Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
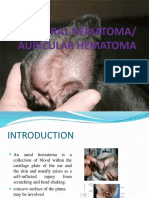
Chemical Restraint in Horses
Загружено:
Muhammad Shahzad Chandia0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров19 страницkj
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документkj
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров19 страницChemical Restraint in Horses
Загружено:
Muhammad Shahzad Chandiakj
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 19
Chemical Restraint in Horses
Relief of pain has been one of the most persistent
pursuits of mankind.
SMITHCORS
Anaesthesia
Anaesthesia is used to denote loss of
sensation to any part or whole of the body,
produced by agents which depress the activity
of nervous tissue either locally or centrally.
It is a reversible process
Terminology
Local Anaesthesia is a loss of sensation in a limited body
area.
Regional Anaesthesia is a loss of sensation or insensibility
in larger, but limited area.
General Anaesthesia is complete unconsciousness.
Surgical Anaesthesia is a state of unconsciousness, where
adequate muscular relaxation is produced to perform
surgical operation painlessly.
Terminology
Analgesia is a relief from pain
Tranquilization is a state of behavioral change in which
the patient is relaxed but unconcerned of his
surroundings.
Sedation is a state of mild degree central
depression,when the patient is awake but calm.
Narcosis is a state of deep sleep accompanied by
analgesia.
Hypnosis is an artifically induced sleep and results from
moderate depression of central nervous system.
Selection of Anaesthetic agent
Time required to perform a surgical procedure and
the amount of help available.
The metabolic rate of an animal
Age of animal
Breed
Specie differences
Type of surgery
Physical state or health of animal
Availability of equipment and personnel
Preanaesthetic Agents
Used to prepare patient for administration of
anaesthetic agents
reduce slivary gland secretion and amount of
general anaesthesia
Easier restraint
Prevent vomition
Block vagovagal reflex
Reduce pain
Preanaesthetic Agents
Preanaesthetic agents can be broadly
classified into four categories
1. Anticholinergics
2. Morphine and its substitutes
3. Tranquilizers
4. Neuroleptanalgesic agents (Tranquilizer-narcotic
combinations)
Anticholinergics
Atropine sulphate:
Antisialogogue
Increase heart rate by blocking vagus
Bronchial musculature is relaxed
Avoid in tachycardia
Horse 40-60 mg I.M
Hyoscine
Glycopyrrolate
Morphine and its derivatives
Morphine:
good sedation
Good analgesic
Depress respiratory center and produces bradycardia
Horse 60mg I.M. or Sub cut
Fentanyl:
50 times as potent as morphine
Cause bradycardia
Used in neuroleptanalgesia mixture with droperidol
Horse 0.2 mg/kg
Morphine and its derivatives
Butorphenol:
used in horses for analgesia
Sedative effect with alfa-2 adrenoreceptors
agonists
Horse 0.1 to 0.4 mg/kg
Pentazocine:
Used for relief of colic pain in horses
Horse 0.5 to 4 mg/kg orally
0.33 mg/kg I.V.
Tranquilizers
Useful in vicious and nervous animals
Sedative and calming effect
Antiemetic properties
Potentiate action of narcotics and
anaesthetics
Some cause central depression
Tranquilizers
Chlorpromazine hydrochloride(largactil):
Antiemetic
Central depressent
Not preffered in horses as it decreases blood pressure
giving rise to panic due to muscle weakness.
Horse 0.4 mg/kg I.M.
Methotrimeprazine:
More effective than chlorpromazine
Horse 0.5 mg/kg I.M.
Tranquilizers
Acetylpromazine meleate (Acepromazine)
Tranquilizer of choice for large and small animals
Potent tranquilizer in veterinary practice
Central nervous depressent
Antiemetic
Anticonvulsant
Hypothermic
Hypotensive
Antispasmodic
Alfa-2 Adrenoceptor agonists
Xylazine:
Potent non-narcotic sedative
Analgesic
Muscle relaxant
Horse 1mg/kg I.V., 2 mg/kg I.M.
Detomidine:
Sedation in horses
Dose dependent sedation
Horse 10-100g/kg. I.V or I.M.
10-20 g/kg suitable for sedation
Neuroleptanalgesic agents
Innovar-Vet (Fentanyl citrate and droperidol)
Analgesic and tranquilizer combination
Reduction to painful stimuli
Methadone- Acepromazine:
Effective and reliable chemical restraint for
horses
Mixture of 50mg of methadone and 50mg
acepromazine, sufficient for about 500 kg horse
Local Anaesthetics
Procaine hydrochloride
Used widely
Non-irritant to tissues
Non-toxic
Mucous membrane penetration is low
Tetracaine
Corneal anaesthesia
Lignocaine hydrochloride(lidocaine)2-3%
Injectible anaesthetic agent
Extreme depression
Mepivacaine hydrochloride(carbocaine)
Equine lameness
Ethyl chloride
Short duration
Surface anaesthesia
Drugs administered with local anaesthetic
agents
Epinephrine
Hyaluronidase
Local Anaesthesia
Surface Anaesthesia
Infiltration Anaesthesia
Field block
Intrasynvial Anaesthesia
Вам также может понравиться
- APMEPA Members ListДокумент9 страницAPMEPA Members ListUsama100% (1)
- Muhammad Usman Saleem (Standard Curve)Документ3 страницыMuhammad Usman Saleem (Standard Curve)Muhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Revised Syllabus CE-2016 10 Jul 2015Документ158 страницRevised Syllabus CE-2016 10 Jul 2015Muhammad Faisal TahirОценок пока нет
- Shahzad Thesis Observation PerformaДокумент1 страницаShahzad Thesis Observation PerformaMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Punjab Public Service CommissionДокумент2 страницыPunjab Public Service CommissionMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Abdul Latif and Rafiq Cleaning Services L.L.CДокумент2 страницыAbdul Latif and Rafiq Cleaning Services L.L.CMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- 66 CheeseДокумент20 страниц66 CheeselucasОценок пока нет
- 66 CheeseДокумент20 страниц66 CheeselucasОценок пока нет
- CV ShahzadДокумент1 страницаCV ShahzadMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Veterinary ToxicologyДокумент289 страницVeterinary ToxicologySamara Muniz100% (7)
- Duck FarmingДокумент52 страницыDuck FarmingMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- International Studentship Form v3.1Документ2 страницыInternational Studentship Form v3.1Muhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Common Lab TestsДокумент2 страницыCommon Lab TestsMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Udder DevelopmentДокумент45 страницUdder DevelopmentMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Protrusion of The Third Eyelid GlandДокумент14 страницProtrusion of The Third Eyelid GlandMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7 Aural HematomaДокумент13 страницLecture 7 Aural HematomaMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- 7 - Disorders of Urinary SystemДокумент27 страниц7 - Disorders of Urinary SystemMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3, Skin GraftingДокумент24 страницыLecture 3, Skin GraftingZartasha KhanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 Dressing and BadageДокумент20 страницLecture 4 Dressing and BadageMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5 Lick GranulomaДокумент7 страницLecture 5 Lick GranulomaMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Basic CVДокумент1 страницаBasic CVMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- CV IjazДокумент1 страницаCV IjazMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- CV TemplateДокумент2 страницыCV TemplateMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Lectue 16 Vaginal ProlapseДокумент6 страницLectue 16 Vaginal ProlapseMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 BurnsДокумент18 страницLecture 2 BurnsMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Muhammad Shahzad: Special QualitiesДокумент1 страницаMuhammad Shahzad: Special QualitiesMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Dr. Muhammad Shahzad Address: Basti Shahgarh P/O Mondka T/D Muzaffar Garh Mobile: (+923411678250) ProfileДокумент3 страницыDr. Muhammad Shahzad Address: Basti Shahgarh P/O Mondka T/D Muzaffar Garh Mobile: (+923411678250) ProfileMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Wound Between Fetlock and Pastern Joint and Maggots InfestationДокумент17 страницWound Between Fetlock and Pastern Joint and Maggots InfestationMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- AmirДокумент1 страницаAmirMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaОценок пока нет
- Production of YogurtДокумент12 страницProduction of YogurtMuhammad Shahzad Chandia100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Mental Health Awareness SpeechДокумент2 страницыMental Health Awareness SpeechThea Angela Longino95% (20)
- LA Low Cost Dog NeuteringДокумент2 страницыLA Low Cost Dog Neuteringtonys71Оценок пока нет
- Preparing A Family For Childbirth and ParentingДокумент5 страницPreparing A Family For Childbirth and ParentingBern NerquitОценок пока нет
- Lse Su Gym: Membership Application FormДокумент2 страницыLse Su Gym: Membership Application Formgregorioalejandro05Оценок пока нет
- Health 10: 3 Quarter Week 7Документ10 страницHealth 10: 3 Quarter Week 7Maria Rose Tariga Aquino50% (2)
- Small TalkДокумент2 страницыSmall TalkHerdeiro DicaprioОценок пока нет
- YDA Nepal - MembersДокумент13 страницYDA Nepal - MembersSulochan LohaniОценок пока нет
- Quality Manual: Pt. Ani Mitra Jaya Frozen ChepalopodДокумент1 страницаQuality Manual: Pt. Ani Mitra Jaya Frozen ChepalopodMia AgustinОценок пока нет
- Weld-On 4 MsdsДокумент2 страницыWeld-On 4 MsdsJosué CubilloОценок пока нет
- PBHCI - Mental Health ScreeningДокумент2 страницыPBHCI - Mental Health ScreeningRoshin Tejero0% (1)
- Lesson 8 - Extent of Factors Affecting Health in KirkleesДокумент8 страницLesson 8 - Extent of Factors Affecting Health in KirkleeswapupbongosОценок пока нет
- DivorceДокумент11 страницDivorceNithesh K MogaveeraОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Science AED G3 Pro - Service ManualДокумент78 страницCardiac Science AED G3 Pro - Service Manualmisu_stefan6141Оценок пока нет
- AICTE CorporateBestPracticesДокумент13 страницAICTE CorporateBestPracticesramar MОценок пока нет
- Senior Thesis - Corry ArcomanoДокумент21 страницаSenior Thesis - Corry Arcomanoapi-407563053Оценок пока нет
- CP of Dexterous ConsultantsДокумент12 страницCP of Dexterous ConsultantsDipankar GhoshОценок пока нет
- Nutrition Case Study Presentation Slides - Jacob NewmanДокумент27 страницNutrition Case Study Presentation Slides - Jacob Newmanapi-283248618Оценок пока нет
- 7 DR BookletДокумент13 страниц7 DR BookletDebraОценок пока нет
- Iriga Zone Ibd List: Nabua AДокумент20 страницIriga Zone Ibd List: Nabua AAnonymous dPCnM2a1Оценок пока нет
- L TyrosineДокумент6 страницL TyrosinecpullerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 020Документ59 страницChapter 020api-263755297Оценок пока нет
- Nerve Injuries: Radial Nerve, Median Nerve and Ulnar NerveДокумент26 страницNerve Injuries: Radial Nerve, Median Nerve and Ulnar NerveaisiyaahОценок пока нет
- MMDSTДокумент4 страницыMMDSTJo Marchianne PigarОценок пока нет
- SM Project 1Документ75 страницSM Project 1reena Mahadik100% (1)
- Liver & Kidney Transplant - A5 Folder - Digital - 2022Документ4 страницыLiver & Kidney Transplant - A5 Folder - Digital - 2022lakshminivas PingaliОценок пока нет
- MRCP 2 PACES Exam Cases From 2011Документ6 страницMRCP 2 PACES Exam Cases From 2011Kolitha KapuduwageОценок пока нет
- Fever Nursing Care PlanДокумент3 страницыFever Nursing Care PlanMarie Anne T85% (39)
- Herald Spelling BeeIntermediateДокумент10 страницHerald Spelling BeeIntermediateTheng RogerОценок пока нет
- SigmaDur 188-520-550 Msds Hardener PDFДокумент17 страницSigmaDur 188-520-550 Msds Hardener PDFMarcos LaraОценок пока нет
- Major Neurological Syndromes PDFДокумент260 страницMajor Neurological Syndromes PDFVirlan Vasile Catalin100% (1)