Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Run-Off and Numericals On Hydropower
Загружено:
Mahesh Lohano0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
103 просмотров25 страницThe document discusses run-off, which is the portion of total precipitation that flows through a catchment area. It is calculated as total precipitation minus total evaporation. Factors that affect run-off include rainfall patterns, the nature of the catchment area, its shape and size, vegetation, and weather conditions. Hydrographs graphically represent variation in discharge or flow over time and provide information about run-off volumes and rates. Flow duration curves show the relationship between flows and the lengths of time they are available. There are two types of run-off river power plants: with and without pondage, depending on whether they have water storage capacity.
Исходное описание:
Numericals on hydrograph
Оригинальное название
Run-Off and Numericals on hydropower
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document discusses run-off, which is the portion of total precipitation that flows through a catchment area. It is calculated as total precipitation minus total evaporation. Factors that affect run-off include rainfall patterns, the nature of the catchment area, its shape and size, vegetation, and weather conditions. Hydrographs graphically represent variation in discharge or flow over time and provide information about run-off volumes and rates. Flow duration curves show the relationship between flows and the lengths of time they are available. There are two types of run-off river power plants: with and without pondage, depending on whether they have water storage capacity.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
103 просмотров25 страницRun-Off and Numericals On Hydropower
Загружено:
Mahesh LohanoThe document discusses run-off, which is the portion of total precipitation that flows through a catchment area. It is calculated as total precipitation minus total evaporation. Factors that affect run-off include rainfall patterns, the nature of the catchment area, its shape and size, vegetation, and weather conditions. Hydrographs graphically represent variation in discharge or flow over time and provide information about run-off volumes and rates. Flow duration curves show the relationship between flows and the lengths of time they are available. There are two types of run-off river power plants: with and without pondage, depending on whether they have water storage capacity.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 25
Run-off
• Rain fall (used in a general sense) or “precipitation” may be
defined as the total condensation of moisture that reaches
the earth in any form.
• It includes all forms of rains, ice, snow, hail or sleet etc.
• “Evaporation” represents practically all of that portion of
the rainfall that does not reach the point of ultimate use as
stream flow.
• evaporation, includes all the rainfall that is returned to the
atmosphere from land and water surfaces.
• Thus total evaporation is:
Run-off
1. Evaporation from land and water surfaces.
2. Evaporation by transpiration which is the vaporization of
water from the breathing pores of vegetable matter.
3. Atmospheric evaporation (evaporation while precipitation
is falling).
• The portion of the total precipitation that flows through the
catchment area is known as “Run-off”.
• The catchment area of a hydro site is the total area behind
the dam, draining water into the reservoir.
Run-off = Total precipitation – Total evaporation
The unit of run-off are m3/s or day-second meter.
Factors Affecting Run-off
1. Rainfall Pattern. Short, hard showers may produce
relatively little run-off. Rains lasting a longer time results
in larger run-off.
2. Nature of Catchement Area. The Topography, shape and
nature of surface and dub surface geology have greater
influence. The Step and rocky surface give more run off
3. Shape & Size of Catchment Area. Large catchment area
give more run off. The run off at point X in Figure a is more
than that in Figure b.
Factors Affecting Run-off
4 Vegetation. Evaporation and seepage are increased by cultivation.
Cultivation opens and roughens the hard, smooth surface and
promotes seepage.
5- Weather Condition: Low Temperature, high relative humidity
and low winds result in high run off because evaporation losses
increases with increase in temperature, decrease in relative
humidity and increase in wind velocity
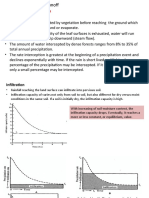
Hydrographs
• A hydrograph is graphical representation that represents
variation of discharge or flow with time
• The following information is available from hydrograph
(i) Rate of flow during any instant during the duration period
(ii) Volume of water during that duration
(iii) Mean annual/monthly run off
(iv) Maximum and Minimum run off
(v) Maximum rate of run off during flood
Hydrographs
Flow Duration Curve
• A flow duration curve shows the relation between
flows and lengths of time during which they are
available.
• The flow duration curve is drawn with magnitudes
of run off as ordinate against the corresponding
percentage of time as abscissa
• The flow duration curve is drawn from available run
off data
Conversion inch to feet
1 m3/s= 35.314 ft3/s
Reservoir Power Plant
• a. Run off river power plants without pondage
This type of hydroelectric power plant, water is not
available all the time.
This type of power station is not suitable for constant
steady load.
There is no pondage or storage facility available in
such type of power plant.
Plant is placed in such a area,where water is coming
directly from the river or pond. This type of
hydroelectric power plant is called run off power
plant without pondage
Reservoir Power Plant
• b. Run off river power plants with pondage
•
This type of plant is used to increase the capacity of
pond.The pond is used as a storage water of hydro
electric power plant.Increased the pond size means
more water is available in the plant,so such type of
hydro electric power plant is used fluctuating load
period depending on the size of pondage.
Pondage Factor
• It is ratio of total inflow hours in a given period to
total number of hours the plant is running during
the same period
SPECIFIC SPEED OF TURBINE
• the specific speed is number of revolutions per
minute at which a given runner would revolve
Вам также может понравиться
- Rain Water HarvestingДокумент30 страницRain Water Harvestingkaran100% (1)
- How To Opérate An Amine PlantДокумент4 страницыHow To Opérate An Amine PlantAry HernandezОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics and Hydrology - Lecture 5 (Surface Runoff)Документ16 страницHydraulics and Hydrology - Lecture 5 (Surface Runoff)joelkyeswa97Оценок пока нет
- Chapter5 Hydrology ClassДокумент72 страницыChapter5 Hydrology Classrienalen placaОценок пока нет
- Hydrograph - Analysis - 2 Hydro PDFДокумент68 страницHydrograph - Analysis - 2 Hydro PDFNurul QurratuОценок пока нет
- Hafta.Документ34 страницыHafta.raiden timberlandОценок пока нет
- Hydrologic Losses: Infiltration, Evaporation and TranspirationДокумент45 страницHydrologic Losses: Infiltration, Evaporation and TranspirationdigdoОценок пока нет
- Precipitation 9Документ24 страницыPrecipitation 9Zain Nabi KhanОценок пока нет
- Hydro-Electric Power Plant: HydrologyДокумент24 страницыHydro-Electric Power Plant: HydrologyPolavarapu Srinivasa RaoОценок пока нет
- Introduction To HydrogeologyДокумент16 страницIntroduction To Hydrogeologydont forgetОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ23 страницыChapter 3arnie_suharnie100% (1)
- Engineering Hydrology: Puan Saedatulfirdaus BT Sa'AraniДокумент26 страницEngineering Hydrology: Puan Saedatulfirdaus BT Sa'AraniHasmittha100% (1)
- 8.1 War 2103 Hydrographs IДокумент8 страниц8.1 War 2103 Hydrographs IAnguzu Olega BrevisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ20 страницChapter 5Sanjaya PoudelОценок пока нет
- Hydrologic Principles and AnalysisДокумент153 страницыHydrologic Principles and AnalysisLurima FariaОценок пока нет
- 7.0 HydrographДокумент31 страница7.0 HydrographSiddhartha SahaОценок пока нет
- HydrographДокумент141 страницаHydrographWarren LeeОценок пока нет
- Week 4 - 13 - Runoff IntroДокумент37 страницWeek 4 - 13 - Runoff IntroyeeОценок пока нет
- Hydrology1 PDFДокумент55 страницHydrology1 PDFSatyam ChandraОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of RunoffДокумент22 страницыCharacteristics of RunoffSaima SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Runoff: BSC Civil Engineering Level 3Документ42 страницыRunoff: BSC Civil Engineering Level 3TeddyОценок пока нет
- Hydrology & Site Selection of Hydro Power PlantДокумент25 страницHydrology & Site Selection of Hydro Power PlantJatinder KumarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9 15Документ70 страницLecture 9 15SHALINI SOLANKEОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Be Civil Imtiaz Ali Khan Su 17-01-074 036 HydrologyДокумент10 страницFinal Exam Be Civil Imtiaz Ali Khan Su 17-01-074 036 HydrologyImtiaz Ali KhanОценок пока нет
- Hydrology & Site Selection of Hydro Power PlantДокумент25 страницHydrology & Site Selection of Hydro Power PlantDadi DahalОценок пока нет
- 7.0 HydrographДокумент31 страница7.0 Hydrographanoop RОценок пока нет
- Evaporation, Transpiration, Interception and Depression StorageДокумент24 страницыEvaporation, Transpiration, Interception and Depression StorageMary Graçe Çanoy100% (1)
- 4 - Flow Into and Thru The SoilДокумент56 страниц4 - Flow Into and Thru The SoilJames PelobilloОценок пока нет
- Abstractions From Precipitation: AbstractionДокумент10 страницAbstractions From Precipitation: AbstractionmarkhanОценок пока нет
- RUNoffДокумент40 страницRUNoffAchyutha Anil100% (1)
- Introduction To Hydrology 1Документ6 страницIntroduction To Hydrology 1Ralph Alexander PulidoОценок пока нет
- War 2103 RunoffДокумент41 страницаWar 2103 RunoffEgana IsaacОценок пока нет
- Chapter Four: INFILTRATIONДокумент16 страницChapter Four: INFILTRATIONmaxamed muuseОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 (A)Документ38 страницUnit 2 (A)Kartik PatelОценок пока нет
- Rainfall-Runoff RelationДокумент58 страницRainfall-Runoff RelationEam100% (2)
- RUNOFFДокумент54 страницыRUNOFFJustin Kurt TesiornaОценок пока нет
- Hydro GraphsДокумент40 страницHydro GraphsSHIVAM GOYAL 4-Yr B.Tech. Civil Engg., IIT (BHU)Оценок пока нет
- CEWB 322 Chapter 1Документ77 страницCEWB 322 Chapter 1moaz zaherОценок пока нет
- RUNOFFДокумент2 страницыRUNOFFBetter guggОценок пока нет
- Topic 1Документ33 страницыTopic 1Nur HananiОценок пока нет
- 1 5 AbstractionДокумент10 страниц1 5 Abstractionhammadjamil730Оценок пока нет
- Hope No One SeesДокумент30 страницHope No One SeesAmaru ShakurОценок пока нет
- 6 EvaporationДокумент23 страницы6 EvaporationAwaisZahidOrakzaiОценок пока нет
- Evaporation,, Interception and Depression Storage: TranspirationДокумент23 страницыEvaporation,, Interception and Depression Storage: TranspirationKaven Joy EquinanОценок пока нет
- Irrigation Engg 2Документ17 страницIrrigation Engg 2Nilesh SarkarОценок пока нет
- Hydrology: Group Of: Kaven Joy A. Equinan Eduardo R. Valencia Jr. Karl Jude P. Pascua Instructor: Engr. Renante C. OrangДокумент23 страницыHydrology: Group Of: Kaven Joy A. Equinan Eduardo R. Valencia Jr. Karl Jude P. Pascua Instructor: Engr. Renante C. OrangKaven Joy EquinanОценок пока нет
- WEEK4 - InfiltrationДокумент46 страницWEEK4 - InfiltrationIsbel100% (1)
- Notes For Prefinal HydrologyДокумент16 страницNotes For Prefinal HydrologysheintigomОценок пока нет
- HydrographДокумент5 страницHydrographKristal AbalosОценок пока нет
- Hydrograph AnalysisДокумент48 страницHydrograph AnalysisSunil DuwalОценок пока нет
- Hydrology Lecture Note-I Hydrologic CycleДокумент29 страницHydrology Lecture Note-I Hydrologic CycleRa INnОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1-Hydrologic Cycle, PrecipitationДокумент35 страницChapter 1-Hydrologic Cycle, PrecipitationMohamed ahmedОценок пока нет
- Unit III Hydrographs - With Unit HydrographДокумент18 страницUnit III Hydrographs - With Unit HydrographAditya RajОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Stream Flow and Runoff 3333Документ37 страницChapter 3 - Stream Flow and Runoff 3333Mohamed ahmedОценок пока нет
- CE 363 Lecture Note Upto Mid TermДокумент29 страницCE 363 Lecture Note Upto Mid TermJhon shonОценок пока нет
- Introduction To HydrometeorologyДокумент21 страницаIntroduction To HydrometeorologyApril JulianoОценок пока нет
- Interception and Depression Storage 2011Документ62 страницыInterception and Depression Storage 2011Muhammad Sandy50% (2)
- Runoff (Streamflow) : K. SrinivasanДокумент43 страницыRunoff (Streamflow) : K. Srinivasanjuliyet strucОценок пока нет
- CIV224 Part 2 of Mod 1Документ60 страницCIV224 Part 2 of Mod 1Santhosh M BОценок пока нет
- Flow Over Immersed Bodies: General CharacteristicsДокумент120 страницFlow Over Immersed Bodies: General CharacteristicsMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- CH 9 Flow Over Immersed BodiesДокумент120 страницCH 9 Flow Over Immersed BodiesMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Unforced OscillationsДокумент15 страницUnforced OscillationsMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Free Vibration of Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF)Документ107 страницFree Vibration of Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF)Mahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- ENGR-1100 Introduction To Engineering Analysis: Simple Trusses, The Method of Joints, & Zero-Force MembersДокумент11 страницENGR-1100 Introduction To Engineering Analysis: Simple Trusses, The Method of Joints, & Zero-Force MembersMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- ME 305 Part 6 Differential Formulation of Fluid Flow PDFДокумент10 страницME 305 Part 6 Differential Formulation of Fluid Flow PDFMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1-ICE UpdateДокумент69 страницChapter 1-ICE UpdateMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- BioenergyДокумент18 страницBioenergyMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ1 страницаAssignment 1Mahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- DiveshДокумент2 страницыDiveshMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Differential Equation Numerical SolutionДокумент5 страницDifferential Equation Numerical SolutionMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Engineering MechanicsДокумент2 страницыEngineering MechanicsMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Loops in MatlabДокумент22 страницыLoops in MatlabMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- How To Use RetscreenДокумент25 страницHow To Use RetscreenMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Solar Energy Basics: Thermal and PVДокумент54 страницыSolar Energy Basics: Thermal and PVMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Air Pollution and Their CausesДокумент30 страницAir Pollution and Their CausesMahesh LohanoОценок пока нет
- Chap 09 Solutions Ex 9 5 Method PDFДокумент13 страницChap 09 Solutions Ex 9 5 Method PDFMahesh Lohano100% (1)
- Red Pot PDFДокумент294 страницыRed Pot PDFArchismita HazraОценок пока нет
- Rheology of The Earth's Mantle: A Historical Review: Gondwana Research July 2010Документ30 страницRheology of The Earth's Mantle: A Historical Review: Gondwana Research July 2010MarcosGouveaОценок пока нет
- Module 1 MOdern Physics FinalДокумент10 страницModule 1 MOdern Physics FinalMary Joy BernasolОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Transitional Metal ChemistryДокумент131 страницаAn Introduction To Transitional Metal ChemistryHafsa KhanОценок пока нет
- Intropostlab Exp4Документ3 страницыIntropostlab Exp4JC NuquiОценок пока нет
- Tran Nitta: BittyДокумент5 страницTran Nitta: BittyNam TranОценок пока нет
- Catalogo CiiДокумент2 страницыCatalogo CiiSergio ChupinaОценок пока нет
- Solubility and Solubility Product ConstanДокумент18 страницSolubility and Solubility Product ConstanNur Masyittah IrmiОценок пока нет
- Product Technical Bulletin: BackgroundДокумент2 страницыProduct Technical Bulletin: BackgroundYolian Andres Aricapa CastañoОценок пока нет
- Design of Flexible and Rigid PavementДокумент29 страницDesign of Flexible and Rigid Pavementrodge macaraegОценок пока нет
- Ceiling PHR PHS Suspension IsolatorsДокумент14 страницCeiling PHR PHS Suspension IsolatorsKunal GujarathiОценок пока нет
- Science 4 Quarter 3 Module 6 Light FinalДокумент13 страницScience 4 Quarter 3 Module 6 Light FinalFrit Zie100% (1)
- FEA Question BankДокумент6 страницFEA Question Bankmenmoli2012Оценок пока нет
- Theory of Plasticity: December 2018Документ28 страницTheory of Plasticity: December 2018Angga Fajar SetiawanОценок пока нет
- Reciprocating Pump Manual 1Документ17 страницReciprocating Pump Manual 1Youssef ChahlaОценок пока нет
- 1.introduction of OrificeДокумент20 страниц1.introduction of OrificeJohn Andre MarianoОценок пока нет
- Bsen1011 3Документ32 страницыBsen1011 3mohamed elmasryОценок пока нет
- Esab Product Catalogue 2010Документ351 страницаEsab Product Catalogue 2010S C Gaur67% (3)
- Naptin ReportДокумент3 страницыNaptin ReportchdiОценок пока нет
- Sawyer-Tower Circuit PDFДокумент27 страницSawyer-Tower Circuit PDFBojan StojadinovićОценок пока нет
- SpaceCAD Model Rocket SoftwareДокумент7 страницSpaceCAD Model Rocket Softwareheric19886445Оценок пока нет
- 1.2.d Single Reaction in A PFR With Heat Exchange - Solution.2023Документ9 страниц1.2.d Single Reaction in A PFR With Heat Exchange - Solution.2023Bastien KamaraОценок пока нет
- Blue-Tip Screw BoltДокумент16 страницBlue-Tip Screw BoltRajed MaglinteОценок пока нет
- Bray Olaya 2023 2022 H Bolton Seed Memorial Lecture Evaluating Liquefaction EffectsДокумент23 страницыBray Olaya 2023 2022 H Bolton Seed Memorial Lecture Evaluating Liquefaction EffectsxfvgОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower DiscussionДокумент10 страницCooling Tower Discussiondhanu_lagwankar100% (1)
- Static Behaviour of Engine Mounting Bracket: ArticleДокумент7 страницStatic Behaviour of Engine Mounting Bracket: ArticlehadiОценок пока нет
- Chemistry /pi Eɪtʃ/ Hydrogen Power Acidity Basicity Aqueous Solution H AlkalineДокумент22 страницыChemistry /pi Eɪtʃ/ Hydrogen Power Acidity Basicity Aqueous Solution H AlkalineCHUKWU VICTORОценок пока нет
- DNV-RP-E305 - 1988 - On-Bottom Stability of Submarine PipelinesДокумент50 страницDNV-RP-E305 - 1988 - On-Bottom Stability of Submarine PipelinesGrant HosieОценок пока нет