Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Institute, Standards Planning and Requirements Committee, Is An Abstract Design Standard For A
Загружено:
jalpa0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров9 страницdbms
Оригинальное название
dbms
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документdbms
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров9 страницInstitute, Standards Planning and Requirements Committee, Is An Abstract Design Standard For A
Загружено:
jalpadbms
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 9
TheANSI-SPARC Architecture, where ANSI-
SPARC stands forAmerican National Standards
Institute, Standards Planning And Requirements
Committee, is an abstract design standard for a
Database Management System(DBMS), first
proposed in 1975.[1]
The ANSI-SPARC model however never became a
formal standard. No mainstream DBMS systems are
fully based on it (they tend not to exhibit full
physical independence or to prevent direct user
access to the conceptual level), but the idea of
logical data independence is widely adopted.
The internal structure of the database should be unaffected by
changes to the physical aspects of the storage: For example, a
changeover to a new disk.
Three level are:
External level
Conceptual level
Internal level
The Three Level Architecture has the aim of enabling users to
access the same data but with a personalised view of it. The
distancing of the internal level from the external level means
that users do not need to know how the data is physically
stored in the database. This level separation also allows the
Database Administrator (DBA) to change the database storage
structures without affecting the users' views.
In this architecture, the overall database
description can be defined at three levels,
namely, internal, conceptual, and external
levels and thus, namedthree-level
DBMS architecture
Three schemas (internal, conceptual and
external) show how the database is
internally and externally structured, and so
this type of database architecture is also
known as the three-schema architecture.
External level
External Level (User Views): A user's
view of the database describes a part of
the database that is relevant to a
particular user. It excludes irrelevant
data as well as data which the user is not
authorised to access.
Theexternal schemasdescribe the
different external views of the data and
there may be many external schemas for
a given database.
External level
The users view of the database.
Consists of a number of different external views of
the DB.
Describes part of the DB for particular group of users.
Provides a powerful and flexible security
mechanism by hiding parts of the DB from
certain users. The user is not aware of the
existence of any attributes that are missing from
the view.
It permits users to access data in a way that is
customized to their needs, so that the same data can
The External or View Level:
The external or view level is the highest level of
abstraction of database. It provides a window on the
conceptual view, which allows the user to see only the
data of interest to them. The user can be either an
application program or an end user. There can be many
external views as any number of external schema can
be defined and they can overlap each other. It consist of
the definition of logical records and relationships in the
external view. It also contains the method of deriving
the objects such as entities, attributes and relationships
in the external view from the conceptual view.
The External Level (User Representation of
Data)
This is the uppermostlevel in the database. It
implements the concept of abstraction as much
as possible. This level is also known as the view
level because it deals with how a user views your
database. The external level is what allows a user
to access a customized version of the data in
your database. Multiple users can work on a
database on the same time because of it.
The external level also hides the
working of the database from your
users. It maintains the security of the
database by giving users access only
to the data which they need at a
particular time. Any data that is not
needed will not be displayed.
.
Вам также может понравиться
- 4 The Three-Level ANSI-SPARC ArchitectureДокумент25 страниц4 The Three-Level ANSI-SPARC Architecturejonnathan mandelaОценок пока нет
- DBMS Architecture OverviewДокумент27 страницDBMS Architecture OverviewanishaОценок пока нет
- Dbms QB Solution Tt-1Документ15 страницDbms QB Solution Tt-1Ojas PatilОценок пока нет
- DBMSДокумент139 страницDBMSkushagraОценок пока нет
- Deck 01 Database TechnologyДокумент29 страницDeck 01 Database TechnologyEida IzanamiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 - Database Schema (ANSI SPARC)Документ14 страницLecture 3 - Database Schema (ANSI SPARC)Njemax PanasheОценок пока нет
- DBMS Chap 01Документ46 страницDBMS Chap 01Kamada Akshay VarmaОценок пока нет
- Three-Level ANSI ArchitectureДокумент20 страницThree-Level ANSI ArchitectureAnonymous 6jZZaDOLkОценок пока нет
- DBMS Chap 01Документ46 страницDBMS Chap 01radwanОценок пока нет
- Database Systems 2Документ17 страницDatabase Systems 2SameedОценок пока нет
- Three Level ArchitectureДокумент24 страницыThree Level Architecturecrybert zinyamaОценок пока нет
- Information System and ArchitectureДокумент4 страницыInformation System and ArchitectureCyrus R. FloresОценок пока нет
- The Database Management System DBMSДокумент15 страницThe Database Management System DBMSRichard LumawagОценок пока нет
- Architecture of DbmsДокумент20 страницArchitecture of Dbmsrr3870044Оценок пока нет
- 1.architecture of DBMSДокумент25 страниц1.architecture of DBMSAyush Pratap SinghОценок пока нет
- RDBMS - M01 - C01 - PPT - Overview of Database Management SystemДокумент47 страницRDBMS - M01 - C01 - PPT - Overview of Database Management SystemAman SharmaОценок пока нет
- Db-Ansi Sparc ArchitectureДокумент8 страницDb-Ansi Sparc ArchitectureAisha KhanОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Part 1Документ66 страницUnit 1 - Part 1Pawan KumarОценок пока нет
- DBMS Chap 01Документ45 страницDBMS Chap 01sanduniОценок пока нет
- Module I: Introduction To DbmsДокумент31 страницаModule I: Introduction To DbmsIshika SinghalОценок пока нет
- CSC9Q5 / ITNP31 (31Q5 / IT31) : Database Principles and ApplicationsДокумент24 страницыCSC9Q5 / ITNP31 (31Q5 / IT31) : Database Principles and ApplicationsgenearesОценок пока нет
- Introduction of DB: Database System Concepts and ArchitectureДокумент23 страницыIntroduction of DB: Database System Concepts and ArchitectureZahid AhmadОценок пока нет
- DBMS Lec3Документ41 страницаDBMS Lec3ZainОценок пока нет
- ANSI-SPARC Three-Level ArchitectureДокумент4 страницыANSI-SPARC Three-Level ArchitectureShaurya Ashutosh BhatnagarОценок пока нет
- Database and Data ModelingДокумент31 страницаDatabase and Data ModelingKudakwashe MotsiОценок пока нет
- ch-1 - Introduction To DbmsДокумент38 страницch-1 - Introduction To DbmsRahul SharmaОценок пока нет
- Three-level architecture separates user views from physical dataДокумент7 страницThree-level architecture separates user views from physical dataShokin AliОценок пока нет
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureДокумент30 страницDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureAyush RathoreОценок пока нет
- Unit No.1 Introduction DBMS - Concepts & ArchitecturesДокумент29 страницUnit No.1 Introduction DBMS - Concepts & ArchitecturesPadre BhojОценок пока нет
- Review Question CHДокумент6 страницReview Question CHnour ghanaymОценок пока нет
- Database Management System: (BCAC-401)Документ16 страницDatabase Management System: (BCAC-401)Akash HalsanaОценок пока нет
- DBMSДокумент61 страницаDBMSsangiwenmoyoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1.1.4 AND 1.1.5 (Architecture of DBMS)Документ19 страницLecture 1.1.4 AND 1.1.5 (Architecture of DBMS)Ankit RajputОценок пока нет
- DBMSДокумент61 страницаDBMSvikrant kumarОценок пока нет
- DBMSДокумент61 страницаDBMSShubham MehtaОценок пока нет
- Databases:Collection of Data DBMS:It Is A Software Used To Manage The Collection of Data. It Is A Software Used To Manage The DatabaseДокумент48 страницDatabases:Collection of Data DBMS:It Is A Software Used To Manage The Collection of Data. It Is A Software Used To Manage The DatabaseNandlal KamatОценок пока нет
- Database Management NotesДокумент20 страницDatabase Management NotesPrachiti ChavanОценок пока нет
- DB02 - Database System ArchitectureДокумент53 страницыDB02 - Database System ArchitectureAli HumairОценок пока нет
- Meatik Lecture6 Intro 2022 2023Документ40 страницMeatik Lecture6 Intro 2022 2023Ad SoyadОценок пока нет
- WINSEM2019-20 CCA3718 TH VL2019205003785 Reference Material I 05-Dec-2019 Schema Arch and Users 2Документ20 страницWINSEM2019-20 CCA3718 TH VL2019205003785 Reference Material I 05-Dec-2019 Schema Arch and Users 2VickyОценок пока нет
- Database Purpose and ViewsДокумент126 страницDatabase Purpose and Viewsrewop sriОценок пока нет
- 0 - Lesson02 DBMS01Документ40 страниц0 - Lesson02 DBMS01Recheleto M. LargusaОценок пока нет
- Data, Information and KnowledgeДокумент12 страницData, Information and KnowledgebirjubrijeshОценок пока нет
- Models of Database and Database Design: Lecture TwoДокумент15 страницModels of Database and Database Design: Lecture TwoStar69 Stay schemin2Оценок пока нет
- Q Define Database, Data, DBMS, State Purpose of DatabaseДокумент20 страницQ Define Database, Data, DBMS, State Purpose of Databasenaresh sainiОценок пока нет
- Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology School of Computer EngineeringДокумент14 страницKalinga Institute of Industrial Technology School of Computer Engineering089ASHUTOSH PATIОценок пока нет
- Databases 2Документ30 страницDatabases 2Shahzeb BashirОценок пока нет
- Ansi SparcДокумент2 страницыAnsi Sparcakha_d6d9Оценок пока нет
- Dbms Schemas:: Internal, Conceptual, ExternalДокумент11 страницDbms Schemas:: Internal, Conceptual, ExternalEichhorst AutomobilesОценок пока нет
- ISYS6508 Database System: Week 1 Introduction To Database & EnvironmentДокумент28 страницISYS6508 Database System: Week 1 Introduction To Database & EnvironmentRapik HardiantoОценок пока нет
- Objectives of ThreeДокумент3 страницыObjectives of ThreeKhaled Ibne Rashid PatwaryОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Three Level ArchitectureДокумент50 страницChapter 2 Three Level ArchitectureAnkit RajputОценок пока нет
- Dbms Unit 1-1Документ87 страницDbms Unit 1-1Raghav SharmaОценок пока нет
- Birara DB AssignmentДокумент9 страницBirara DB AssignmentBarie WakjiraОценок пока нет
- Introduction of DBMSДокумент89 страницIntroduction of DBMSStory TellingОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Part 1Документ44 страницыUnit 1 - Part 1Harsh BhardwajОценок пока нет
- RELATIONAL DATABASES AND SQL FUNDAMENTALSДокумент116 страницRELATIONAL DATABASES AND SQL FUNDAMENTALSjgjeslinОценок пока нет
- 6 IntroductionДокумент44 страницы6 IntroductionAditya AnandОценок пока нет
- To DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeДокумент14 страницTo DBMS: Dulal Ch. Sahana Dept. of Computer Science Bankura Christian CollegeDulal SahanaОценок пока нет
- 2 - Access Layer (Phase 1)Документ32 страницы2 - Access Layer (Phase 1)MostafaEl-sayedОценок пока нет
- JAP305 Lecture 9Документ5 страницJAP305 Lecture 9markjohnОценок пока нет
- File ServerДокумент3 страницыFile Serversami.yaha100% (1)
- Unit 3Документ12 страницUnit 3sreva2703Оценок пока нет
- Resume Print NowДокумент2 страницыResume Print NowDaniel DingОценок пока нет
- MySQL SubQuery Tutorial With ExamplesДокумент3 страницыMySQL SubQuery Tutorial With ExamplesSantosh KumarОценок пока нет
- SE 100 Midterm 2 PDFДокумент12 страницSE 100 Midterm 2 PDFM.SОценок пока нет
- Puppet Manual PDFДокумент459 страницPuppet Manual PDFsmittyraj100% (1)
- 5GLab DescДокумент1 страница5GLab DescNaved AlamОценок пока нет
- AIX 64bit Performance in Focus - sg245103Документ218 страницAIX 64bit Performance in Focus - sg245103iak1973Оценок пока нет
- Review PythonДокумент12 страницReview PythonRachna TomarОценок пока нет
- Performance Description EPLAN Electric P8 v2.5 (EN) PDFДокумент80 страницPerformance Description EPLAN Electric P8 v2.5 (EN) PDFAdhitya ReОценок пока нет
- Experiment NoДокумент30 страницExperiment NoSwati Sharma0% (1)
- Instructions For Using PrintersДокумент8 страницInstructions For Using PrintersbiancaachimОценок пока нет
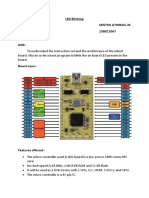
- LED Blinking ExpДокумент7 страницLED Blinking ExpSenthil AthibanОценок пока нет
- Huawei: H13-811 - V3.0 ExamДокумент112 страницHuawei: H13-811 - V3.0 Examia.2023i.epicsОценок пока нет
- Sms 2003 - SCCM 2007 - SCCM - Sms VbscriptДокумент23 страницыSms 2003 - SCCM 2007 - SCCM - Sms VbscriptmikecosoОценок пока нет
- Blue-Sky Conversion ProjectДокумент9 страницBlue-Sky Conversion ProjectNikita JainОценок пока нет
- CN3200 Data SheetДокумент2 страницыCN3200 Data Sheetjr_gm_2Оценок пока нет
- Ancel OBD Bluetooth User ManualДокумент2 страницыAncel OBD Bluetooth User ManualFordiОценок пока нет
- MITRASTAR DSL-2401HNA-T1CC-2016-08-24 DatasheetДокумент2 страницыMITRASTAR DSL-2401HNA-T1CC-2016-08-24 DatasheetCarlosОценок пока нет
- Estimate guidelines summaryДокумент14 страницEstimate guidelines summaryRamelfebea Montedelobenia100% (1)
- Video Pro X EN PDFДокумент434 страницыVideo Pro X EN PDFJ Esmil Rodriguez100% (1)
- 115 CloudДокумент9 страниц115 CloudNuthan Nikky SumaОценок пока нет
- SAP BW/HANA Consultant Jyoti Swanjary ResumeДокумент4 страницыSAP BW/HANA Consultant Jyoti Swanjary ResumeraamanОценок пока нет
- Maintain Master Clocks Slave Clocks GPS ReceiverДокумент13 страницMaintain Master Clocks Slave Clocks GPS Receivernsn_johnОценок пока нет
- Freesat v7 ManualДокумент28 страницFreesat v7 Manualmuhammadpauzi0% (1)
- Guía de Actividades y Rúbrica de Evaluación - Tarea 1 - El Concepto de IntegralДокумент46 страницGuía de Actividades y Rúbrica de Evaluación - Tarea 1 - El Concepto de IntegralDany Fernando RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Opengl CodeДокумент7 страницOpengl CodeGouree DeshpandeОценок пока нет
- 0.0.0.1 Lab - Initializing and Reloading A Router and Switch - ILMДокумент14 страниц0.0.0.1 Lab - Initializing and Reloading A Router and Switch - ILMCarlitosGuardapucllaОценок пока нет