Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
SMAW WELDING Presentasi
Загружено:
Alfian Hari Gunawan100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
184 просмотров20 страницSMAW WELDING is a welding process to melt the base material using heat from electricity between cover metal (electrode) the main welding tools SMAW is a manual work with the equipment includes a power source, electrode wires, work cable, electrode holder, work clamp and electrode.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
SMAW WELDING presentasi.pptx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документSMAW WELDING is a welding process to melt the base material using heat from electricity between cover metal (electrode) the main welding tools SMAW is a manual work with the equipment includes a power source, electrode wires, work cable, electrode holder, work clamp and electrode.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
184 просмотров20 страницSMAW WELDING Presentasi
Загружено:
Alfian Hari GunawanSMAW WELDING is a welding process to melt the base material using heat from electricity between cover metal (electrode) the main welding tools SMAW is a manual work with the equipment includes a power source, electrode wires, work cable, electrode holder, work clamp and electrode.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 20
SMAW WELDING
KELOMPOK 13
1.
WIDYA NANDA PRASTIAWAN
2.
YA ARIF KHOIRUR RHOHIM
3.
ZAKARIA BAGUS AMINANTA
WELDING
welding process is the process of switching between metal
or non-metal that produces an integral part, by heating
the material to be spliced to the specific welding
temperature, with or without pressure, and with or
without filler metal
Smaw welding
SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding) is a welding process to
melt the base material using heat from electricity
between cover metal (electrode).
The main welding tools
SMAW is a manual work with the equipment includes a
power source, electrode wires (electrode cable), work
cable (cable work), electrode holder, work clamp and
electrode. Electrode and the work system is part of the
electrical circuit. The series began with a power source
and cables, including welding, electrode holder, the
connection of the workpiece, the workpiece (weldment),
and welding electrodes.
The main welding tools
As in the AWS (American Welding Society), the principles
of SMAW is using the heat from the arc to melt the base
metal and the tip of a consumable covered electrode
voltage 23-45 volt electricity used, and used for melting
up to 500 amperes of electrical current commonly used
range between 80-200 amperes
In welding with SMAW method, welding begins when an
electric arc is struck to make contact between the tip
electrode and the work system. Intense heat of the arc
melt the tip of the electrode and the work surface near
the bow. Small bubbles of molten metal rapidly formed at
the tip of the electrode, and then transferred through the
arc stream into the molten weld pool.
polarity of welding
SMAW welding process with methods distinguished by the
type of current includes AC and DC current, DC current
which distinguished on DCEN (straight polarity direct
polarity-) and DCEP (reverse polarity - the polarity is
reversed). The difference between SMAW with AC and DC
current are as follows:
AC Polarition
For AC (Alternating Current) voltage drop on the cable
does not much influence, less suitable for weak currents,
not all types of electrodes can be used, the arc starting is
more difficult, especially for small electrode diameter,
the pole can not be exchanged, not a bow arc problem.
DC Polarition
on the current DC (Direct Current) voltage drop is
sensitive to cable length as short as possible, can be used
for small currents with a small electrode diameters, all
types of electrodes can be used, the arc starting easier,
especially for small currents, the pole can be exchanged,
bow arc sensitive to the the tip, or a corner lot
indentation part.
DCEN Polarition
DCEN (Straight Polarity), the base material or the material
to be welded is connected to the positive pole (+) and
elektrode connected to the negative pole (-) DC welding
machines. This way the electric arc moves from the
electrode to the base material so that the collision of
electrons are in the base material resulting in 2/3 the
heat is in the base material and the electrodes are in the
third heat. This will result in melting of the base material
more than elektrode so that the weld has deep
penetration, so that both are used in welding a slow,
narrow areas and for thick plates.
DCEP Polarition
In DCEP (Reversed Polarity), basic material connected with
the negative pole (-) and elektrode connected with the
positive pole (+) of the DC welding machine, so that the
arc moves from the base material to the electrode and the
electrode is in the collision of electrons with the result
2/3 The heat was hot electrode and the third is in the
base material. This will result in melting of the electrode
more so having shallower penetration welds, and both are
used in welding thin plate with a weld bead width.
electrodes
Please also note the AWS classification of SMAW electrodes
denoted by the composition of code as follows:
With the information that:
E: states electrode
XX: optional code that indicates the material tensile
strength
X: optional code that indicates the position of welding
X: optional code that shows cellulose - the type of flow
and the layer
60
Electrode
Tensile Strength
Position
Type of Coating
and Current
Digit
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Type of Coating
High cellulose sodium
High cellulose potassium
High titania sodium
High titania potassium
Iron powder, titania
Low hydrogen sodium
Low hydrogen potassium
Welding Current
DC+
AC, DC+ or DCAC, DCAC, DC+
AC, DC+ or DCDC+
AC, DC+
High iron oxide,iron powder
AC, DC+ or DC-
Low hydrogen potassium, iron
powder
AC, DC+ or DC-
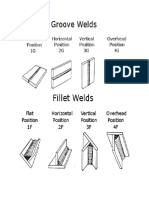
Welding Joint
Butt Joint
Corner joint
Lap Joint
Edge Joint
T Joint
Butt Joint
A joint between two members aligned approximately in the same plane
Lap Joint
A joint between two overlapping members
T Joint
A joint between two members located approximately at right angles
to each other
Corner Joint
A joint between two members located at right angles to each other
Edge Joint
A joint between the edges of two or more parallel or nearly parallel
members
THANK YOU
Вам также может понравиться
- Welding BasicsДокумент37 страницWelding BasicsSnehal DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Shielded Metal Arc WeldingДокумент33 страницыShielded Metal Arc WeldingAit Biñan100% (3)
- Welding Techniques and ProcedureДокумент11 страницWelding Techniques and ProcedureDominic Apollo RoblesОценок пока нет
- Weld Carbon Steel Pipes in Fixed Horizontal (5G) : Prepared By: Robert Anthony S. ArcillaДокумент12 страницWeld Carbon Steel Pipes in Fixed Horizontal (5G) : Prepared By: Robert Anthony S. ArcillaRobert Anthony Arcilla100% (1)
- Gmaw Guide PDFДокумент54 страницыGmaw Guide PDFJorge perezОценок пока нет
- TVL - SM 11 - w8Документ4 страницыTVL - SM 11 - w8CrisTopher L CablaidaОценок пока нет
- TLE - SM 11 - w1Документ4 страницыTLE - SM 11 - w1CrisTopher L CablaidaОценок пока нет
- Welding Procedures Final OutputДокумент16 страницWelding Procedures Final OutputJeremi BajarlaОценок пока нет
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding: by L D PoyyaraДокумент77 страницShielded Metal Arc Welding: by L D Poyyararajesh100% (1)
- 5 Welding EssentialsДокумент4 страницы5 Welding EssentialsdrexОценок пока нет
- Welding Positions. Weld GuruДокумент11 страницWelding Positions. Weld GuruValli RajuОценок пока нет
- Soldering & Brazing: Unit-IvДокумент15 страницSoldering & Brazing: Unit-IvRamu AmaraОценок пока нет
- TLE - SM 11 - w2Документ4 страницыTLE - SM 11 - w2CrisTopher L CablaidaОценок пока нет
- Arc Welding in DetailДокумент34 страницыArc Welding in DetailSohen PatelОценок пока нет
- 6 GtawДокумент30 страниц6 Gtawmasmarkun4444Оценок пока нет
- Welding Lecture and OrientationДокумент57 страницWelding Lecture and OrientationHenry SyОценок пока нет
- Repair Welds: Mark/Locate Weld: DefectsДокумент23 страницыRepair Welds: Mark/Locate Weld: DefectsJhultran KatipunanОценок пока нет
- Trainees Record Book (TRB)Документ4 страницыTrainees Record Book (TRB)Edward LyleОценок пока нет
- 5 Essentials For Proper Welding ProceduresДокумент3 страницы5 Essentials For Proper Welding ProceduresBonifacio BermalОценок пока нет
- 1.introduction To SMAWДокумент74 страницы1.introduction To SMAWRumman Ul AhsanОценок пока нет
- Essentials of WeldingДокумент13 страницEssentials of WeldingRonald AlconisОценок пока нет
- GTAW Lesson PlanДокумент75 страницGTAW Lesson PlanKentDemeterio100% (1)
- Acceptable Weld ProfilesДокумент9 страницAcceptable Weld ProfilesDominic Apollo Robles100% (1)
- Power Point Essentials of WeldingДокумент53 страницыPower Point Essentials of WeldingWilmerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2-Gas WeldingДокумент45 страницChapter 2-Gas Weldingsipi maseleОценок пока нет
- 2 WeldingДокумент30 страниц2 WeldingAndronicoll Mayuga NovalОценок пока нет
- Smaw 12 Module 1 Grade 12Документ39 страницSmaw 12 Module 1 Grade 12HERNAN JAY BUYOK100% (1)
- Smaw (Stick Welding)Документ57 страницSmaw (Stick Welding)Vane VallejoОценок пока нет
- GMAW FundamentalsДокумент18 страницGMAW FundamentalsYusup MulyanaОценок пока нет
- Smaw Facilitator'S Guide: Opening Notes FOR THE TeacherДокумент62 страницыSmaw Facilitator'S Guide: Opening Notes FOR THE TeacherAJ AcuñaОценок пока нет
- Smaw Common 2 Smaw SymbolsДокумент95 страницSmaw Common 2 Smaw SymbolsShiela May SantamenaОценок пока нет
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)Документ16 страницGas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)Akmal Bin Saipul AnuarОценок пока нет
- GTAW and Power SourcesДокумент18 страницGTAW and Power SourcesRavi Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- GMAW Facilitator GuideДокумент42 страницыGMAW Facilitator GuideEng trk100% (1)
- Q1, Module 1, Lesson 2Документ10 страницQ1, Module 1, Lesson 2Jerome A. GomezОценок пока нет
- TIG WeldingДокумент2 страницыTIG WeldingracerdabbaОценок пока нет
- UNIT OF COMPETENCY: Weld Carbon Steel Plates MODULE TITLE: Performing Groove Welding On Carbon Steel PlatesДокумент152 страницыUNIT OF COMPETENCY: Weld Carbon Steel Plates MODULE TITLE: Performing Groove Welding On Carbon Steel PlatesNaive Eilevor100% (2)
- Arc Welding Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницArc Welding Lesson Planlip67% (3)
- ETA Engineering. PVT LTD: A Presentation On Welding TechniqueДокумент48 страницETA Engineering. PVT LTD: A Presentation On Welding TechniqueParag NaikОценок пока нет
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding: Mild Steel I (E7018)Документ41 страницаShielded Metal Arc Welding: Mild Steel I (E7018)greatsteelОценок пока нет
- TR - Smaw NC IДокумент59 страницTR - Smaw NC Ironalit malintadОценок пока нет
- Ddugky Welding Lab ManualДокумент15 страницDdugky Welding Lab ManualprakashОценок пока нет
- GuideДокумент2 страницыGuideSreekumar RajendrababuОценок пока нет
- Welding ParametersДокумент34 страницыWelding ParametersmilindОценок пока нет
- 1G Flat PositionДокумент10 страниц1G Flat PositionAlejandro Jr. TagacayОценок пока нет
- TVL - SM 11 - w6Документ4 страницыTVL - SM 11 - w6CrisTopher L CablaidaОценок пока нет
- Welding ConsumablesДокумент128 страницWelding ConsumablesErick Hogan75% (4)
- Assessor's GuideДокумент8 страницAssessor's GuideShirwin OliverioОценок пока нет
- Panunumpa NG PropesyonalДокумент71 страницаPanunumpa NG PropesyonalHenry SyОценок пока нет
- SMAWДокумент32 страницыSMAWvikasbhadoria9894Оценок пока нет
- Mem661 - Smaw Gtaw LabДокумент49 страницMem661 - Smaw Gtaw LabFIefa100% (1)
- Welding DefectsДокумент47 страницWelding Defects0502raviОценок пока нет
- Gmaw & Fcaw-MsmeДокумент73 страницыGmaw & Fcaw-MsmemilindОценок пока нет
- Basic CompetencyДокумент161 страницаBasic CompetencyVincere Vja0% (1)
- Welding PositionДокумент30 страницWelding PositionTuah Negeri100% (1)
- Smaw and Tig WeldingДокумент46 страницSmaw and Tig WeldingRajesh Kumar Ravi100% (1)
- 5.arc WeldДокумент40 страниц5.arc Weldalinader20022Оценок пока нет
- WWS Group An Introduction To Manual Metal Arc Stick WeldingДокумент11 страницWWS Group An Introduction To Manual Metal Arc Stick WeldingnamkvalОценок пока нет
- I. Welding: (What About Flux Cored Arc Welding??)Документ4 страницыI. Welding: (What About Flux Cored Arc Welding??)Ravi PoudelОценок пока нет
- Shield Metal Arc WeldingДокумент4 страницыShield Metal Arc Weldingகோகுல் இராОценок пока нет
- Isolation GuidelinesДокумент203 страницыIsolation GuidelinesAlifia TrisnaningrumОценок пока нет
- Bahasa Inggris (Inggris)Документ24 страницыBahasa Inggris (Inggris)Alfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Pathway Snake BiteДокумент1 страницаPathway Snake BiteAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Working With DrawingДокумент6 страницWorking With DrawingAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Link SumberДокумент1 страницаLink SumberAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Explaining Test and Experiment MetalДокумент14 страницExplaining Test and Experiment MetalAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Retnaldi Fitriyanto Rico Andhika P Rizkiyan: Find Out MoreДокумент15 страницRetnaldi Fitriyanto Rico Andhika P Rizkiyan: Find Out MoreAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Garsel Shoes Seri E 2015-2016Документ31 страницаGarsel Shoes Seri E 2015-2016Alfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- What Is ThalassemiaДокумент45 страницWhat Is ThalassemiapriyeshdongreОценок пока нет
- Febrile Convulsions: Prepared By: Dr. Basem Abu-Rahmeh Directed By: Dr. Afaf Al-AriniДокумент15 страницFebrile Convulsions: Prepared By: Dr. Basem Abu-Rahmeh Directed By: Dr. Afaf Al-AriniAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Ojn20120400006 97247063Документ7 страницOjn20120400006 97247063Alfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Evaluation A Community Health ProgramДокумент11 страницEvaluation A Community Health ProgramAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Communicable DiseaseДокумент20 страницCommunicable DiseaseAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Basic VirologyДокумент19 страницBasic VirologyAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Journal ScabiesДокумент7 страницJournal ScabiesAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Pengkajian Keluarga: FERY MENDROFA, Mkep, SP - KomДокумент22 страницыPengkajian Keluarga: FERY MENDROFA, Mkep, SP - KomAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Physiologi Neuron (Kuliah I)Документ17 страницPhysiologi Neuron (Kuliah I)Alfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Why Women Are Better in ParentingДокумент6 страницWhy Women Are Better in ParentingAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Jurnal OyedeleДокумент10 страницJurnal OyedeleAlfi Rohmatus SholihahОценок пока нет
- Effects of Music On Depression in Older PeopleДокумент8 страницEffects of Music On Depression in Older PeopleAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Thalassemia 89 90Документ94 страницыThalassemia 89 90Alfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент3 страницыTensesAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Art HR OlogyДокумент23 страницыArt HR OlogyAlfian Hari GunawanОценок пока нет
- Productivity Improvement Through Lean ManufacturingДокумент30 страницProductivity Improvement Through Lean ManufacturingmanikandaprabuОценок пока нет
- Top Drive - Lessons LearnedДокумент8 страницTop Drive - Lessons LearnedRuslan ZakirovОценок пока нет
- Producción de HidrógenoДокумент15 страницProducción de HidrógenoMarielaReyesОценок пока нет
- Forc106 - Module 8 NewДокумент9 страницForc106 - Module 8 Newkimberlyn odoñoОценок пока нет
- Range of Flocculants and Caogulants For Water and Wastewater TreatmentДокумент6 страницRange of Flocculants and Caogulants For Water and Wastewater Treatmentginga716Оценок пока нет
- Ecological and Energetic Assessment of Re-Refining Used Oils To Base OilsДокумент104 страницыEcological and Energetic Assessment of Re-Refining Used Oils To Base OilsFernando SImonelliОценок пока нет
- Help CarlosДокумент141 страницаHelp Carloszarzosa rabanalОценок пока нет
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment Form: AreaДокумент12 страницHazard Identification and Risk Assessment Form: AreaSalman Alfarisi100% (3)
- DB'S Calculation: Energy Conservation-Special Notes GeneralДокумент1 страницаDB'S Calculation: Energy Conservation-Special Notes GeneralAbid AyubОценок пока нет
- Reverse Osmosis SystemsДокумент1 страницаReverse Osmosis SystemsNaresh KhubaniОценок пока нет
- Is 3589Документ19 страницIs 3589kishor.kokate60% (5)
- AEC Air Eraser Parts ListДокумент2 страницыAEC Air Eraser Parts Listspaced_boyОценок пока нет
- IncineratorДокумент72 страницыIncineratorWajih100% (3)
- Service Manual ES523-603-723-853Документ470 страницService Manual ES523-603-723-853Pat FreemanОценок пока нет
- Rina Tannenbaum Resume October 2012Документ33 страницыRina Tannenbaum Resume October 2012Rina TannenbaumОценок пока нет
- Sae Ams 4027 SheetmetalДокумент7 страницSae Ams 4027 Sheetmetaljuan100% (5)
- Prism Cryogenic Oxygen Generators: Reliable On-Site SupplyДокумент4 страницыPrism Cryogenic Oxygen Generators: Reliable On-Site SupplyEdwin RosasОценок пока нет
- Notes On Sprockets and ChainsДокумент6 страницNotes On Sprockets and Chainsjjoohhnn90Оценок пока нет
- PALIMEX R - 855 Product Information PR00331304Документ2 страницыPALIMEX R - 855 Product Information PR00331304Muhammad ThohirОценок пока нет
- (Msia) Guide To Sewer Selection and Installation (Dec2006) - VC Pipe pg17Документ168 страниц(Msia) Guide To Sewer Selection and Installation (Dec2006) - VC Pipe pg17Rachael Hoo100% (7)
- Two Phase FlowДокумент4 страницыTwo Phase FlowsindalvaleriОценок пока нет
- BdeM Taller No. 2Документ2 страницыBdeM Taller No. 2Luisfer PriceОценок пока нет
- DL8000 Emerson PDFДокумент322 страницыDL8000 Emerson PDFAgustin AguilarОценок пока нет
- DWV-1-0910 0910 WebДокумент24 страницыDWV-1-0910 0910 WebHotnCrispy CrispyОценок пока нет
- Effects of Processing Condition On The Filtration Performances of Nonwovens For Bag Filter MediaДокумент6 страницEffects of Processing Condition On The Filtration Performances of Nonwovens For Bag Filter Mediaapi-3733260Оценок пока нет
- MT6050i 8050i Installation 101102Документ8 страницMT6050i 8050i Installation 101102gabyОценок пока нет
- API 570 Piping InspectionДокумент35 страницAPI 570 Piping InspectionIrvansyah Razadin100% (9)
- Canpolat 2004 PDFДокумент5 страницCanpolat 2004 PDFIsha PatelОценок пока нет
- CAD, CAM, CAE Training Centre in Anna NagarДокумент8 страницCAD, CAM, CAE Training Centre in Anna NagarCadd Centre100% (1)
- Aws - The Practical Welding Engineer PDFДокумент154 страницыAws - The Practical Welding Engineer PDFSEGO4EVER100% (5)