Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction FIN - ECFS 2017
Загружено:
niallvvИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction FIN - ECFS 2017
Загружено:
niallvvАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Is there cardiac autonomic dysfunction
among patients with cystic fibrosis?
E Hatziagorou1, S Giannakoulakos2, E Kouidi2, M
Anifanti2, A Kampouras1, A Deligiannis2, J
Tsanakas1
CF Unit, Hippokration Hospital, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
School of Physical Education & Sports Sciences, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
Background
The interaction between cardiac and pulmonary
dysfunction in CF patients, may influence the
autonomic nervous system controlling the heart.
HRV Index
Changes in heart rate variability (HRV) patterns are a
sensitive and early indicator of Cardiac Autonomic
Nervous System dysfunction.
PLOS ONE | 2016
Aim
To assess the cardiac autonomic control by heart
rate variability (HRV) analysis in young patients
with Cystic Fibrosis.
To correlate HRV changes with their respiratory
function.
Methods
2. Cardiopulmonary Exercise
1. Spirometry (FEV1) Testing (VO2peak)
19 stable Godfrey Protocol:
young CF A warm-up period of 3 minutes cycling with 20 Watts
patients Work load was increased by 15 W per minute, for 8-
12 min.
Parameters measured:
Peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak)
Ventilator equivalent ratios for oxygen and
carbon dioxide at peak exercise (VE/VO2,
VE/VCO2)
Anaerobic Threshold (AT)
Breathing reserve at peak exercise (BR%)
Methods
3. HRV Assessment
(24-h Holter monitoring)
TIME DOMAIN MEASURES
Sympatho-vagal balance Standard Deviation of RR Intervals
(SDNN)
Vagal activity Percentage value of RR 50 count
(pNN50)
Square root of the mean of the sum
of the squares of differences
between adjacent RR intervals
(RMSSD)
FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS
Sympathetic activity Low Frequency (LF) component
Vagal activity High Frequency (HF) component
Sympatho-vagal balance LF/HF ratio
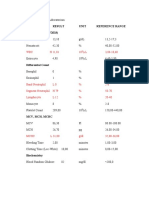
Population characteristics
Mean, sd / N
(%)
Age, year 14.2 4.2
BMI, kg/m2 19.3 3
BMI z score - 0.41 (1.15)
Weight, kg 48.5 13.2
Weight z score -0.58 (0.18)
Height, cm 157 14
Height z score -0.37 (0.53)
F508, Homozygous 4 (21%)
F508, Heterozygous 10 (52.6%)
Pseudomonas 5 (26%)
Aeruginosa
FEV1 % predicted 92.8 (22.10)
Results
CPET Mean (SD)
VO2peak (L/min) 1.85 (0.53)
VO2peak%(%predicted) 75.81 (7.2)
VD/VT (peak exercise) 0.13 (0.05)
VE/VO2 (peak exercise) 32.88 (5.12)
VE/VCO2 (peak exercise) 33.08 (4.98)
Spirometry
FEV1(L) 2.49 (0.93)
% predicted 92.8 (22.10)
FVC(L) 3.37 (0.97)
% predicted 93.66 (16.70)
FEF25-75 2.38 (1.08)
% predicted 75.03 (24.10)
Results - HRV Measurements
CF Normal
values
Mean SD
HR 82.58 (7.65) 60-100
(beats/min)
SDNN (ms) 98.21 (23.69) >110
pNN50 24.36 (11.75) >32
RMSSD (ms) 64.08 (29.73) >100
LF:HF 2.46 (1.18) <1.5
Autonomic dysfunction was not correlated
with FEV1 or VO2peak
140 p=0.984 3.5
120 3.0 p=0.958
100 2.5
80 2.0
SDNN
SDNN
60 1.5
40 1.0
20 0.5
0 0.0
50 70 90 110 130 150 50 70 90 110 130 150
FEV1 VOpeak
SDNN correlation with FEV1 & VO2Peak
Autonomic dysfunction was not correlated
with FEV1 or VO2peak
6 6
5 p= 0.245 5 p=0.135
4 4
LF/HF
LF/HF
3 3
2 2
1 1
0 0
40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
FEV1 Vopeak
LF/HF correlation with FEV1 & VO2Peak
Conclusions
Patients with mild to moderate CF have
moderately depressed heart rate
variability (HRV) and a shift of sympatho-
vagal balance towards sympathetic
predominance and reduced vagal tone.
Heart rate variability (HRV) was not
correlated with cardio-respiratory
function.
The chronic use of -adrenergic agonists
may attribute to the predominance of
sympathetic activity among patients with
Acknowledgements
Paediatric Pulmonology and CF Unit, School of Physical
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki Education
& Sports Sciences,
J Tsanakas Aristotle University of
E Hatziagorou Thessaloniki
F Kirvassilis
A Deligiannis
M Galogavrou
E Chrysochoou E Kouidi
V Avramidou M Anifanti
A Kampouras S Giannakoulakos
E Kalaitzidou
K Bakas
CF families
Вам также может понравиться
- Wesnbhie45oz5jsb0nv5amut PDFДокумент4 страницыWesnbhie45oz5jsb0nv5amut PDFKabir Dhankhar0% (4)
- Progressive Strengthening and Stretching Exercises and Ultrasound For Chronic Lateral EpicondylitisДокумент9 страницProgressive Strengthening and Stretching Exercises and Ultrasound For Chronic Lateral EpicondylitisTomBrambo100% (1)
- A Comparative Study of Pulmonary Function Among TheДокумент22 страницыA Comparative Study of Pulmonary Function Among TheArpana HazarikaОценок пока нет
- COPD - Changing Concepts of Pathogenesis and New Ideas For Old TreatmentsДокумент49 страницCOPD - Changing Concepts of Pathogenesis and New Ideas For Old TreatmentsMikee MoganОценок пока нет
- High Flow Nasal Oxygen PDFДокумент26 страницHigh Flow Nasal Oxygen PDFGulshan kumarОценок пока нет
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Detection, Significance and TreatmentДокумент27 страницLeft Ventricular Hypertrophy: Detection, Significance and TreatmentprobowurОценок пока нет
- Lab 1 - AC Oscilloscope FundamentalsДокумент3 страницыLab 1 - AC Oscilloscope Fundamentalsali basitОценок пока нет
- Examples: Case # 1.: GOLD Spirometric Criteria For COPD SeverityДокумент6 страницExamples: Case # 1.: GOLD Spirometric Criteria For COPD SeverityAjet AsaniОценок пока нет
- Normal Limits of Electrocardiogram and Cut-Off Values For Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Young Adult NigeriansДокумент4 страницыNormal Limits of Electrocardiogram and Cut-Off Values For Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Young Adult Nigeriansaa bbОценок пока нет
- How Does Intravascular ImagingDerived FFR Work and When Should It Be UsedДокумент25 страницHow Does Intravascular ImagingDerived FFR Work and When Should It Be Usedrainmed USОценок пока нет
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 2014Документ10 страницPatent Ductus Arteriosus 2014Neha OberoiОценок пока нет
- Neonatal ICU Monitoring: Lena Hellstro M-Westas, Linda S. de Vries and Ingmar Rose NДокумент16 страницNeonatal ICU Monitoring: Lena Hellstro M-Westas, Linda S. de Vries and Ingmar Rose NJas LimОценок пока нет
- Lab Results For Case StudyДокумент2 страницыLab Results For Case StudyNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDOОценок пока нет
- Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation: Electrical Vs PharmacologicalДокумент29 страницCardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation: Electrical Vs PharmacologicalArleen MatincaОценок пока нет
- 15 Armstrong2016Документ2 страницы15 Armstrong2016Sergio Machado NeurocientistaОценок пока нет
- 677 PulmonaryДокумент295 страниц677 Pulmonarypvs5155Оценок пока нет
- 2011 BioE 210 Lab Report 10Документ4 страницы2011 BioE 210 Lab Report 10Peter SordsОценок пока нет
- MR AckdДокумент16 страницMR AckdHananya ManroeОценок пока нет
- Interpretating Echocardiography Haemodynamic and ManagementДокумент26 страницInterpretating Echocardiography Haemodynamic and ManagementdavitlieОценок пока нет
- @ (White Paper - Cut-Off) RS85 - S-Shearwave Imaging LiverДокумент10 страниц@ (White Paper - Cut-Off) RS85 - S-Shearwave Imaging LiverHajjab AnasОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Output Monitoring - HandoutДокумент49 страницCardiac Output Monitoring - HandoutNakarit SangsirinawinОценок пока нет
- Normal Hemodynamic Parameters and Lab Values - Eu Master PDFДокумент4 страницыNormal Hemodynamic Parameters and Lab Values - Eu Master PDFDavidОценок пока нет
- Laboratory AnalysisДокумент6 страницLaboratory AnalysisJm CoguincoОценок пока нет
- Agung PDFДокумент1 страницаAgung PDFRSCERIA KANDANGANОценок пока нет
- SpirometriДокумент1 страницаSpirometriAri Julian SaputraОценок пока нет
- Normal Hemodynamic Parameters - EDWARDSДокумент4 страницыNormal Hemodynamic Parameters - EDWARDSCristell CardenasОценок пока нет
- ESC Heart Failure - 2022 - DitaliДокумент5 страницESC Heart Failure - 2022 - DitaliL AuliyaRizkyОценок пока нет
- B. Thesis MatterДокумент61 страницаB. Thesis MatterSurya TejaОценок пока нет
- EPДокумент30 страницEPGede SuputraОценок пока нет
- GMM Pivot Phase2Документ30 страницGMM Pivot Phase2tsioryluckyОценок пока нет
- Complete Blood CountДокумент3 страницыComplete Blood CountivantototaeОценок пока нет
- Echo Pocket 2014Документ18 страницEcho Pocket 2014abbouamine100% (2)
- Case 222Документ33 страницыCase 222jovan teopizОценок пока нет
- Kuswanto Ardi Custo Med GMBHДокумент1 страницаKuswanto Ardi Custo Med GMBHRSCERIA KANDANGANОценок пока нет
- DR Susanthy SP.P (K)Документ52 страницыDR Susanthy SP.P (K)dadankОценок пока нет
- F1777 SampleДокумент11 страницF1777 SampleLevi MeccaОценок пока нет
- 婦兒combine 15751380 游家榛之子 ELBW - 28+1weeksДокумент67 страниц婦兒combine 15751380 游家榛之子 ELBW - 28+1weeks鄧沛元醫師Оценок пока нет
- Maximal Oxygen ConsumptionДокумент7 страницMaximal Oxygen Consumptionapi-381656968Оценок пока нет
- Experiment Number ThreeДокумент10 страницExperiment Number ThreeGallardo, Jeny Babe M.Оценок пока нет
- Test Result Unit Reference Range Hematology (23/07/2018) : WBC H 11,01 10 / L 3,80-10,60Документ2 страницыTest Result Unit Reference Range Hematology (23/07/2018) : WBC H 11,01 10 / L 3,80-10,60FrenyОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 5 Objective - IIДокумент56 страницChapter - 5 Objective - IIraman_bhoomi9910Оценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Function Test Results Visit Date 12/4/2018: FVC Fev1 FEV1%Документ2 страницыPulmonary Function Test Results Visit Date 12/4/2018: FVC Fev1 FEV1%Shofiyyah ZahraОценок пока нет
- Echo Final 1Документ1 страницаEcho Final 1alberttablan111Оценок пока нет
- Noriangelys Rojas HДокумент8 страницNoriangelys Rojas HYubraska Marquez HurtadoОценок пока нет
- Hematology Unit: Complete Blood Picture (CBC)Документ1 страницаHematology Unit: Complete Blood Picture (CBC)أبوضحي أحمد علي مهديОценок пока нет
- The Contemporary Pulmonary Artery Catheter Part 2Документ16 страницThe Contemporary Pulmonary Artery Catheter Part 2ElenaCondratscribdОценок пока нет
- Normal Values of TTE - EchopediaДокумент13 страницNormal Values of TTE - Echopediaantonio pereiraОценок пока нет
- M Irfan 14 JuliДокумент1 страницаM Irfan 14 JuliRSCERIA KANDANGANОценок пока нет
- Run Amil Mada Custo Med GMBHДокумент1 страницаRun Amil Mada Custo Med GMBHRSCERIA KANDANGANОценок пока нет
- Morning Report Case: 16th July, 2012Документ20 страницMorning Report Case: 16th July, 2012Felicia adeline ChristianОценок пока нет
- Ruth MoralesДокумент5 страницRuth MoralesFranyelis GutiérrezОценок пока нет
- LabreportnewДокумент4 страницыLabreportnewSatvinder SinghОценок пока нет
- Cunanan, Bryan Don7-27-18Документ2 страницыCunanan, Bryan Don7-27-18RMH Heart StationОценок пока нет
- CHHEM SirikaДокумент23 страницыCHHEM SirikaSirika ChhemОценок пока нет
- Central Venous Pressure (CVP)Документ2 страницыCentral Venous Pressure (CVP)cado_arifОценок пока нет
- 1.results 1.1) DC Measurements: 1.2.1 Common Emitter Amplifier: Low Frequency ResponseДокумент6 страниц1.results 1.1) DC Measurements: 1.2.1 Common Emitter Amplifier: Low Frequency Responsekribz10Оценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 6: Low Pass FilterДокумент8 страницExperiment No. 6: Low Pass FilterMuhammad Haseeb AshiqОценок пока нет
- Basic EchocardiographyДокумент54 страницыBasic Echocardiographyramon100% (23)
- 10 Pulm HTN Florida - 2017Документ81 страница10 Pulm HTN Florida - 2017MОценок пока нет
- Echocardiography in ICUОт EverandEchocardiography in ICUMichel SlamaОценок пока нет
- A Prospective Multi-Centre Study of Tablet and Web-Based Audiometry To Detect Hearing Loss in Adults With Cystic FibrosisДокумент19 страницA Prospective Multi-Centre Study of Tablet and Web-Based Audiometry To Detect Hearing Loss in Adults With Cystic FibrosisniallvvОценок пока нет
- Preview Amphitheatre BriefingДокумент15 страницPreview Amphitheatre BriefingniallvvОценок пока нет
- Emerging Inequality Access To Clinical Trials Drugs Division by PostcodeДокумент20 страницEmerging Inequality Access To Clinical Trials Drugs Division by PostcodeniallvvОценок пока нет
- New Insights in Peripheral Quality Control of CFTRДокумент41 страницаNew Insights in Peripheral Quality Control of CFTRniallvvОценок пока нет
- Wash-In 2. Wash-Out: Infant Expires To Bag Infant Expires To Room AirДокумент2 страницыWash-In 2. Wash-Out: Infant Expires To Bag Infant Expires To Room AirniallvvОценок пока нет
- 44 PDFДокумент19 страниц44 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 87 PDFДокумент14 страниц87 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 84 PDFДокумент14 страниц84 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 85 PDFДокумент11 страниц85 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 86 PDFДокумент15 страниц86 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 72 PDFДокумент17 страниц72 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 83 PDFДокумент19 страниц83 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 82 PDFДокумент21 страница82 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 75 PDFДокумент13 страниц75 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- 73 PDFДокумент20 страниц73 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- Artikel-Systemic and Family Therapy With Socially Disadvantaged Children and YoungДокумент19 страницArtikel-Systemic and Family Therapy With Socially Disadvantaged Children and YoungMiranda SwindleyОценок пока нет
- Ethical Issues in The Constant GardenerДокумент6 страницEthical Issues in The Constant GardenerAstha PriyamvadaОценок пока нет
- Management of Diabetes: DR Rukman Mecca M I 51 ST Batch Calicut Med CollegeДокумент47 страницManagement of Diabetes: DR Rukman Mecca M I 51 ST Batch Calicut Med CollegeRukman MeccaОценок пока нет
- Mental Health of GNM PDFДокумент133 страницыMental Health of GNM PDFSuraj Solanki0% (1)
- Guidelines For Cleaning Toys: Policy DetailsДокумент16 страницGuidelines For Cleaning Toys: Policy DetailsdidikОценок пока нет
- IV PO ConversionsДокумент1 страницаIV PO Conversionsdamondouglas100% (1)
- ST Georges Annual Report 2008 - 2009Документ52 страницыST Georges Annual Report 2008 - 2009St George's Healthcare NHS TrustОценок пока нет
- Case Study StabДокумент7 страницCase Study StabMari Jasmeen Estrada Noveda100% (1)
- Metabolic Acid - Base ImbalancesДокумент5 страницMetabolic Acid - Base Imbalancesmardsz100% (1)
- Main Idea and Text Structure 3Документ1 страницаMain Idea and Text Structure 3Anjo Gianan TugayОценок пока нет
- ShockДокумент5 страницShocknkuligowski100% (2)
- Acupuncture PDFДокумент61 страницаAcupuncture PDFAsha Mahal PandikkadОценок пока нет
- Organizing Nursing Services and Patient Care: Case MethodДокумент23 страницыOrganizing Nursing Services and Patient Care: Case Methodmerin sunilОценок пока нет
- Information For Pharmacists On Managing Warfarin Drug InteractionsДокумент4 страницыInformation For Pharmacists On Managing Warfarin Drug InteractionsBelladonna Perdana PutraОценок пока нет
- Oral & Craniofascial PainДокумент36 страницOral & Craniofascial PainMaria Fudji hastutiОценок пока нет
- Pregabalin An Anticonvulsant DrugДокумент2 страницыPregabalin An Anticonvulsant DrugmeimeiliuОценок пока нет
- CTG Classification PDFДокумент1 страницаCTG Classification PDFganotОценок пока нет
- Indications: PeritonitisДокумент8 страницIndications: PeritonitisIrene Soriano BayubayОценок пока нет
- SYLLABUSДокумент5 страницSYLLABUSArc Angelus Civitas School100% (1)
- Arthrosis of KneeДокумент30 страницArthrosis of Kneebiomechy oktomalioputriОценок пока нет
- Closed Fracture Neck FemurДокумент31 страницаClosed Fracture Neck FemurKiki Said100% (1)
- Soc CardiogenДокумент11 страницSoc CardiogenOlga HMОценок пока нет
- Aflac Claim FormДокумент7 страницAflac Claim FormThomas Barrett100% (2)
- Bereavement and Autism: A Universal Experience With Unique ChallengesДокумент11 страницBereavement and Autism: A Universal Experience With Unique ChallengesBrian A. Wong100% (1)
- NIV ProformaДокумент10 страницNIV ProformaWael N Sh GadallaОценок пока нет
- What Is A Root CanalДокумент5 страницWhat Is A Root CanaljjahaddinОценок пока нет
- InjectomatTivaAgilia PDFДокумент2 страницыInjectomatTivaAgilia PDFBagas AnggerОценок пока нет
- UTSДокумент3 страницыUTSDio NolascoОценок пока нет
- Value Nurses Community April 2003 eДокумент42 страницыValue Nurses Community April 2003 eCarlos RobertoОценок пока нет