Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Energy of A System
Загружено:
arin0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров17 страницОригинальное название
Energy of a System.pptx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров17 страницEnergy of A System
Загружено:
arinАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 17
Energy of a System
Fibryanti Arin Priandini
4201414012
Work Done by a Constant Force
The Scalar Product of Two Vectors
The scalar product of any two vectors A
and B is defined as a scalar quantity
equal to the product of the magnitudes
of the two vectors and the cosine of the
angle u between them:
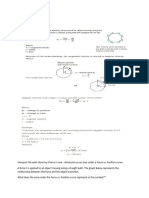
Work Done by a Varying Force
For the general case of a net force whose magnitude and
direction may both vary, we use the scalar product,
Work Done by a Spring
Spring force
The negative sign in
signifies that the force
exerted by
the spring is always directed
opposite the displacement
from equilibrium.
Therefore, the work done by this
applied force (the external agent) on
the system of the block is
This work is equal to the negative
of the work done by the spring
force for this displacement. The
work is negative because the
external agent must push inward on
the spring to prevent it from
expanding, and this direction is
opposite the direction of the
displacement of the point of
application of the force as the block
moves from -xmax to 0.
For an arbitrary displacement of the block, the work done on the
system by the external agent is :
Kinetic Energy and the WorkKinetic
Energy Theorem
The net force on a particle of mass m is equal to the difference
between the initial and final values of a quantity 12mv. This
quantity is so important that it has been given a special name,
kinetic energy :
Kinetic energy represents the energy associated with the
motion of the particle. Note that kinetic energy is a scalar
quantity and has the same units as work.
When work is done on a system and the only change in the
system is in its speed, the net work done on the system equals
the change in kinetic energy of the system.
Potential Energy of a System
Gravitational potential energy
Gravitational potential energy depends only on
the vertical height of the object
above the surface of the Earth
Elastic Potential Energy
The elastic potential energy function associated with the block
spring system is defined by
Conservative and Nonconservative
Forces
Conservative Forces
Conservative forces have these two equivalent properties:
1. The work done by a conservative force on a particle moving
between any two points is independent of the path taken by the
particle.
2. The work done by a conservative force on a particle moving
through any closed path is zero. (A closed path is one for which
the beginning point and the endpoint are identical.)
Nonconservative Forces
A force is nonconservative if it does not satisfy properties 1 and
2 above. The work done by a nonconservative force is pathdependent
Relationship Between Conservative
Forces and Potential Energy
system by a conservative force between the members of the
system does not depend on the path taken by the moving
member. The work depends only on the initial and final
coordinates.
Relation of force between
members of a system to the
potential energy of the system
Energy Diagrams and Equilibrium of a
System
Systems can be in three types of equilibrium configurations
when the net force on a member of the system is zero.
Configurations of stable equilibrium correspond to those for
which U(x) is a minimum.
Configurations of unstable equilibrium correspond to those
for which U(x) is a maximum.
Neutral equilibrium arises when U is constant as a member of
the system moves over some region.
Вам также может понравиться
- Chapter # 07: Energy: The Ability To Do Work. Kinetic Energy: Associated With The State of Motion of AnДокумент12 страницChapter # 07: Energy: The Ability To Do Work. Kinetic Energy: Associated With The State of Motion of AnAbdul MunimОценок пока нет
- Potential Energy 0Документ8 страницPotential Energy 0nettextsОценок пока нет
- CCC Yenching College CKNGДокумент12 страницCCC Yenching College CKNGEmily LukОценок пока нет
- UsahaDanEnergi (Kelompok5)Документ15 страницUsahaDanEnergi (Kelompok5)Novitasr AlОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2pptДокумент116 страницChapter 2pptyohannes lemiОценок пока нет
- 01 Engineering Mechanics 1 PDFДокумент31 страница01 Engineering Mechanics 1 PDFMaria ConceptionОценок пока нет
- KG12403 CHP2 (Part 1)Документ20 страницKG12403 CHP2 (Part 1)Zulizah NatashaОценок пока нет
- Dynamics of Machinery Oral Question BankДокумент22 страницыDynamics of Machinery Oral Question BankSurajKahateRajputОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics-1: Dr. Eng. Ahmed MostafaДокумент28 страницThermodynamics-1: Dr. Eng. Ahmed MostafaHussien HassanОценок пока нет
- Physics Unit 4 Revision NotesДокумент12 страницPhysics Unit 4 Revision Notespraphul4u100% (1)
- Lesson 4-Topic 2 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesДокумент21 страницаLesson 4-Topic 2 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesNicholas Bonn SingОценок пока нет
- Dynamics of Machines Two MarksДокумент13 страницDynamics of Machines Two MarksJegan ParamasivamОценок пока нет
- Ch7 - Work and Kinetic EnergyДокумент23 страницыCh7 - Work and Kinetic EnergyLAVA HASSANОценок пока нет
- Lows and Principles of ForcesДокумент27 страницLows and Principles of Forcesesam eisaОценок пока нет
- Lows and Principles of ForcesДокумент27 страницLows and Principles of Forcesesam eisaОценок пока нет
- Scalars and VectorsДокумент11 страницScalars and VectorsEFRAIM CAMBEОценок пока нет
- 2 - Equilibrium of Particle in 2DДокумент24 страницы2 - Equilibrium of Particle in 2DHielОценок пока нет
- Module-29A: Energy MethodsДокумент2 страницыModule-29A: Energy MethodsjhacademyhydОценок пока нет
- Conservation of Momentum ImpactДокумент7 страницConservation of Momentum ImpactbabsthemanateeОценок пока нет
- Final-IJSO Physics Module (Part-2)Документ56 страницFinal-IJSO Physics Module (Part-2)riddhiОценок пока нет
- 03 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovДокумент25 страниц03 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovKVP LyricsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ37 страницChapter 2Yordanos AbebawОценок пока нет
- Summative 1 ReviewerДокумент11 страницSummative 1 ReviewerJuli BakerОценок пока нет
- Lect. 7, Energy, Power, and WorkДокумент22 страницыLect. 7, Energy, Power, and WorkNawras aliОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Force SystemДокумент45 страницChapter 2 Force SystemeyuducОценок пока нет
- (Phys) Compiled Definitions and Principles For ASlevel Paper 1/paper 2Документ10 страниц(Phys) Compiled Definitions and Principles For ASlevel Paper 1/paper 2qidamadani100% (1)
- Handout GEN PHYSICSДокумент12 страницHandout GEN PHYSICSJV PatindolОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 6 - ReviewerДокумент19 страницCHAPTER 6 - ReviewerEdgiecylin S. GALENOОценок пока нет
- EM - PPT - FinalpptxДокумент28 страницEM - PPT - FinalpptxShawn HunterОценок пока нет
- Session 3 Kinetics of Particles Work Energy PrincipleДокумент34 страницыSession 3 Kinetics of Particles Work Energy PrincipleRosina AdhikariОценок пока нет
- 03 Fundament - of - StaticsДокумент69 страниц03 Fundament - of - StaticsdarshanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particle - Work and EnergyДокумент31 страницаChapter 3 Kinetics of Particle - Work and Energyqwert 12345Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 (Energy of A System) PDFДокумент21 страницаChapter 7 (Energy of A System) PDFJoud Alotaibi.Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 (Energy of A System) PDFДокумент21 страницаChapter 7 (Energy of A System) PDFJoud Alotaibi.Оценок пока нет
- Esm Unit 2Документ25 страницEsm Unit 2deekshithasweety0Оценок пока нет
- Physics DefinitionsДокумент2 страницыPhysics DefinitionsElaine Neo Kai WenОценок пока нет
- ME101 Lecture29 KDДокумент16 страницME101 Lecture29 KDSiddharthaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 (Part 2)Документ35 страницChapter 2 (Part 2)muhammadtalhabilal6666Оценок пока нет
- Module 1 - MechanicsДокумент31 страницаModule 1 - MechanicsAsha AsokОценок пока нет
- Numerical Methods For Field Problems: Notes By: Kishore PochirajuДокумент37 страницNumerical Methods For Field Problems: Notes By: Kishore PochirajuFredОценок пока нет
- Force SystemДокумент28 страницForce SystemahmaadfhОценок пока нет
- Work, Power & EnergyДокумент16 страницWork, Power & EnergyAyush GamerОценок пока нет
- Electric Potential-IДокумент33 страницыElectric Potential-ISumaya Akter Ruhi 2022610642Оценок пока нет
- Session 1: Resultant of Force System: CouplesДокумент4 страницыSession 1: Resultant of Force System: CouplesRhodoralyn Ilagan BalhagОценок пока нет
- SRB Session1 RofsДокумент4 страницыSRB Session1 RofsFullo Flores MarviloneОценок пока нет
- DS - Lec 1Документ7 страницDS - Lec 1Sherif SaidОценок пока нет
- PMMC & Moving IronДокумент51 страницаPMMC & Moving IronNiladri DeyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 05Документ20 страницLecture 05Hamna noorОценок пока нет
- Classification of Instrument PDFДокумент21 страницаClassification of Instrument PDFAnanya SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- 9.3 Motors and Generators NotesДокумент18 страниц9.3 Motors and Generators NotesAmeena TohmeyОценок пока нет
- Group 2Документ14 страницGroup 2Xaviour Luis Mercurio CunananОценок пока нет
- Des-Con 01 Basics of Strength of Material - Weld DesignДокумент62 страницыDes-Con 01 Basics of Strength of Material - Weld DesignRaghu vamshiОценок пока нет
- Lesson-2 (SRB)Документ16 страницLesson-2 (SRB)Christian MagdangalОценок пока нет
- Unit-1 One MarksДокумент6 страницUnit-1 One MarksShri RahulОценок пока нет
- Mechanics: Idealizations: Idealisations Are Used in Mechanics To Simplify The Application of TheoryДокумент48 страницMechanics: Idealizations: Idealisations Are Used in Mechanics To Simplify The Application of TheoryAskkar Ali PОценок пока нет
- 1 400 Questions and AnswerДокумент1 страница1 400 Questions and AnswerJenemarОценок пока нет
- Study Journal Lesson 13 - 23 - LisondraДокумент5 страницStudy Journal Lesson 13 - 23 - Lisondrasenior highОценок пока нет
- Art of War Day TradingДокумент17 страницArt of War Day TradingChrispen MoyoОценок пока нет
- On Animal Language in The Medieval Classification of Signs PDFДокумент24 страницыOn Animal Language in The Medieval Classification of Signs PDFDearNoodlesОценок пока нет
- Outline Calculus3Документ20 страницOutline Calculus3Joel CurtisОценок пока нет
- KundaliniДокумент3 страницыKundaliniAlfred IDunnoОценок пока нет
- SavannahHarbor5R Restoration Plan 11 10 2015Документ119 страницSavannahHarbor5R Restoration Plan 11 10 2015siamak dadashzadeОценок пока нет
- Liquitex Soft Body BookletДокумент12 страницLiquitex Soft Body Booklethello belloОценок пока нет
- SDN Van NotesДокумент26 страницSDN Van Notesmjsmith11Оценок пока нет
- Final Self Hypnosis Paperback For PrintДокумент150 страницFinal Self Hypnosis Paperback For PrintRic Painter100% (12)
- Bioinformatics Computing II: MotivationДокумент7 страницBioinformatics Computing II: MotivationTasmia SaleemОценок пока нет
- C. Robert Mesle (Auth.) - John Hick's Theodicy - A Process Humanist Critique-Palgrave Macmillan UK (1991)Документ168 страницC. Robert Mesle (Auth.) - John Hick's Theodicy - A Process Humanist Critique-Palgrave Macmillan UK (1991)Nelson100% (3)
- Song LyricsДокумент13 страницSong LyricsCyh RusОценок пока нет
- Ti05001 PDFДокумент1 страницаTi05001 PDFanggieОценок пока нет
- Getting Started With Citrix NetScalerДокумент252 страницыGetting Started With Citrix NetScalersudharaghavanОценок пока нет
- Play ClawДокумент2 страницыPlay ClawFrenda SeivelunОценок пока нет
- PGCRSM-01-BLOCK-03 Research Design ExperimentalДокумент29 страницPGCRSM-01-BLOCK-03 Research Design ExperimentalVijilan Parayil VijayanОценок пока нет
- Homeopatija I KancerДокумент1 страницаHomeopatija I KancermafkoОценок пока нет
- 35 Electrical Safety SamanДокумент32 страницы35 Electrical Safety SamanSaman Sri Ananda RajapaksaОценок пока нет
- Working Capital Management 2012 of HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LTD.Документ98 страницWorking Capital Management 2012 of HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LTD.Pratyush Dubey100% (1)
- Lightning Protection Measures NewДокумент9 страницLightning Protection Measures NewjithishОценок пока нет
- Crisis of The World Split Apart: Solzhenitsyn On The WestДокумент52 страницыCrisis of The World Split Apart: Solzhenitsyn On The WestdodnkaОценок пока нет
- Crafer. The Apocriticus of Macarius Magnes (S.P.C.K. Edition) - 1919.Документ188 страницCrafer. The Apocriticus of Macarius Magnes (S.P.C.K. Edition) - 1919.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et OrientalisОценок пока нет
- Women Are Better Managers Than MenДокумент5 страницWomen Are Better Managers Than MenCorazon ValdezОценок пока нет
- Aribah Ahmed CertificateДокумент2 страницыAribah Ahmed CertificateBahadur AliОценок пока нет
- Daily Lesson Log Quarter 1 Week 1Документ5 страницDaily Lesson Log Quarter 1 Week 1John Patrick Famadulan100% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence Practical 1Документ5 страницArtificial Intelligence Practical 1sadani1989Оценок пока нет
- Existentialism in LiteratureДокумент2 страницыExistentialism in LiteratureGirlhappy Romy100% (1)
- PetrifiedДокумент13 страницPetrifiedMarta GortОценок пока нет
- Acetylcysteine 200mg (Siran, Reolin)Документ5 страницAcetylcysteine 200mg (Siran, Reolin)ddandan_2Оценок пока нет
- Table of Specification 1st QДокумент5 страницTable of Specification 1st QVIRGILIO JR FABIОценок пока нет
- Essentials: Week by WeekДокумент18 страницEssentials: Week by WeekHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет