Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Furnaces
Загружено:
Chirag PatelИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Furnaces
Загружено:
Chirag PatelАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Metal Furnaces
ey are used to melt the metal into liquid for casting process.
Types of Metal Furnaces
[A] Crucible furnace
[B] Pot Furnace
[C] Rotary Furnace
[D] Electric Furnace
[E] Cupola Furnace
Prepared By : Patel Chirag B.
Branch : Mechanical (Morning)
Subject : M.E.1
Enrollment No. :
146180319037
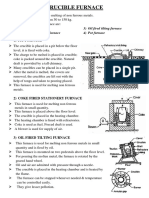
[A] Crucible Furnace
Crucible furnaces are small capacity typically used for small melting applications. Crucible
furnace is suitable for the batch type foundries where the metal requirement is intermittent. The
metal is placed in a crucible which is made of clay and graphite. The energy is applied indirectly to
the metal by heating the crucible by coke, oil or gas. The heating of crucible is done by coke, oil or
gas.
Types of Crucible Furnace
1. Coke Fired Pit Furnace
2. Oil Fired Crucible Furnace
[B] Pot Furnace
Pot Furnace is used to melt non-ferrous metals like Megnesium, Alluminium, Tin, Zinc and Cadmium.
The pot is made up of cast iron or steel.
The furnace may be fired by gasoline oil or coke.
The molten metal is taken out of the pot furnace by using ladles.
Normally the capacity of pot furnace is around 500 kg.
[C] Rotary Furnace
Used to melt 500kg to 2500kg of metal
The kiln is a cylindrical vessel, inclined slightly to the horizontal, which is rotated slowly about its axis. The
material to be processed is fed into the upper end of the cylinder. As the kiln rotates, material gradually moves
down towards the lower end, and may undergo a certain amount of stirring and mixing. Hot gases pass along
the kiln, sometimes in the same direction as the process material (co-current), but usually in the opposite
direction (counter-current). The hot gases may be generated in an external furnace, or may be generated by a
flame inside the kiln. Such a flame is projected from a burner-pipe (or "firing pipe") which acts like a large
bunsen burner. Thefuelfor this may be gas, oil, pulverized petroleum coke or pulverized coal.
[D] Electric Furnace
Types of Electric Furnaces
1. Direct Arc furnace
2. Indirect Arc Furnace
3. Induction Furnace
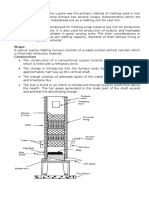
[E] Cupola Furnace
Cupola
Cupola furnaces are tall, cylindrical furnaces used to
melt iron and ferrous alloys in foundry operations.
Alternating layers of metal and ferrous alloys, coke,
and limestone are fed into the furnace from the top.
A schematic diagram of a cupola is shown inFigure.
This diagram of a cupola illustrates the furnace's
cylindrical shaft lined with refractory and the
alternating layers of coke and metal scrap. The
molten metal flows out of a spout at the bottom of
the cupola. .
Operation of Cupola
The cupola is charged with wood at the bottom. On
the top of the wood a bed of coke is built.
Alternating layers of metal and ferrous alloys, coke,
and limestone are fed into the furnace from the top.
The purpose of adding flux is to eliminate the
impurities and to protect the metal from oxidation.
Air blast is opened for the complete combustion of
coke. When sufficient metal has been melted that
slag hole is first opened to remove the slag. Tap
hole is then opened to collect the metal in the ladle.
Вам также может понравиться
- Crucible FurnacesДокумент10 страницCrucible FurnacesZara SaeedОценок пока нет
- Types of Furnaces Used in CastingДокумент29 страницTypes of Furnaces Used in CastingMurali100% (1)
- Crucible Furnace Some MoreДокумент2 страницыCrucible Furnace Some MorePrashanth BnОценок пока нет
- Spaft PresentationДокумент29 страницSpaft PresentationVaishnavi ShringiОценок пока нет
- Crucible FurnacesДокумент10 страницCrucible FurnacesZara Saeed0% (1)
- Crucible Furnace Some More PDFДокумент2 страницыCrucible Furnace Some More PDFikhlas amalОценок пока нет
- Cupola Furnace eДокумент5 страницCupola Furnace eAshok PradhanОценок пока нет
- Foundry I - Complete Lab Manual at WWW.07MET - TKДокумент18 страницFoundry I - Complete Lab Manual at WWW.07MET - TKAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Report On Heat Treatment of Plain Carbon Steel Kuet MeДокумент11 страницReport On Heat Treatment of Plain Carbon Steel Kuet MeAhmed JishanОценок пока нет
- Metal Joining PrcocessДокумент42 страницыMetal Joining PrcocessDheerajSharmaОценок пока нет
- Heat BalanceДокумент11 страницHeat BalanceB V S Kumar100% (1)
- Powder MetallurgyДокумент96 страницPowder Metallurgykhare_girishОценок пока нет
- Induction Heating Handbook: John Davies Peter SimpsonДокумент5 страницInduction Heating Handbook: John Davies Peter SimpsonOthman Ben Cheikh0% (1)
- Heat TreatmentДокумент24 страницыHeat TreatmentOlanrewaju Slyman Damilola100% (1)
- Introduction To FurnacesДокумент16 страницIntroduction To FurnacesMuneeb Rehman100% (1)
- Induction FurnaceДокумент7 страницInduction FurnaceDeepak Velusamy100% (2)
- Gear ClassificationДокумент13 страницGear Classificationprkphani1984100% (1)
- 401 Crucible Furnaces PDFДокумент31 страница401 Crucible Furnaces PDFOscar AtienzaОценок пока нет
- Steel Making IntroductionДокумент17 страницSteel Making IntroductionHari sadu100% (2)
- CH 14 CarbonandAlloySteelsДокумент43 страницыCH 14 CarbonandAlloySteelsMohmmad ShaikhОценок пока нет
- New China Standard-Q345B Changed To Q355BДокумент1 страницаNew China Standard-Q345B Changed To Q355BBAWA ALEXОценок пока нет
- LESSON 4-Solidification of Metals and AlloysДокумент19 страницLESSON 4-Solidification of Metals and Alloysmichael-education KОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - Fits, LimitsДокумент18 страницModule 1 - Fits, LimitsShanhoodОценок пока нет
- A Project Profile On The Steel Melting Shop Prepared by APITCO LimitedДокумент6 страницA Project Profile On The Steel Melting Shop Prepared by APITCO LimitedSrikant MahapatraОценок пока нет
- MM 223 Claw Hammer Literature ReviewДокумент10 страницMM 223 Claw Hammer Literature Reviewdipanshil100% (1)
- Steel Mill: See AlsoДокумент5 страницSteel Mill: See AlsoJustin Alvin P. CaballaОценок пока нет
- Foundry and Forging Lab ManualДокумент15 страницFoundry and Forging Lab ManualManjunatha Babu N.sОценок пока нет
- Thermal Processing of MetalsДокумент63 страницыThermal Processing of MetalsNagaVenkateshGОценок пока нет
- Me8491 em Unit - IIДокумент119 страницMe8491 em Unit - IIParameswara Raja100% (1)
- Oxidation of Iron, Silicon and Manganese: Today's TopicsДокумент11 страницOxidation of Iron, Silicon and Manganese: Today's TopicsMir RafsanОценок пока нет
- Industrial Report On Production Process of Steel Mills LTD: A Study On Ratanpur Steel Re-Rolling MillsДокумент21 страницаIndustrial Report On Production Process of Steel Mills LTD: A Study On Ratanpur Steel Re-Rolling MillsAbid HasanОценок пока нет
- Amt 611 Heat TreatmentДокумент44 страницыAmt 611 Heat TreatmentJhalbert BelmonteОценок пока нет
- 11 Introduction To Engineering MaterialsДокумент20 страниц11 Introduction To Engineering MaterialsomkardashetwarОценок пока нет
- Boilers NotesДокумент10 страницBoilers NotesDr-Bharath Vedashantha MurthyОценок пока нет
- Induction Furnace SparesДокумент3 страницыInduction Furnace SparesskluxОценок пока нет
- Melting FurnacesДокумент11 страницMelting Furnacesabhishek_m_more0% (1)
- Induction FurnaceДокумент29 страницInduction Furnaceadelina ednandaОценок пока нет
- 08108057-Open Hearth ProcessДокумент20 страниц08108057-Open Hearth Processkchoudhary86Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 19-Bulk Deformation ProcessesДокумент90 страницChapter 19-Bulk Deformation ProcessesMuhammad Asif Khan0% (1)
- Gear and Gear TrainДокумент21 страницаGear and Gear Trainm_er100Оценок пока нет
- Engineering MaterialsДокумент25 страницEngineering MaterialsNichan CanilloОценок пока нет
- Energy and Exergy of Electric Arc Furnace PDFДокумент26 страницEnergy and Exergy of Electric Arc Furnace PDFChristopher LloydОценок пока нет
- Iron MakingДокумент26 страницIron Makingsumit ranjanОценок пока нет
- 6 Welding NumericalДокумент9 страниц6 Welding NumericalNavjot WadhwaОценок пока нет
- Casting Manufacturing Processes Fundamentals of Metal Casting Metals For CastingДокумент47 страницCasting Manufacturing Processes Fundamentals of Metal Casting Metals For CastingarobaidiОценок пока нет
- MetalДокумент57 страницMetalPrashant PuriОценок пока нет
- A Report On Steel Melting ShopДокумент18 страницA Report On Steel Melting ShopRahul PandeyОценок пока нет
- Tool SteelsДокумент35 страницTool SteelsHandrizaHanifAsyrafiОценок пока нет
- Foundry PracticeДокумент58 страницFoundry PracticetrishОценок пока нет
- Electric and Automation - Ladle Management A-323eДокумент4 страницыElectric and Automation - Ladle Management A-323eSantosh UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- Blast Furnace OverviewДокумент26 страницBlast Furnace OverviewProfMVSОценок пока нет
- Thesis (V Nashine)Документ95 страницThesis (V Nashine)Salil JainОценок пока нет
- Thermomechanical Processing: 1 ReferencesДокумент2 страницыThermomechanical Processing: 1 ReferencesRajesh YenugulaОценок пока нет
- Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankДокумент7 страницEngineering Materials & Metallurgy Question BankJOHN PAUL V67% (3)
- TIG Presentation.Документ31 страницаTIG Presentation.Md Anamul HoqueОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 PDFДокумент19 страницUnit 2 PDFDevansh SharmaОценок пока нет
- 3furnaces 120520160438 Phpapp01 130806162930 Phpapp02Документ10 страниц3furnaces 120520160438 Phpapp01 130806162930 Phpapp02Ashrav GuptaОценок пока нет
- Casting FurnacesДокумент13 страницCasting Furnacestdm2008Оценок пока нет
- 3furnaces 120520160438 Phpapp01 130806162930 Phpapp02Документ10 страниц3furnaces 120520160438 Phpapp01 130806162930 Phpapp02Amrik SinghОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Multistage Car Parking SystemДокумент4 страницыIntroduction To Multistage Car Parking SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementОценок пока нет
- If You Restyou RustДокумент4 страницыIf You Restyou Rusttssuru9182Оценок пока нет
- SThe Electric Double LayerДокумент1 страницаSThe Electric Double LayerDrishty YadavОценок пока нет
- Guidelines and Standards For External Evaluation Organisations 5th Edition v1.1Документ74 страницыGuidelines and Standards For External Evaluation Organisations 5th Edition v1.1Entrepre NurseОценок пока нет
- 17 Safety InventoryДокумент47 страниц17 Safety Inventorymishrakanchan 2396Оценок пока нет
- Grade 8 For Demo Cigarette SmokingДокумент3 страницыGrade 8 For Demo Cigarette SmokingSteven TaperoОценок пока нет
- NAAC 10.12.1888888 NewДокумент48 страницNAAC 10.12.1888888 Newచిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిОценок пока нет
- Additional Material On CommunicationДокумент15 страницAdditional Material On CommunicationSasmita NayakОценок пока нет
- Bibliografi 3Документ3 страницыBibliografi 3Praba RauОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Assessment, Solution Manual, Electrons in Atoms, Glencoe, ChemistryДокумент9 страницChapter 5 Assessment, Solution Manual, Electrons in Atoms, Glencoe, Chemistrypumeananda100% (3)
- Intro To Geometric Design and Vertical AlignmentДокумент25 страницIntro To Geometric Design and Vertical AlignmentAhsan ArfanОценок пока нет
- (Fanuc Lad 0I-Mc) Ladder Diagram 1Документ160 страниц(Fanuc Lad 0I-Mc) Ladder Diagram 1Ujang NachrawiОценок пока нет
- Sistema A-101 LVSДокумент4 страницыSistema A-101 LVSAdministrador AngloОценок пока нет
- ACFrOgDVly789-6Z8jIbi7pBoLupubEgMyOp7PczEvUguHoW3uj oR2PKzDvuhRzzkIhacYjxXRrU6iA7sHt t6MhtpZFq0t uZL2pF5Ra NNZ kmcl5w7BCQeUegKhjRhNuou88XxLodzWwbsrДокумент14 страницACFrOgDVly789-6Z8jIbi7pBoLupubEgMyOp7PczEvUguHoW3uj oR2PKzDvuhRzzkIhacYjxXRrU6iA7sHt t6MhtpZFq0t uZL2pF5Ra NNZ kmcl5w7BCQeUegKhjRhNuou88XxLodzWwbsrJohn Steven LlorcaОценок пока нет
- Seventh Pay Commission ArrearsДокумент11 страницSeventh Pay Commission Arrearssantosh bharathyОценок пока нет
- Literature 101 Assignment: Step 1: Graphic OrganizerДокумент2 страницыLiterature 101 Assignment: Step 1: Graphic OrganizercatarinaОценок пока нет
- KIT REQUEST FORM - GradДокумент2 страницыKIT REQUEST FORM - Graddamie aadamsОценок пока нет
- Data Structures and Algorithms AssignmentДокумент25 страницData Structures and Algorithms Assignmentعلی احمد100% (1)
- Kelompok CKD - Tugas Terapi Modalitas KeperawatanДокумент14 страницKelompok CKD - Tugas Terapi Modalitas KeperawatanWinda WidyaОценок пока нет
- English Action Plan 2023-2024Документ5 страницEnglish Action Plan 2023-2024Gina DaligdigОценок пока нет
- Student Exploration: Electron Configuration: 8-27-2005 Joshua Perez-LunaДокумент14 страницStudent Exploration: Electron Configuration: 8-27-2005 Joshua Perez-LunaJoshua Perez-Luna67% (3)
- Adsa Ka SyllabusДокумент3 страницыAdsa Ka SyllabusHacker RanjanОценок пока нет
- 1.1. CHILLER 1.2. Centrifugal: 5.2.hrizontalДокумент2 страницы1.1. CHILLER 1.2. Centrifugal: 5.2.hrizontalShah ArafatОценок пока нет
- Tank Top Return Line Filter Pi 5000 Nominal Size 160 1000 According To Din 24550Документ8 страницTank Top Return Line Filter Pi 5000 Nominal Size 160 1000 According To Din 24550Mauricio Ariel H. OrellanaОценок пока нет
- Tridium Europe DatasheetДокумент2 страницыTridium Europe DatasheetHoàngTrầnОценок пока нет
- Pre Post and Infix NotationsДокумент12 страницPre Post and Infix NotationsGolla GirijaОценок пока нет
- Mechatronics Course PlanДокумент3 страницыMechatronics Course PlanMohammad Faraz AkhterОценок пока нет
- A Presentation On Organizational Change ModelДокумент4 страницыA Presentation On Organizational Change ModelSandeepHacksОценок пока нет
- Layers of The EarthДокумент26 страницLayers of The EarthLoo DrBrad100% (1)
- SRM OverviewДокумент37 страницSRM Overviewbravichandra24Оценок пока нет