Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
2.2 Motion Graph
Загружено:
Hannah0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров18 страницThis document discusses analyzing motion graphs, including displacement-time graphs and velocity-time graphs. It provides information on how to interpret the slope and area under various types of graphs to determine properties like velocity, acceleration, displacement, and distance. Examples are given of analyzing sample displacement-time and velocity-time graphs to determine values and describe motion based on the graphs.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
2.2_MOTION_GRAPH
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses analyzing motion graphs, including displacement-time graphs and velocity-time graphs. It provides information on how to interpret the slope and area under various types of graphs to determine properties like velocity, acceleration, displacement, and distance. Examples are given of analyzing sample displacement-time and velocity-time graphs to determine values and describe motion based on the graphs.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров18 страниц2.2 Motion Graph
Загружено:
HannahThis document discusses analyzing motion graphs, including displacement-time graphs and velocity-time graphs. It provides information on how to interpret the slope and area under various types of graphs to determine properties like velocity, acceleration, displacement, and distance. Examples are given of analyzing sample displacement-time and velocity-time graphs to determine values and describe motion based on the graphs.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 18
2.
2 : ANALYSING MOTION
GRAPHS
2 types of linear motion graphs:
i.The displacement- time graph
ii.The velocity- time graph
Displacement- time graph (s-t)
gradient = velocity of motion.
Analysing Displacement - Time
Graph
Gradient = 0
Velocity = 0
* Object is stationary
Analysing Displacement - Time
Graph
Gradient is constant,
Velocity is Uniform/constant
Analysing Displacement - Time
Graph
Gradient is negative and
constant, hence velocity is
uniform and in opposite
direction
Analysing Displacement - Time
Graph
Gradient is increasing,
hence velocity is
increasing.
Analysing Displacement - Time
Graph
Gradient is decreasing,
hence velocity is
decreasing.
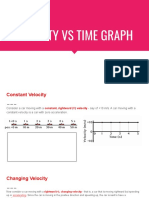
Velocity - Time Graph (v-t)
gradient = acceleration of the object.
The area under the graph = distance/ displacement.
Analysing Velocity-Time Graph
Zero gradient
Constant velocity / zero acceleration
Analysing Velocity-Time Graph
Uniform acceleration
Analysing Velocity-Time Graph
Increasing acceleration
Analysing Velocity-Time Graph
Uniform deceleration
Analysing Velocity-Time Graph
Decreasing acceleration
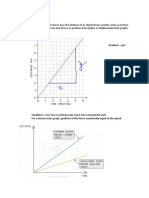
Determine distance, displacement and
velocity from the displacement-time
graph.
Based on the s t graph above:
(a) Describe the motion of the object at:
(i)AB
(ii) BC
(iii) CD
(b) Calculate the velocity at
(i)AB
(ii) BC
(c)Find:
total distance
(iii) CD
(ii) total displacement
(d) Calculate
the average speed
(ii) the average velocity of the moving particle.
(e) Plot velocity time graph for the whole journey.
Determine displacement, velocity and
acceleration from a velocity-time graph
Based on the v t graph above:
(a) Describe the motion of the object at:
(i) OP
(ii) PQ
(iii) QR
(b) Calculate the total displacement.
(c) Calculate the average velocity.
(d) Calculate the acceleration at:
(i) OP
(ii) PQ
(iii) QR
(e) Plot accelerationtime graph for the whole journey.
Вам также может понравиться
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (10)
- 2.2: Analysing Motion GraphsДокумент18 страниц2.2: Analysing Motion GraphsHannahОценок пока нет
- 2.2 Motion Graphs: Part 1: Displacement vs. Time Graph Part 2: Velocity vs. Time GraphДокумент20 страниц2.2 Motion Graphs: Part 1: Displacement vs. Time Graph Part 2: Velocity vs. Time GraphSyaza IzzatyОценок пока нет
- Distance-Time Graphs:: Gradient Y/xДокумент3 страницыDistance-Time Graphs:: Gradient Y/xSaravanakumar VОценок пока нет
- 2.2 Analysing Graph Motion Displacement - Time GraphДокумент2 страницы2.2 Analysing Graph Motion Displacement - Time GraphAnonymous w7ujq3cH2FОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion (2.2)Документ19 страницChapter 2 Force and Motion (2.2)Rachael HoОценок пока нет
- Motion Graphs Displacement-Time GraphsДокумент11 страницMotion Graphs Displacement-Time GraphsprimalОценок пока нет
- Kinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementДокумент7 страницKinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementTorettoОценок пока нет
- Velocity - Time GraphsДокумент31 страницаVelocity - Time GraphsCaloykOoy Danday DueñasОценок пока нет
- Physics 1Документ1 страницаPhysics 1wamexi5918Оценок пока нет
- Understanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity TimeДокумент29 страницUnderstanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity Timeimran siddiquiОценок пока нет
- Accelerated MotionДокумент4 страницыAccelerated Motionapi-296833859Оценок пока нет
- Ppoint-MotionSpeedVelocityAcceleration SUMMARY NOTES WORDДокумент4 страницыPpoint-MotionSpeedVelocityAcceleration SUMMARY NOTES WORDIRFAN ZAIN ULABIDEENОценок пока нет
- Motion GraphsДокумент32 страницыMotion Graphssukhjit78Оценок пока нет
- Motion GraphsДокумент19 страницMotion GraphsJennieОценок пока нет
- Kinema TicsДокумент2 страницыKinema Ticsalquran.queriesОценок пока нет
- C2 Kinematics NotesДокумент8 страницC2 Kinematics Notesmalahim ahmedОценок пока нет
- 05 Graphical Analysis of MotionДокумент31 страница05 Graphical Analysis of MotionAnish Anshuman ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент299 страницPhysicsAansa AsifОценок пока нет
- Describing MotionДокумент30 страницDescribing Motionmimoakal24Оценок пока нет
- Chapter-2 - Kinematics of Linear MotionДокумент27 страницChapter-2 - Kinematics of Linear MotionSherena Peter GovindОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual PhyДокумент67 страницLab Manual PhySanjay SinhaОценок пока нет
- Unit One - MechanicsДокумент118 страницUnit One - MechanicsIbrar MajeedОценок пока нет
- 02 Speed Velocity AccelerationДокумент14 страниц02 Speed Velocity AccelerationAli SalamehОценок пока нет
- Motion in Straight LineДокумент4 страницыMotion in Straight LineSantoshPathakОценок пока нет
- 2 KinematicsДокумент23 страницы2 Kinematicszzrnwdzpsmhs951003Оценок пока нет
- 2 KinematicsДокумент39 страниц2 Kinematicsxxhkkfm69xОценок пока нет
- 2 KinematicsДокумент17 страниц2 KinematicsAmad AliОценок пока нет
- YEAR 11 2022-2023 Chapter 2 Accelerated MotionДокумент19 страницYEAR 11 2022-2023 Chapter 2 Accelerated MotionRiza FirmansyahОценок пока нет
- Kinema TicsДокумент6 страницKinema TicsAlizeh ShoaibОценок пока нет
- Portfolio NotesДокумент14 страницPortfolio Notesapi-302393053Оценок пока нет
- Position-Time and Velocity-Time GraphsДокумент21 страницаPosition-Time and Velocity-Time Graphsdelano619Оценок пока нет
- L4 Graphing MotionДокумент24 страницыL4 Graphing MotiongeraldineОценок пока нет
- Kinematics (Chapter 2)Документ39 страницKinematics (Chapter 2)Ali JawwadОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Describing MotionДокумент25 страницChapter 2 Describing MotionSimple ScienceОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Linear MotionДокумент11 страницAn Introduction To Linear MotionZanderОценок пока нет
- 2.1 & 2.2 & 2.3 Lessons SummaryДокумент8 страниц2.1 & 2.2 & 2.3 Lessons SummaryKingProОценок пока нет
- What Is Motion?Документ11 страницWhat Is Motion?Prisha SinglaОценок пока нет
- Class 9 Phy Chapter 8 MotionДокумент9 страницClass 9 Phy Chapter 8 MotionRubeena NajeebОценок пока нет
- Edexcel IAL Physics A-Level: Topic 1.3: MechanicsДокумент13 страницEdexcel IAL Physics A-Level: Topic 1.3: MechanicsMamun ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Vectors and KinematicsДокумент1 страницаVectors and KinematicsBlaine RogalskiОценок пока нет
- Defenitions Physics LecДокумент11 страницDefenitions Physics Lecjennyvargas1222Оценок пока нет
- 07 Accelerated MotionДокумент17 страниц07 Accelerated Motionapi-27085921Оценок пока нет
- Kinematics One Dimentional Mot. Nov 9 2020Документ14 страницKinematics One Dimentional Mot. Nov 9 2020Golam RabbaniОценок пока нет
- 2.2 Motion GraphДокумент20 страниц2.2 Motion GraphCk Azli100% (1)
- Chapter 02Документ46 страницChapter 02Gio PelobilloОценок пока нет
- Edexcel IAL Physics AS-level: Topic 1.3: MechanicsДокумент13 страницEdexcel IAL Physics AS-level: Topic 1.3: MechanicsDiya FathimaОценок пока нет
- Lec Note PhysicsДокумент13 страницLec Note PhysicsMuntasir AbrarОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion Revision NotesДокумент24 страницыCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Motion Revision NotesBriti DubeyОценок пока нет
- Describing Motion in Terms of Graphical RepresentationДокумент47 страницDescribing Motion in Terms of Graphical RepresentationJohn Christian MejiaОценок пока нет
- The Meaning of Shape For A P-T GraphДокумент7 страницThe Meaning of Shape For A P-T Graphcpverma2811Оценок пока нет
- Uniform Motion:: Measuring The Rate of Motion of An Object: SpeedДокумент7 страницUniform Motion:: Measuring The Rate of Motion of An Object: SpeedLualuaОценок пока нет
- Part D: Kinematic Graphing:: Answer: See Diagram Above Explanations Are Given BelowДокумент3 страницыPart D: Kinematic Graphing:: Answer: See Diagram Above Explanations Are Given BelowEdward Simon BaronОценок пока нет
- M2L6 Velocity-Time GraphДокумент40 страницM2L6 Velocity-Time GraphJoma Guerra ina moОценок пока нет
- 1-Kinematics of Particles 0Документ46 страниц1-Kinematics of Particles 0Rabiatul AdawiahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Motion2DДокумент40 страницChapter 3 Motion2Dredz00Оценок пока нет
- Quantity Symbol Unit Abb. S U V A T: Kinematics Info-SheetДокумент1 страницаQuantity Symbol Unit Abb. S U V A T: Kinematics Info-SheethitmanОценок пока нет
- Forces and MotionДокумент15 страницForces and Motionankur11783officialОценок пока нет
- The Command Economy: Hannah Maryam Binti Mohamad IdhamДокумент4 страницыThe Command Economy: Hannah Maryam Binti Mohamad IdhamHannahОценок пока нет
- Logarithmic Properties: Hannah Maryam Mohamad IdhamДокумент8 страницLogarithmic Properties: Hannah Maryam Mohamad IdhamHannahОценок пока нет
- Dear MR Kilmer ExpressДокумент13 страницDear MR Kilmer ExpressHannahОценок пока нет
- 2.3 InertiaДокумент31 страница2.3 InertiaHannahОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Linear MotionДокумент36 страниц2.1 Linear MotionHannahОценок пока нет