Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
AutoSys Training
Загружено:
Vicky BindassАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AutoSys Training
Загружено:
Vicky BindassАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
AUTOSYS
AutoSys is an automated job control system for
scheduling, monitoring, and reporting. These jobs can
reside on any AutoSys-configured machine that is attached
to a network.
An AutoSys job is any single command, executable,
script,or Windows batch file. Each AutoSys job definition
contains a variety of qualifying attributes,including the
conditions specifying when and where a job should be run.
Classification: GE Pub
AUTOSYS
As with most control systems, there are many ways to
correctly define and implement jobs. It is likely that the
way you utilize AutoSys to address your distributed
computing needs will evolve over time. As you become
more familiar with both the features of AutoSys and the
characteristics of your own jobs, you will also refine your
use of AutoSys.
However, before you install and use AutoSys, it is
important to understand the basic AutoSys system, its
components, and how these components work together.
Classification: GE Pub
AUTOSYS
In the AutoSys environment, a job is a single action that
can be performed on a valid AutoSys client machine. On
UNIX, this action can be any single command or shell
script, and on Windows, this action can be any single
command,executable, or batch file. In addition, job
definitions include a set of qualifying attributes.
Using the AutoSys Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Using the AutoSys Job Information Language (JIL)
through a command-line interface.
Classification: GE Pub
AUTOSYS
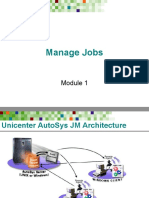
The following are the main AutoSys system components:
Event server (AutoSys database)
Event processor
Remote agent
Classification: GE Pub
AUTOSYS
EVENT SERVER
The event server or AutoSys database (the RDBMS) is the
data repository for all system information and events as
well as all job, monitor, and report definitions.Event server
refers to the database where all the AutoSys information,
events,and job definitions are stored.AutoSys can be
configured to run using two databases, or dual-event
servers.This feature provides complete redundancy.
Therefore, if you lose one event server due to hardware,
software, or network problems, AutoSys operations can
continue on the second event server without loss of
information or functionality.
Classification: GE Pub
AUTOSYS
EVENT PROCESSOR : The event processor is the heart of
AutoSys; it interprets and processes all the events it reads
from the AutoSys database. Sometimes called the
event_demon, the event processor is the program, running
either as a UNIX process or as a Windows service that
actually runs AutoSys. It schedules and starts jobs. After you
start it, the event processor continually scans the database for
events to be processed. When it finds one, it checks whether
the event satisfies the starting conditions for any job in the
database. Based on this information, the event processor first
determines what actions are to be taken, then instructs the
appropriate remote agent process to perform the actions.
Classification: GE Pub
AUTOSYS
REMOTE AGENT
On a UNIX machine, the remote agent is a temporary
process started by the event processor to perform a specific
task on a remote (client) machine. On a Windows machine,
the remote agent is a Windows service running on a
remote (client) machine that is directed by the event
processor to perform specific tasks. The remote agent starts
the command specified for a given job, sends running and
completion information about a task to the event server,
then exits. If the remote agent is unable to transfer the
information, it waits and tries again until it can
successfully communicate with the database.
Classification: GE Pub
AUTOSYS
Classification: GE Pub
AUTOSYS
AutoSys Machines : From a hardware perspective, the
AutoSys architecture is composed of the following two types of
machines attached to a network:
Server Machine
The AutoSys server is the machine on which the event processor, the
event server (database), or both, reside. In a basic configuration, both
the event processor and the event server reside on the same machine.
Client Machine
The AutoSys client is the machine on which the remote agent software
resides, and where AutoSys jobs are to be run. A remote agent must be
installed on the server machine, and it can also be installed on separate
physical client machines.
Classification: GE Pub
10
AUTOSYS
AutoSys Instance
An AutoSys instance is one licensed version of AutoSys software
running as an AutoSys server with one or more clients, on a single
machine or on multiple machines. An AutoSys instance is defined by
the instance ID, which is a capitalized three-letter identifier defined by
the $AUTOSERV environment variable. An instance uses its own event
server and event processor and operates independently of other
AutoSys instances.
You may want to install multiple AutoSys instances. For example, you
may want to have one instance for production and another for
development. Multiple instances can run on the same machine, and
can schedule jobs on the same machines without interfering or
affecting the other instances.
Classification: GE Pub
11
AUTOSYS
Job types:
File Watcher Jobs - A file watcher job is similar to a command job. However, instead
of starting a user-specified command on a client machine, it starts a process that
monitors for the existence and size of a specific operating system file. When that file
reaches a certain minimum size, and is no longer growing in size, the file watcher job
completes successfully, indicating that the file has arrived.
Command Jobs The command can be a shell script or an executable program.
When this type of job is run, the result is the execution of a specified command on a
client machine.
Box Jobs - In the Autosys environment, the box job (or box) is a container of other jobs.
A box job can be used to organize and control process flow. The box itself performs no
actions, although it can trigger other jobs to run. An important feature of this type of job
is that boxes can be put inside of other boxes.
Classification: GE Pub
12
AUTOSYS
Job Attributes:
Command Job Attributes : Job Name, Command, Machine name, Starting
Conditions.
File Watcher Job Attributes : Job Name, File Name to Watch For, Machine Name,
Starting Conditions
Box Job Attributes: Job name, Starting Conditions
Classification: GE Pub
13
AUTOSYS
Job States:
Job State
Status
INACTIVE
The job has not yet been processed. Either the job has never been run, or its
status was intentionally altered to turn offits previous completion status
ACTIVATED
The top-level box that this job is in is now in the RUNNING state, but the job
itself has not started yet.
STARTING
The event processor has initiated the start job procedure with the RA
(Resource Allocation).
RUNNING
The job is running. If the job is a box job, this value simply means that the
jobs within the box may be started (other conditions permitting). If it is a
command or file watcher job,the value means that the process is actually
running on the remote machine.
SUCCESS
The job exited with an exit code equal to or less than themaximum exit code
for success.
FAILURE
The job exited with an exit code greater than the maximum exit code for
success.
Classification: GE Pub
14
AUTOSYS
Job States:
Job State
Status
TERMINATED
The job terminated while in the RUNNING state. A job can be terminated if a
user sends a KILLJOB event or if it was defined to terminate if the box it is in
failed.
RESTART
The job was unable to start due to hardware or application problems, and has
been scheduled to restart.
QUE_WAIT
The job can logically run (that is, all the starting conditions have been met),
but there are not enough machine resources available.
ON_HOLD
This job is on hold and will not be run until it receives the JOB_OFF_HOLD
event.
ON_ICE
This job is removed from all conditions and logic, but is still defined to
Autosys. Operationally, this condition is like deactivating the job. It will
remain on ice until it receives the JOB_OFF_ICE event.
Classification: GE Pub
15
AUTOSYS
ON HOLD
Job A
ON ICE
Force Start Job
Job A
Job B
On Hold
Job B
Job C
Will Not Run
Job C
Classification: GE Pub
Force Start Job
On Ice
Will Run
16
AUTOSYS
JIL ( Job Information Language)
Command Job
insert_job: eedhnonemplc
job_type: c
command: echo adding jobs into box job
machine: UPCLT2D08
owner: 100790@GECISCGW
description: our first autosys job
permission:
std_out_file: c\:\temp\stdoutfile.txt
std_err_file: c\:\temp\stderrfile.txt
alarm_if_fail: 1
Classification: GE Pub
17
AUTOSYS
insert_job: training_box_1
job_type: b
owner: 100790@GECISCGW
Box Jobs
description: our first box job"
alarm_if_fail: 1
insert_job: cmd_job1
training_box_1
job_type: c
box_name: training_box_1
command: echo cmd_job1 inside the box
machine: UPCLT2D08
cmd_job1
owner: 100790@GECISCGW
alarm_if_fail: 1
insert_job: cmd_job2
job_type: c
box_name: training_box_1
command: echo cmd_job2
inside the box
machine: UPCLT2D08
owner: 100790@GECISCGW
Classification: GE Pub
condition: success(cmd_job1)
alarm_if_fail: 1
cmd_job2
18
AUTOSYS
File Watcher Job
insert_job: EOD_watch
job_type: f
machine: tibet
watch_file: /tmp/EOD_trans_file
watch_interval: 60
watch_file_min_size: 50000
Classification: GE Pub
19
AUTOSYS
JIL Sub-commands
insert_job
Inserting a new job.
update_job
Updating characteristics of existing job.
delete_job
Deleting the job from Autosys.
delete_box
Deleting box job from Autosys along with the
container jobs.
override_job
Doing a one-time override of the job.
Classification: GE Pub
20
AUTOSYS
Calendars:
Calendars are defined using the Calendar defn
Window from the Unix GUI. It looks something
like shown here.
insert_job: eedhpittoic
type : c
command: /usr/home/something.bat
start_times:
10:00, 18:00, 23:00
run_calendar: working_days
exclude_calendar: gecis_holidays
Std_out_file: /usr/home/log/eedhpittoic.out
Std_err_file: /usr/home/log/eedhpittoic.err
Classification: GE Pub
21
AUTOSYS
Autosys Commands
autocal
Starts the Graphical Calendar Utility
autocons
Starts the Autosys Operator Console
autoflags -
Shows information about Autosys and system configuration.
gcoasys01:autocorp:COP $ autoflags -a
_G3 SOLAR ORA 4.0 _0208 831256fa gcoasys01
autoping
Verifies that the various AutoSys communication facilities
are correctly configured and functioning.
AutoPinging Machine [corpp076]
AutoPing WAS SUCCESSFUL!
AutoPinging Machine [corpp101]
AutoPing WAS SUCCESSFUL!
AutoPinging Machine [corpt067]
AutoPing WAS SUCCESSFUL!
Classification: GE Pub
22
AUTOSYS
Autosys Commands
autorep
One of the most important commands. Reports information about a
job, jobs within boxes, machines, and machine status. Also
reports information about job overrides and global variables.
gcoasys01:autocorp:COP $ autorep -j epy08b444s01 -d
Job Name
Last Start
Last End
ST Run Pri/Xit
____________________________ ________________ ________________ __ _______ ___
epy08b444s01
07/16/2004 16:13 07/16/2004 16:13 SU 2186141/1
Status/[Event] Time
Ntry ES ProcessTime
Machine
-------------- ------------------- -- -- ------------------- ------[STARTJOB]
07/16/2004 16:12:39 0 PD 07/16/2004 16:12:49
STARTING
07/16/2004 16:12:55 1 PD 07/16/2004 16:13:07 corpgen01
RUNNING
07/16/2004 16:13:00 1 PD 07/16/2004 16:13:13 corpgen01
[COMMENT]
07/16/2004 16:13:08 0 PD 07/16/2004 16:14:51
<ADAPTER: PeopleSoft
HOME: PSP2
Job: epy08b444s01/13377 PAY008>
SUCCESS
07/16/2004 16:13:38 1 PD 07/16/2004 16:14:57
autorep j epy08b444s01 r 1 d
autorep j epy08b444s01 r 2 d
autorep j epy08b444s01
Classification: GE Pub
23
AUTOSYS
Autosys Commands
autorep -
Also used for seeing the JIL of a job.
autorep j jobname q
autorep j ALL q
autorep j jobname q > file1.jil
jil <file1.jil
Classification: GE Pub
24
AUTOSYS
Autosys Commands
autosyslog
-Displays the Event Processor and Remote Agent Log Files
autosyslog -e
tail -f $AUTOUSER/out/event_demon.$AUTOSERV
*** To break out type control-c (^c) ***
[1] [07:36:11.524291] EVENT: CHANGE_STATUS STATUS: STARTING
JOB: ige2
0-bx17b-suces-dj_artfol
[3] [07:36:22.829993] EVENT: CHANGE_STATUS STATUS: RUNNING
JOB: ige2
0-bx27b-ru_busnew
[2] [07:36:23.356991] EVENT: CHANGE_STATUS STATUS: RUNNING
JOB: ige2
0-bx11b-cp_images
[1] [07:36:23.931923] EVENT: CHANGE_STATUS STATUS: RUNNING
JOB: ige2
0-bx17b-suces-dj_artfol
[3] [e250 connected for ige250-bx27b-sync-ru_busnew]
[2] [e250 connected for ige250-bx11b-sync-cp_images]
[1] [07:36:30.221918] EVENT: SET_GLOBAL
GLOBAL: e250-bx04a-method = succe
s
[2] [07:36:35.148583] EVENT: CHANGE_STATUS STATUS: STARTING
JOB: ige2
0-bx27b-sync-ru_busnew
Classification: GE Pub
25
AUTOSYS
Autosys Commands
chase
chk_auto_up
Chase checks if the jobs and remote agents are still running.
E.g
chase A E
Checks if the RDBMS and EP are running
gcoasys01:autogep:GEP $ chk_auto_up
______________________________________________________________________________
[1] Attempting (1) to Connect with Database: gep1.corporate.ge.com
[1] *** Have Connected successfully with Database: gep1.corporate.ge.com. ***
______________________________________________________________________________
Connected with Event Server: gep1.corporate.ge.com
Checking Machine: gcoasys01
Primary Event Processor is RUNNING on machine: gcoasys01
Checking Machine: gcoasys02
No Event Processor is RUNNING on machine: gcoasys02
Classification: GE Pub
26
AUTOSYS
Autosys Commands
eventor
Starts the Event Processor
eventor f -q
in
meaning
-f Specifies that the Event Processor should be brought up
the foreground, and that all of its output should be sent to
the display from which the command was issued.
-q Specifies that eventor should run in quiet mode,
that after the Event Processor has been started, eventor
should not execute the tail f command on the
event_demon log file.
Classification: GE Pub
27
AUTOSYS
Autosys Commands
job_depends
Reports information about the dependencies and
conditions of a job.
job_depends c d -t J jobname
-c Current Condition Status. Prints out the current
state of a job and its job dependency
-d Dependencies Only. Prints out the starting
conditions for a job.
-t Time Dependencies. Prints out the starting
conditions for a job.
Classification: GE Pub
28
AUTOSYS
Autosys Commands
sendevent
Sends events to AutoSys for a variety of purposes,
including starting or stopping AutoSys jobs, stopping
the Event Processor, and putting a job on hold.
sendevent E JOB_ON_ICE j eedhnonemplc
sendevent E JOB_OFF_ICE j eedhnonemplc
sendevent E JOB_ON_HOLD j eedhnonemplc
sendevent E JOB_OFF_HOLD j eedhnonemplc
sendevent E FORCE_STARTJOB j eedhnonemplc
sendevent E KILLJOB j eedhnonempc
sendevent E CHANGE_STATUS j eedhnonemplc s SUCCESS
sendevent E CHANGE_STATUS j eedhnonemplc s INACTIVE
Classification: GE Pub
29
AUTOSYS
JIL Machine Definitions.
insert_machine: vm123
type: n
machine: UPCLT2D08
max_load: 50
machine: UPCLT2D05
max_load: 30
machine: getraining1
max_load: 100
update_job: ak_lb_box1 job_type: b
owner: 100790@GECISCGW
command: echo hello there
permission:
description: "ex 3-4"
alarm_if_fail: 1
update_job: ak_lb1 job_type: c
box_name: ak_lb_box1
machine: vm123
job_load: 10
priority: 1
owner: 100790@GECISCGW
command: notepad.exe
permission:
description: "ex 3-4"
alarm_if_fail: 1
Factor : Indicates the factor to be multiplied by a real machines availabl
cycles in order to determine the relative available CPU cycles.
1 To set the factor for a very high-performance real machine, when a
scale of 0.0-1.0 is in use, you would enter:
factor: 1.0
2 To set the factor for a relatively low-performance real machine, when
a scale of 0.0-1.0 is in use, you would enter something similar to the
following:
factor: 0.4
Max_load: Indicates the maximum load (in load units) which a
machine can
reasonably handle. Load units are arbitrary values, the range
of which is
user-defined;
1 To set the max_load for a very high-performance real
machine, when a
scale of 1100 is in use, you would enter:
max_load: 100
2 To set the max_load for a relatively low-performance real
machine,
when a scale of 1100 is in use, you would enter something
similar to
the following:
max_load: 20
Classification: GE Pub
30
AUTOSYS
Classification: GE Pub
Вам также может понравиться
- AutoSys CheatsheetДокумент10 страницAutoSys Cheatsheetpsp83100% (1)
- Automated job scheduling with AutoSysДокумент30 страницAutomated job scheduling with AutoSysamy_750% (2)
- Autosys Interview QuestionsДокумент37 страницAutosys Interview Questionssubash pradhanОценок пока нет
- Autosys Technical DocumentДокумент40 страницAutosys Technical Documentasalsbalu100% (1)
- Auto SysДокумент4 страницыAuto SysJack MarionОценок пока нет
- Autosys Cheatsheet: Autosys: Unix ./autosys - Ksh.Machine" After Installing Autosys, First Make Sure That The DB Is Up andДокумент11 страницAutosys Cheatsheet: Autosys: Unix ./autosys - Ksh.Machine" After Installing Autosys, First Make Sure That The DB Is Up andSandip BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Autosys DetailsДокумент33 страницыAutosys Detailsrajesh716Оценок пока нет
- Autosys Cheat Sheet From CAДокумент4 страницыAutosys Cheat Sheet From CAwaltert1Оценок пока нет
- Autosys Interview PreparationДокумент9 страницAutosys Interview PreparationVinod KalahОценок пока нет
- Autosys commands guideДокумент39 страницAutosys commands guidesantosh_panditpurОценок пока нет
- Autosys Sheduling ToolДокумент8 страницAutosys Sheduling ToolRathan KumarОценок пока нет
- Control M FAQДокумент8 страницControl M FAQrvijaysubs_764835048Оценок пока нет
- BMC Control-M 7: A Journey from Traditional Batch Scheduling to Workload AutomationОт EverandBMC Control-M 7: A Journey from Traditional Batch Scheduling to Workload AutomationОценок пока нет
- UNICENTER AUTOSYS JM COMMANDS GUIDEДокумент17 страницUNICENTER AUTOSYS JM COMMANDS GUIDE2BatulОценок пока нет
- 4602 - r11x - Bestpractices - AutosysДокумент13 страниц4602 - r11x - Bestpractices - AutosysRavi DОценок пока нет
- AutosysДокумент38 страницAutosysPraful Badola100% (2)
- 11-AutoSys Basic Commands Quick ReferenceДокумент1 страница11-AutoSys Basic Commands Quick Referenceactmon123100% (1)
- Autosys Unix CommandsДокумент4 страницыAutosys Unix CommandsRajesh KumarОценок пока нет
- AutosysДокумент6 страницAutosysravidwhwОценок пока нет
- Reset Autosys job statuses dailyДокумент4 страницыReset Autosys job statuses dailyzipzapdhoomОценок пока нет
- Control-M Question 1Документ8 страницControl-M Question 1Pardeep lalОценок пока нет
- Autosys Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент6 страницAutosys Interview Questions and Answerssenthil100% (1)
- Automate Workloads with Control M Scheduling SoftwareДокумент19 страницAutomate Workloads with Control M Scheduling SoftwareBurhan Malik100% (2)
- Autosys CommandsДокумент5 страницAutosys CommandsNigam PatelОценок пока нет
- Architecture of AutosysДокумент4 страницыArchitecture of Autosysabybaby85Оценок пока нет
- KT Document For PeopleSoftДокумент18 страницKT Document For PeopleSoftravi5dipuОценок пока нет
- AutoSys r11.3 Understanding Job Scheduling Dependencies V3Документ30 страницAutoSys r11.3 Understanding Job Scheduling Dependencies V3shahbazbОценок пока нет
- Autosys TutorialsДокумент1 страницаAutosys Tutorialsj_jeevan_jОценок пока нет
- BMC CONTROL M Enterprise ManagerДокумент95 страницBMC CONTROL M Enterprise ManagerNivedhaa RaghavendranОценок пока нет
- Autosys ResumeДокумент4 страницыAutosys ResumeMohini VermaОценок пока нет
- Autosys CommandsДокумент4 страницыAutosys Commandsnaveenr3Оценок пока нет
- CONTROL M InstructionsДокумент36 страницCONTROL M Instructionsapi-3727814100% (3)
- Autosys Tutorial PlatinumДокумент378 страницAutosys Tutorial PlatinumseenugudduОценок пока нет
- Control-M ManualДокумент28 страницControl-M ManualPraveen Kumar CОценок пока нет
- AutosysДокумент19 страницAutosysAjayОценок пока нет
- Manage Jobs in Unicenter AutoSys JMДокумент43 страницыManage Jobs in Unicenter AutoSys JMsubash pradhanОценок пока нет
- Control-M Workload Automation 8 Job SchedulingДокумент31 страницаControl-M Workload Automation 8 Job Schedulinganantha0k0intiОценок пока нет
- BMC Control-M ArchitectureДокумент13 страницBMC Control-M Architectureraj100% (1)
- Why Do We Need Control-M When I Can Use Cron Jobs or Windows Task Scheduler?Документ8 страницWhy Do We Need Control-M When I Can Use Cron Jobs or Windows Task Scheduler?nadeem baigОценок пока нет
- Application EngineДокумент33 страницыApplication EngineBijay Bhushan SinghОценок пока нет
- r11 Quick Resource Guide: Documentation EducationДокумент1 страницаr11 Quick Resource Guide: Documentation EducationRahul JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Why Control-M is better than other scheduling toolsДокумент8 страницWhy Control-M is better than other scheduling toolsnadeem baigОценок пока нет
- Complete Guide to PeopleSoft Component Interface DevelopmentДокумент73 страницыComplete Guide to PeopleSoft Component Interface Developmentvasubandi8100% (3)
- Control-M For InformaticaДокумент2 страницыControl-M For Informaticaranusofi100% (1)
- Iis FundamentalsДокумент18 страницIis FundamentalsRiyas JacksparowОценок пока нет
- How To Create Autosys CalendarДокумент2 страницыHow To Create Autosys Calendarpk_aniОценок пока нет
- Control-M Agent InstallationДокумент5 страницControl-M Agent Installationrkruck100% (1)
- Main Concepts in OPCДокумент9 страницMain Concepts in OPCRahul Kumar KОценок пока нет
- Control M OverviewДокумент19 страницControl M OverviewMadhuban Singh HansawatОценок пока нет
- Schedule, Monitor and Report Jobs with AutosysДокумент17 страницSchedule, Monitor and Report Jobs with AutosysVivek PandeyОценок пока нет
- What is Autosys? Understanding the basics of this automated job schedulerДокумент15 страницWhat is Autosys? Understanding the basics of this automated job schedulermayur holeОценок пока нет
- AutosysДокумент34 страницыAutosysRknaidu Kondate100% (1)
- Autosys - A Job Scheduling ToolДокумент15 страницAutosys - A Job Scheduling ToolPrAvEeN522Оценок пока нет
- A Quick Refrence Guide For Unix, Scripting & AutosysДокумент26 страницA Quick Refrence Guide For Unix, Scripting & AutosysAnubha Raina DharОценок пока нет
- Quick guide to Autosys job schedulingДокумент9 страницQuick guide to Autosys job schedulingnagaОценок пока нет
- Autosys Quick ReferenceДокумент6 страницAutosys Quick Referencestar_duraiОценок пока нет
- AutosysДокумент6 страницAutosyssomutiruОценок пока нет
- Autosys JOb DocumentДокумент5 страницAutosys JOb DocumentAniya PradhanОценок пока нет
- Torrent LinksДокумент8 страницTorrent LinksVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- TorrentsДокумент10 страницTorrentsVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- NASSCOM's programs and events promoting Indian startupsДокумент1 страницаNASSCOM's programs and events promoting Indian startupsVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- ReadmeДокумент1 страницаReadmeJihadLe-PunkОценок пока нет
- Exceptions in JavaДокумент20 страницExceptions in JavaVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Bangalore FruitsДокумент6 страницBangalore FruitsMahesh GОценок пока нет
- Bangalore FruitsДокумент6 страницBangalore FruitsMahesh GОценок пока нет
- NewДокумент160 страницNewVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Autosys - A Job Scheduling ToolДокумент5 страницAutosys - A Job Scheduling Tooltublu16Оценок пока нет
- Autosys - A Job Scheduling ToolДокумент5 страницAutosys - A Job Scheduling Tooltublu16Оценок пока нет
- Errors in JavaДокумент28 страницErrors in JavaEm Hamza HazeenОценок пока нет
- Hts LogДокумент2 страницыHts LogVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Geometry FormulasДокумент4 страницыGeometry FormulasVamsi KarthikОценок пока нет
- Protein GuideДокумент5 страницProtein GuideReda LefriyekhОценок пока нет
- Introduction to HP ALM (HP ALM GuideДокумент248 страницIntroduction to HP ALM (HP ALM GuideVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Notification NICL Administrative OfficersДокумент7 страницNotification NICL Administrative OfficersRushi BageОценок пока нет
- Walk in Drive2013 Multiple LocationsДокумент12 страницWalk in Drive2013 Multiple LocationsVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- GreenKamut BreakthroughДокумент2 страницыGreenKamut BreakthroughVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- DescriptiveДокумент36 страницDescriptiveMukund KumarОценок пока нет
- Examresult SBI Probationary OfficersДокумент2 страницыExamresult SBI Probationary OfficersJayesh VasavaОценок пока нет
- Types of TrianglesДокумент4 страницыTypes of TrianglesVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Bank Po 17 June 2012Документ26 страницBank Po 17 June 2012Vishal DwivediОценок пока нет
- Informatica Session Properties Presentation1Документ18 страницInformatica Session Properties Presentation1Vicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Hack AdminДокумент1 страницаHack AdminVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Informatica Session Properties Presentation1Документ18 страницInformatica Session Properties Presentation1Vicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Apprenticeship contract registrationДокумент2 страницыApprenticeship contract registrationVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Ethical Hacking at EikontechДокумент11 страницEthical Hacking at EikontechVicky BindassОценок пока нет
- Unicenter Autosys Job Management: Integration With Etrust Access Control User GuideДокумент21 страницаUnicenter Autosys Job Management: Integration With Etrust Access Control User GuideVasundhara AvutiОценок пока нет
- General Database Maintenance - CA Workload Automation AE & Workload Control Center - CA Technologies DocumentationДокумент3 страницыGeneral Database Maintenance - CA Workload Automation AE & Workload Control Center - CA Technologies DocumentationpriyabrataritunОценок пока нет
- Wa Ae Release Enu Release NotesДокумент88 страницWa Ae Release Enu Release Notesmarlou_mac98Оценок пока нет
- Autosys Interview PreparationДокумент9 страницAutosys Interview PreparationVinod KalahОценок пока нет
- CA-Autosys Workload AutomationДокумент9 страницCA-Autosys Workload Automationsanr_85Оценок пока нет
- AutoSys r11.3 Understanding Job Scheduling Dependencies V3Документ30 страницAutoSys r11.3 Understanding Job Scheduling Dependencies V3shahbazbОценок пока нет
- WA AE Admin ENUДокумент271 страницаWA AE Admin ENUSalman AslamОценок пока нет
- Administration GuideДокумент214 страницAdministration Guidemartinthomas07Оценок пока нет
- What Is AutosysДокумент7 страницWhat Is AutosysShiva CHОценок пока нет
- User Guide AutosysДокумент459 страницUser Guide AutosysSandhya NaraboinaОценок пока нет
- CA Workload Automation AE: Overview GuideДокумент35 страницCA Workload Automation AE: Overview GuideSalman AslamОценок пока нет
- CA AutoSys WA-CAAutoSys WCC Workload Automation r11 TroubleshootingДокумент33 страницыCA AutoSys WA-CAAutoSys WCC Workload Automation r11 TroubleshootingsimondclinchОценок пока нет
- AutoSys TrainingДокумент30 страницAutoSys TrainingVicky Bindass0% (1)
- 4602 - r11x - Bestpractices - AutosysДокумент13 страниц4602 - r11x - Bestpractices - AutosysRavi DОценок пока нет
- 253 r11 3 5 CookbookДокумент83 страницы253 r11 3 5 CookbookBalachandra KuppaswamyОценок пока нет
- Auto SysДокумент410 страницAuto Sysrakeshkumar10Оценок пока нет
- Autosys JobДокумент26 страницAutosys JobkondalraodОценок пока нет
- WA AE Impl WIN ENUДокумент323 страницыWA AE Impl WIN ENUvenkateshk1Оценок пока нет