Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Effective Stress Concepts
Загружено:
Clairole Marie QuilantangАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Effective Stress Concepts
Загружено:
Clairole Marie QuilantangАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EFFECTIVE STRESS
CONCEPTS
REPORTED BY:
ASAALI,QUILANTANG,TORREFRANCA
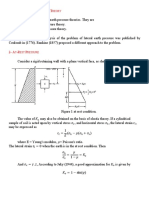
Definition of Terms
Effective Stress Equation
The total stress in a
soil is divided into
two parts: (1) the
neutral stress (pore
water pressure ) and
(2) the effective
stress.
Stresses in Saturated Soil
Without Seepage
Stresses in Saturated Soil
Without Seepage
Variations of the total stress, pore water pressure, and effective
stress, respectively, with depth for a soil layer without seepage
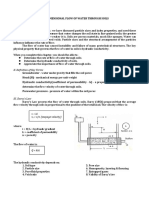
Stresses in Saturated Soils with
Upward Seepage
Water is flowing upward through the soil shown. The stresses in the soil
are calculated at points A, B, and C.
Stresses in Saturated Soils with
Upward Seepage
Variations of the total stress, pore water pressure, and effective stress,
respectively, with depth for a soil layer with upward seepage
Stresses in Saturated Soils with
Downward Seepage
Variations of the total stress, pore water pressure, and effective stress,
respectively, with depth for a soil layer with downward seepage
Stresses in Saturated Soils with
Downward Seepage
Variations of the total stress, pore water pressure, and effective stress,
respectively, with depth for a soil layer with upward seepage
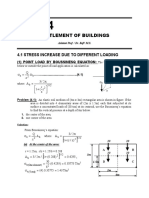
Problem
Figure shows a layer of granular soil where downward seepage is caused by adding
water at the top of the tank. The rate of supply is kept constant. Coefficient of
permeability of soil is 0.1 cm/sec. Saturated unit weight of soil is 18.5 kN/m^3 and
area of tank is 0.5 m^2.
1.
2.
3.
Rate of downward seepage
Critical hydraulic gradient
Value of h causing boiling
END OF REPORT
Вам также может понравиться
- Effective Stress PrincipleДокумент20 страницEffective Stress PrincipleLuis Fernando Medina CasallasОценок пока нет
- Stresses EquationsДокумент12 страницStresses EquationsMartin GriffinОценок пока нет
- Lecture2 - Vertical StressДокумент123 страницыLecture2 - Vertical StressJoseph BaruhiyeОценок пока нет
- Soil ProblemsДокумент3 страницыSoil ProblemsYss CastañedaОценок пока нет
- STRESSES IN SOILДокумент16 страницSTRESSES IN SOILSherline SupnetОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ62 страницыChapter 5Mo Kops100% (1)
- Atterberg Limits FormulaДокумент3 страницыAtterberg Limits FormulaJoshua PrietoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15Документ32 страницыChapter 15Casao JonroeОценок пока нет
- P5 Effective StressДокумент28 страницP5 Effective StressMiguel TabaОценок пока нет
- UC Test Determines Clay StrengthДокумент13 страницUC Test Determines Clay StrengthMuhammad LutfiОценок пока нет
- Soil Moisture, Permeability and StressesДокумент52 страницыSoil Moisture, Permeability and Stressesanon_917763370Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial Chapter 2Документ2 страницыTutorial Chapter 2wendyОценок пока нет
- Geo Tech FormulasДокумент5 страницGeo Tech FormulasJoy KathleenОценок пока нет
- Soil CompactionДокумент13 страницSoil CompactionElizabeth Santiago100% (1)
- WITH SOLUTIONS Pipe Connection and Three ReservoirДокумент46 страницWITH SOLUTIONS Pipe Connection and Three ReservoirMark PulongbaritОценок пока нет
- Shear Strength of SoilДокумент24 страницыShear Strength of SoilKriz Ian Cenabre ArueloОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Shear StrengthДокумент64 страницыChapter 4 Shear StrengthkhuzaimahОценок пока нет
- Problem Set Soil Mechanics Ready To Print CE PaperДокумент6 страницProblem Set Soil Mechanics Ready To Print CE PaperClein BaltazarОценок пока нет
- CH 11 Compressibility of Soil4Документ14 страницCH 11 Compressibility of Soil4Boni ClydeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Stresses in SoilДокумент29 страницChapter 6 - Stresses in SoilJonniel De Guzman0% (1)
- Quick SandДокумент49 страницQuick Sandpavan100% (2)
- Solved Problems in Soil Mechanics: SolutionДокумент5 страницSolved Problems in Soil Mechanics: SolutionMemo LyОценок пока нет
- Consolidation Test by RatiyalaДокумент6 страницConsolidation Test by RatiyalaBhawanujan PerinparajaОценок пока нет
- Module 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressДокумент12 страницModule 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressShane IsorenaОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics - Assignment 3Документ5 страницSoil Mechanics - Assignment 3Srinivasan Narasimhan100% (3)
- Tutorial 2Документ5 страницTutorial 2WHfamilyОценок пока нет
- Practice Problems - Shear Strength (II)Документ2 страницыPractice Problems - Shear Strength (II)Kok Soon ChongОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics HandoutДокумент62 страницыSoil Mechanics HandoutRenz Erick Reveche Delgado100% (1)
- Ch4 Settlement of Buildings (1-34) - 2016Документ34 страницыCh4 Settlement of Buildings (1-34) - 2016Rafi SulaimanОценок пока нет
- Geo Problem Set 2Документ27 страницGeo Problem Set 2Marielle Jane B. TapangОценок пока нет
- Geotechnical Engineering II: Shear Strength of SoilДокумент184 страницыGeotechnical Engineering II: Shear Strength of SoilSaad JuventinoОценок пока нет
- Module 3Документ7 страницModule 3Light HouseОценок пока нет
- CE225 SM 15 Stresses in SoilДокумент46 страницCE225 SM 15 Stresses in SoilM Modood Abbasi AbbasiОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics Assignment 1: Degree of Saturation, Unit Weight, Void RatioДокумент1 страницаSoil Mechanics Assignment 1: Degree of Saturation, Unit Weight, Void RatioArchit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth - Rankine Active and Passive Rev 1Документ22 страницыLateral Earth - Rankine Active and Passive Rev 1mnmusor100% (1)
- 1 - Lateral Earth PressureДокумент7 страниц1 - Lateral Earth Pressureone engОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics Chapter 3 Key RelationshipsДокумент42 страницыSoil Mechanics Chapter 3 Key RelationshipsAbd El Rhman Mohamed50% (2)
- Chapter 1-Answer Key Concept Check: © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All Rights ReservedДокумент46 страницChapter 1-Answer Key Concept Check: © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All Rights ReservedDenise CastilloОценок пока нет
- Index Properties and Determination of SoilsДокумент17 страницIndex Properties and Determination of Soilsvinodh159Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - PermeabilityДокумент44 страницыChapter 4 - PermeabilityAfnan HamimiОценок пока нет
- CMT Laboratory 5 Determination of Surface Moisture of Coarse AggregatesДокумент6 страницCMT Laboratory 5 Determination of Surface Moisture of Coarse AggregatesBryanHarold BrooОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 1: Ce123 - HydraulicsДокумент1 страницаProblem Set 1: Ce123 - HydraulicsZENRIRОценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth Pressure TheoriesДокумент15 страницLateral Earth Pressure Theoriessreendd100% (1)
- CE6405 Soil Mechanics Solved QB PDFДокумент112 страницCE6405 Soil Mechanics Solved QB PDFcivildept maamallanОценок пока нет
- Permeability in SoilsДокумент47 страницPermeability in SoilsRusmar LaverosОценок пока нет
- Unit 4Документ2 страницыUnit 4VENKATA KOTESWARA RAOОценок пока нет
- Extracted Geotechnical Sample ProblemДокумент12 страницExtracted Geotechnical Sample ProblemFrancesca DaisyJaneОценок пока нет
- Consolidation TestДокумент17 страницConsolidation TestAyodele AjayiОценок пока нет
- DR Ahmed Soil Mechanics Notes Chapter 7Документ41 страницаDR Ahmed Soil Mechanics Notes Chapter 7Engr.Towhidul IslamОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8. InflitrationДокумент36 страницChapter 8. InflitrationkamagaraОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic jump experiment rectangular flumeДокумент18 страницHydraulic jump experiment rectangular flumeMohd ShahrizanОценок пока нет
- EFFECTIVE STRESSДокумент32 страницыEFFECTIVE STRESSMuhangi ChristopherОценок пока нет
- L-9 Effective StressДокумент19 страницL-9 Effective Stress22bms010Оценок пока нет
- EFFECTIVE STRESS AND PORE PRESSUREДокумент24 страницыEFFECTIVE STRESS AND PORE PRESSUREAngelica Curambao100% (2)
- CE 353 Geotechnical Engineering: in Situ StressesДокумент12 страницCE 353 Geotechnical Engineering: in Situ StressesKenaouia BahaaОценок пока нет
- Kuliah 5 Insitu StressДокумент41 страницаKuliah 5 Insitu StressFat-hanna Marami SaОценок пока нет
- 9 in Situ StressesДокумент48 страниц9 in Situ StressesZYNNNОценок пока нет
- Quilantang Research ProposalДокумент20 страницQuilantang Research ProposalClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Hardcopy Plate Dynamics-QuilantangДокумент9 страницHardcopy Plate Dynamics-QuilantangClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Plate No. 2: Submitted By: Jiezl Marie N. Yanga BSCE IV-B StudentДокумент6 страницPlate No. 2: Submitted By: Jiezl Marie N. Yanga BSCE IV-B StudentClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Cavendish Was The First To Recognize Hydrogen Gas As A Discrete Substance, by Naming The GasДокумент1 страницаCavendish Was The First To Recognize Hydrogen Gas As A Discrete Substance, by Naming The GasClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Summary of Per CapitaДокумент2 страницыSummary of Per CapitaClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Graduating Student Clearance WMSU MainДокумент1 страницаGraduating Student Clearance WMSU MainEbno MaruhomОценок пока нет
- Fixed Point Iteration Method For Finding Roots of FunctionsДокумент1 страницаFixed Point Iteration Method For Finding Roots of FunctionsClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Legend Summary Report Water Per Capita ConsumptionДокумент1 страницаLegend Summary Report Water Per Capita ConsumptionClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- (Any Color Pokemon If Not Found) : Lawrence RED PikachuДокумент1 страница(Any Color Pokemon If Not Found) : Lawrence RED PikachuClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Sean Gared S. Luna 8-Virgo: Some Uses IncludeДокумент9 страницSean Gared S. Luna 8-Virgo: Some Uses IncludeClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- New Years ChallengesДокумент7 страницNew Years ChallengesClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Single Degree-of-Freedom Systems: Submitted By: Clairole Marie L. Quilantang BSCE IV-B StudentДокумент4 страницыSingle Degree-of-Freedom Systems: Submitted By: Clairole Marie L. Quilantang BSCE IV-B StudentClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Trusses Types and their ApplicationsДокумент3 страницыTrusses Types and their ApplicationsClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Epic Tale Provides Insight Into Korean CultureДокумент8 страницEpic Tale Provides Insight Into Korean CultureClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- A Feasibility Study of Chicken Manure As A Source of Homemade Powered Methane Gas StoveДокумент14 страницA Feasibility Study of Chicken Manure As A Source of Homemade Powered Methane Gas StoveClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Trojan War & Hero's Journey HomeДокумент3 страницыTrojan War & Hero's Journey HomeClairole Marie Quilantang0% (1)
- A Project Proposal of Online Enrollment in WmsuДокумент9 страницA Project Proposal of Online Enrollment in WmsuClairole Marie Quilantang100% (1)
- What Is An Educated FilipinoДокумент2 страницыWhat Is An Educated FilipinoClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Report RainfallДокумент13 страницReport RainfallClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Complex FractionsДокумент7 страницComplex FractionsClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Epic Tale Provides Insight Into Korean CultureДокумент8 страницEpic Tale Provides Insight Into Korean CultureClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- What Are Seismic WavesДокумент9 страницWhat Are Seismic WavesClairole Marie QuilantangОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 and 15 HomeworkДокумент29 страницChapter 14 and 15 HomeworkFatboy91100% (4)
- Pusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 3.3 F.4.PhyДокумент5 страницPusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 3.3 F.4.PhyBazil BoliaОценок пока нет
- NBCC (INDIA) LIMITED Candidate User ID and Test DetailsДокумент25 страницNBCC (INDIA) LIMITED Candidate User ID and Test DetailsSudarshan bhadaneОценок пока нет
- Flexibility Of, and Load Distribution In, Multi-Bolt Lap Joints Subject To In-Plane Axial LoadsДокумент50 страницFlexibility Of, and Load Distribution In, Multi-Bolt Lap Joints Subject To In-Plane Axial LoadsErico Antonio TeixeiraОценок пока нет
- Rubber Elasticity ModelsДокумент20 страницRubber Elasticity ModelsoreamigОценок пока нет
- Seismic Design Guide for Multi-Storey Timber BuildingsДокумент86 страницSeismic Design Guide for Multi-Storey Timber Buildingsprisciliano1Оценок пока нет
- 1ST Quarterly Examination in Science 8 (2023-2024)Документ11 страниц1ST Quarterly Examination in Science 8 (2023-2024)Jonalyn ViernesОценок пока нет
- Friction Coefficient of Steel On Concrete or GroutДокумент7 страницFriction Coefficient of Steel On Concrete or GroutLuis Ernesto Ramirez OsorioОценок пока нет
- Pressure Surges: Resulting FromДокумент7 страницPressure Surges: Resulting Fromshan07011984Оценок пока нет
- Constitutive Equations in Finite Element Codes The INTERATOM Model in ABAQUSДокумент12 страницConstitutive Equations in Finite Element Codes The INTERATOM Model in ABAQUS吴华Оценок пока нет
- Taller de Mecánica de Fluidos.Документ4 страницыTaller de Mecánica de Fluidos.Juan Steven Montenegro PenagosОценок пока нет
- A RANS-based Analysis Ool For Ducted Propeller Systems in Open Water ConditionДокумент23 страницыA RANS-based Analysis Ool For Ducted Propeller Systems in Open Water ConditionLeonardo Duarte MilfontОценок пока нет
- Quantum and Statistical Physics FundamentalsДокумент305 страницQuantum and Statistical Physics Fundamentalsjerry cristianoОценок пока нет
- Influence of Size and Depth On Load Capacities of Shallow Foundations Under Limiting Settlement CriteriaДокумент9 страницInfluence of Size and Depth On Load Capacities of Shallow Foundations Under Limiting Settlement CriteriaAbdelmoez ElgarfОценок пока нет
- Steam SilencerДокумент3 страницыSteam SilencerAntonio Perez100% (1)
- Oil Recovery by Internal Gas DriveДокумент7 страницOil Recovery by Internal Gas DriveDhiaa LaMiОценок пока нет
- Emission Spectrum Light and EnergyДокумент17 страницEmission Spectrum Light and EnergyMarilyn Castro LaquindanumОценок пока нет
- Free Body Diagram Practice ProblemsДокумент4 страницыFree Body Diagram Practice Problemsapi-262120176100% (1)
- Fluid Friction and Head Loss Analysis in Smooth and Roughened PipesДокумент71 страницаFluid Friction and Head Loss Analysis in Smooth and Roughened PipesYara A. Valenzuela Quiros71% (7)
- 15.1 Dispersion of LightДокумент16 страниц15.1 Dispersion of LightRecky LasutОценок пока нет
- STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF HAND RAIL TITLEДокумент3 страницыSTRUCTURAL DESIGN OF HAND RAIL TITLEmsiddiq1100% (1)
- 3 Pilecap DesignДокумент6 страниц3 Pilecap DesignUttam Kumar GhoshОценок пока нет
- Boyle’s Law and Gas Laws ExplainedДокумент4 страницыBoyle’s Law and Gas Laws ExplainedChris HeydenrychОценок пока нет
- Physics Project Work On Hooke's Law and Stress-Strain RelationshipДокумент17 страницPhysics Project Work On Hooke's Law and Stress-Strain RelationshipAbhisek Adhikari100% (2)
- Lecture 4 - Losses in PSДокумент12 страницLecture 4 - Losses in PSLexi BarcelonОценок пока нет
- Modeling and Simulation of Inverted Pendulum System Using Matlab: OverviewДокумент4 страницыModeling and Simulation of Inverted Pendulum System Using Matlab: OverviewShoaib chishtyОценок пока нет
- Molecular Orbital Theory ExplainedДокумент80 страницMolecular Orbital Theory ExplainedMridul Bhaskar0% (1)
- CE66a: Reinforced Concrete Design 1: University of Science and Technology of Southern PhilippinesДокумент55 страницCE66a: Reinforced Concrete Design 1: University of Science and Technology of Southern PhilippinesKatherine Shayne YeeОценок пока нет
- JEE-MAIN - Part Test - 1 - PaperДокумент12 страницJEE-MAIN - Part Test - 1 - PaperApex Institute100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics ManualДокумент36 страницFluid Mechanics ManualHarold Taylor100% (1)