Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
BOM Slides Visit Us at Management - Umakant.info
Загружено:
welcome2jungle0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
5 просмотров12 страницОригинальное название
BOM Slides Visit Us @ Management.umakant.info
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
5 просмотров12 страницBOM Slides Visit Us at Management - Umakant.info
Загружено:
welcome2jungleАвторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 12
Overview
• The need to increase efficiency and
effectiveness has driven the evolution of
management theory
• Job specialization, the division of labor and the
study of how people do things is central to the
pursuit of increased efficiency
F.W. Taylor and Scientific
Management
Scientific Management
The systematic study of the relationships
between people and tasks in order to
redesign the work process for higher
efficiency.
TAKE THE WATCH APART AND
REASSEMBLE IT DIFFERENTLY TO
MAKE IT TICK FASTER.
Scientific Management
• Defined and popularized by Taylor in the
early 1900’s.
• Sought to reduce the time a worker spent on
each task by optimizing the way the task
was done.
• Focused on the process.
Four Principles of Scientific
Management
1) Study the ways jobs are performed and
determine new ways to do them.
• Gather detailed time and motion information.
• Try different methods to see which is best.
Four Principles of Scientific
Management
2) Codify the new methods into rules
and teach all workers
the new method.
Four Principles of Scientific
Management
3) Determine who’s skills best match the rules.
4) Establish fair levels of performance; pay a
premium for higher performance.
• Note: all still done by Toyota today but
improvement process (kaizen) in hands of
employees, not managers – you will see why
this point is important
Fayol’s Principles of
Management
• Division of Labor: allows for job specialization.
– jobs can have too much specialization leading to
poor quality and worker dissatisfaction.
• Authority and Responsibility
– both formal and informal authority resulting from
special expertise.
• Unity of Command
– Employees should have only one boss. If not, chaos
and confusion.
Fayol’s Principles of
Management
• Line of Authority
– A clear chain of command from top to bottom
of the firm.
• Centralization
– The degree to which authority rests at the top
of the organization.
• Unity of Direction
– A single plan of action to guide the
organization.
Fayol’s Principles of
Management
• Equity - The provision of justice and the fair and
impartial treatment of all employees.
• Order - The arrangement of employees in order
to optimize value for the organization and
provide career opportunities.
• Initiative - The fostering of creativity and
innovation by encouraging employees to act on
their own.
Fayol’s Principles of
Management
• Discipline
– Obedient, applied, respectful employees are
necessary for the organization to function.
• Equitable Remuneration of Personnel
– An equitable and uniform payment system
that motivates employees to contribute to
organizational success.
Fayol’s Principles of
Management
• Stability of Personnel Tenure
– Long-term employment is important for the development
of skills that improve the organization’s performance (it
also makes employees feel secure, but beware
complacency)
• Subordination of Individual Interest to the Common
Interest
– The interest of the organization takes precedence over
that of the individual employee.
Fayol’s Principles of
Management
Esprit de corps
– Comradeship and
shared enthusiasm
foster devotion to the
common cause (the
success of the
organization).
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Xerox Project Report, Anupam Kumar, Vvism, HyderabadДокумент41 страницаXerox Project Report, Anupam Kumar, Vvism, Hyderabadanupam kumar barnwalОценок пока нет
- Writing Negative MessagesДокумент29 страницWriting Negative MessagesChen FaiОценок пока нет
- Vedic MultiplicationДокумент4 страницыVedic Multiplicationapi-3771640Оценок пока нет
- Tutoring Services Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент20 страницTutoring Services Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Winz-Final - Reportvisit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент89 страницWinz-Final - Reportvisit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Trade UnionДокумент17 страницTrade Unionpriyanca17Оценок пока нет
- WALMART Visit Us at Management - UmakantДокумент54 страницыWALMART Visit Us at Management - Umakantwelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- OB 4visit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент23 страницыOB 4visit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Workplace Environment and Its Impact On Employee PerformanceДокумент2 страницыWorkplace Environment and Its Impact On Employee PerformancePrashin Patel100% (1)
- Vista Bistro - A Boat RestaurantДокумент9 страницVista Bistro - A Boat RestaurantNitesh R ShahaniОценок пока нет
- UBL Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент16 страницUBL Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- UNIVERSAL Banking Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент92 страницыUNIVERSAL Banking Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- TPMVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент27 страницTPMVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- TT - Installation - DemoVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент30 страницTT - Installation - DemoVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- The MR ProcessДокумент26 страницThe MR Processshubakar reddyОценок пока нет
- The Beauty of MathematicsДокумент12 страницThe Beauty of Mathematicsconnling100% (1)
- The Marketing MixVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент9 страницThe Marketing MixVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Project Report On Travel and Tourism in Travel AgencyДокумент24 страницыProject Report On Travel and Tourism in Travel AgencyRajat Suri77% (77)
- Tertiary Sector of Indian EconmyДокумент10 страницTertiary Sector of Indian Econmywelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- TCSVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент39 страницTCSVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Summer Project Guidelines For Students of MBAДокумент19 страницSummer Project Guidelines For Students of MBAlatsekОценок пока нет
- TACTFUL Visit Us at Management - UmakantДокумент9 страницTACTFUL Visit Us at Management - Umakantwelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Summer Interns ReportДокумент7 страницSummer Interns Reportwelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- SWIFT - PresentationVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент50 страницSWIFT - PresentationVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Summer Internship ReportДокумент29 страницSummer Internship Reportpuneet_kkv80% (5)
- Strategic Management and Strategic CompetitivenessДокумент32 страницыStrategic Management and Strategic CompetitivenessDhiwahar VklОценок пока нет
- Super Hero Movies Visit Us at Management - UmakantДокумент33 страницыSuper Hero Movies Visit Us at Management - Umakantwelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Summer Internship ReportДокумент29 страницSummer Internship Reportpuneet_kkv80% (5)
- Subordinated DebtVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент5 страницSubordinated DebtVisit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- Slides Strategy Management Pearson Book (12) Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infoДокумент25 страницSlides Strategy Management Pearson Book (12) Visit Us at Management - Umakant.infowelcome2jungleОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Sri Dwi Mutiara-Jurnal CRSS OSNE 1Документ11 страницSri Dwi Mutiara-Jurnal CRSS OSNE 1sri dwi mutiaraОценок пока нет
- LTE Interview QuestionsДокумент10 страницLTE Interview QuestionsMahesh Pratap100% (1)
- Effective-Plant-Course Brochure NovДокумент8 страницEffective-Plant-Course Brochure NovAzri HafiziОценок пока нет
- Mineral Processing Course: ThickeningДокумент50 страницMineral Processing Course: ThickeningAdham Elbrawy100% (1)
- Flap System RiginДокумент12 страницFlap System RiginHarold Reyes100% (1)
- Development Drop - Number - Peformance - For - EstimateДокумент11 страницDevelopment Drop - Number - Peformance - For - Estimateanon_459056029Оценок пока нет
- AI Berkeley Solution PDFДокумент9 страницAI Berkeley Solution PDFPrathamGuptaОценок пока нет
- Mini-Com Cat6E - ®TX6 ™ PLUS UTP Coupler ModulesДокумент2 страницыMini-Com Cat6E - ®TX6 ™ PLUS UTP Coupler Moduleslejlas77Оценок пока нет
- Basf Masteremaco Application GuideДокумент15 страницBasf Masteremaco Application GuideSolomon AhimbisibweОценок пока нет
- 6907 6 52 0040Документ35 страниц6907 6 52 0040amitkumar8946Оценок пока нет
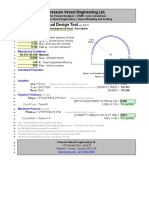
- Hemispherical Head Design ToolДокумент1 страницаHemispherical Head Design Toolnaveen_86Оценок пока нет
- Automation & Control Esst en 200804Документ356 страницAutomation & Control Esst en 200804Sveinn Rúnar JúlíussonОценок пока нет
- GbiДокумент14 страницGbimaurice86Оценок пока нет
- Mid SemДокумент1 страницаMid SemvidulaОценок пока нет
- PLTW: Digital Electronics Syllabus For Mrs. Yusufi: Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and DigitalДокумент5 страницPLTW: Digital Electronics Syllabus For Mrs. Yusufi: Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and DigitalTriston DurbinОценок пока нет
- Formal Analysis of Timeliness in Electronic Commerce ProtocolsДокумент5 страницFormal Analysis of Timeliness in Electronic Commerce Protocolsjuan david arteagaОценок пока нет
- Atpl Formula MergedДокумент74 страницыAtpl Formula Mergeddsw78jm2mxОценок пока нет
- Computers and Operations Research: Yulin Sun, Simon Cong Guo, Xueping LiДокумент12 страницComputers and Operations Research: Yulin Sun, Simon Cong Guo, Xueping LiQuỳnh NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Dayal Bagh: Spircon 2013: Book of AbstractsДокумент202 страницыDayal Bagh: Spircon 2013: Book of AbstractsSant Mat100% (2)
- MD SHAFIUL ISLAM 沙菲 ID;20183290290Документ23 страницыMD SHAFIUL ISLAM 沙菲 ID;20183290290SHAFIUL SETUОценок пока нет
- As Biology Revision L3 Cells Microscopes and IAM PPQ 2Документ7 страницAs Biology Revision L3 Cells Microscopes and IAM PPQ 2Anonymous fFKqcYОценок пока нет
- ¿Cómo Hacerlo?: Dr. Jorge Ramírez Medina, Dr. Guillermo Granados Ruíz EGADE Business SchoolДокумент17 страниц¿Cómo Hacerlo?: Dr. Jorge Ramírez Medina, Dr. Guillermo Granados Ruíz EGADE Business Schoolgalter6Оценок пока нет
- CBL Training ReportДокумент12 страницCBL Training ReportSwapnil Modak100% (1)
- Training Needs Analysis (Managing Training & Development)Документ78 страницTraining Needs Analysis (Managing Training & Development)Henrico Impola100% (1)
- T38N/T48N: Suffix Code Instruction ManualДокумент1 страницаT38N/T48N: Suffix Code Instruction ManualaliОценок пока нет
- 3ADW000379R0301 DCS550 Manual e CДокумент310 страниц3ADW000379R0301 DCS550 Manual e CLaura SelvaОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Pascal Programming MOD 2010Документ5 страницAn Introduction To Pascal Programming MOD 2010Johnas DalusongОценок пока нет
- DodupukegakobemavasevuДокумент3 страницыDodupukegakobemavasevuMartian SamaanОценок пока нет
- 2023 Grades 10-12 Mathematics ATP MediationДокумент14 страниц2023 Grades 10-12 Mathematics ATP Mediationkaybeach007Оценок пока нет
- Assembly Transmission Volvo A40GДокумент52 страницыAssembly Transmission Volvo A40GNanang SetiawanОценок пока нет