Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Virus Herpes
Загружено:
Dian Lestari0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров11 страницHerpes
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документHerpes
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров11 страницVirus Herpes
Загружено:
Dian LestariHerpes
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 11
Human Herpes Virus
Double stranded DNA virus
Envelope,thymidine kinase,DNA po-
lymerase
Lytic,persistent,latent and immor-
talizing infection
HSV(Herpes Simplex Virus)
Tipe 1 dan 2
structure
Replication
Patogenesis
Immunitas
Desease
- cause lifelong infection
- recurrent disease is a source of contagion
- may cause asymptomatic shedding
Transmission
Transmitted in saliva,vaginal secretion and
By contact with lesion fluid
Transmitted orally,sexually and by placement
into eyes and broken skin
HSV-1 generally transmitted orally
HSV-2 by sexually transmitted
Who is at risk?
Children and sexually active individuals
Physicians,nurses,dentist and others in con-
tact with oral/genital secretionsat risk for
infections of fingers( herpetic whitlow)
Immunocompromised and neonates at risk
Oral Herpes
Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
HSV-1 (children)
HSV-2(adult)
Lesion: vesicel ulcerated
palatum,pharyng,gingiva,buccal mucosal and
tounge
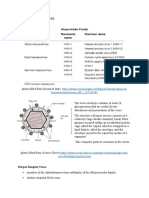
DNA,double stranded,icosahedral,envelope
Encode many protein
Thymidine kinase,DNA polymerasereplicate
a good target for antiviral drugs
Pathogenesis
Cause direct cytopathologi
Avoid antibody by syncytia sel
Reactivates from latency by stress,imun-
suppression
CMI required for resolution with limited role
for antibody
Control:
- Acyclovir (anti viral)
- No vacine is available
- Health care workers: wear gloves to prevent
herpetic whitlow
Text book: medical Mycrobiology
TERIMA KASIH
Вам также может понравиться
- Herpes 2 DoubleDNAДокумент18 страницHerpes 2 DoubleDNACharles SainzОценок пока нет
- HerpervirusesДокумент66 страницHerperviruseskomalsaharan2001Оценок пока нет
- Ulcerative, Vesicular, andДокумент117 страницUlcerative, Vesicular, andvanshikaОценок пока нет
- Herpes Simplex PDFДокумент34 страницыHerpes Simplex PDFAbdul QaharОценок пока нет
- Herpes, Pox, Rhabdo, Arena VIRUSДокумент7 страницHerpes, Pox, Rhabdo, Arena VIRUSErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDОценок пока нет
- Infeksi Virus Pada Rongga MulutДокумент41 страницаInfeksi Virus Pada Rongga MulutFaris MahdaniОценок пока нет
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroДокумент50 страницFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013Оценок пока нет
- Viral Infections of The SkinДокумент59 страницViral Infections of The SkinetОценок пока нет
- Herpetic InfectionsДокумент46 страницHerpetic InfectionsRachel SinghОценок пока нет
- Viral Skin DiseaseДокумент27 страницViral Skin DiseaseRabina PantaОценок пока нет
- Herpesviruses: Department of Microbiology and ParasitologyДокумент96 страницHerpesviruses: Department of Microbiology and Parasitology2013SecBОценок пока нет
- VirologyДокумент24 страницыVirologyRohama Qubra 279Оценок пока нет
- Herpes VirusДокумент80 страницHerpes VirusngussutsegaОценок пока нет
- Viral InfectionsДокумент59 страницViral InfectionsSajin AlexanderОценок пока нет
- Herpes 1 DoubleDNAДокумент13 страницHerpes 1 DoubleDNACharles SainzОценок пока нет
- MF3 - Herpes Simplex VirusДокумент31 страницаMF3 - Herpes Simplex VirusAnnbe BarteОценок пока нет
- Chapter 24Документ55 страницChapter 24Vincent DaoОценок пока нет
- Viral InfectionsДокумент103 страницыViral InfectionsAkash Anilkumar MaliniОценок пока нет
- Viral InfectionsДокумент17 страницViral Infectionsامجد شاكرОценок пока нет
- Viral Diseases With Rashes LastДокумент46 страницViral Diseases With Rashes LastHasan kahhalehОценок пока нет
- Oral Viral Infections Diagnosis and ManagementДокумент13 страницOral Viral Infections Diagnosis and ManagementhunarsandhuОценок пока нет
- Oral Viral Infections Diagnosis and Management PDFДокумент13 страницOral Viral Infections Diagnosis and Management PDFWesley RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Resource Faculties:: Department of Oral Medicine and RadiologyДокумент168 страницResource Faculties:: Department of Oral Medicine and RadiologykishoreОценок пока нет
- Chapter 24 DNA Viruses That Infect HumansДокумент64 страницыChapter 24 DNA Viruses That Infect HumansJJ AlmagroОценок пока нет
- Herpes SimplexДокумент27 страницHerpes SimplexHania KhanОценок пока нет
- Herpes Simplex Virus: Herpesviridae FamilyДокумент9 страницHerpes Simplex Virus: Herpesviridae FamilyANNEОценок пока нет
- LESI ULSERATIF VESIKEL BULOSA Kecil PDFДокумент70 страницLESI ULSERATIF VESIKEL BULOSA Kecil PDFanonymОценок пока нет
- Viroze CutanateДокумент28 страницViroze CutanateMădălina SavaОценок пока нет
- Herpetic StomatitisДокумент21 страницаHerpetic StomatitisZulfahmi RizkiОценок пока нет
- Acute Gingival InfectionsДокумент101 страницаAcute Gingival InfectionsNeelam KhaliaОценок пока нет
- 1.non Keratotic Lesion PDFДокумент57 страниц1.non Keratotic Lesion PDFElamaaraeen MadhvanОценок пока нет
- 33HSVRamaДокумент5 страниц33HSVRamaPriskilla RachmiyantiОценок пока нет
- DNA VirusesДокумент99 страницDNA VirusesCourtny Lenz Maygay GapaОценок пока нет
- Approach in Lymphadenopathy in ChildrenДокумент14 страницApproach in Lymphadenopathy in Childrennahiry100% (1)
- Part IIДокумент32 страницыPart IITofikОценок пока нет
- Krizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsДокумент84 страницыKrizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsTara Oliveros Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- OMIC 311 Lecture 17 Human Papilloma, Herpes, Hepatits VirusДокумент51 страницаOMIC 311 Lecture 17 Human Papilloma, Herpes, Hepatits VirusMaryam XAОценок пока нет
- Ipm-3 EpitelДокумент58 страницIpm-3 EpitelVonny MariaОценок пока нет
- Human Herpes VirusesДокумент8 страницHuman Herpes VirusesSri DurgaОценок пока нет
- Herpesvirida E& Adenoviridae: By: MJ Briones Bsn-IiДокумент93 страницыHerpesvirida E& Adenoviridae: By: MJ Briones Bsn-IiMj BrionesОценок пока нет
- Dr. Taubel's STD Lecture, Part 1Документ61 страницаDr. Taubel's STD Lecture, Part 1f3er3Оценок пока нет
- Herpes VirusesДокумент18 страницHerpes VirusesGarryОценок пока нет
- Child Health Nursing: MumpsДокумент25 страницChild Health Nursing: MumpsmanibharathiОценок пока нет
- Herpes VirusesДокумент71 страницаHerpes VirusesAyioKunОценок пока нет
- Herpesviruses, Poxviruses & Human Papilloma Virus: Fort SalvadorДокумент33 страницыHerpesviruses, Poxviruses & Human Papilloma Virus: Fort SalvadorFort SalvadorОценок пока нет
- 3.viral Inf of Oral Cav FKG Nov06Документ41 страница3.viral Inf of Oral Cav FKG Nov06Akmal SatibiОценок пока нет
- OMD421Документ132 страницыOMD421Noura RihanОценок пока нет
- Oral Inflammation and Ulceration LesionsДокумент27 страницOral Inflammation and Ulceration LesionsVonny MariaОценок пока нет
- Infectious Disease of The Oral Region. FinalДокумент39 страницInfectious Disease of The Oral Region. FinalClancy Anne Garcia NavalОценок пока нет
- Herpes 1 & 2Документ29 страницHerpes 1 & 2Pranjali WeladiОценок пока нет
- Gingival & Periodontal Diseases 5.1.15Документ128 страницGingival & Periodontal Diseases 5.1.15Shameena KnОценок пока нет
- L2 - OmeДокумент14 страницL2 - OmeMoaz AlbabaОценок пока нет
- Overview Agent Penyebab Infeksi MataДокумент31 страницаOverview Agent Penyebab Infeksi MataCharina SitumorangОценок пока нет
- Herpes Viri Dae 1Документ45 страницHerpes Viri Dae 1Michelle RotairoОценок пока нет
- Care of Clients With STDsДокумент30 страницCare of Clients With STDsSarah Jane MaganteОценок пока нет
- Sti Causes 2019Документ115 страницSti Causes 2019Ardhinta SeptardaОценок пока нет
- Natural Alkaline Diets, Water & Medicinal Herbs for Herpes: Detoxify, Cleanse and Nourish Blood, Organs and the Entire Body to be Completely Free from Herpes VirusОт EverandNatural Alkaline Diets, Water & Medicinal Herbs for Herpes: Detoxify, Cleanse and Nourish Blood, Organs and the Entire Body to be Completely Free from Herpes VirusРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (16)
- English in Urgent Care Medicine – Anglictina V Urgentní Medicíne: Textbook – UcebniceОт EverandEnglish in Urgent Care Medicine – Anglictina V Urgentní Medicíne: Textbook – UcebniceОценок пока нет
- The Complete Guide to Genital Herpes: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsОт EverandThe Complete Guide to Genital Herpes: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsОценок пока нет