Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Kanker Ovarium
Загружено:
nia tiyas0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
29 просмотров15 страницbb
Оригинальное название
kanker ovarium
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документbb
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
29 просмотров15 страницKanker Ovarium
Загружено:
nia tiyasbb
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 15
KANKER OVARIUM
Dr. Dino Rinaldy,
Sp.OG(K)Onk
RSUD Dr. H. Abdul Moeloek
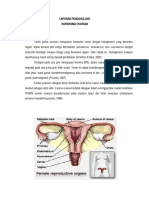
Ovarian tumor
Sering terjadi
Semua usia
Jenis berbeda sesuai usia
Jenis epiteliel mempunyai prognosis
jelek
Pendahuluan
Klasifikasi WHO tahun 1973
Jenis histologi
Ovarain epithelial tumor
Germ cell tumor
Sex-cord stromal cell tumor
Lipid (lipoid) cell tumor
Gonadal blastoma
Non-specific ovarian soft tissue
tumor
Unclassified tumor
Metastatic tumor
Tumor-like lesions
Gejala dan tanda
Tumor jinak
Jika kecil tak bergejala
Pembesaran perut dan adanya
masa pelvik jika tumor ukuran
menengah
Pemeriksaan ginekologi dijumpai
massa disamping uterus
Gejala dan tanda
Kanker ovarium
Stadium dini
asimtomatik, ditemukan tidak disengaja
Stadium lanjut
Pembesaran perut, massa abdominal, asites
Pemeriksaan transvagina-rectnum
massa solid or semi-solid, terfiksir
Complications
Rupture
Frequency about 3%
Traumatic and spontaneous
Symptom
lower abdominal pain
related to the size of rupture
the quality and quantity of cyst fluid
Signs
abdominal tenderness
muscle intensity
ascites
Treatment
emergency surgery
Diagnosis
Benign tumors
No specific symptoms
A mass found occasionally by physical
examination
Ovarian cancer
No specific symptoms
Gynecological examination
bilateral pelvic mass, solid , poor
movability, with ascites, uterus rectum
nest nodules
Diagnosis
Pencitraan
Ultrasonografi
diagnosis lesi primer, akurasi >
90%
Radiologi (X-Ray, CT, MRI)
untuk lesi metastasis
Ultrasonografi kanker ovarium
Diagnosis
Penanda tumor
CA125
meningkat pada 80% kanker epitelial, monitoring
dan prognosis
AFP
meningkat pada endodermal sinus tumor
hCG
choriacarcinoma ovarium
Sex hormone
sex-cord stromal cell tumor
Laparoscopy
Ascitic cytology
Metastatic pathway
Gambaran
Penyebaran luas pada rongga abdomen
Subclinical metastasis
Cara menyebar
langsung
aliran getah bening
melalui aliran darah
Clinical surgical-pathology staging (2000
Stage
FIGO)
I Growth limited to ovaries
Growth limited to one side ovaries; no ascites. No
IA
tumor on external surface; capsules intact
Growth limited to both ovaries; no ascites. No
IB
tumor on external surface; capsules intact
Tumor either IA or IB but with tumor on surface
of one or both ovaries;or with capsule ruptured;
IC
or with ascites containing malignant cells, or with
positive peritoneal washings
II Growth involving one or both ovaries with pelvic extension.
Extension and/or metastasis to the uterus and/or
IIA
tubes.
IIB Extension to other pelvic tissues.
Tumor either Stage IIA or IIB, but with tumor on
surface of one or both ovaries; or with capsule
IIC
ruptured; or with ascites containing malignant
cells, or with positive peritoneal washings.
Tumor involving one or both ovaries with peritoneal implants outside pelvis and/or positive
III
retroperitoneal or inguinal nodes. Superficial liver metastasis equals Stage III.
Tumor grossly limited to true pelvis with negative
nodes, but with histologically confirmed
IIIA
microscopic seeding of abdominal peritoneal
surfaces.
Tumor of one or both ovaries with histologically
confirmed implants to abdominal peritoneal
IIIB
surfaces, none exceeding 2 cm in diameter Nodes
are negative.
Abdominal implants >2 cm in diameter and/or
IIIC
positive retroperitoneal or inguinal nodes.
Growth involving one or both ovaries with distant metastasis. If pleural effusion present, must be
IV
positive cytology to assign a case to Stage IV. Parenchymal live metastasis equals Stage IV.
Terapi
Pembedahan
Tujuan
Konfirmasi diagnosis
Reseksi tumor
Penentuan stadium
Kemotherapi
follow-up
Mudah berulang
Thank you
!
Вам также может понравиться
- Patogenesis CA OvariumДокумент5 страницPatogenesis CA OvariumPusvaNurmalaSariОценок пока нет
- Bab IiДокумент12 страницBab IiOkpita Nur PaziraОценок пока нет
- Kanker Ovrium NewДокумент21 страницаKanker Ovrium NewSyurni SyasmiОценок пока нет
- Udis KMTДокумент19 страницUdis KMTDefisRonald HulkiawarОценок пока нет
- Askep Maternitas Kanker OvariumДокумент13 страницAskep Maternitas Kanker Ovariumyusfi indra gunawanОценок пока нет
- Bahan Makalah Ca Ovarium - Anita FixДокумент11 страницBahan Makalah Ca Ovarium - Anita FixAnita Astuti 2011166006Оценок пока нет
- LP MaternitasДокумент8 страницLP MaternitasRizki Ayu KurniyawatiОценок пока нет
- Askep Maternitas Kanker Ovarium Kel 3 FixДокумент20 страницAskep Maternitas Kanker Ovarium Kel 3 FixMeita RatriОценок пока нет
- LP Minggu 1 Mater - Laila Sa'adah - 2241312064Документ24 страницыLP Minggu 1 Mater - Laila Sa'adah - 2241312064Intan Fitria ArifinОценок пока нет
- Laporan Keperawatan Dasar Profesi ...Документ22 страницыLaporan Keperawatan Dasar Profesi ...Zulyana PutriОценок пока нет
- Kanker Tuba FalopiДокумент12 страницKanker Tuba Falopisri nuralami meldayanti samuddinОценок пока нет
- Tumor OvariumДокумент14 страницTumor Ovariumnurul safitriОценок пока нет
- Askep Kanker OvariumДокумент17 страницAskep Kanker OvariumMyОценок пока нет
- Makalah Ca OvariumДокумент16 страницMakalah Ca OvariumrusmaОценок пока нет
- Ca. OvariumДокумент16 страницCa. OvariumtitadeffaniaОценок пока нет
- Kanker OvariumДокумент17 страницKanker OvariumArfahsiregarОценок пока нет
- PPK Ca OvariumДокумент5 страницPPK Ca OvariumkarrameliaОценок пока нет
- LP Ca OvariumДокумент23 страницыLP Ca OvariumIndah Dkw67% (3)
- KLP 3 (Asuhan Keperawatan Paliatif Pada Pasien Kanker Serviks Di PKM Kassi-Kassi BTG)Документ12 страницKLP 3 (Asuhan Keperawatan Paliatif Pada Pasien Kanker Serviks Di PKM Kassi-Kassi BTG)Fitri AtikahОценок пока нет
- Referat Ca OvariumДокумент25 страницReferat Ca OvariumSahar UntadОценок пока нет
- LP Tumor OvariumДокумент15 страницLP Tumor OvariumDyah WidyaningrumОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ19 страницChapter 2Nyoman DevaОценок пока нет
- KANKER SERVIKS KELOMPOK 8 (Kep. Menjelang Ajal Paliatif)Документ25 страницKANKER SERVIKS KELOMPOK 8 (Kep. Menjelang Ajal Paliatif)Siti anasya CahyaОценок пока нет
- Neoplasia Pada Organ ReproduksiДокумент33 страницыNeoplasia Pada Organ ReproduksiImeldaОценок пока нет
- DVT Pada Ca OvariumДокумент37 страницDVT Pada Ca OvariumsenkonenОценок пока нет
- Ca Ovarium NewДокумент20 страницCa Ovarium Newendah arifahОценок пока нет
- LP Tumor OvariumДокумент16 страницLP Tumor OvariumYundayursianaОценок пока нет
- LP Ca OvarumДокумент16 страницLP Ca OvarumDyahnurma DaniОценок пока нет
- (LP) CA ServiksДокумент29 страниц(LP) CA ServiksaniatinaОценок пока нет
- Ca OvariumДокумент16 страницCa OvariumDwi Woro WidayatiОценок пока нет
- JSJSJJZДокумент17 страницJSJSJJZSikaОценок пока нет
- Pembimbing: Dr. Zufri Spog Oleh: Monica Bil Geni S.KedДокумент32 страницыPembimbing: Dr. Zufri Spog Oleh: Monica Bil Geni S.KedArif KurniawanОценок пока нет
- LP Ca OvariumДокумент17 страницLP Ca OvariumYunitaKhoirotusSalamahОценок пока нет
- CA CervixДокумент20 страницCA CervixMohammad FaridzaОценок пока нет
- Jurnal ReadingДокумент14 страницJurnal ReadingElmayana IlyasОценок пока нет
- Woc Kanker Serviks MeirykeДокумент8 страницWoc Kanker Serviks MeirykeMeiryke LalihatuОценок пока нет
- Askep CA OvariumДокумент10 страницAskep CA OvariumAnisah Devi ShintariniОценок пока нет
- LP Ca Ovarium BaruДокумент26 страницLP Ca Ovarium BaruWayan indah Sanis setiawatiОценок пока нет
- Laporan Kasus Dokter Internship Ca ServiksДокумент42 страницыLaporan Kasus Dokter Internship Ca ServiksshanazОценок пока нет
- CA CERVIK MurniДокумент23 страницыCA CERVIK MurnibintiОценок пока нет
- Ca CervixДокумент30 страницCa CervixjermanОценок пока нет
- Kasus Tumor OvariumДокумент24 страницыKasus Tumor OvariumRidha Mustika ZaifОценок пока нет
- Tumor GinekologiДокумент28 страницTumor Ginekologiantothesaber100% (1)
- ChoriocarcinomaДокумент9 страницChoriocarcinomaFawwaz MeorОценок пока нет
- Woc Kanker ServiksДокумент8 страницWoc Kanker ServiksMeiryke LalihatuОценок пока нет
- Tumor OvariumДокумент13 страницTumor OvariumMade Oka HeryanaОценок пока нет
- LAPORAN PENDAHULUAN Kanker ServiksДокумент12 страницLAPORAN PENDAHULUAN Kanker ServiksSeptri SariОценок пока нет
- Askep Ca Serviks LengkapДокумент26 страницAskep Ca Serviks LengkapAnnisa IchaОценок пока нет
- LP Ca OvaryДокумент12 страницLP Ca OvaryOckta KaruniaОценок пока нет
- Ca OvariumДокумент18 страницCa Ovariumrahayu ramadhaniОценок пока нет
- PPT CA MammaeДокумент31 страницаPPT CA MammaeMhd Soewandi GunawanОценок пока нет
- Seminar Kasus Maternitas RS - Kelompok T2Документ44 страницыSeminar Kasus Maternitas RS - Kelompok T2Tian Nopita SariОценок пока нет
- Ok 6 Radikal HisterektomyДокумент14 страницOk 6 Radikal HisterektomyReni YesОценок пока нет
- LAPORAN PENDAHULUAN CA OVARIUM - RevisiДокумент25 страницLAPORAN PENDAHULUAN CA OVARIUM - RevisiKadek Krisma scoutОценок пока нет
- Ca Ovarium-1Документ19 страницCa Ovarium-1Chesa SafiraОценок пока нет
- Bab 2Документ25 страницBab 2Sara ListiОценок пока нет
- Askep Cancer OvariumДокумент27 страницAskep Cancer OvariumAdistidinda TiaraОценок пока нет
- Slide CA OvariumДокумент26 страницSlide CA OvariumAnastanio D AnugrahОценок пока нет
- PPK Ca CervixДокумент7 страницPPK Ca Cervixuntuk officeОценок пока нет
- Mikrobiologi Perubatan I: Patogen dan Mikrobiologi ManusiaОт EverandMikrobiologi Perubatan I: Patogen dan Mikrobiologi ManusiaРейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (2)
- Kuesioner Audit BaruДокумент9 страницKuesioner Audit Barunia tiyasОценок пока нет
- R. Pelayanan ObatДокумент1 страницаR. Pelayanan Obatnia tiyasОценок пока нет
- No AntrianДокумент13 страницNo Antriannia tiyasОценок пока нет
- KolposkopiДокумент11 страницKolposkopinia tiyasОценок пока нет
- SOP Penggunaan Ambulance RujukanДокумент2 страницыSOP Penggunaan Ambulance RujukanbaguseОценок пока нет
- MTBSДокумент1 страницаMTBSnia tiyasОценок пока нет
- 2.3.17.1 SK Ketersediaan Data Dan InformasiДокумент2 страницы2.3.17.1 SK Ketersediaan Data Dan InformasiZulfadliansyah Nur50% (6)
- SK Penjaga MalamДокумент2 страницыSK Penjaga Malamnia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Kuesioner Audit BaruДокумент9 страницKuesioner Audit Barunia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Struktur Organisasi Program UkmДокумент1 страницаStruktur Organisasi Program Ukmnia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Poa BatraДокумент3 страницыPoa BatraYulika Jaya Susilo100% (3)
- 2.3.17.1 SK Ketersediaan Data Dan InformasiДокумент2 страницы2.3.17.1 SK Ketersediaan Data Dan InformasiZulfadliansyah Nur50% (6)
- Poa BatraДокумент3 страницыPoa BatraYulika Jaya Susilo100% (3)
- SOP Penggunaan Ambulance RujukanДокумент2 страницыSOP Penggunaan Ambulance RujukanbaguseОценок пока нет
- Blanko Program Ukm 2Документ50 страницBlanko Program Ukm 2nia tiyasОценок пока нет
- SK Kebijakan Penanggulangan KebakaranДокумент8 страницSK Kebijakan Penanggulangan KebakaranAby Khan100% (2)
- Sop Pemeliharaan Dan Pemantauan Instalasi Listrik, Air, Ventilasi, GasДокумент4 страницыSop Pemeliharaan Dan Pemantauan Instalasi Listrik, Air, Ventilasi, GasHusna Chusney100% (1)
- PMK No 779 Tentang Standar Pelayanan Anestesiologi Dan Reanimasi PDFДокумент41 страницаPMK No 779 Tentang Standar Pelayanan Anestesiologi Dan Reanimasi PDFImansyah DoankОценок пока нет
- SOP Pengumpulan, Penyimpanan, Dan Retriying (Pencarian Kembali) DataДокумент2 страницыSOP Pengumpulan, Penyimpanan, Dan Retriying (Pencarian Kembali) DataEko Prastyo71% (7)
- Contoh SK KeslingДокумент2 страницыContoh SK Keslingalchudori100% (7)
- Blanko Program Ukm 2Документ50 страницBlanko Program Ukm 2nia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Materi Laporan Hasil AuditДокумент21 страницаMateri Laporan Hasil Auditrdtyou100% (3)
- Kriteria 4.1.3Документ5 страницKriteria 4.1.3nia tiyasОценок пока нет
- SK Pemantauan Lingkungan FisikДокумент2 страницыSK Pemantauan Lingkungan Fisiknia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Sop Menyapu LantaiДокумент15 страницSop Menyapu LantaiHarmonisZipperer100% (5)
- Kartu BerobatДокумент4 страницыKartu Berobatnia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Surat Pernyataan Bersedia Dinyatakan GugurДокумент3 страницыSurat Pernyataan Bersedia Dinyatakan Gugurnia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Kriteria 4.1.3Документ5 страницKriteria 4.1.3nia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Surat Pernyataan Bersedia Dinyatakan GugurДокумент3 страницыSurat Pernyataan Bersedia Dinyatakan Gugurnia tiyasОценок пока нет
- Lapkas Paru Pulmonary EdemaДокумент32 страницыLapkas Paru Pulmonary EdemaNick JuniorОценок пока нет
- Latihan AsertifДокумент25 страницLatihan AsertifEka Putra SangajiОценок пока нет
- Daftar PustakaДокумент4 страницыDaftar PustakadsymncaaОценок пока нет
- LPLPOДокумент17 страницLPLPOWirОценок пока нет