Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Engine Dissection Project
Загружено:
Abdallah MansourОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Engine Dissection Project
Загружено:
Abdallah MansourАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Engine Dissection Project
Your team is dissecting a 3.5 HP
single cylinder, 4 cycle engine,
made by Briggs and Stratton in
Milwaukee, Wisconsin
These engines are typically used
in lawn mowers, snow blowers,
go-carts, etc
(ref. 2, Used by permission of Briggs and Statton, 1992, all rights reserved)
Engine.ppt - 1 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Engine Dissection Project
Start engine.
Dissassemble engine.
Review parts and functions Ask questions!
Reassemble engine.
Re-start engine.
Write individual report on how engine works.
Engine.ppt - 2 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
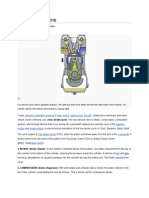
4 Cycle Process
1
Intake Valve
Intake
Manifold
Cylinder
Exhaust Valve
Exhaust
Manifold
Spark
Plug
Piston
Connecting
Rod
Intake Stroke
Intake valve opens,
admitting fuel and air.
Exhaust valve closed
for most of stroke
Crank
Crankcase
Compression Stroke
Both valves closed,
Fuel/air mixture is
compressed by rising
piston. Spark ignites
mixture near end of
stroke.
Power Stroke
Fuel-air mixture burns,
increasing temperature
and pressure, expansion
of combustion gases
drives piston down. Both
valves closed - exhaust
valve opens near end
of stroke
Exhaust Stroke
Exhaust valve open,
exhaust products are
displaced from cylinder.
Intake valve opens
near end of stroke.
Engine.ppt - 3 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Briggs Engine - Intake
Engine.ppt - 4 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Compression
Engine.ppt - 5 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Power Stroke
Engine.ppt - 6 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Exhaust Stroke
Engine.ppt - 7 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Venturi-type Carburetor
Air/Fuel Mixture To Engine
Bernoulli Effect:
P+1/2 V2 = Constant
Throttle Plate
Atomized Fuel
Valve Stem
Fuel Inlet
Float
Venturi
Choke Plate
Bowl
Constant level is
maintained in bowl
-as float moves
down,
valve stem moves
down, allowing more
fuel into bowl, float
moves up and closes
valve
Inlet Air
Fuel
Nozzle
Metering Orifice
Ref. Obert
Engine.ppt - 8 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
How do engines work?
How does the engine complete these Primary Functions?
Hint
Get started?
Suck in fuel?
Suck in air?
Mix air and fuel?
Compress the mixture?
Ignite the mixture (at the right time)?
Make the combusting gases do work?
Make the work available to somebody?
Exhaust the gases?
Shut off?
Think about the parts and processes involved for each.
Engine.ppt - 9 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
How do engines work?
How does the engine complete these Secondary Functions?
Hint
Stay lubricated?
Operate the valves at the right time?
Smooth out the power pulses?
Store the fuel?
Keep cool?
Make it easy to start?
Think about the parts and processes involved for each.
Engine.ppt - 10 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
2 Stroke Process (for
comparison)
Compression
(ports closed)
Air Taken Into
Crankcase
Combustion
(ports closed)
Exhaust
(intake port closed)
Air compressed in crankcase
Scavenging
and Intake
(ports open)
Engine.ppt - 11 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Fuel Injection
port)
(electronic, multi-
Monitored Engine
Operating Conditions:
Manifold Pressure
Engine Speed
Air Temperature
Coolant Temperature
Acceleration
COMPUTER
TRIGGER
INJECTOR DRIVE UNIT
Pressure Regulator
Fuel
Filter
50 psi typical
Fuel
Pump
Injectors
FUEL TANK
Engine.ppt - 12 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Classification of Engines
External vs Internal Combustion
Spark Ignition SI or Compression Ignition CI
Configuration
Valve Location
2 Stroke or 4 Stroke
Engine.ppt - 13 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Engine Configurations
In Line
(Automobile)
Horizontally
Opposed (Subaru)
Radial (Aircraft)
V
(Automobile)
Opposed Piston
(crankshafts geared
together)
Engine.ppt - 14 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
History of Internal Combustion (IC)
Engines
1860 Lenoirs engine (a converted
steam engine) combusted natural
gas in a double acting piston,
using electric ignition
Engine.ppt - 15 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
History - continued
1876 Nikolaus Otto patented the 4 cycle engine, it
used gaseous fuel
1882 Gottlieb Daimler, an engineer for Daimler, left to
work on his own engine. His 1889 twin cylinder V was
the first engine to be produced in quantities. Used
liquid fuel and Venturi type carburetor, engine was
named Mercedes after the daughter of his major
distributor
1893 Rudolf Diesel built successful CI engine which
was 26% efficient (double the efficiency of any other
engine of its time)
Engine.ppt - 16 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Complementary Technologies
for IC Engine-powered
Automobiles
Pneumatic tires (1888, Dunlop)
Cheap liquid fuels (Oil industry born in PA 1859)
Venturi effect carburetor (1892, Willi Maybach)
Variable mechanical transmission (primitive type by
Levassor, 1891)
Electric starter (Kettering 1912)
Engine.ppt - 17 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Parts of
an IC
Engine
Name as many parts as you can
CROSS SECTION OF OVERHEAD VALVE FOUR CYCLE SI ENGINE
Engine.ppt - 18 of 20
Product Dissection 04/07/98
Cylinder head
Air cleaner
Choke
Throttle
Intake manifold
Parts of
an IC
Engine
Exhaust manifold
Piston rings
Piston
Wrist pin
Cylinder block
Connecting rod
Oil gallery to piston
Oil gallery to head
Crankcase
Breather cap
Rocker arm
Valve spring
Valve guide
Pushrod
Sparkplug
Combustion chamber
Tappet
Dipstick
Cam
Camshaft
Water jacket
Wet liner
Connecting rod bearing
Crankpin
Crankshaft
If you scored:
25 - 32 You are a certified Gear Head
15 - 24 Change your own oil
10 - 14 You really need this class
<10 Take your car to Jiffy Lube
Main bearing
Oil pan or sump
Engine.ppt - 19 of 20
Вам также может понравиться
- Dual Ignition PDFДокумент3 страницыDual Ignition PDFSiddharth SharmaОценок пока нет
- The Best Tutorial For Making An RC PlaneДокумент8 страницThe Best Tutorial For Making An RC PlaneJosephRomeraloОценок пока нет
- Stirling Walking Beam EngineДокумент13 страницStirling Walking Beam EngineTomescu PaulОценок пока нет
- Geodesic DomesДокумент6 страницGeodesic DomesMarc Angelo DavidОценок пока нет
- Center Punch Grinding JigДокумент2 страницыCenter Punch Grinding JigmododanОценок пока нет
- Eliminator Torsion Axles: Shock Cord Cross SectionДокумент23 страницыEliminator Torsion Axles: Shock Cord Cross SectionRaju ManjuОценок пока нет
- Fuel Intake SystemДокумент49 страницFuel Intake SystemHitarth ShahОценок пока нет
- Turbo Jet EngineДокумент15 страницTurbo Jet EngineMuhammad Bin RiazОценок пока нет
- VW Aircraft Engine Conversion by Bob HooverДокумент133 страницыVW Aircraft Engine Conversion by Bob HooverJose Toronzo100% (1)
- Four Cylinder Air Engine Dwg.Документ15 страницFour Cylinder Air Engine Dwg.Jitendra BagalОценок пока нет
- EFI Two StrokeДокумент6 страницEFI Two StrokegkarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Suburban Tractor: Here's What It CostsДокумент11 страницSuburban Tractor: Here's What It CostsWojtek WywiałОценок пока нет
- A Review of Free-Piston Engine History and ApplicationsДокумент17 страницA Review of Free-Piston Engine History and ApplicationsĐạt Võ100% (1)
- Modular Worm GearboxДокумент32 страницыModular Worm Gearboxdharmikpanchal100% (1)
- Scavenging in 2 Stroke Engine FinalДокумент35 страницScavenging in 2 Stroke Engine Finalnitin_parwaniОценок пока нет
- Engine 4 StrokeДокумент16 страницEngine 4 Strokeelsoukkary100% (2)
- Crank Shaft: Software Used-Catia V5R20 Submitted To Submitted byДокумент47 страницCrank Shaft: Software Used-Catia V5R20 Submitted To Submitted byYaman Saluja0% (1)
- What Are The Functions of An Exhaust ManifoldДокумент5 страницWhat Are The Functions of An Exhaust Manifoldjameel babooram100% (1)
- F1-Cars SeminarsДокумент25 страницF1-Cars Seminarsphantaman100% (1)
- Engine ComponentsДокумент31 страницаEngine ComponentsKyle Caducio100% (1)
- Dry Fuel Cell ManualДокумент24 страницыDry Fuel Cell ManualniculaenicuОценок пока нет
- 4 Stroke IC Engine Valve Timing DiagramДокумент2 страницы4 Stroke IC Engine Valve Timing DiagramEngineer_SAM75% (4)
- Making Plastic From Potato StarchДокумент4 страницыMaking Plastic From Potato StarchManinderjeet SinghОценок пока нет
- Rocket Propulsion: Liquid & Solid PropellantДокумент9 страницRocket Propulsion: Liquid & Solid PropellantInterogator5Оценок пока нет
- AIAA 2005-2349 Blended-Wing-Body (BWB) Fuselage Structural Design For Weight ReductionДокумент9 страницAIAA 2005-2349 Blended-Wing-Body (BWB) Fuselage Structural Design For Weight ReductionM. Sadiq. A. PachapuriОценок пока нет
- Four Stroke EngineДокумент8 страницFour Stroke EngineVamsidhar ReddyОценок пока нет
- Cryogenic Rocket Engine SeminarДокумент31 страницаCryogenic Rocket Engine SeminarMahaManthra100% (1)
- 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke EngineДокумент5 страниц2 Stroke and 4 Stroke EngineMark AceОценок пока нет
- Baja SAE Collegiate Design Series Report-Brigham Young University-IdahoДокумент5 страницBaja SAE Collegiate Design Series Report-Brigham Young University-IdahoKarlos QuintanaОценок пока нет
- FOR RELEASE: BFP Design Notes and Documentation PDFДокумент39 страницFOR RELEASE: BFP Design Notes and Documentation PDFHassan ZiaОценок пока нет
- 1099935205four SpeedДокумент6 страниц1099935205four SpeedchzhptopОценок пока нет
- CamshaftДокумент8 страницCamshaftanshaj singhОценок пока нет
- A Hive Stand: "In The Beekeeper's Work Shop"Документ7 страницA Hive Stand: "In The Beekeeper's Work Shop"Dinu DavidОценок пока нет
- Install Keihin PE28 Carburetor Kit PDFДокумент4 страницыInstall Keihin PE28 Carburetor Kit PDFJontu In-PhОценок пока нет
- Two Stroke EngineДокумент5 страницTwo Stroke Enginedwarika2006Оценок пока нет
- Free Piston Engine Working PDFДокумент2 страницыFree Piston Engine Working PDFAmyОценок пока нет
- Penny Engine Micro Air Powered EngineДокумент10 страницPenny Engine Micro Air Powered Enginemarius_danila8736Оценок пока нет
- Pulse Detonation Engine: Nitish Kumar Regd No:-0701223318Документ16 страницPulse Detonation Engine: Nitish Kumar Regd No:-0701223318Vishal KumarОценок пока нет
- Heidenhain M Codes & G CODESДокумент18 страницHeidenhain M Codes & G CODESMohamed Ben Salem100% (1)
- Thermal Engineering-2 PracticalДокумент35 страницThermal Engineering-2 PracticalAlok Anand100% (1)
- Generator Bushing DesignsДокумент10 страницGenerator Bushing DesignsPradeep_VashistОценок пока нет
- ChassisДокумент21 страницаChassisphamxuannam2002Оценок пока нет
- A Review On Free Piston EnginesДокумент15 страницA Review On Free Piston EnginesABDUL SHAFI MОценок пока нет
- Basic Introduction To TurbochargingДокумент6 страницBasic Introduction To TurbochargingAngelino Martini de LeonОценок пока нет
- Spark Plug Testing MachineДокумент27 страницSpark Plug Testing MachineJeetDangiОценок пока нет
- Home Made Stirling EngineДокумент11 страницHome Made Stirling EngineDouglas MendesОценок пока нет
- Mini Bike LightДокумент2 страницыMini Bike LightperacОценок пока нет
- Chotia-460 NewManualДокумент8 страницChotia-460 NewManualErin LassleyОценок пока нет
- 55 Watt Gas CO2 Laser TubeДокумент66 страниц55 Watt Gas CO2 Laser TubeFitzwalter100% (1)
- Gyro Skipper PlansДокумент5 страницGyro Skipper PlansJayantha KandegamaОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Hydraulic MotorsДокумент8 страницFundamentals of Hydraulic Motorsswap dОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion Engines: The Worst Form of Vehicle Propulsion - Except For All The Other FormsДокумент62 страницыInternal Combustion Engines: The Worst Form of Vehicle Propulsion - Except For All The Other FormsNebojša NikolićОценок пока нет
- Hand Made CarДокумент33 страницыHand Made CarSahil DhirОценок пока нет
- Research Paper On 4 Stroke EngineДокумент6 страницResearch Paper On 4 Stroke Engineh02ngq6c100% (1)
- REPORT of 4 Stroke EngineДокумент8 страницREPORT of 4 Stroke Enginealibhalli4367% (3)
- Four-Stroke Engine - WikipediaДокумент51 страницаFour-Stroke Engine - Wikipediadevidasmoolya2005Оценок пока нет
- Cooling of 4 Stroke Petrol Engine Using ThermocoupleДокумент26 страницCooling of 4 Stroke Petrol Engine Using ThermocoupleSendhilNathan100% (1)
- 6 Stroke Engine Literature ReviewДокумент8 страниц6 Stroke Engine Literature Reviewafdtakoea100% (1)
- Maintenance and Repair For Diesel EnginesДокумент424 страницыMaintenance and Repair For Diesel EnginesHanafi Ajah100% (5)
- 6 Stroke EngineДокумент14 страниц6 Stroke EngineMayank VyasОценок пока нет
- Types of Pumps-1Документ8 страницTypes of Pumps-1Abdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Pumps TypesДокумент14 страницPumps TypesAbdallah Mansour100% (1)
- Valves PicsДокумент12 страницValves PicsAbdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Petroleum (1) .PPT (Recovered)Документ33 страницыPetroleum (1) .PPT (Recovered)Abdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Valve Types: - Gate Valves, Ball Valves, & Choke ValvesДокумент8 страницValve Types: - Gate Valves, Ball Valves, & Choke ValvesAbdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Making Decisions With InsulationДокумент12 страницMaking Decisions With InsulationAbdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Perforating Technology: China National Logging CorpДокумент39 страницPerforating Technology: China National Logging Corpdarryl_gilbertОценок пока нет
- Vibration Quick ReferenceДокумент49 страницVibration Quick Referencekeepmoshing2Оценок пока нет
- Perforating Technology: China National Logging CorpДокумент39 страницPerforating Technology: China National Logging Corpdarryl_gilbertОценок пока нет
- 3 Idc99courseДокумент50 страниц3 Idc99coursebintangsatuОценок пока нет
- Casting ProcessesДокумент56 страницCasting ProcessesAbdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Gas Sweetening FacilityДокумент28 страницGas Sweetening FacilityAbdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Cast IronsДокумент34 страницыCast IronsAbdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Essential Variables of SmawДокумент7 страницEssential Variables of SmawAbdallah Mansour100% (6)
- MEL 417 Lubrication Lec 170311Документ17 страницMEL 417 Lubrication Lec 170311Akash NairОценок пока нет
- AFA II III OilДокумент74 страницыAFA II III OilAbdallah Mansour100% (1)
- Power CalculationДокумент5 страницPower CalculationAbdallah MansourОценок пока нет
- Slipped CrankshaftДокумент3 страницыSlipped CrankshaftArun SОценок пока нет
- List of Is StandardsДокумент178 страницList of Is StandardsRajesh Chunduru0% (1)
- Group 8, Welding AssignmentДокумент11 страницGroup 8, Welding AssignmentKavish ChandraОценок пока нет
- Energy Resources Availability Management and Environmental Impacts ContentsДокумент11 страницEnergy Resources Availability Management and Environmental Impacts ContentsRangaswamy VittalaОценок пока нет
- WWTFSP App.F10 Energy ManagementДокумент42 страницыWWTFSP App.F10 Energy ManagementHuy NguyenОценок пока нет
- Vertical Turbine Submersible Pump BrochureДокумент12 страницVertical Turbine Submersible Pump BrochuremasatusОценок пока нет
- Policy and Actions Towards Low Carbon Emissions: Bangladesh PerspectiveДокумент14 страницPolicy and Actions Towards Low Carbon Emissions: Bangladesh Perspectivetowhidul alamОценок пока нет
- 72.5kV Dry Air Insulated Dead Tank Vacuum Circuit Breaker: Japan AE Power Systems CorporationДокумент4 страницы72.5kV Dry Air Insulated Dead Tank Vacuum Circuit Breaker: Japan AE Power Systems CorporationBalaji VenkatesanОценок пока нет
- Concentration CellsДокумент16 страницConcentration CellsSURESH33% (3)
- H2 A Level Chemistry Transition Elements Notes Part 2Документ22 страницыH2 A Level Chemistry Transition Elements Notes Part 2Peng Jia XinОценок пока нет
- OECD - Electricity Information 2003.-Organization For Economic Cooperation & Development (Set. 2003)Документ779 страницOECD - Electricity Information 2003.-Organization For Economic Cooperation & Development (Set. 2003)Abdallah MohammedОценок пока нет
- Research ProposalДокумент9 страницResearch Proposalyirga assefa100% (1)
- General 481 BSES Yamuna DISCOM 0Документ35 страницGeneral 481 BSES Yamuna DISCOM 0shashank chawdharyОценок пока нет
- DC1671A - 480-483kW Scania Data SheetДокумент2 страницыDC1671A - 480-483kW Scania Data SheetDenzal Wishington0% (1)
- Design of A Francis Turbine Stage - Httpsblog - adtechnology.comdesign-Of-A-francis-turbine-stageДокумент9 страницDesign of A Francis Turbine Stage - Httpsblog - adtechnology.comdesign-Of-A-francis-turbine-stageIndra DjodikusumoОценок пока нет
- Renewable Community PowerДокумент28 страницRenewable Community PowerNew England WindОценок пока нет
- n8748390 Annotated BibliographyДокумент5 страницn8748390 Annotated BibliographyGaurav BhardwajОценок пока нет
- Cover Letter SIF SyriaДокумент2 страницыCover Letter SIF Syriajeff ospitalОценок пока нет
- IEGC 2010 - VijayДокумент132 страницыIEGC 2010 - Vijayvijay2407Оценок пока нет
- Resolution JNNSMДокумент3 страницыResolution JNNSMKaran DangayachОценок пока нет
- A Simple BLDC Motor Drive For Solar PV PDFДокумент24 страницыA Simple BLDC Motor Drive For Solar PV PDFRylde Bolivar100% (2)
- Short Essay For Kids On Mango: My Hobby-ReadingДокумент9 страницShort Essay For Kids On Mango: My Hobby-ReadingSrimathi RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Statement of PurposeДокумент1 страницаStatement of PurposeRidwan Ibn Akeem100% (1)
- Briquette Moulding MachineДокумент29 страницBriquette Moulding MachineLife of kalyanОценок пока нет
- Major Training ReportДокумент23 страницыMajor Training ReportIshank Gupta100% (1)
- Energies 15 04580 v2Документ16 страницEnergies 15 04580 v2ฉัตรประภา แวววงศ์Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Reaction Engineering MCQ PDFДокумент13 страницChemical Reaction Engineering MCQ PDFKapilSahu50% (6)
- Maintenance & RepairДокумент26 страницMaintenance & RepairGrid Lock100% (1)
- L6S Final Examination Students)Документ12 страницL6S Final Examination Students)Fazliawati MahayuddinОценок пока нет
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestОт EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (28)
- Modern Engine Blueprinting Techniques: A Practical Guide to Precision Engine BlueprintingОт EverandModern Engine Blueprinting Techniques: A Practical Guide to Precision Engine BlueprintingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (9)
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsОт EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsОценок пока нет
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerОт EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (54)
- Allison Transmissions: How to Rebuild & Modify: How to Rebuild & ModifyОт EverandAllison Transmissions: How to Rebuild & Modify: How to Rebuild & ModifyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- CDL Study Guide 2024-2025: Everything You Need to Know to Pass the Commercial Driver’s License Exam on your First Attempt, with the Most Complete and Up-to-Date Practice Tests - New VersionОт EverandCDL Study Guide 2024-2025: Everything You Need to Know to Pass the Commercial Driver’s License Exam on your First Attempt, with the Most Complete and Up-to-Date Practice Tests - New VersionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- How to Fabricate Automotive Fiberglass & Carbon Fiber PartsОт EverandHow to Fabricate Automotive Fiberglass & Carbon Fiber PartsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- OBD-I and OBD-II: A Complete Guide to Diagnosis, Repair, and Emissions ComplianceОт EverandOBD-I and OBD-II: A Complete Guide to Diagnosis, Repair, and Emissions ComplianceОценок пока нет
- Powder Coating: A How-to Guide for Automotive, Motorcycle, and Bicycle PartsОт EverandPowder Coating: A How-to Guide for Automotive, Motorcycle, and Bicycle PartsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (17)
- Why We Drive: Toward a Philosophy of the Open RoadОт EverandWhy We Drive: Toward a Philosophy of the Open RoadРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- Trucking Business Startup: Build a Long-Term, Highly Profitable Trucking Company From Scratch in Just 30 Days Using Up-to-Date Expert Business Success SecretsОт EverandTrucking Business Startup: Build a Long-Term, Highly Profitable Trucking Company From Scratch in Just 30 Days Using Up-to-Date Expert Business Success SecretsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Automotive Master Technician: Advanced Light Vehicle TechnologyОт EverandAutomotive Master Technician: Advanced Light Vehicle TechnologyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Ford AOD Transmissions: Rebuilding and Modifying the AOD, AODE and 4R70WОт EverandFord AOD Transmissions: Rebuilding and Modifying the AOD, AODE and 4R70WРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- Competition Engine Building: Advanced Engine Design and Assembly TechniquesОт EverandCompetition Engine Building: Advanced Engine Design and Assembly TechniquesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (7)
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesОт EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- Automotive Machining: A Guide to Boring, Decking, Honing & MoreОт EverandAutomotive Machining: A Guide to Boring, Decking, Honing & MoreРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (11)