Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Coastal Engineering Lecture # 2
Загружено:
Shheryar Bismil0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
41 просмотров31 страницаTransportation Engineering...Lecture about the Modes of transportation like water ways,Highway Airways and railways etc.
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документTransportation Engineering...Lecture about the Modes of transportation like water ways,Highway Airways and railways etc.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
41 просмотров31 страницаCoastal Engineering Lecture # 2
Загружено:
Shheryar BismilTransportation Engineering...Lecture about the Modes of transportation like water ways,Highway Airways and railways etc.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 31
Advantages
Unlike railways and roads, no special track is
required to be built.
Little motor power per unit load
transportation is required.
Possesses high load carrying capacity.
Most economical mode for foreign trade.
Provides powerful means of defense of
coastline
Assist in industrialization and development of
nations.
Disadvantages
Slow means of transportation.
Subject to storms and hurricanes.
Waves and tides hinder loading and
unloading of ships
Fluctuations of water level causing rubbing of
ship against berths.
Pakistan shares a 1,200 kilometres long coast
line with the Arabian Sea ‐ a mid sea which
joins the strategic oil line of Persian Gulf with
the Indian Ocean. However, owing to the growing
needs of the country, there was a need to
develop other smaller coastal ports into major
cargo handling ports. Besides Karachi, Pasni,
Jiwani, Gadani, Ormara and Gwadar are other
ports which are being developed into world class
ship handling centers. Of these Gwadar is the
latest development.
Pakistan has two operational seaports,
Karachi Port and Port Muhammad Bin Qasim
One deep‐water seaport is under
construction at Gawadar.
Three large fish harbours which are located at
Karachi, Korangi and Gawadar.
Other smaller fishing harbours are Pasni,
Ormara, and Jeewani.
Karachi Shipyard & Engineering Works and a
few small Private Companies Undertake
Limited ship building in Pakistan. Role of
private companies is very limited.
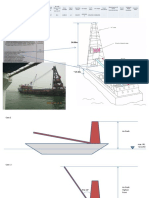
It is a water area partially enclosed and
protected naturally and artificially from storm
and huge destructive wave activity providing
safe and simple accommodation for vessels
seeking refuge, supplies, refueling, repairs
and transfer of cargo.
The facilities Provided Include Protection By
breakwaters, off‐shore moorings, Berthing
and mooring structures within the harbour,
general and bulk cargo handling
facilities and allied supplementary
services.
Natural Harbour. It is an inlet or water area
protected from storm and distinctive wave
activity by the natural configuration of land,
rocky out crops, islands or other physical
features. Its entrance is so formed and located as
to facilitate the movement of ships while
ensuring comparatively quiet environment within
the harbour. To make them more useful to
commercial vessels additional constructions take
place. Well‐known natural harbours are New York,
San Francisco and Rio‐de Janeiro. Port Qasim is
situated at Phitti and Gharo creeks in Pakistan.
Okaha and Bombay are natural ports protected by
Islands.
Semi Natural Harbour. Semi‐natural harbour is an
inlet or water area, sheltered on two sides by the
headland and requiring artificial protection only
at the entrance. Next to the purely natural
harbour, it forms the most desirable harbour site.
Plymouth, Cherbourg, Vishakhapatnan take the
advantage of the natural location, to become
well‐protected harbours by the addition of
detached breakwaters at entrances. Karachi
harbour is also a semi‐natural, protected at the
entrance by Manora breakwater.
Artificial Harbour: It is the one which is
protected from the effect of destructive wave
activities by means of extensive civil works in
the form of breakwaters etc. Extensive
Maintenance dredging may be necessitated.
Eamples are Chennai in India, Hamburg in
Germany.
Commercial Harbour. It is one in which docks
are provided with the necessary facilities for
loading and discharging cargo. Dry docks are
provided sometimes for ship repairs either as
a part of a bigger harbour complex or
independently as a unit. Some times, single
commodity pier or terminal is provided such
as oil terminal, iron & coal pier etc. Port
Qasim is an example of large commercial
harbour in Pakistan.
Refuge Harbour It is a sheltered area that may
be used as heaven for ships in storm or
emergency. It should be accessible during
any condition of weather and state of tide. It
should provide safe and commodious
anchorage system and facilities for repairs
and supplies as well. It may be a part of
commercial harbour. An example of refuge
harbour is sandy bay at the mouth of
Delaware (USA).
Sometimes an outer harbour is constructed
which serves as the anchorage while the
basin within the inner breakwater constitutes
the commercial harbour and refuge harbour.
A fine example of combined commercial
harbour and refuge harbour is Dover in
England. These also serve as naval bases
during the war and therefore equipped with
adequate means of defence.
Fishery Harbour. A fishery harbour is solely
for the operation of small fishing boats,
fishing trawlers and vessels. This may be
naturally or artificially protected. This
harbour must have adequate number of
refrigerated storage. A fishery harbour is
sometimes a part of large port complex or a
commercial harbour. Examples are Karachi
and Gwadar fish harbours in Pakistan. Rohri is
a fish harbour located in Sind.
Military Harbours. It is a harbour providing
naval base for accommodation of vessels,
submarines, gunboats etc for defence of the
country. Pearl Harbour in Hawaii and
Guantanamo in Cuba are examples.
Sea or ocean harbour.
River or Estuary harbour.
Canal harbour.
Lake harbour.
Provide quick, easy and safe access for all
ships, in all stages of tides, throughout the
year. Approach channel should be free from
curves and bends
Have an entrance, which should neither be
too narrow nor too wide. If narrow, chances
of clashes of ships in storms will increase. If
wide, more turbulence is likely to enter
harbour basin making berthing of ships
difficult and hazardous.
Have an entrance whose width should widen
very rapidly inside the harbour to reduce
effects of waves, which enter the harbour
basin.
Ensure safe accommodation for ships by
providing safe anchorage and adequate draft
depth. Soil conditions should be suitable so
that silting is less. Biggest ship in harbour
should get enough draft to reach the berths.
Be capable of accommodating and handling
required number of ships thus avoiding
delays in getting berths
Should provide safe mooring and berthing
with minor wave and current action.
Penetration of damaging wind waves should
be eliminated by structures like breakwater
etc.
Should provide adequate facilities specially
fuel supply, inspection and repair facilities.
– Initial Considerations. These comprise of: ‐
• Cost of development of a harbour is tremendous.
Need for a harbour should be well thought and
carefully evaluated technically.
• Construction of a harbour should be
economically justifiable.
• Foreseeing future expected volume of sea borne
commerce.
• Availability of inland communications by land
and water.
• Impact of harbour construction
Provisional Selection of Site. Requirements of
port authorities are considered and technical
studied are conducted. These are followed by
selecting a suitable site provisionally.
Forecasted arrival of ships will mainly govern
the requirements of a harbour in respect of
its accessibility, size, shape, and salient
features.
– Information required for Design
• Detailed survey of the proposed site.
• Nature of coastline and if any protection is provided.
Consider past trends and changes in coastline.
• Depth of water is considered for suitable draft.
Deeper site is preferred so that dredging cost
reduces.
• Soil information by boring inside the water to
determine suitability for anchorage & deepening.
• Soil information by boring on the shore land, which
helps in designing and construction of wharves,
sheds, railway lines, lifts, cranes etc.
• Presence or otherwise of sea insects
Hydraulic information to include
– Frequency of storms.
– Direction & intensity of winds.
– Tidal range.
– Height of waves and force exerted
Final Selection:
Final Selection of site will be governed by
Technical suitability
Cost of construction and maintenance of
marine structures.
Initial dredging cost.
Recurrent dredging cost for maintenance of
design depth.
Port is a harbor with marine terminal
facilities such as landing of passengers,
cargo handling and storing. Port is portion of
a harbor which serves as base of commercial
activity. Harbor and port are complementary.
-Afford shelter, allied facilities and repairs for visiting
ships.
– Have a hard surface coastline to avoid frequent
repairs to docks and buildings etc.
– Have adequate area for future expansion.
– Have communication links specially railway links.
– Have entrance channel providing easy entrance and
exit.
– Have suitable turning basin.
– Be strategically located to guard against aggression.
– Be capable of handling good tonnage of cargo.
– Be in area having advanced culture, trade and
industry.
Вам также может понравиться
- Ports and Harbors PDFДокумент4 страницыPorts and Harbors PDFBeah Francia De la CruzОценок пока нет
- Harbour EngineeringДокумент64 страницыHarbour EngineeringshankaregowdaОценок пока нет
- Policarpio, Ma. Elizabeth Agquiz, Christine Joy Umali, Niel Patrick Samson, Mark ArisДокумент65 страницPolicarpio, Ma. Elizabeth Agquiz, Christine Joy Umali, Niel Patrick Samson, Mark Arismacs_smacОценок пока нет
- Exogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition) : 30 August 2018 1Документ78 страницExogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition) : 30 August 2018 1Marjorie BrondoОценок пока нет
- Calculo Impacto DefensasДокумент22 страницыCalculo Impacto DefensasRuben Bartolome GarciaОценок пока нет
- Brochure Portcoast DesignДокумент89 страницBrochure Portcoast DesignVăn LiễnОценок пока нет
- The Marine EnvironmentДокумент12 страницThe Marine EnvironmentRONNEL MALONGОценок пока нет
- The Water Framework Directive & Port Management / Operation IssuesДокумент14 страницThe Water Framework Directive & Port Management / Operation IssuesbastocaОценок пока нет
- SEAPORT Case StudyДокумент194 страницыSEAPORT Case StudyArch Chet AlabaОценок пока нет
- Passenger Ship in A Shipyard at Papenburg, Ger. © Meyer-Werft/Press and Information Office of TheДокумент69 страницPassenger Ship in A Shipyard at Papenburg, Ger. © Meyer-Werft/Press and Information Office of TheVinoth KumarОценок пока нет
- Installation ManualДокумент18 страницInstallation ManualNadeem AbbasiОценок пока нет
- Port Planning and Investment ToolkitДокумент168 страницPort Planning and Investment ToolkitChristian BethlenОценок пока нет
- Wharf - Dock Fender Design Manual-ENДокумент56 страницWharf - Dock Fender Design Manual-ENSteven SebastianОценок пока нет
- Aluminum Internal Floating Roofs Perimeter Seal Systems Oil / Water Separator Covers For Api Separator BasinsДокумент8 страницAluminum Internal Floating Roofs Perimeter Seal Systems Oil / Water Separator Covers For Api Separator BasinsLDPОценок пока нет
- Basic Wave Theory Review by Graham WarrenДокумент33 страницыBasic Wave Theory Review by Graham WarrennthongОценок пока нет
- MIKE21Документ16 страницMIKE21Defza HuristuОценок пока нет
- H&OE - Brochure-Final-2018-2019Документ24 страницыH&OE - Brochure-Final-2018-2019NaveenОценок пока нет
- Floating Dolphins Floating Dolphins Floating Dolphins: 650.01 GeneralДокумент12 страницFloating Dolphins Floating Dolphins Floating Dolphins: 650.01 GeneralsivakumarОценок пока нет
- Coastal Structures: Wave LoadsДокумент15 страницCoastal Structures: Wave LoadsSanthi KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Looe Marina Presentation GROUP 2Документ33 страницыLooe Marina Presentation GROUP 2Thomas ClarkОценок пока нет
- Mooring Assessment FormДокумент4 страницыMooring Assessment FormSAGAMIОценок пока нет
- NAV 04 Pilot Card REV 5.0 by A. TarkovДокумент9 страницNAV 04 Pilot Card REV 5.0 by A. TarkovirakliОценок пока нет
- PortsДокумент127 страницPortsoumaima100% (1)
- Emr 2411 Lecture Notes 1Документ27 страницEmr 2411 Lecture Notes 1yassinОценок пока нет
- 2014 PGN Annual ReportДокумент496 страниц2014 PGN Annual ReportAndiAndaKacongОценок пока нет
- Fishery Ports - RHDHVДокумент29 страницFishery Ports - RHDHVDao Ba ThanhОценок пока нет
- Harbour Works (Break Water) 15. - 17.01.2023 PDFДокумент50 страницHarbour Works (Break Water) 15. - 17.01.2023 PDFFahim ShahriarОценок пока нет
- BreakwatersДокумент5 страницBreakwatersRamz AshieОценок пока нет
- Wave Attenuators Info PDFДокумент32 страницыWave Attenuators Info PDFMicah Ironfalcon ArceñoОценок пока нет
- Crest Modifications To Reduce Wave OvertДокумент20 страницCrest Modifications To Reduce Wave OvertDinar IstiyantoОценок пока нет
- BreakwatersДокумент26 страницBreakwatersnithesh kumar jОценок пока нет
- Catalog Rakuna IVДокумент8 страницCatalog Rakuna IVJia Hann TanОценок пока нет
- Fetch PDFДокумент5 страницFetch PDFPatricio Castillo ManquecoyОценок пока нет
- Extension of Existing Quay Wall - ACRPS - Cadiz - SpainДокумент4 страницыExtension of Existing Quay Wall - ACRPS - Cadiz - SpainIgnatius SamrajОценок пока нет
- Quay Walls - Combined - Wall - Buckling - TubesДокумент12 страницQuay Walls - Combined - Wall - Buckling - TubesHugo LeiteОценок пока нет
- Quay Wall Bottom Protection PDFДокумент12 страницQuay Wall Bottom Protection PDFdndudcОценок пока нет
- Derrick LighterДокумент2 страницыDerrick Lighterhessian123Оценок пока нет
- Jetty Technicalreporttotalmarineltdwithplansdated13072018 PDFДокумент18 страницJetty Technicalreporttotalmarineltdwithplansdated13072018 PDFAjay JainОценок пока нет
- Docks Harbours Day3Документ28 страницDocks Harbours Day3Gopi RajuОценок пока нет
- Presentation #2 - Wind Driven WavesДокумент20 страницPresentation #2 - Wind Driven WavesGarry DartОценок пока нет
- Matlab TutorialДокумент55 страницMatlab TutorialSahil JawaОценок пока нет
- Port of AntwerpДокумент5 страницPort of AntwerpMichael DixonОценок пока нет
- Volume I Main Report - S PDFДокумент234 страницыVolume I Main Report - S PDFJesperОценок пока нет
- Tables Design Tables and EquationsДокумент23 страницыTables Design Tables and Equationsامين الزريقيОценок пока нет
- Manual HS 2023 - BS VersionДокумент416 страницManual HS 2023 - BS VersionSander KosterОценок пока нет
- M21MT SciDocДокумент42 страницыM21MT SciDocAhmad Safii MaarifОценок пока нет
- Steel Sheet Piles Ing.D.Kohnen-DK PDFДокумент33 страницыSteel Sheet Piles Ing.D.Kohnen-DK PDFSaravanan MuthuramanОценок пока нет
- EOE 1 LatestДокумент37 страницEOE 1 LatestSanjitОценок пока нет
- Trabajo Tablestacas (Cricaldi)Документ5 страницTrabajo Tablestacas (Cricaldi)Orlando Carlos Ricaldi VictorioОценок пока нет
- Rubble-Mound BreakwaterДокумент1 страницаRubble-Mound BreakwaterlocasОценок пока нет
- Foundation Solutions For Projects: Harbour ConstructionДокумент138 страницFoundation Solutions For Projects: Harbour ConstructionAnonymous U353mI1Оценок пока нет
- Dam Foundation Treatment: GroutingДокумент27 страницDam Foundation Treatment: GroutingZeleke TaimuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10: Beaches, Shoreline Processes and The Coastal OceanДокумент82 страницыChapter 10: Beaches, Shoreline Processes and The Coastal OceanCarol GirottoОценок пока нет
- IntrodutionДокумент32 страницыIntrodutionsatydevsinghnegiОценок пока нет
- Port Master Plan Beira FinalДокумент303 страницыPort Master Plan Beira Finalkhayaq001Оценок пока нет
- Full Paper 200 PDFДокумент16 страницFull Paper 200 PDFMahdi FekiОценок пока нет
- Geotech ELДокумент6 страницGeotech ELnithesh kumar jОценок пока нет
- Empirical Equations For Deformation Capacity of Conventional RC Shear WallsДокумент12 страницEmpirical Equations For Deformation Capacity of Conventional RC Shear WallsCarsonBakerОценок пока нет
- Harbors 1Документ51 страницаHarbors 1bhupendra singhОценок пока нет
- Airport, Seaport and Harbour EngineeringДокумент84 страницыAirport, Seaport and Harbour EngineeringAchii AchuОценок пока нет
- Dampness: Construction EngineeringДокумент17 страницDampness: Construction EngineeringShheryar BismilОценок пока нет
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology Mirpur AJK Civil Engineering Department Geotechnical Engineering LabДокумент4 страницыMirpur University of Science and Technology Mirpur AJK Civil Engineering Department Geotechnical Engineering LabShheryar BismilОценок пока нет
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology (MUST) Bill of Quantities Construction Project Management HOUSE SIZE 35'X39' 5-Marla HouseДокумент1 страницаMirpur University of Science and Technology (MUST) Bill of Quantities Construction Project Management HOUSE SIZE 35'X39' 5-Marla HouseShheryar BismilОценок пока нет
- Sci-Lab Software Works: Used t0 Find Out SFD & BMD in Multiple Applied Points LoadingsДокумент6 страницSci-Lab Software Works: Used t0 Find Out SFD & BMD in Multiple Applied Points LoadingsShheryar BismilОценок пока нет
- Terms Related To Docks and HarboursДокумент7 страницTerms Related To Docks and Harboursحاجى صاحبОценок пока нет
- 3 Question BankДокумент4 страницы3 Question BankDipika GuptaОценок пока нет
- Harbors 1Документ51 страницаHarbors 1bhupendra singhОценок пока нет
- IcelandДокумент7 страницIcelandĐÌNH HIẾU PHẠMОценок пока нет
- Harbour MaterialДокумент62 страницыHarbour MaterialBalaji vОценок пока нет
- Water Transportation Is The Intentional Movement by Water Over Large DistancesДокумент3 страницыWater Transportation Is The Intentional Movement by Water Over Large Distancesmarvin fajardoОценок пока нет
- Ports and HarborsДокумент31 страницаPorts and HarborsEviaОценок пока нет
- University of Juba-1Документ10 страницUniversity of Juba-1marekmanyielОценок пока нет
- Harbour Engineering NotesДокумент21 страницаHarbour Engineering Notes022bshivanshОценок пока нет
- 2022.09.18 Fowze CE6315 GC OffshoreДокумент45 страниц2022.09.18 Fowze CE6315 GC OffshoreAshan Udaya PushpakumaraОценок пока нет
- Ir. H. Isnugroho, CES: Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Program Study Muhammadiyah University of SurakartaДокумент31 страницаIr. H. Isnugroho, CES: Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Program Study Muhammadiyah University of SurakartaRhezader AgОценок пока нет
- Ports & Harbour Engineering - 1 - Harbours & Natural PhenomenaДокумент39 страницPorts & Harbour Engineering - 1 - Harbours & Natural Phenomenaraghav Varma75% (4)
- Harbours and Ports SayyadДокумент93 страницыHarbours and Ports SayyadchetanОценок пока нет
- Upang Cea 4bsce Cie128 P3Документ23 страницыUpang Cea 4bsce Cie128 P3Robby BajamondeОценок пока нет
- Port Planning - NotesДокумент6 страницPort Planning - Notesmail2arunjithОценок пока нет
- Port Planning MemosДокумент58 страницPort Planning MemosPanoran CharlengОценок пока нет
- DESIGN OF WATER TRANSPORTATION FACILITIES (Group-8)Документ13 страницDESIGN OF WATER TRANSPORTATION FACILITIES (Group-8)Bryan YuОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Good Harbours: Presentation by - Fajardo, Marvin E. 30820Документ40 страницCharacteristics of Good Harbours: Presentation by - Fajardo, Marvin E. 30820marvin fajardoОценок пока нет
- UNIT-5 Harbour EngineeringДокумент20 страницUNIT-5 Harbour EngineeringsuryaОценок пока нет
- Agent Orange and Blue Water NavyДокумент1 страницаAgent Orange and Blue Water NavyEd Ball100% (1)
- Harbour NotesДокумент18 страницHarbour NotesTirumala Chakrapani EtiОценок пока нет
- Harbor - WikipediaДокумент25 страницHarbor - Wikipediayeni maratussОценок пока нет
- Ref Cli GB 2019 Core-LocДокумент7 страницRef Cli GB 2019 Core-LocMohamed AdelОценок пока нет
- Harbour and DocksДокумент20 страницHarbour and DocksDiya ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Dock Harbour EnggДокумент4 страницыDock Harbour Enggsiva gubbalaОценок пока нет
- Review of Selected Standards For: Floating Dock DesignsДокумент24 страницыReview of Selected Standards For: Floating Dock DesignsmadsonbaknaОценок пока нет
- Planning and Design of AДокумент13 страницPlanning and Design of ApavaihouseОценок пока нет
- Harbour, Port, and JettyДокумент4 страницыHarbour, Port, and JettyWan HaziqОценок пока нет
- M MM M MM: Prepared By: Rohi Muthyala NIT Hamirpur (2008-12) BatchДокумент53 страницыM MM M MM: Prepared By: Rohi Muthyala NIT Hamirpur (2008-12) BatchRohi Reddy67% (3)
- Assignment 2Документ4 страницыAssignment 2albackup098Оценок пока нет