Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
1.ternakruminan Vs Non Ruminan
Загружено:
yahya arif0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
65 просмотров45 страницTERAANK NON RUMINAN
Оригинальное название
1.Ternakruminan vs Non Ruminan
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документTERAANK NON RUMINAN
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
65 просмотров45 страниц1.ternakruminan Vs Non Ruminan
Загружено:
yahya arifTERAANK NON RUMINAN
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 45
Objective:
Describe the function and major
parts of the digestive system of
ruminants.
Animals with complex digestive systems
Capable of digesting material with a high
fiber concentration
Uses microbial fermentation
• Cattle
• Sheep
• Goats
• Deer
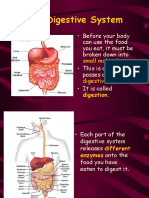
Ruminant Digestive System
Mouth
• Bites and chews
Esophagus
• Connection
Four Compartment Stomach
• Rumen
• Reticulum 85% of the
• Omasum capacity
• Abomasum
Ruman
• Largest of the four parts “room-in-it”
• Filled with bacteria
• Converts large amounts of roughage to amino
acids
Fact!!!!
The average cow rumen can hold over 160 liters (40
gallons)
The large microbe is a type of protist
The creature that looks like a tadpole
attached to the side of the protist is a
fungal spore
The smaller, rod-shaped organism lining
the underside of the protist are bacteria.
Reticulum
• Compartment where liquid goes
• Honeycomb in structure
Omasum
• Grinds and squeezes
• Removes some liquid
Abomasum
• True stomach
• Enzymes and acids
Small Intestine
• Partially digested feed is
mixed
Bile
Pancreatic juice
Intestinal juice
• Most of the food nutrient is
absorbed
Villi or Papillae
Large intestine
• Main function is to absorbed
water
• Add mucus to undigested feed
Feces
Objective:
Describe the function and major
parts of the digestive system of
non-ruminants.
Simple digestive system
• (Monogastric)
• Feed must be highly quality concentrates
• Cannot digest large amounts of fiber
Human
Dogs
Cats
Rabbits
Pigs
Horses????
Mouth
Esophagus
Stomach
• Enzymes acts on feed
• Churns and mixes
Small intestine
Large intestine
Accessory system
• Liver
Produces bile that acts on fat
• Pancreas
Produces insulin
Anus
• End of the digestive tract
Simple Digestive System
Objective: Describe the function and major
parts of the digestive system of non-ruminants.
Chickens
Turkeys
Ducks
Geese
Mouth or beak
• Can not chew food
Esophagus
• Connects mouth to crop
Crop
• Stores feed
Gizzard
• Crushes feed
Contains grit and gravel
• Mixes feed with digestive juices
Liver
Small and Large Intestine
Vent
• Removes solid and liquid waste
Esophagus
• Tube like structure
Stomach
• Pouch with undigested feed
Liver
• Large brown organ beneath the stomach or crop
Small intestine
• Long tube
• Gray colored partially digested feed
Large intestine
• Large relatively short compartment
• Contains fecal material
Competency: Distinguish the
functions and sources of feed
nutrients for farm animals
Objective: Identify the six major groups
of nutrients
Composed of sugar, starches, cellulose
and lignin
Provide energy and heat
Make up the largest quantity of livestock
feed
• Carbon
• Hydrogen
• Oxygen
2.25 times the energy value of
carbohydrates
At body temperature fat are solids and
oils are liquid
• Example: cooking lard
Extra carbohydrates are stored as fats
• Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Carriers fat-soluble vitamins
Major component of muscles and tissues
Made up of amino acids
Continuously needed to replace dying
body cells
Young animals need large amounts for
growth
Needed in small quantities
Helps regulate body functions
Designated by letters
• A,B,C,D,E,K
Sources:
• Naturally found in feed
• Feed additives made from animal by-
products
• Made by the body itself
Needed in small amounts
• Calcium, phosphorus, sodium, etc.
Regulates body functions
Provide growth for:
• Bone
• Teeth
• Tissue
Example: calcium is needed in poultry for
eggshell development
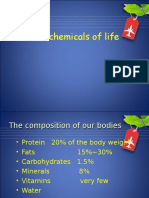
Makes up 40% to
60% of the animals
body
Dissolves other
nutrients and helps
carry them to parts
of the body
Carbohydrates
• Cereal grains
corn
wheat
oats
rye
barley
sorghum
Proteins
• Plant sources
Soybean meal
Cottonseed meal
Alfalfa meal
• Animal sources
Meat meal
Fishmeal
Dried milk
Synthetic nitrogen source called urea
Fats and Oils
• Grains and protein concentrates
Vitamins and Minerals
• Most feed ingredients
• Supplements
Pre-mixes
Mineral blocks
Other sources and exceptions:
• Alfalfa (roughage) can be used to provide
energy and fiber
• Molasses
Improve taste (palatability)
Reduce feed dust
High in Nutrient Value
Grains
• Corn
• Barley
• Wheat
High in Fiber
Forage Crops
• Silage
• Hay
• Pasture Grass
Total Digestible Nutrients
Concentrates are high in TDN
Roughages are low in TDN
Вам также может понравиться
- 2001 Ford F150 ManualДокумент296 страниц2001 Ford F150 Manualerjenkins1100% (2)
- Sample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersДокумент16 страницSample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersPooja PawarОценок пока нет
- Igcse NutritionДокумент125 страницIgcse NutritionLai Kee Kong100% (2)
- NutritionДокумент101 страницаNutritionAlexandra CardosoОценок пока нет
- Animal Digestion and NutritionДокумент36 страницAnimal Digestion and Nutritionelliequinn5100% (1)
- Negative Feedback AmplifierДокумент31 страницаNegative Feedback AmplifierPepОценок пока нет
- Rubber Band Arrangements - Concert BandДокумент25 страницRubber Band Arrangements - Concert BandJonatas Souza100% (1)
- ObesityДокумент85 страницObesitycoolradiodoll1121Оценок пока нет
- Ans311 Notes - Sept. 2020Документ141 страницаAns311 Notes - Sept. 2020Joy.B mwanzaОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Biology Chapter4 The Chemicals of LifeДокумент24 страницыIGCSE Biology Chapter4 The Chemicals of Lifeddddddffdfdf75% (4)
- VerificationManual en PDFДокумент621 страницаVerificationManual en PDFurdanetanpОценок пока нет
- 2011-11-09 Diana and AtenaДокумент8 страниц2011-11-09 Diana and AtenareluОценок пока нет
- Animal Nutrition: 11 Agri 1& 2Документ54 страницыAnimal Nutrition: 11 Agri 1& 2Christel StephensonОценок пока нет
- Animal Digestion System PDFДокумент38 страницAnimal Digestion System PDFpsmanasseОценок пока нет
- Milking CattleДокумент47 страницMilking CattleAdsclicker AashishОценок пока нет
- Thedigestivesyste MДокумент27 страницThedigestivesyste MrisaОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System: By: Mrs. BourlandДокумент27 страницThe Digestive System: By: Mrs. BourlandrisaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ36 страницChapter 7HC GamerОценок пока нет
- Digestive PowerpointДокумент44 страницыDigestive PowerpointMauricio BeltranОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System: By: Mrs. BourlandДокумент26 страницThe Digestive System: By: Mrs. BourlandlolapeichОценок пока нет
- Feeds and Feeding in RumantsДокумент33 страницыFeeds and Feeding in RumantsMacharia JosephОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System: By: Mrs. BourlandДокумент26 страницThe Digestive System: By: Mrs. Bourlandbjbitscs21Оценок пока нет
- Pseudo RuminantДокумент61 страницаPseudo RuminantMurl CasteloОценок пока нет
- Digestive Physiology Feeding of LivestockДокумент58 страницDigestive Physiology Feeding of LivestockChristian Ramos NievesОценок пока нет
- CH 41 Animal NutritionДокумент70 страницCH 41 Animal NutritionHazel EdillorОценок пока нет
- Today's Objectives: vs. Hind-Gut FermenterДокумент21 страницаToday's Objectives: vs. Hind-Gut Fermenterfitria tsani fardaОценок пока нет
- Biology Chapter 6 (6.4)Документ34 страницыBiology Chapter 6 (6.4)Shirmei WangОценок пока нет
- Food Is Taken In, Taken Apart, and Taken Up in The Process of Animal Nutrition - in General, Animals Fall Into Three CategoriesДокумент42 страницыFood Is Taken In, Taken Apart, and Taken Up in The Process of Animal Nutrition - in General, Animals Fall Into Three Categoriesamarizol_4124995Оценок пока нет
- Classification of Nutrients Without VidДокумент93 страницыClassification of Nutrients Without VidNyze RiveraОценок пока нет
- The Digestive SystemДокумент27 страницThe Digestive SystemAmrit1995Оценок пока нет
- Digestive System: (Animals)Документ20 страницDigestive System: (Animals)Nikki Marie Magallanes GuanzonОценок пока нет
- Digestion: By: Kenia Amaya AlvearДокумент9 страницDigestion: By: Kenia Amaya AlvearLauraValeroMОценок пока нет
- Submitted By: Natural Science Reg. No. 13375008Документ21 страницаSubmitted By: Natural Science Reg. No. 13375008anooppunnakkadanОценок пока нет
- Human Digestive SystemДокумент48 страницHuman Digestive SystemSharifah NurainОценок пока нет
- 10-Animal Nutrition and DigestionДокумент29 страниц10-Animal Nutrition and DigestionArdina KusumaningtyasОценок пока нет
- Anatomifisiologimanusia Pencernaan 120923110823 Phpapp02Документ124 страницыAnatomifisiologimanusia Pencernaan 120923110823 Phpapp02api-268725095Оценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate and Protien DigestionДокумент57 страницCarbohydrate and Protien DigestionpvzvsrqzcdОценок пока нет
- Digestion 2 AДокумент55 страницDigestion 2 AElaine ChoiОценок пока нет
- Nutrition & Dietetics ..Документ202 страницыNutrition & Dietetics ..kasimudibiyalОценок пока нет
- The Digestive SystemДокумент33 страницыThe Digestive SystemHida Az ZahraОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System: A&P QQI Level 5 Leah DunneДокумент39 страницThe Digestive System: A&P QQI Level 5 Leah DunneBlanca Marco de la IglesiaОценок пока нет
- 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested FoodДокумент13 страниц6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested Foodkiongoc100% (1)
- Lecture 9 Animal NutritionДокумент40 страницLecture 9 Animal NutritionRAISAL CHRISTIAN COОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент33 страницыCarbohydratesPadmanaaban PrabhuОценок пока нет
- Digestive System: Hona Dedi WeruДокумент37 страницDigestive System: Hona Dedi WeruSelena VaswaniОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 - Digestive SystemДокумент31 страницаUnit 4 - Digestive SystemAbdullah MohammedОценок пока нет
- CARBOHYDRATESДокумент16 страницCARBOHYDRATESRon ChongОценок пока нет
- 13 DigestionДокумент21 страница13 DigestionElmerОценок пока нет
- QUIZ Sheet of PaperДокумент33 страницыQUIZ Sheet of PaperGab FgilzcheОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент17 страницDigestive SystemAli MaherОценок пока нет
- 1.study of Physiological Functions of Digestive System of Farm AnimalsДокумент58 страниц1.study of Physiological Functions of Digestive System of Farm AnimalsKashifОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент83 страницыDigestive SystemjosskevynbonifacioОценок пока нет
- B6 Animal Nutrition: Cambridge BiologyДокумент12 страницB6 Animal Nutrition: Cambridge Biology星梦Оценок пока нет
- Bio 2 MurДокумент18 страницBio 2 Muryr44grf94kОценок пока нет
- Functions of Digestive SystemДокумент20 страницFunctions of Digestive SystemHara Shelle AcompaniadoОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 Charateristics of Feedstuffs - AGA 312Документ118 страницTopic 2 Charateristics of Feedstuffs - AGA 312Izukanji KayoraОценок пока нет
- Digestive System Post LabДокумент29 страницDigestive System Post LabMaxine MangaoangОценок пока нет
- The Digestive SystemДокумент9 страницThe Digestive SystemDil da DakuОценок пока нет
- Digestive System Power PointДокумент17 страницDigestive System Power PointAlyssa Mae DapadapОценок пока нет
- Science Chapter 3 Form 2Документ22 страницыScience Chapter 3 Form 2Muhammad SafwanОценок пока нет
- PROTEINДокумент46 страницPROTEINMabookgm MaОценок пока нет
- 02 Nutrition Feeding Digestion Ch6 2Документ79 страниц02 Nutrition Feeding Digestion Ch6 2nuo chenОценок пока нет
- Balanced DietДокумент30 страницBalanced DietDaniel AmonОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System: By: Mrs. BourlandДокумент26 страницThe Digestive System: By: Mrs. Bourlandbocah_britpopОценок пока нет
- Junos ErrorsДокумент2 страницыJunos ErrorsrashidsharafatОценок пока нет
- Key Performance Indicators - KPIsДокумент6 страницKey Performance Indicators - KPIsRamesh Kumar ManickamОценок пока нет
- Lakh Only) Being The Amount Covered Under The Aforesaid Dishonoured Cheque, and So AlsoДокумент2 страницыLakh Only) Being The Amount Covered Under The Aforesaid Dishonoured Cheque, and So AlsoShivam MishraОценок пока нет
- What Is A Fired Heater in A RefineryДокумент53 страницыWhat Is A Fired Heater in A RefineryCelestine OzokechiОценок пока нет
- Weg CFW500 Enc PDFДокумент32 страницыWeg CFW500 Enc PDFFabio Pedroso de Morais100% (1)
- A Brief Tutorial On Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets and SystemsДокумент10 страницA Brief Tutorial On Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets and SystemstarekeeeОценок пока нет
- Case No. Class Action Complaint Jury Trial DemandedДокумент43 страницыCase No. Class Action Complaint Jury Trial DemandedPolygondotcom50% (2)
- BluePrint & High Pressure Pascalization (HPP)Документ3 страницыBluePrint & High Pressure Pascalization (HPP)Prof C.S.PurushothamanОценок пока нет
- What Are Some of The Best Books On Computer ScienceДокумент9 страницWhat Are Some of The Best Books On Computer ScienceSarthak ShahОценок пока нет
- Mobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesДокумент3 страницыMobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S Chargeskumarvaibhav301745Оценок пока нет
- Comparitive Study of Fifty Cases of Open Pyelolithotomy and Ureterolithotomy With or Without Double J Stent InsertionДокумент4 страницыComparitive Study of Fifty Cases of Open Pyelolithotomy and Ureterolithotomy With or Without Double J Stent InsertionSuril VithalaniОценок пока нет
- SRS Document Battle Royale Origins - V2Документ36 страницSRS Document Battle Royale Origins - V2Talha SajjadОценок пока нет
- April 2021 BDA Case Study - GroupДокумент4 страницыApril 2021 BDA Case Study - GroupTinashe Chirume1Оценок пока нет
- SodiumBenzoate PDFДокумент3 страницыSodiumBenzoate PDFyotta024Оценок пока нет
- DevOps Reference CardДокумент2 страницыDevOps Reference CardIntizarchauhanОценок пока нет
- Report-Smaw Group 12,13,14Документ115 страницReport-Smaw Group 12,13,14Yingying MimayОценок пока нет
- Profibus Adapter Npba-02 Option/Sp Profibus Adapter Npba-02 Option/SpДокумент3 страницыProfibus Adapter Npba-02 Option/Sp Profibus Adapter Npba-02 Option/Spmelad yousefОценок пока нет
- Work Site Inspection Checklist 1Документ13 страницWork Site Inspection Checklist 1syed hassanОценок пока нет
- APA Citation Method For ERLACS: Reference Citations in TextДокумент8 страницAPA Citation Method For ERLACS: Reference Citations in Textdanny_alfaro_8Оценок пока нет
- Waswere Going To Waswere Supposed ToДокумент2 страницыWaswere Going To Waswere Supposed ToMilena MilacicОценок пока нет
- Reference by John BatchelorДокумент1 страницаReference by John Batchelorapi-276994844Оценок пока нет
- 02 Chapter 2 - Corporate Governance MechanismДокумент19 страниц02 Chapter 2 - Corporate Governance MechanismHanis ZahiraОценок пока нет
- Mangement of Shipping CompaniesДокумент20 страницMangement of Shipping CompaniesSatyam MishraОценок пока нет
- KiSoft Sort & Pack Work Station (User Manual)Документ41 страницаKiSoft Sort & Pack Work Station (User Manual)Matthew RookeОценок пока нет