Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
1 MO Theory Topic 1
Загружено:
archery2000Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1 MO Theory Topic 1
Загружено:
archery2000Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
MODULE
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
Topic 1: Electrons in Atoms
Felipe Garcia (Assistant Professor)
CY1101: Principles of Modern Chemistry
School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, NTU
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to:
Interpret atomic quantum numbers
Recognise wavefunctions and their angular and radial parts
Define radial distribution function (RDF)
Construct an RDF from a wavefunction graphically
Represent s, p and d orbital graphically
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 2
Atomic Orbitals
Orbitals and Quantum Numbers: Electrons in atoms occupy different orbitals (imagined as a specific energy level).
For example,
1s orbital two electrons
Any given orbital can only
2s orbital two electrons accommodate two electrons.
2p orbitals (px, py and pz) two electrons respectively
3d orbitals (dxy, dxy, dyz, dx2-y2 and dz2)
7f-orbitals.
Orbitals that have the same energy are described as degenerate.
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 3
Atomic Orbitals
Quantum Numbers and Their Properties
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 4
Atomic Orbitals
Generally, there is no need to specify ms (the spin) since it is the same for all electrons (ms =1/2).
No orbital (defined by its quantum numbers n, l, and ml) may contain more than two electrons. When there are
two, they only differ on their opposing spins (ms = +1/2 and ms = −1/2).
Any electron in an atom has a unique set of four quantum numbers. This is one form of the Pauli Principle.
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 5
Wavefunctions
A function is a mathematical tool into which we can feed a number to derive a new value.
The properties of an electron can be described by a mathematical function called wave function (ψ). This function
depends on n, l and ml. Hence, every electron is defined by n, l and ml.
Ψn,l ,ml (x,y,z)
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 6
Wavefunctions
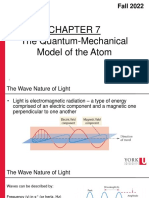
The wave function can also be represented in polar coordinates (r, θ, ϕ) rather than Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z).
One of the advantages of polar coordinates over Cartesian coordinates is that the wave function ψ can be written
as the product two functions, 0 ≤ q ≤ p and 0 ≤ f ≤ 2p.
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 7
Wavefunctions
The angular function is determined by the quantum number l and ml.
shape of the orbitals orientation of the orbital in the space
The different shading of the lobes represents different signs of the wave function ψ.
Useful to know the sign for qualitative bonding purposes
The radial function is determined by the quantum numbers n and l.
Describes the electron density at different distances from the nucleus
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 8
Hydrogen Atom Wave Functions: Radial Functions
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 9
Hydrogen Atom Wave Functions: Angular Functions
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 10
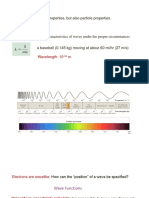
The Radial Distribution Function (RDF)
A common way of representing the orbitals graphically is by showing the probability of finding an electron at a
given distance (electron density at a set distance), r (distance from the nucleus), summed over all angles (θ and φ).
This function is called the Radial Distribution Function (RDF) or radial probability function.
Interpreted as the total electron density in a thin shell at a distance (r) from the nucleus.
The RDF helps show which orbitals are most likely to be involved in reactions.
RDF = [Rn,l(r)]2 x 4pr2
[Rn,l(r)] is the radial part of the wavefunction
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 11
The Radial Distribution Function (RDF)
EXAMPLE
Compare the radial wave function (Rn,l(r), left) and RDF (RDF = [Rn,l(r)]2 x 4pr2, right) for 1s electrons. Radial
distribution functions and radial wave functions for 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals are shown below:
Rn,l(r) RDF = [Rn,l(r)]2 x 4pr2,
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 12
Wave Function Nodes
The sign of the wave function changes from positive to negative as it crosses the x-axis (there is a point at which
ψ=0). Such a position is called a node.
TOTAL NUMBER OF NODES = n-1
Number of angular noder = l
Number of radial nodes = n-l-1
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 13
3D Representation of the Orbitals
A wave function has a value at any point in the space. So for better understanding for the value at any given q, f
and r, 3D plots are extremely useful.
s-orbitals
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 14
3D Representation of the Orbitals
p-orbitals
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 15
3D Representation of the Orbitals
d-orbitals
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 16
3D Representation of the Orbitals
f-orbitals
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 17
Summary
The principal quantum number (n) describes the size of the orbital.
The angular quantum number (l) describes the shape of the orbital.
The magnetic quantum number (m), describes the orientation in space of a particular orbital.
Generally, there is no need to specify ms (the spin) since it is the same for all electrons (ms =1/2).
Any electron in an atom has a unique set of four quantum numbers.
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 18
Summary
Each wavefunction has two parts the radial part which changes with distance from the nucleus and an angular part
whose changes correspond to different shapes.
SIZE is determined by Rnl(r) = radial part of the wave function.
SHAPE determined by Yl,ml+ (q,f).
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 19
Summary
The Radial Distribution Function (RDF) represents the probability of finding an electron at a given distance from
the nucleus (r), summed over all angles (θ and φ).
RDF = [Rn,l(r)]2 x 4pr2
A node is a point at which ψ=0.
TOTAL NUMBER OF NODES = n-1
Number of angular nodes = l
Number of radial nodes = n-l-1
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 20
Summary
Orbital shapes are
s p
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 21
Contact Details
Email : Fgarcia@ntu.edu.sg
Office: CBC-05-19
Module One Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory 22
Вам также может понравиться
- Lecture 4 Wavefunction NewДокумент53 страницыLecture 4 Wavefunction NewkedirОценок пока нет
- Lecture 04Документ13 страницLecture 04sandrajychungОценок пока нет
- L3 Che101Документ28 страницL3 Che101Musa Ahammed MahinОценок пока нет
- ACFrOgC xiuXYskoUCylB1F9L1IEJcj Ta KoLk6CTvaGqltDFWA2qAIKTeqUvP 0 7U6kDWb0J0D4WA8tzfPGbl3oDF5E2WbfWJwsRiEHl3syXtQRSt2h85SwNwBgДокумент71 страницаACFrOgC xiuXYskoUCylB1F9L1IEJcj Ta KoLk6CTvaGqltDFWA2qAIKTeqUvP 0 7U6kDWb0J0D4WA8tzfPGbl3oDF5E2WbfWJwsRiEHl3syXtQRSt2h85SwNwBgJihanaisyОценок пока нет
- Schroedinger Equation Atomic Wave Functions Atomic Orbitals Quantum NumbersДокумент45 страницSchroedinger Equation Atomic Wave Functions Atomic Orbitals Quantum NumbersRishit JakhariaОценок пока нет
- CH 6 (Cont'd)Документ5 страницCH 6 (Cont'd)PineraserОценок пока нет
- Lecture-10 - 11-11-22Документ37 страницLecture-10 - 11-11-22Alkit SharmaОценок пока нет
- CHEM 1004 - Inorganic Chemistry Atomic Structure: H P H MVДокумент13 страницCHEM 1004 - Inorganic Chemistry Atomic Structure: H P H MVNicholas OwОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts: Atoms: Discovery of Atomic Structure Rutherford (1910)Документ19 страницChapter 1 - Basic Concepts: Atoms: Discovery of Atomic Structure Rutherford (1910)Anulisa DasОценок пока нет
- Inorganic Chem. I Ch. 1Документ98 страницInorganic Chem. I Ch. 1Shifa GhannamОценок пока нет
- The Electronic Structure of AtomsДокумент54 страницыThe Electronic Structure of AtomsElijah PunzalanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure CHEMISTRYДокумент16 страницChapter 1 - Atomic Structure CHEMISTRYMaite Aícua UbiernaОценок пока нет
- Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati: CH101 Class 11 Physical ChemistryДокумент5 страницIndian Institute of Technology, Guwahati: CH101 Class 11 Physical ChemistryMihir Kumar MechОценок пока нет
- Quantum NumbersДокумент39 страницQuantum NumbersTin SumangaОценок пока нет
- Wave Model - Hydrogen Case - 2023-2024Документ36 страницWave Model - Hydrogen Case - 2023-2024rahmaderradji23Оценок пока нет
- The Quantum Mechanical ModelДокумент15 страницThe Quantum Mechanical ModelNatalia SadekОценок пока нет
- Lectures 5,6-Electronic Structure of AtomsДокумент96 страницLectures 5,6-Electronic Structure of AtomsKatto - Darling in the PianoОценок пока нет
- Junoon e Jee Atomic Structures 2Документ127 страницJunoon e Jee Atomic Structures 2Parth ShelarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ41 страницаChapter 1Nguyen NhatОценок пока нет
- Quantum Numbers: Are Required To Describe The Distribution ofДокумент17 страницQuantum Numbers: Are Required To Describe The Distribution ofIrfan Sayeem SultanОценок пока нет
- Chem Notes Chapter 7 - AlkanesДокумент66 страницChem Notes Chapter 7 - AlkanesjohnОценок пока нет
- BITS Pilani Chemistry Hamilton OperatorДокумент11 страницBITS Pilani Chemistry Hamilton OperatorNaresh SehdevОценок пока нет
- AtomsFirst2e Day6 Sec3.7-3.8 CHMY171 Fall 2015Документ17 страницAtomsFirst2e Day6 Sec3.7-3.8 CHMY171 Fall 2015Claudius MorpheusОценок пока нет
- CHEMF111 Lecture5 Aug12 2016 - BPHCДокумент23 страницыCHEMF111 Lecture5 Aug12 2016 - BPHCAshish GuptaОценок пока нет
- AtomsFirst2e Day6 Sec3.7-3.8 CHMY171 Fall 2015Документ17 страницAtomsFirst2e Day6 Sec3.7-3.8 CHMY171 Fall 2015Xenia Mae FloresОценок пока нет
- Inorganic Chemistry I: Prof. A D L I M, M.SCДокумент28 страницInorganic Chemistry I: Prof. A D L I M, M.SCFiTri Yani SyarbiniОценок пока нет
- CHME 222 - Lecture 7Документ40 страницCHME 222 - Lecture 7islam.lukmanov2003Оценок пока нет
- Atomic StructureДокумент28 страницAtomic StructurePavan GoudОценок пока нет
- Diklic TNSДокумент17 страницDiklic TNSJosipa DiklićОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Atomic StructureДокумент68 страницChapter 8 Atomic StructureHaqnawaz100% (1)
- Chapter 2Документ62 страницыChapter 2kere evaОценок пока нет
- P11 AДокумент9 страницP11 ADana CapbunОценок пока нет
- Radial and Angular Parts of Atomic OrbitalsДокумент7 страницRadial and Angular Parts of Atomic OrbitalsArchisman MisraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Part 2Документ29 страницChapter 7 Part 2lalachin729Оценок пока нет
- PC General Chemistry E WAДокумент21 страницаPC General Chemistry E WAAdabala Durgarao NaiduОценок пока нет
- Atomic Orbitals: Quantum NumbersДокумент16 страницAtomic Orbitals: Quantum NumberslostgirlОценок пока нет
- Electronic Structure of The AtomДокумент55 страницElectronic Structure of The AtomAlekhoy Pakz100% (1)
- Lecture 3 NotesДокумент5 страницLecture 3 Notesabdurmasood0811Оценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure: Atomic Structure: Overview of Bohr's Atomic ModelДокумент38 страницAtomic Structure: Atomic Structure: Overview of Bohr's Atomic Modelmanoj kumarОценок пока нет
- Electronic Theory of ChemistryДокумент43 страницыElectronic Theory of ChemistryMaheshОценок пока нет
- Handout of Physical Chemistry: Course: Vikaas (Ja) Target: Jee (Advanced)Документ6 страницHandout of Physical Chemistry: Course: Vikaas (Ja) Target: Jee (Advanced)Naunidh Singh MadhokОценок пока нет
- q2 General Chemistry Rev (Complete)Документ14 страницq2 General Chemistry Rev (Complete)rosedancel52Оценок пока нет
- Issues To Address... : What Promotes Bonding? What Types of Bonds Are There?Документ40 страницIssues To Address... : What Promotes Bonding? What Types of Bonds Are There?Medet AbdulОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts: Atoms: Prerequisite KnowledgeДокумент20 страницChapter 1 - Basic Concepts: Atoms: Prerequisite KnowledgemahyarbОценок пока нет
- Radial and Angular Parts of Atomic OrbitalsДокумент3 страницыRadial and Angular Parts of Atomic OrbitalsW47K3R 27886Оценок пока нет
- CH 7Документ60 страницCH 7Paul ArcillaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - 02 (Atomic Structure and Basic Concepts of Chemistty) (VSK Sir)Документ4 страницыWorksheet - 02 (Atomic Structure and Basic Concepts of Chemistty) (VSK Sir)Daksha SubrhamanyaОценок пока нет
- Density Function Theory - PDF 1Документ6 страницDensity Function Theory - PDF 1sanju jarwalОценок пока нет
- General Chemistry Lecture 3Документ80 страницGeneral Chemistry Lecture 3Aaron Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Lectures 2018Документ119 страницAn Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Lectures 2018Nataliya LyutenkoОценок пока нет
- How To Use Quantum Numbers To Describe AnДокумент11 страницHow To Use Quantum Numbers To Describe AnAntonio Exal ColladoОценок пока нет
- De Broglie Relation: EinsteinДокумент19 страницDe Broglie Relation: EinsteinMaisha MaimunaОценок пока нет
- Structure of AtomДокумент29 страницStructure of AtomAbhisek DehuriОценок пока нет
- Mechanics VI: Gravitation: 1 Computing FieldsДокумент22 страницыMechanics VI: Gravitation: 1 Computing FieldsRandomОценок пока нет
- The Quantum Mechanical Model of An AtomДокумент24 страницыThe Quantum Mechanical Model of An AtomKim Christian CombaterОценок пока нет
- DME I Year CHEДокумент91 страницаDME I Year CHERadha KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Junior ChemistryДокумент72 страницыJunior ChemistryjahnavikidambiОценок пока нет
- Variable Phase Equation in Quantum Scattering: Vitor D. Viterbo, Nelson H.T. Lemes, Jo Ao P. BragaДокумент5 страницVariable Phase Equation in Quantum Scattering: Vitor D. Viterbo, Nelson H.T. Lemes, Jo Ao P. BragaMilton AlvesОценок пока нет
- Rotational Motion: Rotation in Two Dimensions: A Particle On A RingДокумент41 страницаRotational Motion: Rotation in Two Dimensions: A Particle On A RingAdelia Ayu WandiraОценок пока нет
- Optics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyОт EverandOptics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Multiple Linear RegressionДокумент26 страницMultiple Linear RegressionMarlene G Padigos100% (2)
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children: CC MagbanuaДокумент52 страницыUrinary Tract Infection in Children: CC MagbanuaVanessa YunqueОценок пока нет
- ASME-Y14.5.1M 1994 Mathematical Definition of Dimensioning and Tolerancing Principles PDFДокумент89 страницASME-Y14.5.1M 1994 Mathematical Definition of Dimensioning and Tolerancing Principles PDFwulfgang66Оценок пока нет
- August Strindberg's ''A Dream Play'', inДокумент11 страницAugust Strindberg's ''A Dream Play'', inİlker NicholasОценок пока нет
- India: SupplyДокумент6 страницIndia: SupplyHarish NathanОценок пока нет
- Approaches To Violence in IndiaДокумент17 страницApproaches To Violence in IndiaDeepa BhatiaОценок пока нет
- Accomplishment Report: For Service Credits (Availment/claim) Election May 2019Документ1 страницаAccomplishment Report: For Service Credits (Availment/claim) Election May 2019Glazy Kim Seco - JorquiaОценок пока нет
- Far Eastern University-Institute of Nursing In-House NursingДокумент25 страницFar Eastern University-Institute of Nursing In-House Nursingjonasdelacruz1111Оценок пока нет
- Calcined Clays For Sustainable Concrete Karen Scrivener, AurÇlie Favier, 2015Документ552 страницыCalcined Clays For Sustainable Concrete Karen Scrivener, AurÇlie Favier, 2015Débora BretasОценок пока нет
- The Handmaid's Tale - Chapter 2.2Документ1 страницаThe Handmaid's Tale - Chapter 2.2amber_straussОценок пока нет
- Quadrotor UAV For Wind Profile Characterization: Moyano Cano, JavierДокумент85 страницQuadrotor UAV For Wind Profile Characterization: Moyano Cano, JavierJuan SebastianОценок пока нет
- Evidentiary Value of NarcoДокумент2 страницыEvidentiary Value of NarcoAdv. Govind S. TehareОценок пока нет
- Multicutural LiteracyДокумент3 страницыMulticutural LiteracyMark Alfred AlemanОценок пока нет
- CV Michael Naughton 2019Документ2 страницыCV Michael Naughton 2019api-380850234Оценок пока нет
- Eet 223 (1) Analog Electronics JagjeetДокумент79 страницEet 223 (1) Analog Electronics JagjeetMahima ArrawatiaОценок пока нет
- BGL01 - 05Документ58 страницBGL01 - 05udayagb9443Оценок пока нет
- Preliminaries Qualitative PDFДокумент9 страницPreliminaries Qualitative PDFMae NamocОценок пока нет
- 4 Major Advantages of Japanese Education SystemДокумент3 страницы4 Major Advantages of Japanese Education SystemIsa HafizaОценок пока нет
- 10-C# Forms InteractionДокумент22 страницы10-C# Forms InteractionMaria Anndrea MendozaОценок пока нет
- LittorinidaeДокумент358 страницLittorinidaeSyarif Prasetyo AdyutaОценок пока нет
- The Gower Handbook of Project Management: Part 1: ProjectsДокумент2 страницыThe Gower Handbook of Project Management: Part 1: ProjectschineduОценок пока нет
- History of Drugs (Autosaved)Документ68 страницHistory of Drugs (Autosaved)Juan TowTowОценок пока нет
- Nespresso Case StudyДокумент7 страницNespresso Case StudyDat NguyenОценок пока нет
- DigoxinДокумент18 страницDigoxinApril Mergelle LapuzОценок пока нет
- Crime Scene Manual FullДокумент19 страницCrime Scene Manual FullMuhammed MUZZAMMILОценок пока нет
- 800 Pharsal Verb Thong DungДокумент34 страницы800 Pharsal Verb Thong DungNguyễn Thu Huyền100% (2)
- How To Create Partner Function in SAP ABAPДокумент5 страницHow To Create Partner Function in SAP ABAPRommel SorengОценок пока нет
- Favis vs. Mun. of SabanganДокумент5 страницFavis vs. Mun. of SabanganAyra CadigalОценок пока нет
- What Is Thesis Plural FormДокумент8 страницWhat Is Thesis Plural Formtracyjimenezstamford100% (2)
- University of Dar Es Salaam MT 261 Tutorial 1Документ4 страницыUniversity of Dar Es Salaam MT 261 Tutorial 1Gilbert FuriaОценок пока нет