Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Educ430 - 012 - Course Map 2
Загружено:
api-458590618Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Educ430 - 012 - Course Map 2
Загружено:
api-458590618Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
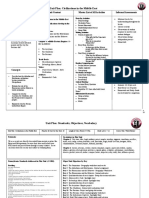
World History Course Map
Hayden Herc
First
First 9 weeks
9 weeks Techniques Techniques Third 9Third
weeks
9 weeks
Time Content Concept Essential Question Standards Time Content Concept Essential Question Standards
1.5 weeks Chapter 2: Early Civilizations: 6000 • Geography play an important role in the 1. Why do all ancient civilizations all start in 8.1.9.C, 8.1.9.D, 8.1.12.C 8.1.9.8, 1 week Chapter 17: Explorers and Explorations: 1450 • Three reasons why the Spaniards came to the 1. Why did Portugal and Spain want to 5.2.12.A, 5.2.12.B, 8.4.12.A (3)
B.C to 30 B.C history of civilization river valleys? 8.4.9.B (2), 8.4.9.C 5.1.12.A, 7.1.9.B (5), to 1650 Americas find a water route to China and India? 5.4.9.C, 8.1.9.D (4), 8.4.12.A (1),
• Ancient civilizations form around river 2. Why is geography important to history? 8.4.9.B (2) Europeans Search for New Trade Rounds • Why some European nations search for a all 2. Why did so many Native Americans die 8.4.12.A (3), 8.4.12.B (1),
Ancient India valleys 3. What are the three facts about Hinduism? Exploring New Lands water route to China and India under Spanish rule? 8.4.12.C (4) 8.1.12.C (3),
The History of Ancient India • Hinduism The Spanish Conquer Two Empires in • What Spanish conquest did to the Native 3. What new plants did the Europeans 8.4.12.A (2), 8.4.12.A (3),
Hinduism America American population find in the Americas and how did these 8.4.12.B (1), 8.4.12.B (2),
Ancient China Spain Establishes Colonies in Americas • Why Portugal introduced African slavery into change European civilizations? 8.4.12.C (4) 7.3.9.D (2), 7.3.12.C
The History of Ancient China The Growth of the Slave Trade the new world (3), 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.C (4),
The Results of Exploring 8.4.12.D (5)
1.5 weeks Chapter 3: Civilizations develop in • Describe how the Akkadian and 1. What gifts did the Sumerian's give to us? 7.1.9.B (2), 7.1.9.B (5), 7.3.12.A (1),
the Middle East Babylonian civilizations became 2. Why do we remember Hammurabi? 8.4.9.B (1) 5.1.9.B, 5.1.12.A, 5.1.12.B, 1 week Chapter 18: The Age of Reason: 1687 to 1789 • Why historians call this period the Age of 1. Why do historians call the years 1687 to 5.1.12.A, 8.1.12.D (4), 8.4.12.A
The Sumerians powerful in Mesopotamia 3. In what way did the Hebrew people differ from 5.1.12.C 7.4.9.B (1), 7.4.12.A (2), In Search of Natural Laws Reason 1789 the Age of Reason? (2), 8.4.12.B (1), 8.4.12.C (4)
The Akkadians and the Babylonians • Evaluate the role of the Phoenicians and other ancient people? 8.4.9.B (2), 8.4.9.B (3), 8.4.9.C (1) New Theories on Government • Compare the views of Thomas Hobbes and 2. Why do historians also call these years 8.4.12.A (2), 8.4.12.A (3),
The Phoenicians and the Hebrews the Hebrew in world civilization 8.1.9.B (5), 8.4.9.B (2), 8.4.9.B (3) The Influence of Enlightened Thinkers John Locke the Enlightenment? 8.4.12.B (1), 8.4.12.C (4) 5.1.9.C
• Compare the way the Assyrians, the 4. What helped the Assyrians become a war 8.4.9.B (1), 8.4.9.C (3) Enlightenment Ideas Influence Artists • What are enlighten thinkers, rules, musicians, 3. What did Hobbs and Locke agree and (4), 5.1.9.E (4), 5.1.9.E (5),
Chapter 4: Middle-Eastern Empires: Chaldeans, and the Persian treated machine?
and writers disagree about with regard to the 5.1.9.E (8), 5.3.9.K (4)
8– B.C to 330 B.C conquered peoples. 5. What was the difference between the way the
government
The Assyrians • Explain the way the Persian unified their Assyrians treated defeated people and the way
The Chaldeans Empire the Persians did?
1 week Chapter 19: The Industrial Revolution: 1750 • The economic conditions needed for 1. Why do historians use the word 6.1.12.D, 6.2.9.H (1), 6.2.12.L,
The Persians
to 1850 industrialization to take place revolution to describe the industrial 6.4.9.A-C , .3.12.D (2), 7.3.12.D
1 week Chapter 5: Egypt – The Gift of the • The Nile river importance to Egypt 1. Why was the Neil River so important to the 7.1.9.B (5), 7.3.9.A (3), 7.3.9.B(2), The Industrial Revolution Begins in England • The benefits and problems of industrialization changes that took place in England (3), 7.3.12.E (2), 7.4.12.A (1)
Nile: 3100 B.C to 30 B.C • Differences between the Old and the Egyptians? 7.3.9.C (1) 7.4.9.B (1), 8.1.9.A (4), The Growth of the First Modern Industries • Important inventions that helped during the 1700s?
The Nile River Middle Kingdoms 2. How did the tree kingdoms of Egypt differ? 8.1.9.C (4), 8.4.9.B (2) 7.1.12.B (3), Transportation Improves industrialization 2. What three conditions are necessary for
The Old Kingdom • Contributions Egypt has made to world 3. Why were the Hyksos and later invaders able to 7.3.12.B (2), 7.4.9.B (1), 8.4.9.B (2) Industry Brings Change and Problems • What was revolutionary about the industrial an industrial revolution to take place in
The Middle Kingdom civilization defeat the Egyptians? revolution in England a country?
The New Kingdom 3. Why is a good transportation system
Gifts From the Egyptians needed for the growth of the industry?
2 weeks Chapter 6: Greek Civilization: 2000 • The geography of Greece influence its 1. Greece is on a peninsula and rocky mountains. 8.4.9.A (2), 8.4.9.C (4), 8.4.9.D (5) 1 week Chapter 20: An Age of Revolution: 1775 to • Causes of the American Revolution 1. What were the colonist rebelling .3.12.A (1), 8.3.12.D (1),
B.C. to 323 B.C civilizations What effect did this geography have on its 5.1.9.B (1), 5.1.12.B, 5.2.9.A (2) 8.1.9.D 1815 • How the American Revolution changed the against during American Revolution? 8.3.12.D (5), 6.4.9.D (3),
Early Civilizations of the Aegean Sea • Identify the differences between Athens history? (4), 8.1.12.D (4), 8.4.9.A (1), 8.4.9.C (4), Revolution in the American Colonies world 2. What were the French rebelling against 6.5.12.B, 6.5.12.F
The Greek City-States and Sparta 2. Why did the Greeks want to defeat the Persian 8.4.9.D (5) 5.3.9.K (3), 5.3.12.K (2), The American Revolutionary War • Causes of the French Revolution during the French Revolution
Athens • The importance of Alexander the Great Empire? 8.4.9.A (3), 8.4.9.B (1), 8.4.9.B (2) The French Revolution • The Reign of Terror 3. What is one way in which the American
Sparta • Contributions that ancient Greek made 3. What are three contributions the Greek 8.4.9.A (1), 8.4.9.B (1), 8.4.9.C (3), Revolutionary Reforms and Terror in France • Accomplishments and failures of Napoleon Revolution changed Europe and one
War Tests the Greeks to world civilization civilization made to the world? 8.4.9.C (4) Napoleon and the French Empire way in which the French Revolution
Greek Cultural Contributions changed Europe?
Alexander the Great Spreads
1 week Chapter 21: Reaction, Reforms, and • Purpose and outcome in the Congress of 1. What is nationalism? 8.1.12.C (5), 8.3.12.D (5),
Revolutions: 1814 to 1850 Vienna 2. Why did the leaders at the Congress of 8.4.12.A (1) 5.4.9.B, 5.4.9.C,
1 week Chapter 7: The Roman Republic: 753 • The organization of the Roman 1. Explain how each of the following was important 5.1.9.B, 5.1.9.C (3), 5.3.9.K (4), 5.3.12.K The Congress of Vienna Meets • Differences between radicals, conservatives, Vienna fear nationalism? 5.4.12.B, 5.4.12.E (1), 7.3.12.B
B.C to 27 B.C Republican form of government for the Roman Republic: two consuls; the (4) 6.2.12.F (1), 6.4.12.B, 8.4.9.A (1), Nationalism Becomes Powerful and liberals 3. How did events in France in the (1), 8.4.12.D (2)
Early Rome • Define the term republic senate; the veto; the tribunes; the Law of the 5.1.9.B (1), 5.1.12.B, 8.4.9.A (2), 8.4.9.B Wars for Independence in Latin America • The ideas of socialists ninetieth century influence other
Rome Becomes a Republic • How Rome lost its republican form of Twelve Tables (2) 8.4.9.B (1), 8.4.9.C (4), 8.4.9.D (1) New Revolution and Reform in Europe • Wars of national liberation in the 19th century European and colonial revolutionaries?
Roman Expands Its Boundaries government 2. What was one difference between the patricians 8.4.9.C (4), 8.4.9.D (1), 8.4.9.D (5) The Year of Revolutions - 1848
The Republic Faces Problems and the plebeians?
The End of the Republic 3. Why did the Roman patricians need the Roman 2 weeks Chapter 22: Nationalism and Imperialism: • Characteristics of nationalism and imperialism 1. What is imperialism? 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.C (4),
plebeians? 1840 to 1914 • Larders of Italian unification of Germany 2. Which countries became imperial 8.4.12.D (5) 7.1.9.B (4), 8.4.12.C
Strategies 10 Themes of NCSS Nationalism
Growing Nationalism in Italy
The Unification of Germany
• Reasons and effects of imperialism on Asia
and China
powers during nineteenth century? (3), 8.4.12.C (4), 8.4.12.D (5)
8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.C (4),
8.4.12.D (5)
1 week Chapter 8: The Roman Empire: 27 • Distinguish Rome good and emperors 1. In what ways were the Romans a practical 7.1.9.B (5), 7.3.9.A (3), 7.3.9.B(2), Imperialism
B.C to A.D 476 • How did the Roman Empire treat Jewish people? 7.3.9.C (1) 7.4.9.B (1), 8.1.9.A (4), The Effect of Imperialism on Asia
The Age of Augustus children 2. Why did the Roman Empire decline and then 8.1.9.C (4), 8.4.9.B (2) 7.1.12.B (3),
Governing the Roman Empire • Major conflict between Rome and fall? 7.3.12.B (2), 7.4.9.B (1), 8.4.9.B (2) Culture The Effect of Imperialism on Africa
Concept definition map, frayer model, semantic feature analysis, semantic mapping,
The Rise of Christianity Christians 1 week Chapter 23: World War 1: 1914 to 1919 1. What were the causes of World War I?
The Fall of the Roman Empire
Rome’s Contributions to Civilization
• Reasons for the decline of the Roman
Empire
Vocabulary everyday vocab (flash cards, word wall, vocab checks), and prefix/suffix/root The Causes of the War
The War Years: 1914 – 1918
2. What were three terms of the Treaty of
Versailles?
Making Peace 3. What were three economic effects of
World War I Changed the World World War I?
Time, Continuity, and Change
Second
Second 9 weeks
9 weeks Analysis- primary documents, artifacts, political cartoons, map analysis, written Fourth 9 weeks
Fourth 9 weeks
Time Content Concept Essential Question Standards documents, motion picture, photographs, posters, speeches, Supreme Court decisions, Time Content Concept Essential Question Standards
2 weeks Chapter 9: The Middle Ages in Europe: A.D. 500 to 1500 • Compare the Byzantine and the 1. Why did Constantine call 5.1.9.B (1), 5.1.9.B (2), 5.1.9.E (1), graphs, charts 1 week Chapter 24: The Russian Revolution and the Communist • Life in czarist Russia 1. Why did the Russians revolt 5.1.12.B, 5.1.12.C 7.4.9.B (1),
People, Places, and Environments
The Byzantine Empire
The Russians
Roman Empires
• Why historians call this period the
Constantinople the “new Rome”?
2. What is one good thing and one
5.2.9.A (1) 8.1.9.B (5), 8.1.12.4 (2),
8.1.12.A (3) 8.4.9.C (3), 8.4.9.D (2),
Critical Thinking Thinking- propaganda techniques, fallacies of arguments, facts from opinion, point of
Life in Czarist Russia
Russia Moves Toward Revolution
• Causes and effects of the
Communist Revolution
against Czar Nicholas II?
2. What is one way in which life
7.4.12.A (2), 8.4.9.B (2), 8.4.9.B (3),
8.4.9.C (1) 8.1.9.B (5), 8.4.9.B (2),
Europe During the Middle Ages “dark ages” bad thing that resulted form the 8.4.9.D (5) 8.4.9,8 (1), 8.4.9.B (2), view The Bolsheviks Take Over the Government • Relationship between WWI and improved for the common 8.4.9.B (3) 8.4.9.B (1), 8.4.9.C (3)
• The rule of the Roman Catholic crusades? 84.9.C (4) 6.4.12.D, 7.3.9.A (2), The Soviet Union Under Stalin Communist Revolution person under Stalin?
Chapter 10: Life in the Middle Ages: A.D. 1050 to A.D. 1500 church in the middle ages in 3. What are the five basic duties 7.3.9.D (2) • Life in the Soviet Union 3. What is one way in which life got
Writing- argument, persuasive • Characteristics of a totalitarian worse for the common person
The Church During the Middle Ages Europe each Muslim must accept?
Feudalism • Describe feudalism state under Stalin?
Culture in the Middle Ages • Cause and effects of the crusades
• Describe the Mayan, Aztec, and
Individual Development and Identity
Chapter 11: Africa and the Americans: A.D. 300 to 1590 Incan civilizations of Central 1 week Chapter 25: Revolutions and the Rise of Dictators: 1911 to • Characteristics of a fascist 1. Why did Italy and Germany .4.9.A, 8.4.12.A (2), .2.12, A,
The Rise of Islam America 1938 government choose fascism and dictators 8.1.12.D (3), 8.4.12.0 (4), .5.12.A (2),
Islamic Civilization
trade books- study guides classroom library, text sets, self-selected reading, group The Fascist Gain Power in Italy • How China became a modern after World War I? 8.1.12.D (4), 8.4.12.C (4), 8.4.12.D
African Kingdoms models, teacher read aloud, sustain silent reading, reader response The Nazis Gain Power in Germany nation 2. What are six things Hitler did (3)
Early Civilizations in the Americans Reading textbooks- graphic organizers writing summaries, Cornell note taking, annotations, study
The Chinese Begin to Build A Modern Nation
Military Leaders Take Over in Japan
• How military leaders took over
the Japanese government
when he became the dictator of
Germany?
•
2 weeks Chapter 12: India, China, and Japan: 563: B.C o A.D 1620 • Compare Buddhism and Hinduism 1. What is one gift India has given 7.1.9.B (5), 7.3.9.A (3), 7.3.9.B(2), Comprehension guides, SQ3R Individuals, Groups, and Institutions
Rise of the Nazi power in
Germany
3. What are four things that
Japan’s government had in
Buddhism • Why did Japan and China turn to to world civilization? 7.3.9.C (1) 7.4.9.B (1), 8.1.9.A (4), common with Nazi Germany and
India isolationism 2. What is one gift China has given 8.1.9.C (4), 8.4.9.B (2) 7.1.12.B (3), general strategies- predict, question, summarize fascist Italy during the 1930s?
China • What made ancient China the to world civilization? 7.3.12.B (2), 7.4.9.B (1), 8.4.9.B (2)
The Mongols Conquer China richest and most powerful 3. What is one thing that is the 1 week Chapter 26: World War II: 1939 to 1945 • Major causes of WWII 1. What are seven causes of World 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.D (1) 7.3.9.B (1),
Japan country in the world same and one thing that is The basic Causes of World War II • Allie and Axis powers War II? 8.4.12.C (3) 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.B
Japan Develops Its Own Culture different between Japanese and Fascism Threatens Other Countries • Failure of the police of 2. What caused the United States (1), 8.4.12.C (1) 6.4.12.G (1), 7.1.9.B
The Tokugawa Unify Japan European feudalism?
Standardized Test ACT/SAT, Test preparation, and practice
Power, Authority, and Governance Axis Successes in Europe and Asia
The Tide Turns in Favor of the Allies •
appeasement
Why WWII ended
to stop being neutral and to
enter World War II?
(4), 8.4.12.D (2)
1 week Chapter 13: The Renaissance: 1348 to 1600
The Troubles Fourteenth Century
• Why historians use the term
Renaissance for this period
1. How did the Black Death change
Europe?
8.1.12.C (3), 8.1.12.D (4), 8.4.9.A
(3), 8.4.9.B (1) 8.4.12.A (3), 8.4.12.B
Preparation 1 week Chapter 27: The Aftermath of World War II: 1945 to 1955 • Social economic and political 1. What is one social, one 7.1.9.B (4) 6.1.12.D, 8.2.12.A (2),
The Spirit of the Renaissance • The beliefs of humanism 2. Why was Leonardo da Vinci a (1), 8.4.12.B (2) 8.4.12.A (3), Results of World War II results of WWII economic, and one political 8.4.12.D (2) 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.D
The Renaissance Begins in Italy • The quality of a Renaissance Renaissance man? 8.4.12.B (1) 8.4.12.A, 8.4.12.C (4), The United Nations • Makeup of the United Nations outcome of World War II? (1) 8.3.12.D (5), 8.4.12.C (3) 8.4.12.A
Renaissance Art and Literature men and women 8.4.12.D (2) 8.4.12.A (3), 8.4.12.B The Cold War Begins • Beginning of the Cold War What are the six major branches (1), 8.4.12.A (3), 8.4.12.D (1)
Leonardo da Vinci – A “Renaissance Man” (1), 8.4.12.C (4)
Discussion Whole group, small pairs, pairs, debate, role playing, games, simulation, and current events Conflicts Between the Superpowers • Americas role in rebuilding
Europe
of the United Nations and what
do they do?
1 week Chapter 14: The Reformation: 1415 to 1650 • The importance of Martin 1. What was one cause of the 6.2.9.E, 6.4.12.A, 6.4.12.B 6.4.9.C, Production, Distribution, and 2. How did the Marshall Plan to
People Challenge the Church’s Authority Luther and the reformation Reformation? 8.1.12.D (4), 8.4.12.C (1), 8.4.12.D Consumption help Europe?
Martin Luther Leads the Reformation • The beliefs of Calvinism 2. How did Calvin's reforms differ (2), 8.4.9.D (4) 6.4.9.C, 8.4.12.C (3),
Luther Starts His Own Church • The Counter-Reformation of the form Luther’s and Kind Henry 8.4.12.D (2) 7.3.9.B (3), 8.1.12.B (5), Informal- homework, journals, summarizing, letters, editorial, opinion, and observational 1 week Chapter 28: New Nations Emerge: 1946 to 1999 • Countries of Africa gain 1. Why did India divide into two 8.4.9.A (2), 8.4.9.B (2) 8.4.9.B (1),
Many African Colonies Become Nations independence counties? 8.4.9.C (4), 8.4.9.D (1) 8.4.9.C (4),
Protestant Ideas Spread to England
John Calvin Organizes a New Religion
catholic church VIII’s?
3. What was one thing the Catholic
8.4.12.C (3)
Writing writing A New Nation in the Middle East Brings War
India Gains Its Independence
• Problems between Israelis and
Palatines
2. What two Chinese groups fought
over control of China? Which
8.4.9.D (1), 8.4.9.D (5)
The Counter- Reformation Church did as it tried to counter Formal- 5 paragraph theme, essay question, research paper, biography, and news story
the Reformation? • Events of Vietnam War side won? Why?
• Unifying India 3. Why did the United States fight a
1 week Chapter 15: The New Science: 1540 to 1750 • The five steps of the scientific 1. What are the five steps of the 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.B (2), 8.4.9.D (2) • Control over China war in Vietnam?
The Development of Modern Science method scientific method? 7.1.9.B (3), 7.3.9.B (2), 7.3.9.B (3), Trade books, field trips, competition, clubs, projects, guest speaker, computer, bulletin Science, Technology, and Society
Copernicus
Galileo
• Copernicus's new theory of the
universe
2. Before Copernicus, what did
most scholars believe about the
8.4.12.D (4) 5.1.9.E (3), 7.3.9.C (1),
8.4.12.B (2), 8.4.12.D (4) 6.4.12.D,
Enrichment boards, maps, cause and effect, timelines, and political cartoons 2 weeks Chapter 29: A Changing World: 1950 to the Present
African Nations Face Many Challenges
•
•
Problems Africa faces today
Conflict in the Middle East
1. What is one problem that
Africa's face today?
7.3.9.B(2), 7.3.9.C (1) 7.4.9.B (1),
8.1.9.A (4), 8.1.9.C (4), 8.4.9.B (2)
Isaac newton • The role Isaac Newton played in earth and the heavens? 8.4.12.D (2) 6.1.12.C, 6.2.12.F (3), The Middle East Remains in Conflict • Why communism fails 2. What is one problem that people 7.1.12.B (3), 7.3.12.B (2), 7.4.9.B (1),
Other Early Scientist the history of science 3. How did Newton build on the 6.4.12.B Asians Countries Face Economic Challenges • Problems in Latin America in the Middle East face today? 8.4.9.B (2)
work of Copernicus, Kepler, and Reforming the Soviet Union • Change in Europe and Asian 3. What is one problem that people
Galileo?
Interdisciplinary Art, music, architecture, technology, drama, poem, language, and culture
Global Connections and Geography
Europe Experiences Great Change
Latin American Struggles to Overcome Its Problems
countries in Asia face today?
1 week Chapter 16: The Age of Kings: 1519 to 1715 • Compare feudalism and 1. What is the difference between 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.A (2), 8.4.12.B 1 week Chapter 30: A New Century Begins: 1990 to the Present • Importance of global trade 1. What is one way that mass 8.4.9.< (4). 7.3.9.B (2), 8.1.9.C (3),
The Rise of Nations nationalism feudalism and nationalism? (1), 8.4.12.D (5) 5.1.9.A, 5.3.9.K, The Earth As a Global Village • Environmental problems communication has helped 8.4.9.B (2) 6.4.9.B, 6:4.12.D, 7.3.9.D
The Rise and Fall of Spain • Rule by “divine right” 2. What does ruling by “diving 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.B (2), 8.4.12.B Energy and Technology Create the Global Village • Economic interdependence of create a global village? (2), 8.4.9.A (25, 8.4.9.B (1)
English Monarchs Struggle for Power • England’s constitutional right” mean? (3) 5.1.9.C (1), 5.1.9.E (2), 8.1.9.D Global Trade and Economic Development modern industrial nations and 2. What is one source of energy
England Rejects Absolute Monarchy
Absolute Monarchy in France •
monarchy
Rise and fall of Spain
3. What is the difference between
and absolute monarchy and a
(4), 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.D (1),
8.4.12.D (5) 8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.C
Differentiated Very process (different methods), content (materials), and products (assessments)
Global Environmental Concerns
•
developing countries
New technology
that may be safe and may not
pollute our environment
Russia and Prussia Produce Strong Monarchs • How Prussia became powerful constitutional monarchy? (4), 8.4.12.D (5) 5.3.12.K (1), 3. What is one problem that
Civic Ideals and Practices
8.4.12.A (1), 8.4.12.D (5) Instruction Student diversity and characteristics, (RTI) Response To Intervention developing countries
have?
Вам также может понравиться
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- What Is Sikolohiyang PilipinoДокумент2 страницыWhat Is Sikolohiyang PilipinoJeffrey Manzano100% (1)
- Curse, Possession and Other Worlds Magic and Witchcraft Among The BosniaksДокумент35 страницCurse, Possession and Other Worlds Magic and Witchcraft Among The BosniaksMahomad AbenjúcefОценок пока нет
- Marriott Management PhilosophyДокумент11 страницMarriott Management Philosophyremon4hrОценок пока нет
- A Survey Course in British Literature - ANA-MARIA TUPANДокумент690 страницA Survey Course in British Literature - ANA-MARIA TUPANkryykettОценок пока нет
- Introducing Visual CultureДокумент6 страницIntroducing Visual CulturebabushajanОценок пока нет
- SECTION 3 - Principles and Theories On School CultureДокумент30 страницSECTION 3 - Principles and Theories On School CultureFelie Rose Escartin100% (1)
- Letter HomeДокумент1 страницаLetter Homeapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Educ430 Tri FoldДокумент2 страницыEduc430 Tri Foldapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Constitution Scavenger HuntДокумент8 страницConstitution Scavenger Huntapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Letter HomeДокумент1 страницаLetter Homeapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Weekly JournalsДокумент26 страницWeekly Journalsapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Hayden Herc Classroom Management PlanДокумент33 страницыHayden Herc Classroom Management Planapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Sub Lesson PlanДокумент1 страницаSub Lesson Planapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Classroom DesignДокумент1 страницаClassroom Designapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Sub Lesson PlanДокумент1 страницаSub Lesson Planapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Bill of Rights ProjectДокумент2 страницыBill of Rights Projectapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Standards MapДокумент5 страницStandards Mapapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Unit Plan Content Outline 2Документ2 страницыUnit Plan Content Outline 2api-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Special Ed MatrixДокумент1 страницаSpecial Ed Matrixapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Hayden Herc ResumeДокумент2 страницыHayden Herc Resumeapi-458590618Оценок пока нет
- Catch Me If You Learn Valuable Communication SkillsДокумент10 страницCatch Me If You Learn Valuable Communication SkillsadilaОценок пока нет
- 1real Estates MFR Eligible List For 2010-2011Документ21 страница1real Estates MFR Eligible List For 2010-2011Praveen SmartОценок пока нет
- SesajenДокумент43 страницыSesajenPutri A RamadhaniОценок пока нет
- Teaching Staff DetailsДокумент16 страницTeaching Staff DetailsEEEDEPTGECОценок пока нет
- Connectivity FND Teachers Book SampleДокумент24 страницыConnectivity FND Teachers Book SampleНаталія МоторнаОценок пока нет
- Arts 7 Week 3-4Документ6 страницArts 7 Week 3-4Jomar MendrosОценок пока нет
- Travel Memories and Cultural IdentityДокумент9 страницTravel Memories and Cultural Identitytantalus11Оценок пока нет
- Arm Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницArm Lesson Planapi-252035920Оценок пока нет
- Malibu Residence maximizes ocean viewsДокумент4 страницыMalibu Residence maximizes ocean viewsninadelsolОценок пока нет
- Al Shindagha PDFДокумент9 страницAl Shindagha PDFAlbina AbdrakhmanovaОценок пока нет
- Bucker Poutsma 2010Документ17 страницBucker Poutsma 2010Andreea ApetreiОценок пока нет
- BelizeДокумент5 страницBelizeVirgilio CusОценок пока нет
- Unit 2Документ3 страницыUnit 2api-302381333Оценок пока нет
- Journal of Bengali Studies Vol.3 No.2Документ304 страницыJournal of Bengali Studies Vol.3 No.2bengalistudies100% (2)
- UCSP Week 2 OCRДокумент7 страницUCSP Week 2 OCRRocky FresnidoОценок пока нет
- Dreams and Challenges in Maxine Hong Kingston's - China MenДокумент10 страницDreams and Challenges in Maxine Hong Kingston's - China MenPrincess Joy CastroОценок пока нет
- In Vitro Anti-Cancer Activity of Piper Betel Leaf Extract On HA - 29 and Its Anti-Oxidant ActivityДокумент4 страницыIn Vitro Anti-Cancer Activity of Piper Betel Leaf Extract On HA - 29 and Its Anti-Oxidant ActivityEditor IJTSRDОценок пока нет
- The Impacts and Influences of Western Thoughts To FilipinosДокумент3 страницыThe Impacts and Influences of Western Thoughts To FilipinosHanna LamsenОценок пока нет
- Individualism in American CultureДокумент3 страницыIndividualism in American CultureMadalina CojocariuОценок пока нет
- Conklin 1978 (The Revolutionary Weaving Inventions of The Early Horizon)Документ19 страницConklin 1978 (The Revolutionary Weaving Inventions of The Early Horizon)José A. Quispe HuamaníОценок пока нет
- Nizozmeska Konjanici KacigeДокумент15 страницNizozmeska Konjanici KacigeLuka BruketaОценок пока нет
- Scert Unit 8 Suresh IAS AcademyДокумент229 страницScert Unit 8 Suresh IAS AcademySundar Pk78% (9)
- Communication Theory of Identity - in - The International Encyclopedia of Intercultural CommunicationДокумент9 страницCommunication Theory of Identity - in - The International Encyclopedia of Intercultural CommunicationMarielleJustineChingОценок пока нет
- Introducing Culture Power Point PresentationДокумент16 страницIntroducing Culture Power Point PresentationApphia Jaimee DavidОценок пока нет