Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biomass: Alternative Sources of Green Energy
Загружено:
CrichelleMae0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
34 просмотров12 страницBiomass
Оригинальное название
Biomass
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документBiomass
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
34 просмотров12 страницBiomass: Alternative Sources of Green Energy
Загружено:
CrichelleMaeBiomass
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 12
BIOMASS
ALTERNATIVE SOURCES OF GREEN ENERGY
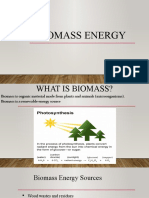
WHAT IS BIOMASS?
It is biological material derived from living, or recently living organisms.
In the context of biomass for energy this is often used to mean plant
based material, but biomass can equally apply to both animal and
vegetable derived material.
is carbon based and is composed of a mixture of organic molecules
containing hydrogen, usually including atoms of oxygen, often
nitrogen and also small quantities of other atoms, including alkali,
alkaline earth and heavy metals. These metals are often found in
functional molecules such as the porphyrins which include chlorophyll
which contains magnesium.
PLANT MATERIAL
The carbon used to construct biomass is absorbed from the atmosphere as
carbon dioxide (CO2) by plant life, using energy from the sun. Plants may
subsequently be eaten by animals and thus converted into animal biomass.
However the primary absorption is performed by plants.
If plant material is not eaten it is generally either broken down by micro-
organisms or burned:
If broken down it releases the carbon back to the atmosphere, mainly as
either carbon dioxide (CO2) or methane (CH4), depending upon the
conditions and processes involved.
If burned the carbon is returned to the atmosphere as CO2. These processes
have happened for as long as there have been plants on Earth and is part of
what is known as the carbon cycle.
FOSSIL FUEL
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas are also derived from biological material,
however material that absorbed CO2 from the atmosphere many millions of
years ago.
As fuels they offer high energy density, but making use of that energy
involves burning the fuel, with the oxidation of the carbon to carbon dioxide
and the hydrogen to water (vapour). Unless they are captured and stored,
these combustion products are usually released to the atmosphere, returning
carbon sequestered millions of years ago and thus contributing to increased
atmospheric concentrations.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN BIOMASS
AND FOSSIL FUEL
The vital difference between biomass and fossil fuels is one of time scale.
Biomass takes carbon out of the atmosphere while it is growing, and returns it
as it is burned. If it is managed on a sustainable basis, biomass is harvested
as part of a constantly replenished crop. This is either during woodland or
arboricultural management or coppicing or as part of a continuous
programme of replanting with the new growth taking up CO2 from the
atmosphere at the same time as it is released by combustion of the previous
harvest.
This maintains a closed carbon cycle with no net increase in atmospheric
CO2 levels.
CATEGORIES OF BIOMASS
MATERIALS
The realities of the economics mean that high value material for which there is an
alternative market, such as good quality, large timber, are very unlikely to become
available for energy applications. However there are huge resources of residues, co-
products and waste that exist in the UK which could potentially become available, in
quantity, at relatively low cost, or even negative cost where there is currently a
requirement to pay for disposal. There are five basic categories of material:
Virgin wood, from forestry, arboricultural activities or from wood processing
Energy crops: high yield crops grown specifically for energy applications
Agricultural residues: residues from agriculture harvesting or processing
Food waste, from food and drink manufacture, preparation and processing, and
post-consumer waste
Industrial waste and co-products from manufacturing and industrial processes.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
ADVANTAGES OF BIOMASS
1. No Harmful Emissions: Biomass energy, for the most part, creates no harmful
carbon dioxide emissions. Many energy sources used today struggle to control their
carbon dioxide emissions, as these can cause harm to the ozone layer and increase
the effects of greenhouse gases, potentially warming the planet. It is completely
natural, has no such carbon dioxide side effects in its use.
2. Clean Energy: Because of its relatively clean use, biomass energy, when used in
commercial businesses such as airlines, receives tax credit from the US government.
This is good for the environment and good for business. It does release carbon
dioxide but captures carbon dioxide for its own growth. Carbon dioxide released by
fossil fuel are released into the atmosphere and are harmful to the environment
3. Abundant and Renewable: Biomass products are abundant and renewable. Since
they come from living sources, and life is cyclical, these products potentially never
run out, so long as there is something living on earth and there is someone there to
turn that living things components and waste products into energy. In the United
Kingdom, biomass fuels are made from recycled chicken droppings. In the United
States and Russia, there are plentiful forests for lumber to be used in the production
of biomass energy.
ADVANTAGES OF BIOMASS
4. Reduce Dependency on Fossil Fuels: It has developed as an alternate
source of fuel for many homeowners and have helped them to reduce their
dependency on fossil fuels.
5. Reduce Landfills: Another benefit of this energy is that it can take waste
that is harmful to the environment and turn it into something useful. For
instance, garbage as landfill can, at least partially, be burned to create
useable biomass energy.
6. Can be Used to Create Different Products: Biomass energy is also versatile,
as different forms of organic matter can be used to create different
products. Ethanol and similar fuels can be made from corn and other crops.
With so many living things on the planet, there is no limit to how many ways it
can be found and used.
DISADVANTAGES OF BIOMASS
1. Expensive: Firstly, its expensive. Living things are expensive to care for, feed, and
house, and all of that has to be considered when trying to use waste products from
animals for fuel.
2. Inefficient as Compared to Fossil Fuels: Secondly, and connected to the first, is the
relative inefficiency of biomass energy. Ethanol, as a biodiesel is terribly inefficient
when compared to gasoline, and it often has to be mixed with some gasoline to
make it work properly anyway. On top of that, ethanol is harmful to combustion
engines over long term use.
3. Harmful to Environment: Thirdly, using animal and human waste to power engines
may save on carbon dioxide emissions, but it increases methane gases, which are
also harmful to the Earths ozone layer. So really, we are no better off
environmentally for using one or the other. And speaking of using waste products,
there is the smell to consider. While it is not physically harmful, it is definitely
unpleasant, and it can attract unwanted pests (rats, flies) and spread bacteria and
infection.
DISADVANTAGES OF BIOMASS
4. Consume More Fuel: Finally, using trees and tree products to power
machines is inefficient as well. Not only does it take a lot more fuel to do the
same job as using conventional fuels, but it also creates environmental
problems of its own. To amass enough lumber to power a nation full of
vehicles or even a power plant, companies would have to clear
considerable forest area. This results in major topological changes and
destroys the homes of countless animals and plants.
5. Require More Land: Combustion of biomass products require some land
where they can easily be burnt. Since, it produces gases like methane in
atmosphere; therefore it can be produced in those areas which are quite far
from residential homes.
APPLICATIONS OF BIOMASS
Biomass systems range from small stoves used in homes for heating or
cooking to large power plants used by centralized utilities to produce
electricity.
In residential applications, biomass can be used for space heating or for
cooking. Wood is the most common source of fuel, although many different
materials are used. New designs for woodstoves can improve the efficiency
of the cooking or heating system, decreasing the amount of fuel that is
needed.
Industry and businesses use biomass for several purposes including space
heating, hot water heating, and electricity generation. Many industrial
facilities, such as lumber mills, naturally produce organic waste.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Holy Rosary - Ang Santo Rosaryo (Bookfold)Документ4 страницыThe Holy Rosary - Ang Santo Rosaryo (Bookfold)Filipino Ministry Council89% (148)
- Advanced Biomass Gasification: New Concepts for Efficiency Increase and Product FlexibilityОт EverandAdvanced Biomass Gasification: New Concepts for Efficiency Increase and Product FlexibilityРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Jonathan's Last Day: True FalseДокумент2 страницыJonathan's Last Day: True FalseDiego Luis Gonzalez RestrepoОценок пока нет
- Animal Research Protocol FormДокумент8 страницAnimal Research Protocol FormMary Angelique UyОценок пока нет
- Biomass Power PlantДокумент4 страницыBiomass Power PlantAldi ErzanuariОценок пока нет
- BiomassДокумент5 страницBiomassbabeОценок пока нет
- BIOMASSДокумент25 страницBIOMASSAnri LiuОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент8 страницAssignmentsandhyabhargava945Оценок пока нет
- BiomassДокумент6 страницBiomassSaddang SaputraОценок пока нет
- Renewable Energy Lecture 8Документ17 страницRenewable Energy Lecture 8TABARK SHAKIRОценок пока нет
- Bioenergy, Biomass, and Its Products - PradnyaДокумент31 страницаBioenergy, Biomass, and Its Products - PradnyaPradnya BedekarОценок пока нет
- Biomass Properties and Handling: Pre-LabДокумент29 страницBiomass Properties and Handling: Pre-LabRiju DuttaОценок пока нет
- Biomass PresentationДокумент17 страницBiomass Presentationمحمد الرشدانОценок пока нет
- Waste To EnegryДокумент80 страницWaste To EnegryFaizan KhanОценок пока нет
- Bioenergy (VoiceДокумент18 страницBioenergy (VoiceVrij Mohan VidyarthiОценок пока нет
- The Basics of BiomassДокумент24 страницыThe Basics of BiomassAngelica Cabuco0% (1)
- Biofuels By: Prof. Ashish BandewarДокумент80 страницBiofuels By: Prof. Ashish BandewarCpt. ZeeNicОценок пока нет
- BRL Files 2011 10 BRL Biomassprop StudentДокумент27 страницBRL Files 2011 10 BRL Biomassprop StudentDusan LakovicОценок пока нет
- Biomass EnergyДокумент6 страницBiomass EnergyStevenОценок пока нет
- Lecture Biomass3Документ3 страницыLecture Biomass3asaminew awokeОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 NCES PDFДокумент68 страницUnit 3 NCES PDFashu soniОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5Документ55 страницLecture 5Kauthar MaalimОценок пока нет
- Fis Ling EnergyДокумент26 страницFis Ling EnergyBarageОценок пока нет
- 3.0 Biofuel TechnologyДокумент2 страницы3.0 Biofuel TechnologyDineswar SmkboyzОценок пока нет
- POPLADE Final PaperДокумент11 страницPOPLADE Final PaperRacОценок пока нет
- Biomass As An Energy SourceДокумент24 страницыBiomass As An Energy Sourceodebunmi taiwoОценок пока нет
- Non Food Base Biomass: Group # 11 Roll# 2011-ch-238 2011-ch-244 2011-ch-268Документ19 страницNon Food Base Biomass: Group # 11 Roll# 2011-ch-238 2011-ch-244 2011-ch-268Anonymous b9fcR5Оценок пока нет
- Biomass EnergyДокумент9 страницBiomass EnergyHj JayatheerthaОценок пока нет
- Bio Pallets Advantages & DisadvantagesДокумент3 страницыBio Pallets Advantages & DisadvantagesImran HaqОценок пока нет
- Biomass 3Документ5 страницBiomass 3Claudia Garrote FuilleratОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5Документ42 страницыLecture 5Kauthar MaalimОценок пока нет
- Biomass Is Defined As The Biological Degradable Fraction of Products, Waste and ResiduesДокумент9 страницBiomass Is Defined As The Biological Degradable Fraction of Products, Waste and Residuesadil malikОценок пока нет
- Fuel For Future THE Algae Biofuel: Zahraa Abbas (Student of Environmental Engineering)Документ15 страницFuel For Future THE Algae Biofuel: Zahraa Abbas (Student of Environmental Engineering)ado cОценок пока нет
- M4. BioconversionДокумент57 страницM4. Bioconversionvikash21ugОценок пока нет
- BiogasДокумент26 страницBiogasTALLURI LAKSHMI PRASANNAОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three 3. Project Title (Case Study) Assessing The Advantage of Using Biomass As Fuel Over Furnace Oil To Produce Steam in BoilerДокумент8 страницChapter Three 3. Project Title (Case Study) Assessing The Advantage of Using Biomass As Fuel Over Furnace Oil To Produce Steam in BoileretayhailuОценок пока нет
- BiomassДокумент53 страницыBiomassrajiv kundalaОценок пока нет
- Biomass To Energy TeofistoДокумент13 страницBiomass To Energy TeofistoCarren MarquezОценок пока нет
- Biomass Energ Final1)Документ19 страницBiomass Energ Final1)Bishal BОценок пока нет
- "Biomass Research": Private University Antenor OrregoДокумент5 страниц"Biomass Research": Private University Antenor OrregoRaysa Ortiz CorreaОценок пока нет
- BiomassДокумент12 страницBiomassSainadh Reddy Syamala AP21110010703Оценок пока нет
- Biomass-Renewable Energy From Plants and AnimalsДокумент4 страницыBiomass-Renewable Energy From Plants and AnimalsSin Navier StokesОценок пока нет
- Biomass and Biofuels PDFДокумент81 страницаBiomass and Biofuels PDFElliot ThokzОценок пока нет
- Group 3Документ41 страницаGroup 3Marcelo AmandoronОценок пока нет
- What Is BiomassДокумент19 страницWhat Is BiomassWrenhartingОценок пока нет
- 9.1 Biomass Production: 9.1.1 Direct MethodsДокумент18 страниц9.1 Biomass Production: 9.1.1 Direct MethodssahitОценок пока нет
- Biomass: Sustainable EnergyДокумент10 страницBiomass: Sustainable EnergyNagendrababu RamisettyОценок пока нет
- Where Do Trees Get Their Mass FromДокумент37 страницWhere Do Trees Get Their Mass FromPunjajiОценок пока нет
- Lecture Biomass Biofuel 012129Документ11 страницLecture Biomass Biofuel 012129Kenzie WalipiОценок пока нет
- Handling of Biomass, Convert This Problem To Opportunity: Prasoon Kumar Gupta 187048 Chemical Engineering DepartmentДокумент21 страницаHandling of Biomass, Convert This Problem To Opportunity: Prasoon Kumar Gupta 187048 Chemical Engineering DepartmentprasoonОценок пока нет
- Bioenergy: Arch. Shereen Omar Khashaba Cairo University Ph.D.Документ19 страницBioenergy: Arch. Shereen Omar Khashaba Cairo University Ph.D.Ahmad ZaeniОценок пока нет
- Biomass Energy: Mubashir Imdad 02-134191-118 BS (CS) - 1BДокумент4 страницыBiomass Energy: Mubashir Imdad 02-134191-118 BS (CS) - 1BMubashir ImdadОценок пока нет
- 143 Are Biofuels Carbon NeutralДокумент2 страницы143 Are Biofuels Carbon NeutralSan SiddzОценок пока нет
- BiomassДокумент21 страницаBiomassDaniele Joseph HizonОценок пока нет
- Biomass Power PlantДокумент5 страницBiomass Power Plantmikko intalОценок пока нет
- BiomassДокумент2 страницыBiomassJasmine AustriaОценок пока нет
- Conversion of Biomass: Presented By-Gurpreet Singh L-2K16-AE - 178-MДокумент86 страницConversion of Biomass: Presented By-Gurpreet Singh L-2K16-AE - 178-Mkannan000Оценок пока нет
- Bi0mass EnergyДокумент29 страницBi0mass EnergyVRUSHABHОценок пока нет
- 18cho101t Unit 3 Biomass EnergyДокумент66 страниц18cho101t Unit 3 Biomass EnergyHruday CoolkidОценок пока нет
- BiomassДокумент22 страницыBiomassrevilomisa0821Оценок пока нет
- (EG - Energy Resources - 2020/07/03) BiofuelДокумент40 страниц(EG - Energy Resources - 2020/07/03) BiofuelPrasanth mallavarapuОценок пока нет
- A Project Report On Designing of A Biogas PlantДокумент11 страницA Project Report On Designing of A Biogas PlantJafar JilaniОценок пока нет
- Bio Ethanol DBGДокумент30 страницBio Ethanol DBGGhulam RabbaniОценок пока нет
- India Bix 2Документ59 страницIndia Bix 2CrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Computer ProgrammingДокумент129 страницIntroduction To Computer ProgrammingCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Eset Nod32 Antivirus Keys Valid 2020Документ2 страницыEset Nod32 Antivirus Keys Valid 2020CrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes in Discrete Mathematics: Marcel B. Finan Arkansas Tech University C All Rights ReservedДокумент224 страницыLecture Notes in Discrete Mathematics: Marcel B. Finan Arkansas Tech University C All Rights ReservedGerardo L. Lo50% (2)
- Basic Units of Data StorageДокумент3 страницыBasic Units of Data StorageCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Special Purpose Op Amp Circuits 2Документ7 страницSpecial Purpose Op Amp Circuits 2CrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- INDIABIX (MCQs Elecs)Документ94 страницыINDIABIX (MCQs Elecs)CrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- PESOSENSE Ipon Challenge 2018 Shade and Save PDFДокумент1 страницаPESOSENSE Ipon Challenge 2018 Shade and Save PDFCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Daily ScripturesДокумент8 страницDaily ScripturesCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Chemical Energy To Electrical Energy ConversionДокумент37 страницChemical Energy To Electrical Energy ConversionCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- PESOSENSE Ipon Challenge 2018 Shade and Save PDFДокумент1 страницаPESOSENSE Ipon Challenge 2018 Shade and Save PDFCrichelleMae0% (1)
- Pope Francis's Invitation: Catholic Moral TheologyДокумент7 страницPope Francis's Invitation: Catholic Moral TheologyCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- QuestionsДокумент32 страницыQuestionsCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Transducer ClassificationsДокумент34 страницыTransducer ClassificationsCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- AnswersДокумент6 страницAnswersCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Bluetooth HC 05Документ13 страницBluetooth HC 05Jaime Leonardo CruzОценок пока нет
- Lalaganan Name Ta Sa IDДокумент2 страницыLalaganan Name Ta Sa IDCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- The Natural and Artificial Concepts of Family Planning SeminarДокумент2 страницыThe Natural and Artificial Concepts of Family Planning SeminarCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Bluetooth HC 05Документ13 страницBluetooth HC 05Jaime Leonardo CruzОценок пока нет
- Apperture Antennas and Horn Antennas: CACERES, Crichelle Mae August 22, 2017Документ7 страницApperture Antennas and Horn Antennas: CACERES, Crichelle Mae August 22, 2017CrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- TransducerДокумент47 страницTransducerCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Radio PropagationДокумент67 страницRadio Propagationmarouen111Оценок пока нет
- Other Types of TransducersДокумент17 страницOther Types of TransducersCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Fossil FuelДокумент10 страницFossil FuelCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Combination 1 (Figure 1)Документ2 страницыCombination 1 (Figure 1)CrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Compound Excited DC MotorДокумент9 страницCompound Excited DC MotorCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Alternative Sources of Green EnergyДокумент61 страницаAlternative Sources of Green EnergyCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Formatted Paper Integral CalculusДокумент1 страницаFormatted Paper Integral CalculusCrichelleMaeОценок пока нет
- Are You Ready For Food Created by An AI - NotCo Is Now Making Its AI Available To Food Companies - by Mercedes' Lens - Jan, 2023 - MediumДокумент5 страницAre You Ready For Food Created by An AI - NotCo Is Now Making Its AI Available To Food Companies - by Mercedes' Lens - Jan, 2023 - MediumMerce CarrizoОценок пока нет
- Travefy Free Itinerary TemplateДокумент5 страницTravefy Free Itinerary TemplateAman kumarОценок пока нет
- Forage Crops WORDДокумент15 страницForage Crops WORDmichael hobayanОценок пока нет
- Grammar Space Beginner 2 WB KeysДокумент23 страницыGrammar Space Beginner 2 WB Keysrahmad bedhoeОценок пока нет
- Exam Question: (ENGLISH) IGCSE A Raisin in The Sun: 479962727Документ2 страницыExam Question: (ENGLISH) IGCSE A Raisin in The Sun: 479962727Jane ChangОценок пока нет
- Talking Tesco: How We CompeteДокумент28 страницTalking Tesco: How We Competepjr007Оценок пока нет
- Periodical Test English 6Документ3 страницыPeriodical Test English 6Clifton MillerОценок пока нет
- Jnana Yoga BookДокумент125 страницJnana Yoga BookFarhana AbirОценок пока нет
- BIOL3401 Analysis 6694Документ16 страницBIOL3401 Analysis 6694Rindy SimОценок пока нет
- Sith Kop 004Документ16 страницSith Kop 004musabОценок пока нет
- SampledatafoodinfoДокумент51 страницаSampledatafoodinfoJunior Fernando Parada CabreraОценок пока нет
- 12 The Malaysian Agricultural Industry in The New MillenniumДокумент20 страниц12 The Malaysian Agricultural Industry in The New MillenniumZainudin MohamedОценок пока нет
- The Fruit of Ancient PersiaДокумент12 страницThe Fruit of Ancient PersiaRafael Esteban Benitez AvendanoОценок пока нет
- Itl Public School Sector - 9, Dwarka: SESSION 2014 - 2015Документ3 страницыItl Public School Sector - 9, Dwarka: SESSION 2014 - 2015ik62299Оценок пока нет
- Ravished by The Wolf Alpha Male Succub Alexander AshleeДокумент162 страницыRavished by The Wolf Alpha Male Succub Alexander AshleeKathy030878% (9)
- Ethnic Culture of The Khasia and Mendi: Prof. Dr. Ashit Boran PaulДокумент17 страницEthnic Culture of The Khasia and Mendi: Prof. Dr. Ashit Boran PaulWorld's GalleryОценок пока нет
- Takdang Aralin SA Filipino "Kasaysayan NG Egypt": Renier Jake S.GalzoteДокумент8 страницTakdang Aralin SA Filipino "Kasaysayan NG Egypt": Renier Jake S.GalzoteRenier Jake GalzoteОценок пока нет
- Homework No. 2: GO Ian Patrick Q. April 9, 2020 BSPH 2AДокумент3 страницыHomework No. 2: GO Ian Patrick Q. April 9, 2020 BSPH 2AArman Renz PauloОценок пока нет
- Dairy Business PlanДокумент19 страницDairy Business Planvinay kumar0% (1)
- English Lum Xii Mars 2024 & KunciДокумент5 страницEnglish Lum Xii Mars 2024 & KunciZhye Anhae ShieyОценок пока нет
- Star ThugsДокумент160 страницStar ThugsGlyn PulmanОценок пока нет
- Coffee Recipes - Hot and Cold Coffee and Espresso Beverages To Make at HomeДокумент66 страницCoffee Recipes - Hot and Cold Coffee and Espresso Beverages To Make at HomeGiancarlo Braccio100% (2)
- WSM West Salem MachineryДокумент7 страницWSM West Salem Machinerymostafa sherifОценок пока нет
- Tiwari S PaperДокумент26 страницTiwari S Paperमान तुम्साОценок пока нет
- Important Drug Nutrient Interactions: Pamela MasonДокумент35 страницImportant Drug Nutrient Interactions: Pamela MasonRijantono Franciscus MariaОценок пока нет
- Inspire 9th NLEPCДокумент4 страницыInspire 9th NLEPCKaushik Kumar HotaОценок пока нет
- Native American Video Student-All AnswersДокумент4 страницыNative American Video Student-All AnswersTony ChoОценок пока нет
- 2Документ47 страниц2Kishor RaiОценок пока нет