Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Starters For IM-ACMC
Загружено:
Bhavik Prajapati0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
45 просмотров15 страницStarters for IM-ACMC
Оригинальное название
Starters for IM-ACMC
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документStarters for IM-ACMC
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
45 просмотров15 страницStarters For IM-ACMC
Загружено:
Bhavik PrajapatiStarters for IM-ACMC
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 15
Sigma Institute Of Engineering
Electrical Engineering Department
Bakrol, Vadodara
Active Learning Assignment Topic On:
Prepared By- Guided By-
Nikunj Bariya (130500109004) Mr Deep Thanki
Nimesh Bariya (130500109005) Asst. Professor
Juhil Bhadresha (130500109006) Electrical Dept.
Nirav Mistry (130500109024) SIE - Bakrol
Aditya Parikh (130500109027)
Suraj Salunke (130500109045)
FLOW OF PRESENTATION
• Introduction (Necessity Of Starters)
• Types of Starters
• Direct On Line Starters
• Primary Resistor (Reactor)
• Auto transformers (Auto starter)
• Star Delta Switch
• Rotor Resistance
INTRODUCTION
• It is shown that a plain induction motor works as a polyphase transformer
with short circuited secondary. Therefore, if normal supply voltage is
applied to a motor, then, as in case of a transformer, a very large initial
current will flow through the motor, though for a very short while.
• Induction motors when supplied with voltage draw 5-7 times the full load
current and develop on 1.5 to 2.5 times their full load torque. The initial
excessive current may damage the windings and the motor.
• Hence to limit this excessive current some resistances have to be applied
before applying the voltage. This work is done by devices known as
STARTERS.
TYPES OF STARTERS
To resist the starting current, the starters are used.
There are the following types of starters used in Induction Motors:
• Direct On Line Starter
• Primary Resistor (Reactor)
• Auto-transformer (Auto starter)
• Star Delta Starter
• Rotor Resistance
Direct On Line Starters
• This is the most common starting method available on the market and at
basic starter for all motor application. The starting equipment consists of
only a main contactor and thermal or electronic overload relay. The
disadvantage with DOL starter is that it gives the highest possible starting
current.
• A normal value is between 6 to 7 times the rated motor current but values
of up to 9 or 10 times the rated current exist. Besides then DOL starter
draw the starting current there also exists a current peak that can rise up
to 14 times the rated current since the motor is not energized from the
first moment when starting.
• The values are dependent on the design and size of the motor, but in
general, a smaller motor gives higher values than a larger one.
• During a direct on line start, the starting torque is also very high, and is
higher than necessary for most applications. The torque is the same as the
force, and an unnecessary high force gives unnecessary high stresses on
couplings and the driven application
PRIMARY RESISTANCE STARTER
• Their purpose is to drop some voltage and hence reduce the applied voltage
across the motor terminals. In this way, the initial current drawn by the motor
is reduced.
• However it should be noted that whereas the current varies directly as the
voltage, the torque varies as square of the applied voltage. If the voltage
applied across the terminals is reduced by 50% starting current will reduce by
50% and the torque will reduce to 25% of the full voltage value.
• It is obvious that the ratio of the starting torque to full load torque is x2 of
that obtained with direct switching or across the line starting. This method is
useful for smooth starting of small machines only.
PRIMARY RESISTANCE (REACTOR)
AUTO-TRANSFORMERS
• Such starters, known variously as auto-starters or compensators, consist of an
auto- transformer with necessary switches. We may use two auto transformers
connected in delta or three auto transformers connected as usual .
• Can be used for both star and delta connected motors.
• A reduced voltage is applied across the motor terminals. When the motor has
run up to say 80% of its normal speed, the connections are so changed that auto
transformers are cut out and full supply voltage is applied across the motor.
• The switch making these changes ‘start’ to ‘run’ may be airbreak or may be oil
immersed to reduce sparking. There is also provision for NVC and OLC protection
along with a time-delay device so that momentary interruption of voltage or
momentary overload do not disconnect the motor from the supply.
• Most of the auto transformers are supplied with 3 sets of taps so as to reduce
voltage to 80%, 65 or 50% of the line voltage to suit the local conditions of
supply.
• The V connected transformer is commonly used because it is cheaper although
the currents are unbalanced during starting period.
• This is however no much objectionable firstly, because current imbalance is
about 15% and secondly, because imbalance is restored as soon as the running
conditions are attained.
AUTO-TRANSFORMER
STAR-DELTA STARTER
• This method is used in the case of motors which are built to run normally with a
delta connected stator winding. It consists of a two way switch which connects
the motor in star for starting and then in delta for normal running.
• When star connected, the applied voltage over each motor phase is reduced by
a factor 1√3 and hence the torque developed becomes 1/3 of that which would
have been developed if motor were directly connected in delta.
• The line current is reduced to 1/3.
• Hence, during the starting period when the motor is Y connected, it takes 1/3rd
as much starting current and develops 1/3rd as much torque as would have been
developed when it is directly connected in delta.
• This method is cheap and effective provided the starting torque is required not
to be more than 1.5 times the full load torque.
• Hence, it is used for machine tools, pumps, motor-generators, etc..
STAR DELTA STARTER
ROTOR RESISTANCE
• These motors are practically started with full line voltage applied across the
stator terminals. The value of starting current is adjusted by introducing a
variable resistance in the rotor circuit. The controlling resistance is in the form
of a rheostat connect in star, the resistance being gradually cut out of the rotor
circuit as the motor gathers speed.
• By increasing the rotor resistance, not only is the rotor current reduced but at
the same time the starting torque is also increased due to improvement in
power factor.
• The controlling rheostat is either of stud or contactor type and may be hand
operated or automatic.
• The started unit usually contains a line switching contactor for the stator along
with NVC and OLC protection devices.
• There is some form of interlocking to ensure the proper operation of the line
contactor and the starter. This interlocking prevents the closing of the stator
contactor unless the starter is ‘all in’.
• The introduction of resistance in the rotor enables the motor to develop high
starting torque with moderate starting current.
ROTOR RESISTANCE
Вам также может понравиться
- 3 Phase Induction Motor StarterДокумент28 страниц3 Phase Induction Motor StarterDivanshu GargОценок пока нет
- AIM: Comparative Study of Different Types of Starters Used For Three-Phase Induction MotorДокумент8 страницAIM: Comparative Study of Different Types of Starters Used For Three-Phase Induction MotorRD GamingОценок пока нет
- Starting Techniques of Three-Phase Induction MotorsДокумент33 страницыStarting Techniques of Three-Phase Induction MotorsMarco SamehОценок пока нет
- Starting Methods of Three Phase Induction Motors: Direct-On-Line (DOL) StartersДокумент4 страницыStarting Methods of Three Phase Induction Motors: Direct-On-Line (DOL) Startersrajat nimjeОценок пока нет
- Operation of PumpsДокумент25 страницOperation of PumpsPrajval ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Motor Starters PresentationДокумент24 страницыMotor Starters PresentationCosmin Calițcho100% (1)
- Starters For Electrical MotorsДокумент17 страницStarters For Electrical Motorssiva prakashОценок пока нет
- Unit 3: Control of Three Phase Induction MotorДокумент52 страницыUnit 3: Control of Three Phase Induction MotorSidra BegumОценок пока нет
- Direct On Line StarterДокумент6 страницDirect On Line Starterabhijit.adgube3376Оценок пока нет
- Starting Method1Документ6 страницStarting Method1neo100% (5)
- Star Delta Starter Using Three Phase IndДокумент5 страницStar Delta Starter Using Three Phase Indhichamkassem22Оценок пока нет
- Motor StarterДокумент8 страницMotor StartercalecaleОценок пока нет
- Starting Methods For Induction MotorsДокумент3 страницыStarting Methods For Induction MotorsKrishnamoorthy Ayyasami100% (1)
- How Induction Motor StartДокумент3 страницыHow Induction Motor StartDipa SuwidyaОценок пока нет
- Starting Methods of Induction MotorsДокумент8 страницStarting Methods of Induction MotorsChathuranga Nagasinghe100% (1)
- Unit 3Документ20 страницUnit 3shaik WajidОценок пока нет
- Essential guide to motor starters: Types, working, applications and wiring diagramsДокумент21 страницаEssential guide to motor starters: Types, working, applications and wiring diagramsIshan 96Оценок пока нет
- Three-Phase Motor Control StartersДокумент13 страницThree-Phase Motor Control Startersfaisal shaikОценок пока нет
- What Is Industrial HazardДокумент13 страницWhat Is Industrial HazardTokyoОценок пока нет
- Types of Motor StarterДокумент8 страницTypes of Motor StarterRane Siddesh100% (1)
- Emlab 2Документ21 страницаEmlab 2hafizrahimmitОценок пока нет
- Good Day!: Tanjuatco, Jahriel P. BseeДокумент32 страницыGood Day!: Tanjuatco, Jahriel P. BseeTanjuatco JahrielОценок пока нет
- Electrical Department: Element of Electric DesignДокумент20 страницElectrical Department: Element of Electric Designbree789Оценок пока нет
- Starting Methods of Induction MotorsДокумент4 страницыStarting Methods of Induction MotorsSasareka GunawardanaОценок пока нет
- Induction Motor Starting Methods: HVAC: Heating, Ventilation & Air-Conditioning / by Guruvignesh / Mechanical EngineeringДокумент12 страницInduction Motor Starting Methods: HVAC: Heating, Ventilation & Air-Conditioning / by Guruvignesh / Mechanical EngineeringLincolyn MoyoОценок пока нет
- IJRPR3553Документ4 страницыIJRPR3553everhealthlifesciencesОценок пока нет
- Unit-4-Electrical Machines: Lecture-3 Starting methods of 3-Φ Induction MotorДокумент13 страницUnit-4-Electrical Machines: Lecture-3 Starting methods of 3-Φ Induction MotorPratik SarkarОценок пока нет
- Motor StarterДокумент32 страницыMotor StarterMssnMurthy100% (1)
- Types of Starters: It'S Features and Advantages& DisadvantagesДокумент30 страницTypes of Starters: It'S Features and Advantages& DisadvantagesGrace ZuluetaОценок пока нет
- REDUCED VOLTAGE STARTING USING PART WINDING TECHNIQUEДокумент8 страницREDUCED VOLTAGE STARTING USING PART WINDING TECHNIQUEKennethОценок пока нет
- Induction Generator Starting MethodsДокумент5 страницInduction Generator Starting MethodsChathuranga NagasingheОценок пока нет
- KAWALAN MOTOR English VersionДокумент59 страницKAWALAN MOTOR English VersionSuzaini Supingat0% (1)
- Starting and Speed Control of 3 Phase Induction MotorДокумент38 страницStarting and Speed Control of 3 Phase Induction MotorSree ShobhaОценок пока нет
- Star Delta StarterДокумент11 страницStar Delta Starterasus zenfone5Оценок пока нет
- Motor Starting TransientДокумент20 страницMotor Starting TransientJevan CalaqueОценок пока нет
- Three Phase Induction Motor Interview Questions 2 1Документ24 страницыThree Phase Induction Motor Interview Questions 2 1Kulshresth Joshi100% (1)
- 3-P Induction MotorДокумент10 страниц3-P Induction MotorPrem SagarОценок пока нет
- Unit3 EDCДокумент13 страницUnit3 EDCKarthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuОценок пока нет
- Chapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesДокумент43 страницыChapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesMuket AgmasОценок пока нет
- AC motors starting and protection guideДокумент32 страницыAC motors starting and protection guideTarek MohamedОценок пока нет
- Starting Methods of Induction MotorsДокумент5 страницStarting Methods of Induction MotorsRiyah_Rae86% (7)
- Motor Control and ProtectionДокумент64 страницыMotor Control and ProtectionRaghuram PatriОценок пока нет
- 4-EM Section 4 Motor Starting MethodsДокумент70 страниц4-EM Section 4 Motor Starting Methodsmhafidz49Оценок пока нет
- Unit-3: (This Unit Covers Criteria P4, P5, P7, D2) Motor StartersДокумент15 страницUnit-3: (This Unit Covers Criteria P4, P5, P7, D2) Motor StartersMuhja AljaserОценок пока нет
- Three Phase Electrical Wiring Installation in HomeДокумент10 страницThree Phase Electrical Wiring Installation in HomeMeetoo SharvamОценок пока нет
- Starting Methods of 3-Phase Induction Motor: Instructed By: - Mr. N. KankanamgeДокумент5 страницStarting Methods of 3-Phase Induction Motor: Instructed By: - Mr. N. KankanamgeSEPIRTUSОценок пока нет
- What Is A Star Delta Starter and How Does It WorkДокумент8 страницWhat Is A Star Delta Starter and How Does It WorkArunkumar GujetiОценок пока нет
- Starting Methods of IMДокумент24 страницыStarting Methods of IMChamila SumathiratnaОценок пока нет
- Starting Methodologies PDFДокумент10 страницStarting Methodologies PDFReynee Shaira Lamprea MatulacОценок пока нет
- Starting Methods of 3-Phase Induction MotorsДокумент5 страницStarting Methods of 3-Phase Induction MotorsroshanzoonОценок пока нет
- Relay Switches: AIM: To Study Different Starters What Is A Motor Starter?Документ6 страницRelay Switches: AIM: To Study Different Starters What Is A Motor Starter?sudheeshОценок пока нет
- Slip Ring PresentationДокумент12 страницSlip Ring PresentationMynampati Sai SrinivasОценок пока нет
- Types of Soft Starters An IntroductionДокумент4 страницыTypes of Soft Starters An Introductionsiddhant103Оценок пока нет
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaОт EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaОценок пока нет
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Рейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (3)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesОт EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesОценок пока нет
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationОт EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- Choco Beginner With Logo-3Документ1 страницаChoco Beginner With Logo-3Bhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Save Money With PV-Diesel SystemsДокумент2 страницыSave Money With PV-Diesel SystemsvignesaaОценок пока нет
- KS Wind Guide To Off Grid PDFДокумент28 страницKS Wind Guide To Off Grid PDFBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- KSG-3.2K-DM to KSG-5.2K-DM PV Inverter SpecsДокумент2 страницыKSG-3.2K-DM to KSG-5.2K-DM PV Inverter SpecsBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Reaffirmed 2001Документ88 страницReaffirmed 2001joydeep_d3232Оценок пока нет
- KSG-1K-SM / KSG-1.5K-SM / KSG-1.9K-SM / KSG-2K-SM KSG 1K SM/KSG 1.5K SM/KSG 1.9K SM/KSG 2K SMДокумент2 страницыKSG-1K-SM / KSG-1.5K-SM / KSG-1.9K-SM / KSG-2K-SM KSG 1K SM/KSG 1.5K SM/KSG 1.9K SM/KSG 2K SMBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Tata Power ELCB Testing ProcedureДокумент11 страницTata Power ELCB Testing ProcedurePraveen Kumar100% (2)
- THALETEC 2016 wall calendar and leadership changesДокумент9 страницTHALETEC 2016 wall calendar and leadership changesBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Dwija Enterprise Provides Comprehensive Renewable Energy SolutionsДокумент10 страницDwija Enterprise Provides Comprehensive Renewable Energy SolutionsBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Solar PCU Inverter Three Phase PDFДокумент2 страницыSolar PCU Inverter Three Phase PDFHarish Kumar GОценок пока нет
- KSG-1K-SM / KSG-1.5K-SM / KSG-1.9K-SM / KSG-2K-SM KSG 1K SM/KSG 1.5K SM/KSG 1.9K SM/KSG 2K SMДокумент2 страницыKSG-1K-SM / KSG-1.5K-SM / KSG-1.9K-SM / KSG-2K-SM KSG 1K SM/KSG 1.5K SM/KSG 1.9K SM/KSG 2K SMBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- 64.290.17.00166.03 CERT - AttestationДокумент1 страница64.290.17.00166.03 CERT - AttestationBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Net metering agreement for rooftop solar PV projectsДокумент8 страницNet metering agreement for rooftop solar PV projectsBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- 1 3.2KW-5.2KW PDFДокумент2 страницы1 3.2KW-5.2KW PDFBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- KS Wind Guide To Off Grid PDFДокумент28 страницKS Wind Guide To Off Grid PDFBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Cost Profit AnalysisДокумент17 страницCost Profit AnalysisBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Lightning Protection Risk Assessment NEWДокумент6 страницLightning Protection Risk Assessment NEWTigrillo100% (1)
- Net Metering Aggrement 2019-2020 PDFДокумент8 страницNet Metering Aggrement 2019-2020 PDFBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Cable Laying MethodlogyДокумент9 страницCable Laying MethodlogyVaibhav JainОценок пока нет
- Is Iec 61725 1997Документ10 страницIs Iec 61725 1997vijay_rainaОценок пока нет
- Annual Rate Contract For The Supply of Electrical Items at IIM IndoreДокумент22 страницыAnnual Rate Contract For The Supply of Electrical Items at IIM IndoreBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- KS Wind Guide To Off GridДокумент28 страницKS Wind Guide To Off GridBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- New Doc 2020-02-28 20.36.04Документ2 страницыNew Doc 2020-02-28 20.36.04Bhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- IEEE Guide For Array and Battery Sizing in Stand-Alone Photovoltaic (PV) SystemsДокумент34 страницыIEEE Guide For Array and Battery Sizing in Stand-Alone Photovoltaic (PV) SystemsJimmy F Hernandez100% (1)
- Solar Panelpanel Design (22.8.12)Документ12 страницSolar Panelpanel Design (22.8.12)Battinapati ShivaОценок пока нет
- Sumanben PDFДокумент2 страницыSumanben PDFBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Save Money With PV-Diesel SystemsДокумент2 страницыSave Money With PV-Diesel SystemsvignesaaОценок пока нет
- New Doc 2020-02-28 20.36.04 PDFДокумент2 страницыNew Doc 2020-02-28 20.36.04 PDFBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент2 страницыPDFBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- RadhavallabhДокумент2 страницыRadhavallabhBhavik PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- C J L F S: Vinod TiwariДокумент21 страницаC J L F S: Vinod TiwariVinod TiwariОценок пока нет
- Savable Data Page - Its Configuration, Usage & ExecutionДокумент20 страницSavable Data Page - Its Configuration, Usage & ExecutionsurmanpaОценок пока нет
- AssemblyinstructionsДокумент12 страницAssemblyinstructionsPriscila AzevedoОценок пока нет
- Method Statement of Static Equipment ErectionДокумент20 страницMethod Statement of Static Equipment Erectionsarsan nedumkuzhi mani100% (4)
- ABN AMRO Holding N.V. 2009 Annual ReportДокумент243 страницыABN AMRO Holding N.V. 2009 Annual ReportF.N. HeinsiusОценок пока нет
- 272 Concept Class Mansoura University DR Rev 2Документ8 страниц272 Concept Class Mansoura University DR Rev 2Gazzara WorldОценок пока нет
- ViscosimetroДокумент7 страницViscosimetroAndres FernándezОценок пока нет
- M Series CylindersДокумент61 страницаM Series CylindersAndres SantanaОценок пока нет
- Current Affairs Q&A PDF June 9 2023 by Affairscloud 1Документ21 страницаCurrent Affairs Q&A PDF June 9 2023 by Affairscloud 1Yashika GuptaОценок пока нет
- Managing operations service problemsДокумент2 страницыManaging operations service problemsJoel Christian Mascariña0% (1)
- Activate Adobe Photoshop CS5 Free Using Serial KeyДокумент3 страницыActivate Adobe Photoshop CS5 Free Using Serial KeyLukmanto68% (28)
- 10 Consulting Frameworks To Learn For Case Interview - MConsultingPrepДокумент25 страниц10 Consulting Frameworks To Learn For Case Interview - MConsultingPrepTushar KumarОценок пока нет
- Career Guidance Activity Sheet For Grade IiДокумент5 страницCareer Guidance Activity Sheet For Grade IiJayson Escoto100% (1)
- Case Study Infrastructure ProjectsДокумент1 страницаCase Study Infrastructure ProjectsAnton_Young_1962Оценок пока нет
- Unit 13 AminesДокумент3 страницыUnit 13 AminesArinath DeepaОценок пока нет
- UKBM 2, Bahasa InggrisДокумент10 страницUKBM 2, Bahasa InggrisElvi SОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 - Materials That Undergo DecayДокумент14 страницLesson 3 - Materials That Undergo DecayFUMIKO SOPHIA67% (6)
- 63db2cf62042802 Budget Eco SurveyДокумент125 страниц63db2cf62042802 Budget Eco SurveyNehaОценок пока нет
- Synopsis: A Study On Customer Satisfaction AT Nerolac Paints LTD., KadapaДокумент5 страницSynopsis: A Study On Customer Satisfaction AT Nerolac Paints LTD., KadapaAnu GraphicsОценок пока нет
- Industry Life Cycle-Plant Based CaseДокумент3 страницыIndustry Life Cycle-Plant Based CaseRachelle BrownОценок пока нет
- Fact Sheet Rocket StovesДокумент2 страницыFact Sheet Rocket StovesMorana100% (1)
- ДСТУ EN ISO 2400-2016 - Калибровочный блок V1Документ11 страницДСТУ EN ISO 2400-2016 - Калибровочный блок V1Игорь ВадешкинОценок пока нет
- Congress Policy Brief - CoCoLevyFundsДокумент10 страницCongress Policy Brief - CoCoLevyFundsKat DinglasanОценок пока нет
- Capran+980 CM en PDFДокумент1 страницаCapran+980 CM en PDFtino taufiqul hafizhОценок пока нет
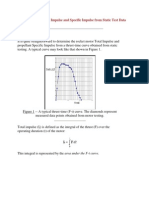
- Determining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test DataДокумент4 страницыDetermining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test Datajai_selvaОценок пока нет
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsДокумент13 страницRenewable and Sustainable Energy ReviewsMohammadreza MalekMohamadiОценок пока нет
- Best Homeopathic Doctor in SydneyДокумент8 страницBest Homeopathic Doctor in SydneyRC homeopathyОценок пока нет
- Part 9. Wireless Communication Towers and Antennas 908.01 Purpose and IntentДокумент12 страницPart 9. Wireless Communication Towers and Antennas 908.01 Purpose and IntentjosethompsonОценок пока нет
- Leyte Geothermal v. PNOCДокумент3 страницыLeyte Geothermal v. PNOCAllen Windel BernabeОценок пока нет
- JWCh06 PDFДокумент23 страницыJWCh06 PDF007featherОценок пока нет