Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
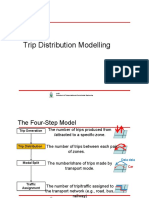
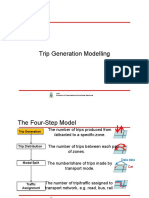
Trip Distribution
Загружено:
Ervina AhyudanariИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Trip Distribution
Загружено:
Ervina AhyudanariАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip Distribution
Additional suggested reading: Chapter 5 of Ortuzar
& Willumsen, third edition
November 2004
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip Distribution Objectives
Replicate spatial pattern of trip making
Account for spatial separation among origins and destinations (proximity in terms of time, cost, & other factors)
Account for attractiveness among TAZs
Reflect human behavior
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip Distribution
Convert Production and Attraction Tables into Origin Destination (O - D) Matrices
TAZ
1
2
3
4
5
6
Sum
P
15
13
26
18
8
13
93
A
22
6
5
52
2
6
93
Origins
1
2
3
4
5
6
Sum
1
T11
T21
T31
T41
T51
T61
D1
Destinations
2
3
4
5
T12 T13 T14 T15
T22 T23 T24 T25
T32 T33 T34 T35
T42 T43 T44 T45
T52 T53 T54 T55
T62 T63 T64 T65
D 2 D3 D 4 D5
6
T16
T26
T36
T46
T56
T66
D6
Sum
O1
O2
O3
O4
O5
O6
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Crude approximation for HBW
Zone ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
Total
Production Attraction
P
A
15
22
13
6
26
5
18
52
8
2
13
6
93
93
Crude OD
Calculation
O=D=(P+A)/2
18.5
9.5
15.5
35
5
9.5
93
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip Distribution, Methodology
General Equation:
Tij = Ti P(Tj)
Tij = calculated trips from zone i to zone j
Ti
= total trips originating at zone i
P(Tj) = probability measure that trips will be attracted
to zone j
Constraints:
Singly Constrained
Sumi Tij = Dj
OR
Sumj Tij = Oi
Doubly Constrained
Sumi Tij = Dj
AND
Sumj Tij = Oi
GEOG 111/211A
Trip Distribution Models
Growth Factor / Fratar Model
Tij = Ti (Tj / T)
Tij = present trips from zone i to zone j
Ti = total trips originating at zone i
Tj = total trips ending at zone j
T = total trips in the entire study
Tij* = Tij (Fi Fj) / F
Fi = Ti* / Ti
Fj = Tj* / Tj
F = T* / T
* = estimated future trips
Transportation Planning
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip Distribution Models
Gravity Model
Tij = Ti
Aj / Cij
a
Sum (Ax / Cix)
You can consider this as the
probability spatial distribution
P(Tj)
Tij = trips from zone i to zone j
Ti = total trips originating at zone i
Aj = attraction factor at j
Ax = attraction factor at any zone x
Cij = travel friction from i to j expressed as a generalized cost
function
Cix = travel friction from i to any zone x expressed as a
generalized cost function
a = friction exponent or restraining influence
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip Distribution Models
Intervening - Opportunities Model
Tij = Ti (e-LT - e-LT(T + Tj) )
Tij = trips from zone i to zone j
T = trip destination opportunities closer in time to zone
i than those in zone j
Ti = trip end opportunities in zone i
Tj = trip end opportunities in zone j
L = probability that any destination opportunity will be
chosen
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Model Comparison
Model
Advantages
Disadvantages
Growth Factor
Simple
Easy to balance origin and
destination trips at any
zone
Specific account of friction
and interaction between
zones
Does not require origin destination data
Claimed to bear a better
fit to actual traffic
Does not reflect changes in the
frictions between zones
Does not reflect changes in the
network
Requires extensive calibration
Long iterative process
Gravity
Intervening Opportunities
Accounts for only relative
changes in time - distance
relationship between zones
Arbitrary choice of
probability factor
New: Destination choice models build on intervening opportunities
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Gravity Model Process
1. Create Shortest Path Matrix
- Minimize Link Cost between Centroids
2. Estimate Friction Factor Parameters
- Function of Trip Length Characteristics by Trip Purpose
3. Calculate Friction Factor Matrix
4. Convert Productions and Attractions to Origins and
Destinations
5. Calculate Origin - Destination Matrix
6. Enforce Constraints on O - D Matrix
- Iterate Between Enforcing Total Origins and Destinations
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Shortest Path Matrix
Matrix of Minimum Generalized Cost from any
Zone i to any Zone j (see OW p. 153)
Distance, Time, Monetary Cost, Waiting Time, Transfer
Time, etc.. may be used in Generalized Cost
Time or Distance Often Used
Matrix Not Necessarily TAZ
TAZ ID
Symmetric (Effect of ID 1 2 3 4 5 6
1
C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16
One - Way Streets)
2
C21 C22 C23 C24 C25 C26
3
4
5
6
C31
C41
C51
C61
C32
C42
C52
C62
C33
C43
C53
C63
C34
C44
C54
C64
C35
C45
C55
C65
C36
C46
C56
C66
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Example: travel time matrix for 6 TAZs
Travel time table (minutes)
Zone ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
2
1
3
4
5
6
3
3
1.5
2
3
4
5
4
4
2
2
1
3
4
5
5
3
2
2
1
4
6
6
4
3
3
2
1
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Friction Factor Models
Exponential:
f(cij) = e- c (cij)
c>0
Inverse Power:
f(cij) = cij- b
b>0
Gamma:
f(cij) = a cij- b e- c (cij)
Trip Purpose
HBW
HBP
NHB
a
28507
139173
219113
a > 0, b > 0, c > 0
b
0.020
1.285
1.332
c
0.123
0.094
0.010
ref. NCHRP 365 / TransCAD UTPS Manual pg. 80
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Example friction factors using
travel times alone
Zone ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
1.349859
1.822119
2.459603
3.320117
4.481689
6.049647
2
1.822119
1.349859
2.459603
3.320117
4.481689
6.049647
3
2.459603
1.568312
1.822119
2.459603
3.320117
4.481689
4
3.320117
1.822119
1.822119
1.349859
2.459603
3.320117
Friction ij = 1/exp(-0.03* Timeij)
5
4.481689
2.459603
1.822119
1.822119
1.349859
3.320117
6
6.049647
3.320117
2.459603
2.459603
1.822119
1.349859
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Friction Factor Matrices
Matrix of Friction from any Zone i to any Zone j, by Trip Purpose
Each Cell of a Friction Factor Matrix is a Function of the Corresponding Cell of the Shortest Path Matrix
Each Trip Purpose has a separate Friction Factor Matrix
Because Trip Making
Behavior Changes for
Each Trip Purpose
TAZ
ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
TAZ ID
3
4
F11
F21
F31
F41
F51
F61
F12
F22
F32
F42
F52
F62
F13
F23
F33
F43
F53
F63
F14
F24
F34
F44
F54
F64
F15
F25
F35
F45
F55
F65
F16
F26
F36
F46
F56
F66
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip Conversion(Approximate)
Home Based Trips:
Non - Home Based Trips:
Oi = (Pi + Ai) / 2 Oi = Pi
Di = (Pi + Ai) / 2 Di = Ai
Oi = origins in zone i (by trip purpose)
Di = destinations in zone i (by trip purpose)
Pi = productions in zone i (by trip purpose)
Ai = attractions in zone i (by trip purpose)
Note: This Only Works for a 24 Hour Time Period
If our models are for one period in a day we prefer to
work directly with Origins-Destinations
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
O - D Matrix Calculation
Calculate Initial Matrix By Gravity Equation, by Trip
Purpose
Each Cell has a Different Friction, Found in the
Corresponding Cell of the Friction Factor Matrix
Enforce Constraints in Iterative Process
Sum of Trips in Row i Must Equal Origins of TAZ i
If Not Equal, Trips are Adjusted Proportionally
Sum of Trips in Column j Must Equal Destinations of TAZ j
If Not Equal, Trips are Adjusted Proportionally
Iterate Until No Adjustments Required
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
O - D Matrix Example:
Origins
1
2
3
4
5
6
Sum
1
T11
T21
T31
T41
T51
T61
D1
2
T12
T22
T32
T42
T52
T62
D2
Destinations
3 4 5
T13 T14 T15
T23 T24 T25
T33 T34 T35
T43 T44 T45
T53 T54 T55
T63 T64 T65
D3 D4 D5
6
T16
T26
T36
T46
T56
T66
D6
Sum
O1
O2
O3
O4
O5
O6
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Attraction/friction matrix
Aj/friction factor Table
Zone ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
16.298
12.074
8.945
6.626
4.909
3.637
2
3.293
4.445
2.439
1.807
1.339
0.992
3
2.033
3.188
2.744
2.033
1.506
1.116
4
15.662
28.538
28.538
38.523
21.142
15.662
5
0.446
0.813
1.098
1.098
1.482
0.602
6 Total
0.992
38.724
1.807
50.865
2.439
46.203
2.439
52.526
3.293
33.670
4.445
26.453
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Gravity model probability
Gravity Model Probability
Zone ID
1
1
0.421
2
0.237
3
0.194
4
0.126
5
0.146
6
0.137
2
0.085
0.087
0.053
0.034
0.040
0.037
3
0.052
0.063
0.059
0.039
0.045
0.042
Aj / frictionij
Sum (Ax / frictionix)
4
0.404
0.561
0.618
0.733
0.628
0.592
5
0.012
0.016
0.024
0.021
0.044
0.023
6 Total
0.026
0.036
0.053
0.046
0.098
0.168
1
1
1
1
1
1
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip Interchange - iteration 1
TIJ iteration 1
Zone ID
1
2
1
7.8
1.6
2
2.3
0.8
3
3.0
0.8
4
4.4
1.2
5
0.7
0.2
6
1.3
0.4
Total
19.5
5.0
Dj
18.5
9.5
Ratio
0.949099 1.907311
3
4
5
1.0
7.5
0.2
0.6
5.3
0.2
0.9
9.6
0.4
1.4
25.7
0.7
0.2
3.1
0.2
0.4
5.6
0.2
4.5
56.8
1.9
15.5
35
5
3.47064 0.615986 2.630148
6 Total
0.5
18.5
0.3
9.5
0.8
15.5
1.6
35
0.5
5
1.6
9.5
5.3
93
9.5
1.77888
For each cell value we apply the gravity equation once - in this iteration after this we use the ratio to adjust the values in the cells - until row and
column targets are satisfied - see also OW - chapter 5
Target
Oi
18.5
9.5
15.5
35
5
9.5
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip interchange - iteration 2
TIJ iteration 2
Zone ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
Total
1
7.4
2.1
2.8
4.2
0.7
1.2
18.5
2
3.0
1.6
1.6
2.3
0.4
0.7
9.5
3
3.4
2.1
3.2
4.7
0.8
1.4
15.5
4
4.6
3.3
5.9
15.8
1.9
3.5
35
5
0.6
0.4
1.0
1.9
0.6
0.6
5
6 Total
Oi
0.8
19.8
0.6
10.1
1.5
15.9
2.9
31.8
0.9
5.2
2.8
10.2
9.5
93
18.5
9.5
15.5
35
5
9.5
Using the ratios from before we succeed in getting the targets for the sums
of cells for each column - look at the other ratios
Ratio
0.935588
0.943096
0.973293
1.100092
0.956075
0.932966
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip interchange - iteration 3
TIJ iteration 3
Zone ID
1
2
3
4
5
6 Total
1
6.9
2.8
3.2
4.3
0.5
0.8
18.5
2
2.0
1.5
1.9
3.1
0.4
0.6
9.5
3
2.8
1.5
3.1
5.7
0.9
1.4
15.5
4
4.6
2.5
5.2
17.4
2.1
3.2
35
5
0.7
0.4
0.7
1.8
0.6
0.8
5
6
1.2
0.6
1.3
3.2
0.5
2.6
9.5
Total
18.1
9.3
15.4
35.6
5.0
9.4
93
Ratio
1.020289 1.016843 1.004978 0.982477 0.991224 1.007046
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Trip interchange - iteration 4
TIJ iteration 4
Zone ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
Total
1
7.1
2.1
2.8
4.7
0.7
1.2
18.5
2
2.9
1.5
1.5
2.6
0.4
0.6
9.5
3
3.2
2.0
3.1
5.2
0.7
1.3
15.5
4
4.2
3.0
5.6
17.1
1.8
3.2
35
5
0.5
0.4
0.9
2.1
0.5
0.5
5
6 Total
Oi
0.8
18.6
0.6
9.5
1.4
15.5
3.2
34.9
0.8
5.0
2.7
9.5
9.5
93
We get both rows and columns to produce the sums we want!
18.5
9.5
15.5
35
5
9.5
Ratio
0.993094
0.997665
1.000101
1.003991
1.001637
1.000214
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Multiple Matrices
For each trip purpose obtain different OriginDestination Tij matrices
Usually these are 24 hour Matrices (number of trips
from one zone to another in a 24 hour period)
In assignment we will need a matrix of vehicles
moving from a zone to another during a specific
period (peak usually) in a typical day
GEOG 111/211A
Transportation Planning
Final O - D Matrix (simplified)
Combine (Add) O - D Matrices for Various Trip Purposes
Scale Matrix for Peak Hour
Scale by Percent of Daily Trips Made in the Peak Hour
0.1 Often Used (10% of daily trips)
Scale Matrix for Vehicle Trips
Scale by Inverse of Ridership Ratio to Convert Person Trips to
Vehicle Trips
0.95 to 1 Often Used
Note: Mode Split Process / Models More Accurate, - we will
explore them in class
Вам также может понравиться
- Overhead Traveling Crane, Hoist & Monorail System World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryОт EverandOverhead Traveling Crane, Hoist & Monorail System World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryОценок пока нет
- Trip DistributionДокумент26 страницTrip Distributionthouseef06Оценок пока нет
- Neues verkehrswissenschaftliches Journal - Ausgabe 16: Capacity Research in Urban Rail-Bound Transportation with Special Consideration of Mixed TrafficОт EverandNeues verkehrswissenschaftliches Journal - Ausgabe 16: Capacity Research in Urban Rail-Bound Transportation with Special Consideration of Mixed TrafficОценок пока нет
- Trip DistributionДокумент26 страницTrip Distributionthouseef06Оценок пока нет
- Terramechanics and Off-Road Vehicle Engineering: Terrain Behaviour, Off-Road Vehicle Performance and DesignОт EverandTerramechanics and Off-Road Vehicle Engineering: Terrain Behaviour, Off-Road Vehicle Performance and DesignРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Trip GenerationДокумент39 страницTrip GenerationLemis Sean VerasОценок пока нет
- TR 631 LT 2.3 Trip Distribution ModellingДокумент36 страницTR 631 LT 2.3 Trip Distribution ModellingGilbert MaroОценок пока нет
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: Lecture # 5Документ51 страницаPolytechnic University of The Philippines: Lecture # 5Daisy AstijadaОценок пока нет
- Transportation Modes: DR RawidДокумент24 страницыTransportation Modes: DR RawidMuhammad UmairОценок пока нет
- CEE 6505 Transportation Planning: Moinul Hossain Cee, IutДокумент51 страницаCEE 6505 Transportation Planning: Moinul Hossain Cee, IutRifat HasanОценок пока нет
- Trip DistributionДокумент21 страницаTrip DistributionHanamant HunashikattiОценок пока нет
- Traffic Characteristics, Traffic Studies and Analysis: Prepared By: Guided byДокумент28 страницTraffic Characteristics, Traffic Studies and Analysis: Prepared By: Guided byJagan JОценок пока нет
- UTP - Unit 4 1Документ36 страницUTP - Unit 4 1Dasarathy A KОценок пока нет
- TR 631 LT 2.2 Trip Generation ModellingДокумент12 страницTR 631 LT 2.2 Trip Generation ModellingGilbert MaroОценок пока нет
- PPT-MSTT-Trip-Distribution-01Документ16 страницPPT-MSTT-Trip-Distribution-01abdul marufОценок пока нет
- Transporation Forecasting ProcessДокумент53 страницыTransporation Forecasting ProcessVince AlanОценок пока нет
- Trip Generation: The First Step in Transportation ForecastingДокумент27 страницTrip Generation: The First Step in Transportation ForecastingJohn BarrogaОценок пока нет
- Vehicle Routing and SchedulingДокумент54 страницыVehicle Routing and SchedulingIbrahimОценок пока нет
- Transportation Demand AnalysisДокумент32 страницыTransportation Demand AnalysisAgerico FunelasОценок пока нет
- Salem Performance Measure SummaryДокумент7 страницSalem Performance Measure SummaryStatesman JournalОценок пока нет
- Notes 8Документ45 страницNotes 8---Оценок пока нет
- Travel Demand ForecastingДокумент51 страницаTravel Demand ForecastingGraciele Sera-RevocalОценок пока нет
- Plan 214 ReportДокумент30 страницPlan 214 ReportPaolo Angelo GutierrezОценок пока нет
- UEMX 3813 Highway and TransportationДокумент39 страницUEMX 3813 Highway and TransportationMOBA UNIОценок пока нет
- Design of Urban Transportation Models: Group 3Документ30 страницDesign of Urban Transportation Models: Group 3Vincent CruzОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 KA34802Документ35 страницChapter 3 KA34802ISMANOORIFAH BINTI ISMAIL -Оценок пока нет
- Modelling of Turning Traffic Volume in Ibadan, Nigeria Using Linear and Hybrid Furness-Fratar TechniquesДокумент8 страницModelling of Turning Traffic Volume in Ibadan, Nigeria Using Linear and Hybrid Furness-Fratar TechniquesIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalОценок пока нет
- 5 Trip Distribution Lecture 12-13.unlockedДокумент23 страницы5 Trip Distribution Lecture 12-13.unlockedTanmay Sahni100% (1)
- Ilovepdf MergedДокумент146 страницIlovepdf MergedJoshua A. EboraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - Lecture 3-Geometric Design - Horizontal AlignmentДокумент29 страницChapter 5 - Lecture 3-Geometric Design - Horizontal Alignmentsudhir_921995600Оценок пока нет
- Transportation Forecasting ProcessДокумент36 страницTransportation Forecasting ProcessKristelle GinezОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 7 Trip Distribution: I J IjДокумент4 страницыChapter - 7 Trip Distribution: I J IjSwopnil KalikaОценок пока нет
- Intersection Control and designIIДокумент27 страницIntersection Control and designIIKwaku SoloОценок пока нет
- Lecture3 Trip DistributionДокумент10 страницLecture3 Trip DistributionEng Bedri BederОценок пока нет
- Traffic Studies and Analysis of DataДокумент78 страницTraffic Studies and Analysis of DataPeter John RoblesОценок пока нет
- Trip Distribution NotesДокумент30 страницTrip Distribution Notesp141677Оценок пока нет
- 2022 Presentation 2Документ54 страницы2022 Presentation 2lehlabileОценок пока нет
- 2.4 - Victorian Integrated Transport ModelДокумент39 страниц2.4 - Victorian Integrated Transport ModelcitilabsОценок пока нет
- GRP 1Документ13 страницGRP 15002- Ajay.RОценок пока нет
- Lecture 11 Design of Signalised IntersectionsДокумент37 страницLecture 11 Design of Signalised IntersectionsRespicus RJОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Networks Approaches in Vehicle Delay ModelingДокумент19 страницComparison of Fuzzy Logic and Artificial Neural Networks Approaches in Vehicle Delay ModelingJulio CésarОценок пока нет
- Trip Generation & Trip DistributionДокумент14 страницTrip Generation & Trip DistributionHari PОценок пока нет
- Extra Notes Traffic32019Документ48 страницExtra Notes Traffic32019Jeffery LiewОценок пока нет
- L3 Intro Transport PlanningДокумент35 страницL3 Intro Transport PlanningddОценок пока нет
- Signal Timing and DesignДокумент12 страницSignal Timing and DesignVirtual RealityОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Principals of Traffic FlowДокумент50 страницFundamental Principals of Traffic Flowsofyan ElnederОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 - FRATAR AlgorithmДокумент27 страницLecture 3 - FRATAR Algorithmethernalx100% (1)
- Stages of Traffic Planning and ModellingДокумент20 страницStages of Traffic Planning and Modelling14.kr.saurabhОценок пока нет
- Transport Planning: ISTTT TutorialДокумент91 страницаTransport Planning: ISTTT TutorialAluscia76Оценок пока нет
- TR 631 LT 2.4 Mode Choice ModellingДокумент67 страницTR 631 LT 2.4 Mode Choice ModellingGilbert MaroОценок пока нет
- Utsp 2Документ18 страницUtsp 2Dhrubajyoti DattaОценок пока нет
- Topic 5 - Analysis Signalized IntersectionДокумент33 страницыTopic 5 - Analysis Signalized IntersectionKyle SmithОценок пока нет
- Batch 10A Mini ProjectДокумент24 страницыBatch 10A Mini ProjectRaghu Vamsi KrishnaОценок пока нет
- CIVE461A: Transportation Engineering and Lab Unit E: Traffic Analysis at Signalized IntersectionsДокумент27 страницCIVE461A: Transportation Engineering and Lab Unit E: Traffic Analysis at Signalized Intersectionsanthony mikhaelОценок пока нет
- Module - 1, Continued. Traffic Parameter Studies and AnalysisДокумент18 страницModule - 1, Continued. Traffic Parameter Studies and AnalysisPraveen M balaramОценок пока нет
- Intersection AnalysisДокумент59 страницIntersection AnalysisfuchiguisОценок пока нет
- Transportation PlanningДокумент79 страницTransportation PlanningNixnew Lim100% (1)
- Geometric Design of HighwaysДокумент34 страницыGeometric Design of HighwaysRespicus RJОценок пока нет
- Trip DistributionДокумент86 страницTrip DistributionTaqwa Hadidi100% (1)
- Maire Pav 5 Final ProgramДокумент12 страницMaire Pav 5 Final ProgramErvina AhyudanariОценок пока нет
- Traffic Engineering: Instructor: Dr. Shou-Ren HuДокумент21 страницаTraffic Engineering: Instructor: Dr. Shou-Ren HuErvina AhyudanariОценок пока нет
- A Comparative Analysis of Bicycle Lanes Versus Wide Curb Lanes: Final ReportДокумент104 страницыA Comparative Analysis of Bicycle Lanes Versus Wide Curb Lanes: Final ReportErvina AhyudanariОценок пока нет
- Climate ScenariosДокумент84 страницыClimate ScenariosErvina AhyudanariОценок пока нет
- List of Tropical Countries - TropicalДокумент4 страницыList of Tropical Countries - TropicalErvina AhyudanariОценок пока нет
- Finite ElementДокумент186 страницFinite ElementErvina AhyudanariОценок пока нет
- Street Directory 1Документ1 страницаStreet Directory 1Ervina AhyudanariОценок пока нет
- Take-Off Field LengthДокумент4 страницыTake-Off Field LengthErvina Ahyudanari100% (1)
- Career Orientation QuestionnaireДокумент5 страницCareer Orientation QuestionnaireApple May100% (1)
- Gates Crimp Data and Dies Manual BandasДокумент138 страницGates Crimp Data and Dies Manual BandasTOQUES00Оценок пока нет
- HCH - 15 04 004Документ5 страницHCH - 15 04 004NarvaxisОценок пока нет
- Contribution of Medieval MuslimДокумент16 страницContribution of Medieval Muslimannur osmanОценок пока нет
- Causal Emergence - HoelДокумент18 страницCausal Emergence - HoelFelipe LopesОценок пока нет
- 2018-2019 Annual Algebra Course 1 Contest: InstructionsДокумент2 страницы2018-2019 Annual Algebra Course 1 Contest: InstructionsNaresh100% (1)
- IU IIDC Time Management and Organizational SkillsДокумент40 страницIU IIDC Time Management and Organizational SkillsAsger HamzaОценок пока нет
- Diltoids Numberletter Puzzles Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 38486Документ5 страницDiltoids Numberletter Puzzles Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 38486sinirsistemiОценок пока нет
- Ad For Guru Ned'S Enlightenment Masterclass 1 of 33Документ33 страницыAd For Guru Ned'S Enlightenment Masterclass 1 of 33ElliuggОценок пока нет
- SAP Solution Manager - CHARM - Retrofit - Change Request Management Enhanced RetrofitДокумент61 страницаSAP Solution Manager - CHARM - Retrofit - Change Request Management Enhanced RetrofitARPITA BISWASОценок пока нет
- Slup 230Документ24 страницыSlup 230Jelena TodorovicОценок пока нет
- Combinational Logic-Part-2 PDFДокумент25 страницCombinational Logic-Part-2 PDFSAKSHI PALIWALОценок пока нет
- Zgouras Catherine Team Together 1 Teachers BookДокумент257 страницZgouras Catherine Team Together 1 Teachers Booknata86% (7)
- Conflict Management A Practical Guide To Developing Negotiation Strategies Barbara A Budjac Corvette Full ChapterДокумент67 страницConflict Management A Practical Guide To Developing Negotiation Strategies Barbara A Budjac Corvette Full Chapternatalie.schoonmaker930100% (5)
- Formulae HandbookДокумент60 страницFormulae Handbookmgvpalma100% (1)
- Tekla SoakwayДокумент2 страницыTekla SoakwayBalaji Naik100% (1)
- Most Dangerous City - Mainstreet/Postmedia PollДокумент35 страницMost Dangerous City - Mainstreet/Postmedia PollTessa VanderhartОценок пока нет
- 22 Thành NG Quen Thu C Trên Ielts - FirefighterДокумент2 страницы22 Thành NG Quen Thu C Trên Ielts - FirefighterNinh NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Second Periodical Test in Organization and Management SY 2018-2019Документ3 страницыSecond Periodical Test in Organization and Management SY 2018-2019Merida BravoОценок пока нет
- DLL Drafting 7Документ4 страницыDLL Drafting 7Ram Dacz100% (3)
- 00.diesel Engine Power Plant Design PDFДокумент4 страницы00.diesel Engine Power Plant Design PDFmardirad100% (1)
- 4 PDFДокумент81 страница4 PDFMohammad K. NassouraОценок пока нет
- Drsent PT Practice Sba OspfДокумент10 страницDrsent PT Practice Sba OspfEnergyfellowОценок пока нет
- History of Psychotherapy FinalДокумент38 страницHistory of Psychotherapy FinalMarco BonettiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5Документ20 страницLecture 5Paylaşım KanalıОценок пока нет
- Finding Targets PDFДокумент9 страницFinding Targets PDFSteve TangОценок пока нет
- Code of Federal RegulationsДокумент14 страницCode of Federal RegulationsdiwolfieОценок пока нет
- KSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsДокумент22 страницыKSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsRohan BhatiaОценок пока нет
- SD-NOC-MAR-202 - Rev00 Transfer of Personnel at Offshore FacilitiesДокумент33 страницыSD-NOC-MAR-202 - Rev00 Transfer of Personnel at Offshore Facilitiestho03103261100% (1)
- Dpb6013 HRM - Chapter 3 HRM Planning w1Документ24 страницыDpb6013 HRM - Chapter 3 HRM Planning w1Renese LeeОценок пока нет