Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
1.1 Understanding Waves
Загружено:
Cik Rokiah GhaniИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1.1 Understanding Waves
Загружено:
Cik Rokiah GhaniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 1 Waves
2.1Understanding
Arah Mata Angin
1.1
Waves
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
The Nature Of Waves
Waves
Travelling disturbance through a medium from a vibrating or
oscillating source
The medium is a substance or material that transports
the wave from its source to another place
The particles to the medium only vibrate but do not
travel together with the wave
Medium
Transfers energy in the direction of its propagation but do not
transfers matter.
Chapter 1 Waves
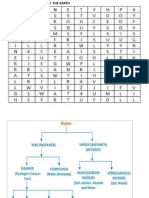
Jenis gelombang
Gelombang melintang
Gelombang membujur
Zarah medium bergetar
pd arah yg berserenjang
dengan arah
perambatan gelombang
Zarah mediumbergetar
pd arah yg selari
dengan arah
perambatan gelombang
contoh
contoh
air
Elektromagnetik
bunyi
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Wavefront
An imaginary line that
joins all the points on the
points on the crest of a
wave
Circular wavefronts
The direction of
wavefront is
perpendicular to the
direction ot the
propagation of its wave
Plane wavefronts
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Oscillating System
An oscillating system is a system that undergoes a periodic toand-fro movement
Examples
A simple pendulum
A loaded spring
PQRQP
R
Q
A
Amplitude, A = maximum displacement form its rest position (meter, m)
Period,
T = time for one complete oscillation / vibration (second, s)
Frequency, f = number of complete oscillation / vibration in one second
(Hertz, Hz)
Wavelength, = distance
between two successive crests (meter, m)
Wave speed, v = distance moved by a wave in one second (meter per
second, ms-1)
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Example :
In an experiment, siti observes that a simple
pendulum completes 40 oscillation in 48.0
seconds. What is
a) the period of oscillation
b) the frequency of oscillation
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Displacement-Time Graph
T
A
A
T
A = amplitude
T = Period
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Example
Figure below shows the displacement time graph of the
oscillating of mass on a spring
From the graph state
a)Amplitude
b)Period
c)frequency
5
0.02
-5
0.04
0.06
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Displacement-Distance Graph
A
A
A = amplitude
T = Period
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Example
Figure below shows the displacement distance graph of
A wave
From the graph find
a)Amplitude
b)Wavelength of the wave
8
3.7
-8
7.4
11.1
distance
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Speed Of Waves
v = wave speed
v = f
f = wave frequency
= wavelength
Example 1
The frequency of a wave moving to the
shore is 6 Hz and the length between two
waves trough is 3m. What is the speed of
the wave?
v=f
=63
= 18 ms-1
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Speed Of Waves
Example 2
A teacher attaches a slinky to the wall and begins introducing pulses
with different amplitudes. Which of the two pulses (A or B) below will
travel from the hand to the wall in the least amount of time?
Answer
Both of the pulses reach the wall at the same time
because the amplitude of the wave does not affect the
speed of the wave.
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Damping In An Oscillating System
Oscillating System In
Vacuum
No energy loss (the system
oscillates forever)
Oscillating System In
The Air
Amplitude decreases
Energy loss to the surroundings due
to air resistance and friction
Damping is said to have occurred in an oscillating system when there is
a loss of energy to the surroundings.
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
Resonance
An oscillating system is at resonance when it is driven at its natural
frequency by a periodic force.
At resonance, the amplitude of the ascillating system rises to
maxiumum.
Bartons Pendulum
Since the length of the pendulum B string = length of the pendulum string E,
both pendulums B and E have the same natural frequency.
Therefore, pendulum E is at resonance with pendulum B and will oscillate
with larger amplitude.
Chapter 1 Waves
Understanding Waves
END OF CHAPTER
1.1 Understanding Waves
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K3 No SkemaДокумент16 страницTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K3 No SkemaCikgu FaizalОценок пока нет
- 1.7 Analysing Electromagnetic WavesДокумент5 страниц1.7 Analysing Electromagnetic WavesCik Rokiah GhaniОценок пока нет
- 1.5 Analysing Interference of WavesДокумент10 страниц1.5 Analysing Interference of WavesCik Rokiah GhaniОценок пока нет
- 1.4 Analysing Diffraction of WavesДокумент4 страницы1.4 Analysing Diffraction of WavesCik Rokiah GhaniОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Analysing Reflection of WavesДокумент3 страницы1.2 Analysing Reflection of WavesCik Rokiah GhaniОценок пока нет
- Chap 4 f1Документ13 страницChap 4 f1Cik Rokiah GhaniОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Sample PREP-31 Standard Sample Preparation Package For Rock and Drill SamplesДокумент1 страницаSample PREP-31 Standard Sample Preparation Package For Rock and Drill SampleshОценок пока нет
- MCVM: Monte Carlo Modeling of Photon Migration in Voxelized MediaДокумент12 страницMCVM: Monte Carlo Modeling of Photon Migration in Voxelized MediaĐô Lê PhiОценок пока нет
- Double Helix Revisited PDFДокумент3 страницыDouble Helix Revisited PDFPaulo Teng An SumodjoОценок пока нет
- Comparative Analysis of Oyo & Ginger Grp-9 PDFДокумент31 страницаComparative Analysis of Oyo & Ginger Grp-9 PDFadityakr2410100% (1)
- Psionic Bestiary - Phrenic HegemonyДокумент12 страницPsionic Bestiary - Phrenic HegemonyEduardo Ferreira SuzartОценок пока нет
- SyllogismДокумент6 страницSyllogismjj3problembearОценок пока нет
- Mexico For Sale. Rafael GuerreroДокумент12 страницMexico For Sale. Rafael GuerreroGabriela Durán ValisОценок пока нет
- Sequential StatementДокумент12 страницSequential Statementdineshvhaval100% (1)
- 9th Computer Notes Full BookДокумент14 страниц9th Computer Notes Full BookKot Abdul Malik High SchoolОценок пока нет
- Black-Scholes Excel Formulas and How To Create A Simple Option Pricing Spreadsheet - MacroptionДокумент8 страницBlack-Scholes Excel Formulas and How To Create A Simple Option Pricing Spreadsheet - MacroptionDickson phiriОценок пока нет
- Talon Star Trek Mod v0.2Документ4 страницыTalon Star Trek Mod v0.2EdmundBlackadderIVОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics 4Документ3 страницыFluid Mechanics 4Pugao SpikeОценок пока нет
- PROII Data Transfer System User GuideДокумент91 страницаPROII Data Transfer System User Guidemfruge7Оценок пока нет
- Role of ICT & Challenges in Disaster ManagementДокумент13 страницRole of ICT & Challenges in Disaster ManagementMohammad Ali100% (3)
- Walter BenjaminДокумент15 страницWalter BenjaminAndrea LO100% (1)
- Is Euclidean Zoning The New Pig in The Parlor?: The Coming of Age of Form-Based Zoning (Damon Orobona)Документ19 страницIs Euclidean Zoning The New Pig in The Parlor?: The Coming of Age of Form-Based Zoning (Damon Orobona)Damon Orobona100% (1)
- Subliminal Perception and Extrasensory PerceptionДокумент19 страницSubliminal Perception and Extrasensory PerceptionAnne Jenette CastilloОценок пока нет
- A Brand Building Literature ReviewДокумент17 страницA Brand Building Literature ReviewUdaya Kumar SОценок пока нет
- Andrew Haywood CV 2010Документ6 страницAndrew Haywood CV 2010Dobber0Оценок пока нет
- Project Management GUIDE 2020: Revision 1Документ27 страницProject Management GUIDE 2020: Revision 1lorranaОценок пока нет
- EnMS. MayДокумент7 страницEnMS. MayRicky NoblezaОценок пока нет
- It'S Not A Lie If You Believe It: LyingДокумент2 страницыIt'S Not A Lie If You Believe It: LyingNoel ll SorianoОценок пока нет
- Fhwa HRT 04 043Документ384 страницыFhwa HRT 04 043hana saffanahОценок пока нет
- Topic 1.2 FormativeДокумент3 страницыTopic 1.2 FormativeJunior Alexis Julon Ventura0% (1)
- Manual ViscosimetroДокумент55 страницManual ViscosimetroLUIS XV100% (1)
- MercerДокумент33 страницыMercersadir16100% (4)
- Sales Presentation of K&N ChickenДокумент25 страницSales Presentation of K&N ChickensanahansmukhОценок пока нет
- STC 2010 CatДокумент68 страницSTC 2010 Catjnovitski1027Оценок пока нет
- 240-2 - Review Test 2 - 2Документ4 страницы240-2 - Review Test 2 - 2Nathaniel McleodОценок пока нет
- An Integrative Review of Relationships Between Discrimination and Asian American HealthДокумент9 страницAn Integrative Review of Relationships Between Discrimination and Asian American HealthAnonymous 9YumpUОценок пока нет