che198 Thermodynamics DrillsДокумент8 страницChe198 Thermodynamics DrillsTrebob GardayaОценок пока нет
- Thermo 1 & 2Документ4 страницыThermo 1 & 2Oloj YuОценок пока нет
- H&MT - Lesson 6. Numericals On ConductionДокумент18 страницH&MT - Lesson 6. Numericals On ConductionadimeghaОценок пока нет
- Finals ThermoiДокумент4 страницыFinals ThermoiVon Eric DamirezОценок пока нет
- 3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsДокумент4 страницы3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsbackseeОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 11 SolutionsДокумент11 страницProblem Set 11 SolutionsBrai'Lly COncordiaОценок пока нет
- Phychem Lecture 1Документ62 страницыPhychem Lecture 1Allen de GuzmanОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент163 страницыPhysicsOnline EducatorОценок пока нет
- Appendix F - SteamTableДокумент76 страницAppendix F - SteamTableGregory WhiteОценок пока нет
- Thermopdynamics PDFДокумент12 страницThermopdynamics PDFNillОценок пока нет
- Basic Thermodynamic For Power Plant OperationДокумент65 страницBasic Thermodynamic For Power Plant Operationmag2grin100% (2)
- First Law of ThermodynamicsДокумент107 страницFirst Law of ThermodynamicsAmante Rivera Jr100% (1)
- 05 Thermodynamics v2Документ62 страницы05 Thermodynamics v2Jose Manuel BrotonsОценок пока нет
- Lab 5 Extraction 3 Trimyristin From Nutmeg FS2010Документ3 страницыLab 5 Extraction 3 Trimyristin From Nutmeg FS2010Sandip ThorveОценок пока нет
- WS - ICSE - VIII - Chem - Atomic StructureДокумент4 страницыWS - ICSE - VIII - Chem - Atomic StructureShruthiОценок пока нет
- ALFANOVA RZ018 Press Test ProcedureДокумент3 страницыALFANOVA RZ018 Press Test ProceduresalamrefighОценок пока нет
- Junior Design Project Meat Grinder 2016 2Документ44 страницыJunior Design Project Meat Grinder 2016 2api-328800450100% (10)
- InggrissinkholeДокумент2 страницыInggrissinkholeRika Rika SilvianaОценок пока нет
- Enthalpy 2Документ11 страницEnthalpy 2SB KPОценок пока нет
- 2013Документ302 страницы2013Alexandra Dumitrescu100% (1)
- Lighting and ShadingДокумент44 страницыLighting and Shadingpalaniappan_pandianОценок пока нет
- BillDipenser NCR 5633Документ166 страницBillDipenser NCR 5633Amanda Brown100% (1)
- 0.the Water Vapour Permeability Mechanical Properties and Solubility of Fish Gelatin Chitosan Films Modified With Transglutaminase or 1 Ethyl 3 3 DimethДокумент6 страниц0.the Water Vapour Permeability Mechanical Properties and Solubility of Fish Gelatin Chitosan Films Modified With Transglutaminase or 1 Ethyl 3 3 DimethValentina RoznovОценок пока нет
- Research Note On Aluminium Alloy Property PDFДокумент80 страницResearch Note On Aluminium Alloy Property PDFpenghzОценок пока нет
- 4.3 Well Stimulation PDFДокумент60 страниц4.3 Well Stimulation PDFJohn CooperОценок пока нет
- Vignan University VSAT 2013 Entrance Test Model Question PaperДокумент5 страницVignan University VSAT 2013 Entrance Test Model Question PaperPremKumarKalikiri67% (3)
- Low Stress Mechanical Properties of Woven Silk Fabrics (Part-1)Документ6 страницLow Stress Mechanical Properties of Woven Silk Fabrics (Part-1)Mohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Penerapan Metode Sonikasi Terhadap Adsorpsi FeIIIДокумент6 страницPenerapan Metode Sonikasi Terhadap Adsorpsi FeIIIappsОценок пока нет
- "Quantum Physics" - S. GasiorowiczДокумент522 страницы"Quantum Physics" - S. Gasiorowicz11111__11__1111100% (2)
- Final School TranscriptДокумент3 страницыFinal School TranscriptSteven TeguhОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 2Документ12 страницLab Report 2Fatihah AlhataОценок пока нет
- Spwla 2014 HHHДокумент12 страницSpwla 2014 HHHclimaco20Оценок пока нет
- Paper 2 2001Документ20 страницPaper 2 2001DisturbedPotatoОценок пока нет
- Document: Syllabus Course Code: Memael20 Copies Issued To: Date of Effectivity / Revision: Course Title: Machine Elements - LectureДокумент7 страницDocument: Syllabus Course Code: Memael20 Copies Issued To: Date of Effectivity / Revision: Course Title: Machine Elements - LectureArvin VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- History of Photography Timeline Assignment 1Документ14 страницHistory of Photography Timeline Assignment 1api-357703158Оценок пока нет
- Microsoft Word - Introduction V3Документ220 страницMicrosoft Word - Introduction V3glennОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3Документ3 страницыAssignment 3VenkatGollaОценок пока нет
- JAMB Physics SyllabusДокумент20 страницJAMB Physics SyllabusWhinhosaОценок пока нет
- Vectors DPPДокумент13 страницVectors DPPAchyuth DaggumatiОценок пока нет
- 2011121503-3-Wannate 8221enДокумент2 страницы2011121503-3-Wannate 8221en8612106535Оценок пока нет
- Solution: A 160 200 B 300 C 100 D 140 E 160Документ2 страницыSolution: A 160 200 B 300 C 100 D 140 E 160A.Kh.SОценок пока нет
- Autopano Giga 2.6 User ManualДокумент80 страницAutopano Giga 2.6 User ManualMiBayatiОценок пока нет
- Special Types of Matrices: By: Engr. Glenda Alega - de MesaДокумент22 страницыSpecial Types of Matrices: By: Engr. Glenda Alega - de Mesasairin parkОценок пока нет