Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lesson 4 - PF and Parallel AC Circuits
Загружено:
Michael Salvahan0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
165 просмотров12 страницpower factor and parallel ac circuits
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документpower factor and parallel ac circuits
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
165 просмотров12 страницLesson 4 - PF and Parallel AC Circuits
Загружено:
Michael Salvahanpower factor and parallel ac circuits
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 12
Electric Circuits Theory 2
Lesson 4
Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
Prepared by:
Engr. Michael M. Salvahan, ECE, ECT
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
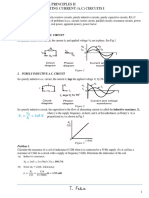
Power Triangle and Power Factor
Apparent Power the product of the current and voltage of
the circuit.
Real Power the capacity of the circuit for performing work
in a particular time.
Reactive Power power that continuously bounce back
and forth between source and load.
Power Factor defined as the ratio of the real power
flowing to the load, to the apparent power in the circuit and
is a dimensionless number in the closed interval of -1 to 1.
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
Power Triangle and Power Factor
Power
Apparent Power (S)
True or Active Power (P)
Reactive Power (Q)
Formula
Unit
Voltamperes (VA)
Watts (W)
Reactive Voltamperes (VAR)
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
Power Triangle and Power Factor
Sample Problems:
1. A pure inductance is connected to a 150 V, 50 Hz supply,
and the apparent power of the circuit is 300 VA. Find the
value of the inductance.
Answer: L = 0.239 H
2. A transformer has a rated output of 200 kVA at a power
factor of 0.8. Determine the rated power output and the
corresponding reactive power.
Answer: P = 160 kW, Q = 120 kVAR
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
Power Triangle and Power Factor
Sample Problems:
3. The power taken by an inductive circuit when connected to a 120 V, 50
Hz supply is 400 W and the current is 8 A. Calculate (a) the resistance,
(b) the impedance, (c) the reactance, (d) the power factor, and (e) the
phase angle between voltage and current.
Ans: R = 6.25 , Z = 15 , XL = 13.64 , P.F. = 0.4167, = 6522 lagging
4. A circuit consisting of a resistor in series with a capacitor takes 100
watts at a power factor of 0.5 from a 100 V, 60 Hz supply. Find (a) the
current flowing, (b) the phase angle, (c) the resistance, (d) the
impedance, and (e) the capacitance.
Ans: I = 2 A, = 60 leading, R = 25 , Z = 50 , X C = 61. 26 F
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
Parallel AC Circuits
In parallel circuits, the voltage is common to each branch of
the network and is thus taken as the reference phasor when
drawing phasor diagrams.
1.
2.
3.
4.
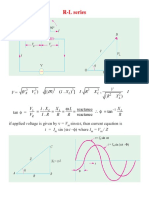
RL Parallel Circuit
RC Parallel Circuit
LC Parallel Circuit
RL-C Parallel Circuit
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
RL Parallel AC Circuit
Sample Problem:
1. A 20 resistor is connected in parallel with an
inductance of 2.387 mH across a 60 V, 1 kHz supply.
Calculate (a) the current in each branch, (b) the supply
current, (c) the circuit phase angle, (d) the circuit
impedance, and (e) the power consumed.
Answer:
IR = 3 A, IL = 4 A, I = 5 A,
= 538 lagging, Z = 12 , P = 180 W
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
RC Parallel AC Circuit
Sample Problem:
2. A 30 F capacitor is connected in parallel with an 80
resistor across a 240 V, 50 Hz supply. Calculate (a) the
current in each branch, (b) the supply current, (c) the
circuit phase angle, (d) the circuit impedance, (e) the
power dissipated, and (f) the apparent power.
Answer:
IR = 3 A, IC = 2.262 A, I = 3.757 A,
= 371 leading, Z = 63.88 , P = 720 W, S = 901.7 VA
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
RC Parallel AC Circuit
Sample Problem:
3. A capacitor C is connected in parallel with a resistor R
across a 120 V, 200 Hz supply. The supply current is 2 A
at a power factor of 0.6 leading. Determine the values of
C and R.
Answer:
R = 100 , C = 10.61 F
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
LC Parallel AC Circuit
Sample Problem:
4. A pure inductance of 120 mH is connected in parallel
with a 25 F capacitor and the network is connected to a
100 V, 50 Hz supply. Determine (a) the branch currents,
(b) the supply current and its phase angle, (c) the circuit
impedance, and (d) the power consumed.
Answer:
IL = 2.653 A, IC = 0.786 A, I = 1.867 A, Z = 53.56 , P = 0 W
Lesson 4: Power Factor and Parallel AC Circuits
RL-C Parallel AC Circuit
Sample Problem:
5. A coil of inductance 159.2 mH and resistance 40 is connected in
parallel with a 30 F capacitor across a 240 V, 50 Hz supply. Calculate
(a) the current in the coil and its phase angle, (b) the current in the
capacitor and its phase angle, (c) the supply current and its phase
angle,(d) the circuit impedance, (e) the power consumed, (f) the
apparent power, and (g) the reactive power.
Answer:
ILR = 3.748 A, LR = 5120 lagging,
IC = 2.262 A, C = 90 leading,
I = 2.434 A, = 1550 lagging
Z = 98.60 , P = 562 W, S = 584.2 VA, Q = 159.4 VAR
Things
turn out best for the
people who make the best of
the way things turn out.
Вам также может понравиться
- Electrical Question BankДокумент4 страницыElectrical Question BankAmar Wali0% (1)
- Unit-2 QuestionsДокумент3 страницыUnit-2 Questionsabhioptimus00Оценок пока нет
- Topic 3 Alternating Current Circuits I PDFДокумент20 страницTopic 3 Alternating Current Circuits I PDFFeddy BlaizОценок пока нет
- EE103 Homework 2Документ4 страницыEE103 Homework 2Hubert Semeniano100% (1)
- EEE Assignment1 AC Fundamental1 2011-12Документ8 страницEEE Assignment1 AC Fundamental1 2011-12Arpit ShahОценок пока нет
- Assignment 7Документ2 страницыAssignment 7Pavan KhetrapalОценок пока нет
- Circuits-2 Review B PDFДокумент16 страницCircuits-2 Review B PDFCristele Mae GarciaОценок пока нет
- EE1000 Problem Single Phase AC CircuitsДокумент4 страницыEE1000 Problem Single Phase AC CircuitsAmit DipankarОценок пока нет
- Circuits 2 Quiz 3Документ2 страницыCircuits 2 Quiz 3John Lenard SanchezОценок пока нет
- EEE SyllabusДокумент11 страницEEE Syllabussamarpit_anandОценок пока нет
- Probleme Curent Alternativ Example 7.1Документ6 страницProbleme Curent Alternativ Example 7.1Mihai BogdanОценок пока нет
- DEE M1.2B Slides V4-WebinarДокумент34 страницыDEE M1.2B Slides V4-Webinartcn ganmoОценок пока нет
- Electrical Network Analisis Ppt1Документ38 страницElectrical Network Analisis Ppt1Isaac P PlanОценок пока нет
- Assignment 30 Qa CircuitsДокумент9 страницAssignment 30 Qa Circuitskamisatoayaka010Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3Документ4 страницыTutorial 3DavidОценок пока нет
- Electrical Circuits: Topic 1.2B Webinar Presented by - Deepak PaisДокумент37 страницElectrical Circuits: Topic 1.2B Webinar Presented by - Deepak PaisjunaidОценок пока нет
- Physics II Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Assign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Документ4 страницыAssign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Sunil JainОценок пока нет
- Mid Bee Paper Set 3Документ6 страницMid Bee Paper Set 3raghusabale1Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 8-RLC CircuitsДокумент17 страницLecture 8-RLC CircuitsMAENYA BRUCE OYONDIОценок пока нет
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch28 Test BankДокумент13 страницWolfson Eup3 Ch28 Test Bankifghelpdesk0% (1)
- SM Ych Iyw Aq Ulf 4 Wy 508 RДокумент24 страницыSM Ych Iyw Aq Ulf 4 Wy 508 Rsagarshivnathsingh18818Оценок пока нет
- BEE Tutorial 6Документ3 страницыBEE Tutorial 6Atharva NairОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - Key - ExerciseДокумент6 страницChapter 7 - Key - Exercisevenkatalakshmi civilОценок пока нет
- Single-Phase - Problems - With SolutionДокумент3 страницыSingle-Phase - Problems - With SolutionVachist WangelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ2 страницыChapter 7Monisha RОценок пока нет
- Assignment 8Документ1 страницаAssignment 8Pavan KhetrapalОценок пока нет
- MET-2.2 QuestionsДокумент20 страницMET-2.2 QuestionsApoorv SinghОценок пока нет
- ASSIG202Документ2 страницыASSIG202Carolina Ticona VargasОценок пока нет
- Assessment in Circuits - EE Review - Technological Institute of The PhilippinesДокумент5 страницAssessment in Circuits - EE Review - Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDollesin Joseph Jr.Оценок пока нет
- ReviewerДокумент36 страницReviewerKaye BacomoОценок пока нет
- Ac Circuits Part IIIДокумент26 страницAc Circuits Part IIIblehОценок пока нет
- Tutorials 1Документ20 страницTutorials 1Sahil KumarОценок пока нет
- Lect 3 CH 3 PDFДокумент9 страницLect 3 CH 3 PDFكرار عبدالحسين قاسمОценок пока нет
- Lect 3 CH 3Документ9 страницLect 3 CH 3كرار عبدالحسين قاسم مسائي 23 BОценок пока нет
- Lect 3 CH 3 PDFДокумент9 страницLect 3 CH 3 PDFكرار عبدالحسين قاسمОценок пока нет
- RLC SERIES& Parallel QUIZДокумент3 страницыRLC SERIES& Parallel QUIZMoshotle InnocentОценок пока нет
- Basic Types of Circuit. The Study of Circuits Involves Three Basic Types of Units and Four PossibleДокумент13 страницBasic Types of Circuit. The Study of Circuits Involves Three Basic Types of Units and Four PossibleEduard LauronОценок пока нет
- D.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Документ5 страницD.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Pritam Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 04Документ2 страницыDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 04Kumar ShivamОценок пока нет
- Problem SetДокумент3 страницыProblem SetAJ REPECILOОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2 Single Phase Power Tutorial QuestionsДокумент17 страницCHAPTER 2 Single Phase Power Tutorial QuestionsFilbert OmbongiОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuit 1 - New SДокумент4 страницыTutorial 12 Alternating Current Circuit 1 - New STan Nian HanОценок пока нет
- Physics II Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Ac XiiДокумент4 страницыWorksheet Ac XiiYug GandhiОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 5 Single Phase Three Phase With AnswerДокумент2 страницыTutorial 5 Single Phase Three Phase With AnswernisasoberiОценок пока нет
- Kee-101 TutДокумент2 страницыKee-101 TutsanidhyaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3Документ2 страницыTutorial 3risabh bantaiОценок пока нет
- Unit-Ii: Ω and impedance of circuit is 10 Ω, then find power factor,Документ1 страницаUnit-Ii: Ω and impedance of circuit is 10 Ω, then find power factor,002Pradeep002Оценок пока нет
- Module2 Qbank 2023-24Документ3 страницыModule2 Qbank 2023-24Aqsa MohammadiОценок пока нет
- An alternating voltage V = 30 sin 50t+40 cos 50t is applied to a resistor of resistance 10Ω. The rms value of current through resistor is (a) 5/√2 A (b) 10/√2 A (c) 7/√2 A (d) 7AДокумент7 страницAn alternating voltage V = 30 sin 50t+40 cos 50t is applied to a resistor of resistance 10Ω. The rms value of current through resistor is (a) 5/√2 A (b) 10/√2 A (c) 7/√2 A (d) 7ASharanya BhattacharjeeОценок пока нет
- CBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Alternating Current)Документ7 страницCBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Alternating Current)anjanaroy35325Оценок пока нет
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisДокумент4 страницыPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soОценок пока нет
- CH 7 Ac Worksheet 2022Документ5 страницCH 7 Ac Worksheet 2022Hamad FarooqueОценок пока нет
- ECT&T 7th Ed Chap 17 SolsДокумент21 страницаECT&T 7th Ed Chap 17 SolsGelou Robert RazonОценок пока нет
- A 2Документ2 страницыA 2Rohit GuptaОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical Engineering Problem Sheet 2Документ5 страницBasic Electrical Engineering Problem Sheet 2ud54Оценок пока нет
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsОт EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsОт EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- LU Decomposition PDFДокумент12 страницLU Decomposition PDFSurender ReddyОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1.1 What Is SAFETYДокумент24 страницыLesson 1.1 What Is SAFETYMichael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 - KineticsДокумент7 страницLesson 2 - KineticsMichael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- Assignment No 1 - VectorДокумент2 страницыAssignment No 1 - VectorMichael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 - Dot and CrossДокумент10 страницLecture 2 - Dot and CrossMichael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes Vector Analysis MATH 332: Ivan AvramidiДокумент118 страницLecture Notes Vector Analysis MATH 332: Ivan AvramidiAdewole Adeyemi Charles100% (3)
- Tomasi OutlinedДокумент82 страницыTomasi OutlinedMichael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- Comms 1 Lecture 2Документ12 страницComms 1 Lecture 2Michael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- KennedyДокумент4 страницыKennedyMichael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- New Lecture in CommsДокумент6 страницNew Lecture in CommsMichael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- Spread Spectrum 2Документ15 страницSpread Spectrum 2Michael SalvahanОценок пока нет
- 4B - Urp - Shavya's FarmДокумент22 страницы4B - Urp - Shavya's FarmSnehansh KishoreОценок пока нет
- Low Speed Aerators PDFДокумент13 страницLow Speed Aerators PDFDgk RajuОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - Industrial Engineering & Ergonomics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inДокумент15 страницUnit 2 - Industrial Engineering & Ergonomics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSACHIN HANAGALОценок пока нет
- Caradol sc48 08Документ2 страницыCaradol sc48 08GİZEM DEMİRОценок пока нет
- CRISTIAN COLCERIU - PERSONALITATI CLUJENE Prof - Dr.ing - POMPILIU MANEAДокумент21 страницаCRISTIAN COLCERIU - PERSONALITATI CLUJENE Prof - Dr.ing - POMPILIU MANEAcristian colceriu100% (2)
- Planetary Gear DesignДокумент3 страницыPlanetary Gear DesignGururaja TantryОценок пока нет
- 1.co - Deb4113 - Industrial ManagementДокумент10 страниц1.co - Deb4113 - Industrial ManagementrohaizadОценок пока нет
- Reaction Paper FinalДокумент5 страницReaction Paper FinalJelo RoxasОценок пока нет
- Cpar Characteristics and Functions Week 3Документ128 страницCpar Characteristics and Functions Week 3christianwood0117Оценок пока нет
- Aero Ebook - Choosing The Design of Your Aircraft - Chris Heintz PDFДокумент6 страницAero Ebook - Choosing The Design of Your Aircraft - Chris Heintz PDFGana tp100% (1)
- Iec Codes PDFДокумент257 страницIec Codes PDFAkhil AnumandlaОценок пока нет
- KundaliniДокумент3 страницыKundaliniAlfred IDunnoОценок пока нет
- Vocabulary FceДокумент17 страницVocabulary Fceivaan94Оценок пока нет
- Concrete Specification (BS8500)Документ3 страницыConcrete Specification (BS8500)teh100% (1)
- Enrico Fermi Pioneer of The at Ted GottfriedДокумент156 страницEnrico Fermi Pioneer of The at Ted GottfriedRobert Pérez MartinezОценок пока нет
- Persuasive Speech 2016 - Whole Person ParadigmДокумент4 страницыPersuasive Speech 2016 - Whole Person Paradigmapi-311375616Оценок пока нет
- Possessive Determiners: A. 1. A) B) C) 2. A) B) C) 3. A) B) C) 4. A) B) C) 5. A) B) C) 6. A) B) C) 7. A) B) C)Документ1 страницаPossessive Determiners: A. 1. A) B) C) 2. A) B) C) 3. A) B) C) 4. A) B) C) 5. A) B) C) 6. A) B) C) 7. A) B) C)Manuela Marques100% (1)
- Homeopatija I KancerДокумент1 страницаHomeopatija I KancermafkoОценок пока нет
- European Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaДокумент40 страницEuropean Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaRainbootОценок пока нет
- DNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAДокумент10 страницDNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAKienlevyОценок пока нет
- The Time Machine Was First Published in 1984 As A Story Under The Name The Time Traveller in The National ObserverДокумент1 страницаThe Time Machine Was First Published in 1984 As A Story Under The Name The Time Traveller in The National ObservermarceОценок пока нет
- Community Architecture Concept PDFДокумент11 страницCommunity Architecture Concept PDFdeanОценок пока нет
- Marine Cargo InsuranceДокумент72 страницыMarine Cargo InsuranceKhanh Duyen Nguyen HuynhОценок пока нет
- Extract The .Msi FilesДокумент2 страницыExtract The .Msi FilesvladimirОценок пока нет
- GCP Vol 2 PDF (2022 Edition)Документ548 страницGCP Vol 2 PDF (2022 Edition)Sergio AlvaradoОценок пока нет
- Procter and Gamble - MarketingДокумент10 страницProcter and Gamble - MarketingIvana Panovska100% (5)
- Research Group 3 11abmb1Документ32 страницыResearch Group 3 11abmb1arianeОценок пока нет
- SICHEM Brochure 2023Документ8 страницSICHEM Brochure 2023krishnarao badisaОценок пока нет
- Tài Liệu Hướng Dẫn Cài Đặt Rơ Le MPS 3000Документ55 страницTài Liệu Hướng Dẫn Cài Đặt Rơ Le MPS 3000nguyenquangtonОценок пока нет
- SDN Van NotesДокумент26 страницSDN Van Notesmjsmith11Оценок пока нет