Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Elastic Properties of Materials, Tensile Test: Xingbo Liu
Загружено:
Shkelzen ShabaniОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Elastic Properties of Materials, Tensile Test: Xingbo Liu
Загружено:
Shkelzen ShabaniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
West Virginia University
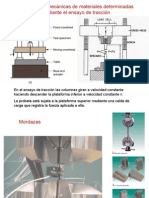
Elastic Properties of Materials, Tensile Test
Xingbo Liu
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Engineering Stress:
E = F/A0
Engineering Strain:
E = (L-L0)/L = L / L
Hooks Law:
= E E
=G
Generalized Hooks Law:
x = x/E - y/E- z/E
y = y/E - x/E- z/E
z = z/E - y/E- x/E
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test
(a)
Linear
Nonlinear
(b)
(c)
Typical F vs L plots of linear and nonlinear materials
under tensile loading
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
Typical F/A0 vs L/L0 plots of linear and nonlinear
materials under tensile loading
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
Proportionality Limit: Last point where stress and strain are
linearly related. (Point a.)
Elastic Limit:
Last point from which after removal of load,
there is no permanent strain. (Point b.)
Yield Point:
Technically the same as the elastic limit but
usually associated with the gross onset of
permanent strain. Many materials do not
exhibit a clearly defined yield point and so
this point is often taken to correspond to a
certain offset of strain. Point c is the yield
point for 0.2% (0.002 strain) offset
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
Yield Strength:
Stress at yield point, y.
Tensile Strength:
Sometimes called the Ultimate Tensile
Strength (UTS) and is the maximum stress
reached during the loading. Point d.
Material Toughness:
The area under the elastic and the plastic
portion of the stress-strain curve. It is the
total energy required to stress the material to
the point of fracture
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
Elongation:
(Plastic) strain after fracture, or tensile
ductility. The broken pieces are put together
and measured, and f = (L-L0)/L0.
Reduction of Area:
The maximum decrease in cross-sectional
area. RA = (A - A0)/A0
Resilience:
The ability of a material to absorb energy
when deformed elastically and to return it
when unloaded.
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
True Stress:
T = F/A
= F(E+1)/A0
True Strain:
T = ln (L/L0) = ln (E +1)
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
Comparison of engineering and true stress-strain curves
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
At Maximum Load:
E Fmax / A0
A0
T ln( )
A
T Fmax / A
Eliminating Fmax yields
A0
T
T E
Ee
A
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
True Fracture Stress: The load at fracture divided by the crosssectional area at fracture.
T fracture
Ffracture
Afracture
Ffracture A0
A0 Afracture
A0
Afracture
True Fracture Strain: The true fracture strain ef is the true
strain based on the original area A0 and
the area after fracture Af
T fracture
A0
1
ln(
) ln(
)
Afracture
1 RA
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd)
True Uniform Strain: True strain based only on the strain up to
maximum load. It may be calculated from either the specimen
cross-sectional area Au or the gage length Lu at maximum load.
The uniform strain is often useful in estimating the formability of
metals from the results of a tension test.
T uniform
A0
ln( )
Au
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd) Work Hardening
n is the strain-hardening exponent
K is the strength coefficient
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd) Work Hardening
Log/log plot of true stress-strain curve
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Tensile Test (Contd) Work Hardening
Various forms of power curve =K* n
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
West Virginia University
Values for n and K for metals at room temperature
Metal
Condition
K, psi
0,05% C steel
Annealed
0,26
77000
SAE 4340 steel
Annealed
0,15
93000
0,60% C steel
Quenched and tempered 1000oF
0,10
228000
0,60% C steel
Quenched and tempered 1300oF
0,19
178000
Copper
Annealed
0,54
46400
70/30 brass
Annealed
0,49
130000
Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
Вам также может понравиться
- Mechanical Behavior of Materials: Tensile TestingДокумент34 страницыMechanical Behavior of Materials: Tensile TestingSebut Saja IrwanОценок пока нет
- Tensile Testing of Metals: ObjectiveДокумент1 страницаTensile Testing of Metals: ObjectiveAhmadОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1: Fig. 1: Llyod Testing Machine in Materials Testing LabДокумент34 страницыExperiment 1: Fig. 1: Llyod Testing Machine in Materials Testing LabRogie Neth AbatayoОценок пока нет
- Exp1 TensileTesting HandoutДокумент6 страницExp1 TensileTesting HandoutHarshit RastogiОценок пока нет
- MSM Unit No.2 NotesДокумент39 страницMSM Unit No.2 NotesPratik SaindanePatilОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsДокумент61 страницаMechanical Properties of MaterialsSeira MolinaОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials: 1 M Concrete MixerДокумент9 страницStrength of Materials: 1 M Concrete Mixermeda012Оценок пока нет
- Uji TarikДокумент49 страницUji Tarikberlian pulungОценок пока нет
- Test TensileДокумент31 страницаTest Tensilejosel213Оценок пока нет
- Class 3Документ50 страницClass 3aksgupta24Оценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials 2015 by S K MondalДокумент471 страницаStrength of Materials 2015 by S K MondalNaman Jain100% (1)
- Som 2013 - 001 PDFДокумент431 страницаSom 2013 - 001 PDFKumar SamreshОценок пока нет
- AAU Strength of Materials Lecture Notes 09-05-21Документ66 страницAAU Strength of Materials Lecture Notes 09-05-21Tahir Aed100% (7)
- MT Lab ManualДокумент62 страницыMT Lab ManualArun Chandra BabuОценок пока нет
- TITLE: Experiment Write-Up (EW)Документ5 страницTITLE: Experiment Write-Up (EW)mritunjay1987Оценок пока нет
- Exp 3 - Tensile Test AluminumДокумент9 страницExp 3 - Tensile Test AluminumFiras Abu talebОценок пока нет
- Strength of MaterialДокумент80 страницStrength of Materialpriyankar007Оценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials by S K Mondal PDFДокумент171 страницаStrength of Materials by S K Mondal PDFajaykrishna_99Оценок пока нет
- Mechanical Testing (Tension)Документ33 страницыMechanical Testing (Tension)ZANTHERОценок пока нет
- EAT203 - Lab ReportДокумент24 страницыEAT203 - Lab ReportRavi VarmanОценок пока нет
- Elasticity: Material PropertiesДокумент37 страницElasticity: Material PropertiesAmeen ShahidОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ48 страницChapter 4Zhiyi HeОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three: Mechanical Properties of MaterialsДокумент31 страницаChapter Three: Mechanical Properties of MaterialsOmar AlzoubiОценок пока нет
- Second Course HERU MKMДокумент12 страницSecond Course HERU MKMRyndra KusumaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ30 страницLecture 2hania dogar0% (1)
- Mse2 1Документ55 страницMse2 1binoОценок пока нет
- Tension TestДокумент7 страницTension TestmanmathkОценок пока нет
- Tensile Strength of Mild SteelДокумент11 страницTensile Strength of Mild SteelPavan Ps50% (2)
- Strength of Materials by S K MondalДокумент429 страницStrength of Materials by S K MondalSaajal Sharma88% (26)
- Addis Ababa University Lecture NoteДокумент65 страницAddis Ababa University Lecture NoteTADY TUBE OWNER100% (9)
- Simple Stresses and Strains1Документ106 страницSimple Stresses and Strains1Vinayak PrabhuОценок пока нет
- Thermal StressДокумент104 страницыThermal Stressmanishtopsecrets100% (1)
- Tensile Test PresentationДокумент36 страницTensile Test PresentationalkharfaneОценок пока нет
- Thermal StressДокумент104 страницыThermal Stressgaspardo123100% (1)
- Lecture 1Документ54 страницыLecture 1nofal AdreesОценок пока нет
- EMTL 250 Lab 1 - Tensile Lab Handout 2018Документ5 страницEMTL 250 Lab 1 - Tensile Lab Handout 2018Desiree FabianОценок пока нет
- Yield Stress Von MIses Stress Strength of Materials - Mechanics of MaterialsДокумент3 страницыYield Stress Von MIses Stress Strength of Materials - Mechanics of MaterialsGnabBangОценок пока нет
- Som 2013Документ151 страницаSom 2013Jaya NagarОценок пока нет
- Iit Delhi: General OutlineДокумент14 страницIit Delhi: General OutlinePuneetSindhuОценок пока нет
- Chapter6 Mechanical PropertiesДокумент30 страницChapter6 Mechanical Propertieszerimar333100% (1)
- Beam Design and Deflections: NotationДокумент5 страницBeam Design and Deflections: NotationarcharishОценок пока нет
- SOM 2014 BhopalДокумент454 страницыSOM 2014 Bhopaljagdish8696168751Оценок пока нет
- Tensile Testing of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous AlloyДокумент7 страницTensile Testing of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Alloyrama100% (1)
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksОт EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Оценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresОт EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionОт EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionОценок пока нет
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionОт EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionРейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (4)
- Autocad 2Документ24 страницыAutocad 2Shkelzen ShabaniОценок пока нет
- FGM For L/L1 0.2 N 10 A/b 0.2 A/b 0.4 A/b 0.6 A/b 0.8 A/b 0Документ7 страницFGM For L/L1 0.2 N 10 A/b 0.2 A/b 0.4 A/b 0.6 A/b 0.8 A/b 0Shkelzen ShabaniОценок пока нет
- Vibration Analysis of Beam With Varying Crack Location: AbstractДокумент10 страницVibration Analysis of Beam With Varying Crack Location: AbstractShkelzen ShabaniОценок пока нет
- Vibration Analysis of Composite Beams Wi PDFДокумент4 страницыVibration Analysis of Composite Beams Wi PDFShkelzen ShabaniОценок пока нет
- QRG - Online Exam Setup For WindowsДокумент2 страницыQRG - Online Exam Setup For WindowsShkelzen ShabaniОценок пока нет
- Elastic Buckling Behavior of Beams: CE579 - Structural Stability and DesignДокумент45 страницElastic Buckling Behavior of Beams: CE579 - Structural Stability and DesignjcpolicarpiОценок пока нет
- Hardening of Metals - Diffusion: Mechanical & Aerospace EngineeringДокумент27 страницHardening of Metals - Diffusion: Mechanical & Aerospace EngineeringShkelzen ShabaniОценок пока нет
- Venn DiagramsДокумент14 страницVenn DiagramsShkelzen ShabaniОценок пока нет