Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cataract Jem
Загружено:
JemsMei Comparativo Mensurado0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров17 страницA cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of the eye that prevents light from passing through clearly and can cause vision loss. It develops when protein builds up in the lens, making it cloudy. Symptoms include blurry or cloudy vision, sensitivity to light, and problems seeing at night. Risk factors include increasing age, diabetes, smoking, and sun exposure. Diagnosis involves eye exams to check vision and examine the lens. Treatment is usually surgery to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial lens, with phacoemulsification being a common procedure. Maintaining eye health can help prevent cataracts.
Исходное описание:
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision. Most cataracts are related to aging. Cataracts are very common in older people.
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документA cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of the eye that prevents light from passing through clearly and can cause vision loss. It develops when protein builds up in the lens, making it cloudy. Symptoms include blurry or cloudy vision, sensitivity to light, and problems seeing at night. Risk factors include increasing age, diabetes, smoking, and sun exposure. Diagnosis involves eye exams to check vision and examine the lens. Treatment is usually surgery to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial lens, with phacoemulsification being a common procedure. Maintaining eye health can help prevent cataracts.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров17 страницCataract Jem
Загружено:
JemsMei Comparativo MensuradoA cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of the eye that prevents light from passing through clearly and can cause vision loss. It develops when protein builds up in the lens, making it cloudy. Symptoms include blurry or cloudy vision, sensitivity to light, and problems seeing at night. Risk factors include increasing age, diabetes, smoking, and sun exposure. Diagnosis involves eye exams to check vision and examine the lens. Treatment is usually surgery to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial lens, with phacoemulsification being a common procedure. Maintaining eye health can help prevent cataracts.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 17
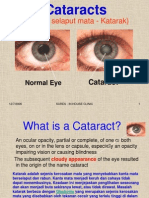
CATARACT
• A cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of
your eye.
Lens
• The lens is composed of
transparent, flexible tissue
and is located directly behind
the iris and the pupil.
• It is the second part of your
eye, after the cornea, that
helps to focus light and
images on your retina.
Anatomy of the Eye
• For people who have cataracts, seeing through cloudy
lenses is a bit like looking through a frosty or fogged-
up window.
• Most cataracts develop slowly and don't disturb your
eyesight early on. But with time, cataracts will
eventually interfere with your vision.
• At first, stronger lighting and eyeglasses can help you
deal with cataracts.
• But if impaired vision interferes with your usual
activities, you might need cataract surgery.
Fortunately, cataract surgery is generally a safe,
effective procedure.
What Causes Cataracts?
You develop them when protein builds up in the lens
of your eye and makes it cloudy. This keeps light from
passing through clearly. It can cause you to lose some
of your eyesight.
Different types of cataracts.
• Age-related.
• Congenital.
• Secondary.
• Traumatic.
What Are the Symptoms?
• Vision that’s cloudy, blurry, foggy, or filmy
• Nearsightedness (in older people)
• Changes in the way you see color
• Problems driving at night (glare from oncoming headlights,
for example)
• Problems with glare during the day
• Double vision in the affected eye
• Trouble with eyeglasses or contact lenses not working well
• The need for bright light when reading and performing
other tasks
• Fading or yellowing of colours
Risk factors
• Increasing age
• Diabetes
• Excessive exposure to sunlight
• Smoking
• Obesity
• High blood pressure
• Previous eye injury or inflammation
• Previous eye surgery
• Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol
Diagnostic Tests
• Visual acuity test. Using a
chart or a viewing device with
progressively smaller letters,
your eye doctor determines
if you have 20/20 vision or if
your vision shows signs of
impairment.
• Slit-lamp examination. The
microscope is called a slit lamp
because it uses an intense line of
light, a slit, to illuminate your
cornea, iris, lens, and the space
between your iris and cornea.
The slit allows your doctor to
view these structures in small
sections, which makes it easier
to detect any tiny abnormalities.
• Retinal exam. To prepare for a retinal exam, your
eye doctor puts drops in your eyes to open your
pupils wide (dilate). This makes it easier to examine
the back of your eyes (retina). Using a slit lamp or a
special device called an ophthalmoscope, your eye
doctor can examine your lens for signs of a
cataract.
Prevention
• Have regular eye examinations.
• Quit smoking.
• Manage other health problems.
• Choose a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits
and vegetables.
• Wear sunglasses.
• Reduce alcohol use.
Surgeries
• Phacoemulsification, or phaco. A small incision is made on the
side of the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers
the front of the eye. Your doctor inserts a tiny probe into the
eye.This device emits ultrasound waves that soften and break up
the lens so that it can be removed by suction.
• Laser-assisted cataract surgery (LACS )or laser
cataract surgery — is a modern variation of the
standard phaco cataract procedure. In laser cataract
surgery, a number of steps that traditionally have been
performed with a hand-held surgical instrument are
instead done with a computer-controlled, high-speed
laser for added precision. These steps include: making
the initial incisions in the eye; creating an opening in
the anterior capsule of the lens to gain access to the
cataract; and fragmenting the cloudy lens prior to its
removal from the eye.
Prepared by: Jems Mae Mensurado
Вам также может понравиться
- Ospe Ophthalmology CorrectedДокумент55 страницOspe Ophthalmology CorrectedGgah Vgggagagsg100% (1)
- CataractДокумент6 страницCataractKarel LuОценок пока нет
- Eye Disorders: Presented by Carmelita Ramos, RNДокумент65 страницEye Disorders: Presented by Carmelita Ramos, RNJayme_Galang_7078100% (1)
- Cataract: What You Should KnowДокумент24 страницыCataract: What You Should KnowshinhyejjОценок пока нет
- Abuse and ViolenceДокумент30 страницAbuse and ViolenceJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Retinal DetachmentДокумент6 страницRetinal DetachmentNader Smadi100% (3)
- Magnetic Apparatus For The Treatment of Cataracts & Other Eye ConditionsДокумент6 страницMagnetic Apparatus For The Treatment of Cataracts & Other Eye ConditionswobblegobbleОценок пока нет
- Cataract and Glaucoma Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentДокумент6 страницCataract and Glaucoma Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentSairileenDoradoОценок пока нет
- Cataract: By: Charmagne MaranonДокумент28 страницCataract: By: Charmagne MaranonCham'cham Araneta MarañonОценок пока нет
- CataractДокумент7 страницCataractNader Smadi100% (2)
- Sics Steps: Divisi Katarak Dan Bedah Refraktif Rumah Sakit Mata Bali MandaraДокумент74 страницыSics Steps: Divisi Katarak Dan Bedah Refraktif Rumah Sakit Mata Bali MandaraPande GustianaОценок пока нет
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsОт EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsОценок пока нет
- Biometry..Iol CalculationДокумент86 страницBiometry..Iol CalculationSristi Thakur0% (1)
- Brochure Centurion Vision System With Active SentryДокумент16 страницBrochure Centurion Vision System With Active SentrySalma El MamouniОценок пока нет
- CataractДокумент17 страницCataractrhopmaeОценок пока нет
- Cataracts: What Are They?Документ3 страницыCataracts: What Are They?RSarkawyОценок пока нет
- Cataract and Eye Care DCaДокумент26 страницCataract and Eye Care DCaSamuil SumpalОценок пока нет
- CataractsДокумент7 страницCataractsOktovia KakaОценок пока нет
- Cataracts The Mayo ClinicДокумент6 страницCataracts The Mayo ClinicJandz MNОценок пока нет
- Cataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureДокумент16 страницCataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureAmandeep Singh GandhiОценок пока нет
- Cataract InformationДокумент25 страницCataract Informationvasanth_1515Оценок пока нет
- Dr. Ashraf Sayeed: Department of OphthalmologyДокумент49 страницDr. Ashraf Sayeed: Department of Ophthalmologysaiful haque100% (1)
- Cataract surgery guideДокумент9 страницCataract surgery guidegandikotavtpsОценок пока нет
- Cataract-Case Study - ADOMPINGДокумент8 страницCataract-Case Study - ADOMPINGboogeyman6dimakutaОценок пока нет
- Lens Iris Pupil Retina: Cataract OverviewДокумент5 страницLens Iris Pupil Retina: Cataract Overviewrizky_kurniawan_14Оценок пока нет
- A Cataract Is A Clouding of The EyeДокумент5 страницA Cataract Is A Clouding of The EyeHikari 光 ShidouОценок пока нет
- CataractДокумент5 страницCataractAbhinandan SharmaОценок пока нет
- 04 CataractsurgeryДокумент16 страниц04 Cataractsurgeryapi-3695929Оценок пока нет
- Retinal DetachmentДокумент19 страницRetinal DetachmentJohn Hans CaturasОценок пока нет
- Cataracts (Ejmontibon)Документ28 страницCataracts (Ejmontibon)Edelainne Joyce Blanco MontibonОценок пока нет
- LASIK surgeryДокумент10 страницLASIK surgerymandukhai tsogtsaikhanОценок пока нет
- Cataract CasestudyДокумент3 страницыCataract CasestudyJamal AgontongОценок пока нет
- Cataract Service - 1Документ11 страницCataract Service - 1sanjuОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need to Know About CataractsДокумент25 страницEverything You Need to Know About CataractsDr Kirti ChhapiaОценок пока нет
- Cataract: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniДокумент46 страницCataract: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniSaha DirllahОценок пока нет
- CATARACTДокумент15 страницCATARACTCharmilli PotestasОценок пока нет
- Symptoms and Detection: Crystalline Lens Eye Opacity MyopiaДокумент5 страницSymptoms and Detection: Crystalline Lens Eye Opacity MyopiaNica Joy CandelarioОценок пока нет
- CataractsДокумент21 страницаCataractsRobert L G MabongaОценок пока нет
- Cataract Visual Defect AdultsДокумент6 страницCataract Visual Defect AdultsRaul Suarez MargollesОценок пока нет
- Reference Summary: X-Plain LasikДокумент0 страницReference Summary: X-Plain LasikUSMP FN ARCHIVOSОценок пока нет
- Article On Cataract 2Документ7 страницArticle On Cataract 2Chandana KarthikОценок пока нет
- LASIK (Laser Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) :: MyopiaДокумент18 страницLASIK (Laser Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) :: MyopiaFawaz Bin AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Uses of Lenses in Eyes and Optical DevicesДокумент18 страницUses of Lenses in Eyes and Optical DevicesRanz PanganibanОценок пока нет
- Cataract InformationДокумент25 страницCataract InformationDr.K.M. AbdullaОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need to Know About AstigmatismДокумент4 страницыEverything You Need to Know About AstigmatismLucian SupliJenОценок пока нет
- Desry Sevti Eka Putri 1410070100105Документ11 страницDesry Sevti Eka Putri 1410070100105Diah FebruarieОценок пока нет
- Cataract: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentДокумент9 страницCataract: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentHemant SharmaОценок пока нет
- 1.CATARACTДокумент31 страница1.CATARACTsnehalОценок пока нет
- Cataract Extraction The Procedure and Why It Is DoneДокумент2 страницыCataract Extraction The Procedure and Why It Is DoneSheenam ChopraОценок пока нет
- Biology - The Eye (Cateracts)Документ5 страницBiology - The Eye (Cateracts)Shannen NaraceОценок пока нет
- Cataracts PACESДокумент2 страницыCataracts PACESDheeshana SayakkarageОценок пока нет
- Advance Trends in Eye Care: DR Divya Kesarwani Consultant Cataract and Glaucoma ServicesДокумент42 страницыAdvance Trends in Eye Care: DR Divya Kesarwani Consultant Cataract and Glaucoma ServicesdrdivyakesarwaniОценок пока нет
- CataractДокумент19 страницCataractSushrut ManwatkarОценок пока нет
- Ears, Eyes, Nose & ThroatДокумент132 страницыEars, Eyes, Nose & ThroatMarnelli_Iris__4261Оценок пока нет
- Cataract SurgeryДокумент14 страницCataract SurgeryRenato AbellaОценок пока нет
- Activity3 (Refraction-Errors)Документ8 страницActivity3 (Refraction-Errors)Gabbii CincoОценок пока нет
- Sight SavingДокумент3 страницыSight SavingenelrahОценок пока нет
- Resume CataractДокумент3 страницыResume CataractFadila PadmariniОценок пока нет
- Activity5 (Retinal Detachment)Документ3 страницыActivity5 (Retinal Detachment)Gabbii CincoОценок пока нет
- Cataracts: Intraocular Lens (IOL)Документ10 страницCataracts: Intraocular Lens (IOL)Razele Ann RamosОценок пока нет
- CataractsДокумент17 страницCataractsdubutwice29Оценок пока нет
- Cataract Surgery Recovery Time GuideДокумент10 страницCataract Surgery Recovery Time GuideAnonymous 52e0CIОценок пока нет
- Retinal DetachmentДокумент7 страницRetinal Detachmentjay dewanagnОценок пока нет
- Guide to Cataract Surgery RecoveryДокумент16 страницGuide to Cataract Surgery Recoverydokumen kuОценок пока нет
- Cover PageДокумент1 страницаCover PageJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Table of ContentsДокумент1 страницаTable of ContentsJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- BFS Uti 111Документ65 страницBFS Uti 111JemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Narrative PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаNarrative PathophysiologyJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Stat ResultsДокумент11 страницStat ResultsJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Acute IllnessДокумент6 страницAcute IllnessJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Stugeron ForteДокумент4 страницыStugeron ForteJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Stugeron ForteДокумент4 страницыStugeron ForteJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 32222222Документ3 страницыChapter 2 32222222JemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- ResultsДокумент2 страницыResultsJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Acute Pain Is A Type of Pain That Typically Lasts Acute Confusion: Abrupt Onset of A Cluster ofДокумент2 страницыAcute Pain Is A Type of Pain That Typically Lasts Acute Confusion: Abrupt Onset of A Cluster ofJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Stat ResultsДокумент11 страницStat ResultsJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Pediatricians On The Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Community Acquired Pneum - 1 PDFДокумент2 страницыKnowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Pediatricians On The Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Community Acquired Pneum - 1 PDFCarina SuarezОценок пока нет
- NeurologicДокумент7 страницNeurologicFarrah ErmanОценок пока нет
- Psychosexual DisordersДокумент14 страницPsychosexual DisordersJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- HepatitisДокумент18 страницHepatitisJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- AcknowledgementДокумент1 страницаAcknowledgementJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Geno GramДокумент1 страницаGeno GramJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- ACKNOWLEDGEMENTДокумент1 страницаACKNOWLEDGEMENTJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- The ParentsДокумент11 страницThe ParentsJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Principles of LearningДокумент16 страницPrinciples of LearningJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- ACKNOWLEDGEMENTДокумент1 страницаACKNOWLEDGEMENTJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- B.F. Skinner's Operant Conditioning TheoryДокумент10 страницB.F. Skinner's Operant Conditioning TheoryJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- How to Optimize Learning Retention Through Active ParticipationДокумент16 страницHow to Optimize Learning Retention Through Active ParticipationJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- The ParentsДокумент11 страницThe ParentsJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoОценок пока нет
- Cataract: Presented By: HomipalДокумент12 страницCataract: Presented By: Homipalankita singhОценок пока нет
- Intraocular Lens Power Calculation in Eyes With Previous Corneal Refractive SurgeryДокумент10 страницIntraocular Lens Power Calculation in Eyes With Previous Corneal Refractive Surgerymoni7777Оценок пока нет
- Logbook New 1Документ61 страницаLogbook New 1Shantanu SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Aphakia Presentation OverviewДокумент77 страницAphakia Presentation OverviewSiva LoveОценок пока нет
- Biology For Engineers Question Bank Module 1-3Документ22 страницыBiology For Engineers Question Bank Module 1-3Edu techОценок пока нет
- Phacoemulsification Versus Small Incision Cataract Surgery For Treatment ofДокумент7 страницPhacoemulsification Versus Small Incision Cataract Surgery For Treatment ofRagni MishraОценок пока нет
- Ophthalmology Question BankДокумент40 страницOphthalmology Question BankMuathОценок пока нет
- Comparison of The Mechanical Properties of The Anterior Lens Capsule in Senile Cataract, Senile Cataract With Trypan Blue Application, and Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome.Документ8 страницComparison of The Mechanical Properties of The Anterior Lens Capsule in Senile Cataract, Senile Cataract With Trypan Blue Application, and Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome.Anonymous iInKGkMCОценок пока нет
- Guide to Cataract Surgery RecoveryДокумент16 страницGuide to Cataract Surgery Recoverydokumen kuОценок пока нет
- Orbis Guide To Ophthalmic EquipmentДокумент16 страницOrbis Guide To Ophthalmic EquipmentmohammedОценок пока нет
- Complications of Hypermature Cataract and Its Visual OutcomeДокумент5 страницComplications of Hypermature Cataract and Its Visual OutcomejoyfullОценок пока нет
- A Cost-Benefit Analysis of 2018 Cataract Surgery in The United StatesДокумент13 страницA Cost-Benefit Analysis of 2018 Cataract Surgery in The United StatesasclepiuspdfsОценок пока нет
- Color Atlas of Anterior SegmentДокумент170 страницColor Atlas of Anterior Segmentxakos16766Оценок пока нет
- Physiological Modeling of the Eye Using Mechanical ComponentsДокумент3 страницыPhysiological Modeling of the Eye Using Mechanical ComponentsMohammad MashhoodОценок пока нет
- 0322CRSTEuro BVI Whitepaper No.2Документ1 страница0322CRSTEuro BVI Whitepaper No.2anandprasad244Оценок пока нет
- SofPort AOV Patient LeafletДокумент8 страницSofPort AOV Patient LeafletGp MishraОценок пока нет
- Phacoemulsification of The Rock-HardДокумент12 страницPhacoemulsification of The Rock-Hardshetya_8212Оценок пока нет
- Case Review - EndophthalmitisДокумент4 страницыCase Review - EndophthalmitisDr Shawgat Ul Karim KhanОценок пока нет
- Modified Sewing Machine Technique For IridodialysiДокумент8 страницModified Sewing Machine Technique For IridodialysiRonal PerinoОценок пока нет
- Aladdin 3.0 BrochureДокумент16 страницAladdin 3.0 Brochuredarkspawn69Оценок пока нет
- Relationship Between Age, Corneal Astigmatism, and Ocular Dimensions With Reference To Astigmatism in Eyes Undergoing Routine Cataract SurgeryДокумент8 страницRelationship Between Age, Corneal Astigmatism, and Ocular Dimensions With Reference To Astigmatism in Eyes Undergoing Routine Cataract Surgeryandrema123Оценок пока нет
- IOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsДокумент8 страницIOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsShimaa MersalОценок пока нет
- AECS model for eradicating blindnessДокумент7 страницAECS model for eradicating blindnessShubha Brota RahaОценок пока нет
- Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (Ecce)Документ9 страницExtracapsular Cataract Extraction (Ecce)Nica Lopez FernandezОценок пока нет
- Primarya Angle Closure Glaucoma 2021Документ147 страницPrimarya Angle Closure Glaucoma 2021robeyeОценок пока нет