Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Influences On Operations Management
Загружено:
Jacob Mos0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
45 просмотров22 страницыInfluences on Operations Management
Оригинальное название
Influences on Operations Management
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документInfluences on Operations Management
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
45 просмотров22 страницыInfluences On Operations Management
Загружено:
Jacob MosInfluences on Operations Management
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 22
© Karen Devine 2011
Globalisation
Environmental
Technology
Sustainability
Influences
on
Operations
Legal Quality
Regulation Expectations
Government Cost-based
Policies competition
© Karen Devine 2011
The global or world
economy includes all
trade, investment,
labour, technological
and speculative activity
which occurs across
international borders.
© Karen Devine 2011
The global economy is an
integrated economic
system and due to
changes in technology,
communications and the
computer age, businesses
can now choose how to
conduct their operations
internationally.
© Karen Devine 2011
Today there is:
a) globalisation of markets:
an international market
place for goods, services,
labour and finance.
b) globalisation of
production: an
international market for
purchasing components
used in the production
process.
© Karen Devine 2011
There have been
significant increases
in the global flows
of:
a) finance
b) labour
c) goods and
services.
© Karen Devine 2011
These increased
global flows have led
to greater integration
of markets.
Hence, in a sense,
the world is “a
smaller place”.
© Karen Devine 2011
Global trade in goods has
risen astronomically.
Nations now use the
principle of comparative
advantage and specialise
in those goods in which
real cost is lowest.
Such cost decisions
impact on operations
managers worldwide.
© Karen Devine 2011
Technological change
occurs at a rapid rate and
impacts on the business
community.
Improvements in technology
are most significant in the
following areas:
a) Robotics
b) CAD
c) CAM
d) Information technology
e) Communications
technology.
© Karen Devine 2011
The pace of technological
change often outstrips a
business’ ability to cope
with it.
Technological change has
increased the speed and
amount of communication
and has also expanded the
client base for most
businesses.
© Karen Devine 2011
Technological
change has altered
the workplace
significantly and
has meant that
many people can
now work from
home.
© Karen Devine 2011
Technological change has
been significant in the areas
of:
a) email
b) voice mail
c) the internet
d) video conferencing
e) mobile internet phones
f) pagers
g) eCommerce.
© Karen Devine 2011
Effective operations
management also involves
cost control measures.
Management must
examine fixed and
variable costs as a change
in business operations can
affect the level of variable
costs.
© Karen Devine 2011
Sourcing of cost increases is also important.
If increases can be sourced to a particular
department or business area these are called
cost centres.
Cost centres may have:
a) direct costs: sourced to a particular area
b) indirect costs: sourced to many areas,
projects or departments.
© Karen Devine 2011
Revenue controls over
sales and pricing are
essential to cover costs
and ensure profitability.
Changes to the sales
mix by diversifying or
extending a product
range or ceasing
production of an item
may be necessary.
© Karen Devine 2011
Changes to the pricing
policy may also be required
by specifically examining:
a) costs
b) prices of the competition
c) the psychological effect of
prices
d) the price and product
ranges.
© Karen Devine 2011
Governmental factors can impact upon
operations management including:
a) Political: political change and elections can
affect the decisions made by business and
consumers.
b) Legal: changes to legislation and policy
are influential on business behaviour.
c) Regulatory: laws and government bodies
influence marketing decisions and
business activity. Eg: Carbon Tax.
© Karen Devine 2011
Significant legal changes have occurred in the
following areas:
a) regulation/deregulation
b) competition
c) fair trade
d) OHS
e) environmental protection.
f) consumer protection
g) industrial relations
h) trade practices.
These changes impact on business’ activity, ability
to compete, trade and operate efficiently.
© Karen Devine 2011
Environmental
concern has grown
in recent times
with greenhouse
gas emissions and
global warming
dominating the
world’s agenda.
© Karen Devine 2011
For many environmentalists
the key solution is “think
globally, act locally”.
Businesses have made some
commitment to
environmental protection,
yet governments often
ignore environmental issues
in favour of increasing
business development.
© Karen Devine 2011
Businesses will act ethically regarding the
environment when they:
a) perform an environmental impact assessment
b) take intergenerational equity into account
c) evaluate a development’s ecological
sustainability
d) demonstrate environmental integrity
e) make reparations.
© Karen Devine 2011
What does it
mean to “think
globally and act
locally”?
© Karen Devine 2011
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- MC DonaldДокумент23 страницыMC DonaldMuhammad Javed KhurshidОценок пока нет
- 1 Overview of Macroeconomics - Week01Документ20 страниц1 Overview of Macroeconomics - Week01Aldo SitumorangОценок пока нет
- Lipton Yellow LabelДокумент6 страницLipton Yellow LabelFaHEEM DILAWAR100% (1)
- Ambush MarketingДокумент81 страницаAmbush MarketingTaran RainaОценок пока нет
- 14000024catalagodedura-Tuff 20131218220037.631 XДокумент18 страниц14000024catalagodedura-Tuff 20131218220037.631 XCarlos Rudas RamirezОценок пока нет
- A Study On Consumer Satisfaction of Supermarket in Mysore City, MysoreДокумент7 страницA Study On Consumer Satisfaction of Supermarket in Mysore City, MysoreYuvnesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Macro Chap 12 Exercise Macsg12-Aggregate-Demand-In-The-Money-Goods-And-Current-Markets PDFДокумент30 страницMacro Chap 12 Exercise Macsg12-Aggregate-Demand-In-The-Money-Goods-And-Current-Markets PDFAA BB MMОценок пока нет
- Legal Implications of AdvertisementДокумент67 страницLegal Implications of Advertisementjsofv5533Оценок пока нет
- NiveaДокумент35 страницNiveaabhinav33% (3)
- Olper's Milk: Give Your Day A Fresh Start With OlpersДокумент6 страницOlper's Milk: Give Your Day A Fresh Start With OlpersZohab BaigОценок пока нет
- E Business Chapter 4 TurbanДокумент15 страницE Business Chapter 4 TurbanAbdulla75% (4)
- Chapter III. The Market Research and AnalysisДокумент3 страницыChapter III. The Market Research and Analysismillie jeonОценок пока нет
- 5 Case StudiesДокумент1 страница5 Case StudiesSahfirah FirahОценок пока нет
- PESTEL Analysis of NetflixДокумент11 страницPESTEL Analysis of Netflixpreet parmar50% (2)
- Sustainable Competitive Advantage Burger KingДокумент7 страницSustainable Competitive Advantage Burger KingAinul Mardhiyah0% (1)
- The Future of PaymentsДокумент6 страницThe Future of Paymentszing65Оценок пока нет
- Research PaperДокумент41 страницаResearch PaperCidrick CorpuzОценок пока нет
- Marketing Management: Business Environment SWOT Analysis PESTLE Analysis Trends in New Economy Business ConceptsДокумент28 страницMarketing Management: Business Environment SWOT Analysis PESTLE Analysis Trends in New Economy Business ConceptsPrakriti Hagar ABSRAIОценок пока нет
- PDF NiveaДокумент6 страницPDF NiveaLucky MauryaОценок пока нет
- Customer SatisfactionДокумент2 страницыCustomer SatisfactionWaseem Akbar100% (1)
- Sample Test 1Документ12 страницSample Test 1Heap Ke XinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Beverage ManagementДокумент32 страницыChapter 8 Beverage ManagementNatasha AzlanОценок пока нет
- Role of Statistics in Business & FinanceДокумент20 страницRole of Statistics in Business & Financenitinvohra_capricornОценок пока нет
- Agv Ok Agv Ok Repair Tag Repair Tag: By: - Date: - By: - DateДокумент1 страницаAgv Ok Agv Ok Repair Tag Repair Tag: By: - Date: - By: - DateBagus Rizal SetiawanОценок пока нет
- Ratio Calculations of Reject ShopДокумент3 страницыRatio Calculations of Reject ShopSurya ChandraОценок пока нет
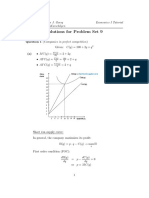
- Problem Set 9 - SolutionsДокумент4 страницыProblem Set 9 - SolutionsKapeLatte (카페라떼)Оценок пока нет
- Chap017 - Text Bank (1) - SolutionДокумент26 страницChap017 - Text Bank (1) - SolutionJoshi YamaОценок пока нет
- Consumer Trends For 2020 - BrandwatchДокумент28 страницConsumer Trends For 2020 - BrandwatchHafian FuadОценок пока нет
- Louis Vuitton v. My Other Bag - Decision PDFДокумент31 страницаLouis Vuitton v. My Other Bag - Decision PDFMark JaffeОценок пока нет
- Creating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsДокумент18 страницCreating Long-Term Loyalty RelationshipsHudha100% (1)