Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
The Nervous System
Загружено:
misterbrowner@yahoo.com0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
124 просмотров21 страницаThe central nervous system (cns) is the control center of the body. The CNS interprets and responds to information from the environment. The Peripheral Nervous System Contains sensory neurons and motor neurons. Motor neurons send commands from The CNS to muscles and other organs.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe central nervous system (cns) is the control center of the body. The CNS interprets and responds to information from the environment. The Peripheral Nervous System Contains sensory neurons and motor neurons. Motor neurons send commands from The CNS to muscles and other organs.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
124 просмотров21 страницаThe Nervous System
Загружено:
misterbrowner@yahoo.comThe central nervous system (cns) is the control center of the body. The CNS interprets and responds to information from the environment. The Peripheral Nervous System Contains sensory neurons and motor neurons. Motor neurons send commands from The CNS to muscles and other organs.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 21
The Nervous System
Neurons Conduct Electrical Signals
• Neurons are
nerve cells,
specialized cells
that transmit
information
throughout the
body
Structure of a Neuron
• Dendrites are the ‘antennae’ of the
neuron. Dendrites receive information
from other cells.
• An Axon is a long extension that
conducts nerve impulses. The axon
carries the nerve impulse ‘away’ from
the neuron.
• Nerves are bundles of neurons.
Structure of a Neuron
Some Neurons are Insulated
• Many neurons have a fatty outer layer
called a myelin sheath.
• The myelin sheath causes nerve
impulses to move faster down the axon.
• The myelin sheath is interrupted at
intervals called nodes of Ranvier.
Action Potential
• A nerve impulse is also called an action
potential.
• An action potential involves a change in
the charge of the membrane and
involves the movement of sodium and
potassium ions.
Neurons Use Neurotransmitters to
Communicate
• Nerve impulses must be transmitted
across gaps called synapses.
• Neurotransmitters are signal molecules
that transmit nerve impulses across
synapses.
Release of Neurotransmitters
Central Nervous System
• Brain
• Spinal Cord
• The CNS is the control center of the
body.
• The CNS interprets and responds to
information from the environment and
from within the body.
Peripheral Nervous System
• Contains sensory neurons and motor
neurons.
• Sensory neurons send information from
sense organs, such as the skin to the CNS.
• Motor neurons send commands from the
CNS to muscles and other organs.
Peripheral Nervous System
• The PNS is subdivided into the
autonomic nervous system and the
somatic nervous system.
Autonomic Nervous System
• Involuntary
• Two divisions
– Sympathetic – fight-or-flight responses
– Parasympathetic – body at rest
Somatic Nervous System
• Cranial and spinal nerves
• Reflexes – automatic responses to
stimuli
The Brain
• The brain is the body’s main processing
center.
• The brain has four lobes:
– Frontal
– Parietal
– Occipital
– Temporal
Sensory Receptors
• Sensory receptors detect stimuli and then
transmit impulses that can be interpreted
by the brain.
Types of Sensory Receptors
Receptor Type Stimulus Location
Thermoreceptors Temperature Skin,
hypothalamus
Pain receptors Tissue damage All tissues and
organs (but the
brain)
Mechanorectors Movement, Skin, ears
pressure, tension
Photoreceptors Light Eyes
Chemoreceptors Chemical Tongue, nose
Вам также может понравиться
- Test Dos InglesДокумент4 страницыTest Dos Inglesgbøniillaa75% (4)
- Kamasutra LengkapДокумент104 страницыKamasutra LengkapTjap TjoeanОценок пока нет
- DND 5e Races and SubracesДокумент3 страницыDND 5e Races and SubracesCursedLich89% (9)
- Concept PaperДокумент2 страницыConcept PaperMa'am Abegail Acohon88% (8)
- Nervous SystemДокумент23 страницыNervous SystemAnonymous 3OKQDoiJОценок пока нет
- Ch2 PsychДокумент61 страницаCh2 PsychJupiter BassettОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент56 страницNervous SystemSitiqoniahqanaahОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент22 страницыNervous SystemDarryl CalimlimОценок пока нет
- NURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDДокумент50 страницNURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDJacia’s SpaceshipОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 - Nervous System in Mammals IДокумент54 страницыChapter 13 - Nervous System in Mammals Iapi-3728508100% (2)
- Nervous System Report, Langam, Aclao, Aguipo, DapacДокумент21 страницаNervous System Report, Langam, Aclao, Aguipo, Dapachenrylangam100% (1)
- Nervous SystemДокумент22 страницыNervous SystemJohn Gil GomezОценок пока нет
- Pertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinДокумент43 страницыPertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinErsha PutriОценок пока нет
- Nervous System: Submitted By: Talha Saleem Semester: SecondДокумент49 страницNervous System: Submitted By: Talha Saleem Semester: SecondБакытОценок пока нет
- Myer's AP Psychology 8th Edition Chapter 2 VocabДокумент4 страницыMyer's AP Psychology 8th Edition Chapter 2 Vocabcardenass100% (3)
- Psy 100 Week4 NeuroscienceДокумент57 страницPsy 100 Week4 NeuroscienceseckinalpkargiОценок пока нет
- NERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)Документ52 страницыNERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)nadeemyakubu47Оценок пока нет
- Neuron Is The Scientific Name For A Nerve CellДокумент10 страницNeuron Is The Scientific Name For A Nerve Cellirene_bayubaycuteОценок пока нет
- Introduction To CNS 1Документ50 страницIntroduction To CNS 1Sefrinmi AyodejiОценок пока нет
- Ch3 Anatomy of The NSДокумент59 страницCh3 Anatomy of The NSJoshua TuguinayОценок пока нет
- Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology: Nature or NurtureДокумент43 страницыPsychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology: Nature or Nurtureapi-293070066Оценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент20 страницNervous SystemJewel Angeline MartinezОценок пока нет
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiДокумент53 страницыFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiKholid DamriОценок пока нет
- Part 3 Nervous SystemДокумент18 страницPart 3 Nervous SystemRoland ApareceОценок пока нет
- The Nervous SystemДокумент63 страницыThe Nervous SystemLance PerezОценок пока нет
- Neuropsychology Summary BookletДокумент12 страницNeuropsychology Summary Bookletapi-642709499Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Документ64 страницыAnatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Batot EvaОценок пока нет
- A System That Controls All of The Activities of The BodyДокумент49 страницA System That Controls All of The Activities of The BodynelsonОценок пока нет
- Nervous System PhysiologyДокумент43 страницыNervous System PhysiologyManoj100% (1)
- Nervous System Unit - 3Документ26 страницNervous System Unit - 3anupama_rani_2Оценок пока нет
- C3 Coordination and ResponseДокумент160 страницC3 Coordination and ResponseFoh Lian HuaiОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент22 страницыNervous SystemAltaf Hussain Khan50% (2)
- NeuroscienceДокумент50 страницNeuroscienceDenise MathreОценок пока нет
- NervesДокумент26 страницNerveskentОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Документ7 страницChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayОценок пока нет
- SENSORY Physiology EditДокумент235 страницSENSORY Physiology Editnapoleon tesfayeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Nervous System NHR 2021Документ70 страницChapter 2 - Nervous System NHR 2021Yusman Hakim100% (1)
- Nervous SystemДокумент8 страницNervous Systemvictory IsaacОценок пока нет
- CNS 1Документ63 страницыCNS 1Prabhu KiranОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент5 страницNervous Systemkmakabe78Оценок пока нет
- Prepared by Dr. Saiful Quasar H#37, RD# 122, GULSHAN-1Документ32 страницыPrepared by Dr. Saiful Quasar H#37, RD# 122, GULSHAN-1Coc DonoОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент36 страницNervous SystemSamir KadiyaОценок пока нет
- Psy 100 Week4 NeuroscienceДокумент49 страницPsy 100 Week4 Neurosciencebillym319Оценок пока нет
- Nervous System - 1555715323 - Unlocked - English - 1561543586Документ9 страницNervous System - 1555715323 - Unlocked - English - 1561543586Aghna Tiyas Mandal100% (1)
- Human Physiology: The Nervous SystemДокумент29 страницHuman Physiology: The Nervous Systemzandrex delunaОценок пока нет
- Nervous System1Документ26 страницNervous System1KJ CaluscusaoОценок пока нет
- NERVOUSДокумент78 страницNERVOUSsarathnta9Оценок пока нет
- Care of The Patient With A Neurological DisorderДокумент162 страницыCare of The Patient With A Neurological DisorderOmar Duran Castro100% (1)
- Nervous System PowerpointДокумент45 страницNervous System Powerpointabisantiago6131100% (3)
- 2 Biological BasisДокумент57 страниц2 Biological Basisbrillaboy266Оценок пока нет
- Control & CoordinationДокумент12 страницControl & CoordinationRajvir tradaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To NeurologyДокумент105 страницIntroduction To NeurologyaboubakarylwabukobaОценок пока нет
- Describe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous SystemДокумент29 страницDescribe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous Systemsiska yantiОценок пока нет
- Nervous System 4 PDF FreeДокумент15 страницNervous System 4 PDF FreeZedy GullesОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент26 страницNervous Systemhanimunch0% (1)
- Nervous SystemДокумент7 страницNervous SystemDeejay BeekayОценок пока нет
- Neuro 2Документ41 страницаNeuro 2Cosmina CorbeanuОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System Powerpoint To PrintoutДокумент47 страницThe Nervous System Powerpoint To PrintoutKaye GelieОценок пока нет
- AnP Nervous SystemДокумент90 страницAnP Nervous SystemNicole JohnsonОценок пока нет
- CELLULAR S OF NS Updated 29022024 123331pmДокумент54 страницыCELLULAR S OF NS Updated 29022024 123331pmaz.rah.e.khudiОценок пока нет
- 7 Nervous SystemДокумент43 страницы7 Nervous Systembabaaijaz01Оценок пока нет
- EE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLДокумент29 страницEE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLtmkiran100% (1)
- Unit 3 Nervous System Part 1Документ62 страницыUnit 3 Nervous System Part 1Shehzad Haider100% (1)
- Final Study GuideДокумент16 страницFinal Study Guidemisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Communites & Biomes PresentationДокумент20 страницCommunites & Biomes Presentationmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Astronomy Study Guide KeyДокумент4 страницыAstronomy Study Guide Keymisterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (2)
- Predation PresentationДокумент25 страницPredation Presentationmisterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Energy Flow Through An Ecosystem PresentationДокумент29 страницEnergy Flow Through An Ecosystem Presentationmisterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (4)
- Symbiosis PresentationДокумент7 страницSymbiosis Presentationmisterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Populations: More Free Powerpoints atДокумент18 страницPopulations: More Free Powerpoints atmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- A Major Regional Terrestrial Community With Its Own Type of Climate, Vegetation, and Animal LifeДокумент27 страницA Major Regional Terrestrial Community With Its Own Type of Climate, Vegetation, and Animal Lifemisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System - Fill in NotesДокумент4 страницыThe Nervous System - Fill in Notesmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Nitrogen CycleДокумент8 страницNitrogen Cyclemisterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (2)
- Biogeochemical Cycles (Water and Carbon Cycles)Документ13 страницBiogeochemical Cycles (Water and Carbon Cycles)misterbrowner@yahoo.com67% (3)
- Catapult Project DescriptionДокумент2 страницыCatapult Project Descriptionmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Greenhouse Project DescriptionДокумент2 страницыGreenhouse Project Descriptionmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Greenhouse RubricДокумент2 страницыGreenhouse Rubricmisterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Types of BehaviorДокумент18 страницTypes of Behaviormisterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Physical Science Study Guide - AstronomyДокумент4 страницыPhysical Science Study Guide - Astronomymisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Catapult RubricДокумент2 страницыCatapult Rubricmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Astronomy Project RubricДокумент2 страницыAstronomy Project Rubricmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Origin of The Solar SystemДокумент20 страницOrigin of The Solar Systemmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Life of A StarДокумент28 страницLife of A Starmisterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (1)
- The Moon: A Look at Our Nearest Neighbor in Space!Документ58 страницThe Moon: A Look at Our Nearest Neighbor in Space!misterbrowner@yahoo.com100% (5)
- AsteroidsДокумент33 страницыAsteroidsmisterbrowner@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- ImpressionДокумент7 страницImpressionAnnisa Nur AmalaОценок пока нет
- Reading SMPДокумент43 страницыReading SMPSharah RahmawatiОценок пока нет
- Sitting Fox: Materials KeyДокумент7 страницSitting Fox: Materials KeyVerónica TОценок пока нет
- Tuberculosis: What Is It and How Do We Keep Healthy?: A Presentation For Pacific Island Schools and CommunitiesДокумент17 страницTuberculosis: What Is It and How Do We Keep Healthy?: A Presentation For Pacific Island Schools and CommunitiesKailash NagarОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Admission Procedure of Women in LabourДокумент30 страницUnit 3 Admission Procedure of Women in LabourNishaThakuriОценок пока нет
- Cómo Hacer FigurasДокумент8 страницCómo Hacer FigurasAlberto Delfino100% (1)
- ES Syok Anafilaktik Gangguan Darah Pencernaan Es Sensitisasi I Sepsis I Osteomielitis I Endokarditis Sifilis RespiratoryДокумент4 страницыES Syok Anafilaktik Gangguan Darah Pencernaan Es Sensitisasi I Sepsis I Osteomielitis I Endokarditis Sifilis RespiratorysmapuchiОценок пока нет
- Yh 5302Документ17 страницYh 5302Elizabeth FernandezОценок пока нет
- 8A1 - Test 19.9Документ4 страницы8A1 - Test 19.9Yun YumiОценок пока нет
- The Wax # 9Документ54 страницыThe Wax # 9Emmanuel MilwaukeeОценок пока нет
- Wildlife Fact File - Birds - 31-40Документ20 страницWildlife Fact File - Birds - 31-40ClearMind84100% (2)
- Reanimation of Rats From Body Temperatures Between 0 and 1°c by Microwave DiathermyДокумент6 страницReanimation of Rats From Body Temperatures Between 0 and 1°c by Microwave DiathermyLJОценок пока нет
- UnconsciousnessДокумент16 страницUnconsciousnessAkhilesh BabuОценок пока нет
- Developing The Straight Body Cast To HandstandДокумент6 страницDeveloping The Straight Body Cast To HandstandValentin Uzunov100% (1)
- Marvel - Loki (ING)Документ11 страницMarvel - Loki (ING)Romy FernandezОценок пока нет
- Exporters DirectoryДокумент1 страницаExporters DirectoryMipta KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan - RabiesДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan - Rabiesderic89% (9)
- 2 MCQ - Grammar & SpellingДокумент6 страниц2 MCQ - Grammar & SpellingMunniswarran Sharon100% (1)
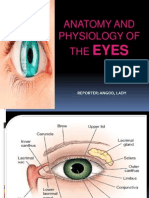
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesДокумент20 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesLaidy Aizahlyn Indoc Angod100% (2)
- MasterMind 2 Unit 1 WordlistДокумент3 страницыMasterMind 2 Unit 1 WordlistRolando Guzman MartinezОценок пока нет
- Lambert 2016Документ71 страницаLambert 2016Iqbal FitriantoОценок пока нет
- A Brief List of Old Wives TalesДокумент3 страницыA Brief List of Old Wives TalesMelissaОценок пока нет
- Clavus, Ingrown Nail, Skin Epithelial CystsДокумент11 страницClavus, Ingrown Nail, Skin Epithelial CystsRafiОценок пока нет
- Properties of LanguageДокумент2 страницыProperties of LanguageNurul IzzatiОценок пока нет
- Ujian August Pemahaman Bah AДокумент5 страницUjian August Pemahaman Bah Afarah julianaОценок пока нет
- Jack's Head (Siggy Shade)Документ101 страницаJack's Head (Siggy Shade)parikhaastha1804Оценок пока нет