Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biological Fermentation of Syngas
Загружено:
Semana de Engenharia '2010Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biological Fermentation of Syngas
Загружено:
Semana de Engenharia '2010Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
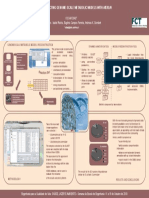
BIOLOGICAL FERMENTATION OF SYNGAS
University of Minho JOANA I. ALVES*
School of Engineering
Centre of Biological Engineering Supervisors: Madalena Alves, Diana Z. Sousa
* joana.alves@deb.uminho.pt
Introduction Methods Results and Conclusions
Syngas or synthesis gas is produced during the gasification of In order to study the potential of different inocula for the 55 ºC | 10% CO | 35 days incubation
different materials, e.g. coal, oil and natural gas, tar sands, synthesis of various interesting products from syngas, synthetic
recalcitrant wastes, lignocellulosic biomass, and sewage sludge. mixtures of CO, CO2 and H2 with different CO:CO2:H2 ratios and
The principal components of syngas are carbon monoxide (CO), different operational conditions, namely temperature and
hydrogen (H2), and carbon dioxide (CO2). Both catalytic and pressure, were tested in batch assays.
biological processes can be used for the production of biofuels
Mesophilic
and bulk chemicals from syngas. The development of novel Substrate:
suspended
bioprocesses for syngas conversion to added-value products is slugde synthetic syngas
37 °C 5% CO mixture, diluted
a promising field comprising some advantages over the with H2/CO2
10% CO The thermophilic suspended slugde used offers potential
chemical processes. However, potential for biological
conversion of syngas is still rather unexplored within the Phosphate advantages over the use of mesophilic suspended slugde,
Thermophilic buffer 20 mM related to the CO consumption.
bioprocess engineering community.
suspended
slugde
The main goal of this work is to explore the potencial of 55 °C 5% CO pH ≈ 7.0
After more than 5 successive transfers (that correspond to more
biogas or other valuable compounds production from 10% CO
P total ≈ 2.5 bar than 100 days of incubation) and increasing the CO
syngas. 20% CO
concentration from 5% to 60%, by using a phase contrast
microscope, it was observed only two different morphological
Low biodegradable substrates to biofuels types of microorganisms. This fact indicates a specialization of
low biodegradable wastes Headspace composition (H2, CO2, CH4, CO) the inocula in CO-consuming microorganisms.
cellulosic material
GC-TCD
Gasification Syngas
Process (H2, CO, CO2) Volatile fatty-acids and alcohols
HPLC
Successive transfers with syngas as a substrate, with different
Study of the microbial Anaerobic Process
physiology of syngas concentrations of CO, are being performed, aiming the isolation
e.g.:
fermenting CO + 3H2 CH4 + H2O of novel syngas- or CO-utilizing microorganisms.
Microbial dynamics of syngas-enriched cultures
microorganims in order 4CO + 8H CH (CH )3OH + 3H O
2 3 2 2
to enhance its
conversion to biofuels or 2CO + 2H2 CH3COO- + H+ Total DNA isolation
other added-value Acknowledgements
16s rRNA gene amplification
chemicals. (PCR) The financial support from Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
Biofuels (FCT) trough the PhD grant SFRH/BD/48965/2008 given to Joana
Usable chemicals Microbial diversity and shifts (DGGE)
I. Alves is gratefully acknowledged.
Engenharia para a Qualidade de Vida: SAÚDE, LAZER E AMBIENTE– Semana da Escola de Engenharia -11 a 16 de Outubro de 2010
Вам также может понравиться
- Modelling The Cyclic Behaviour of RC StructuresДокумент1 страницаModelling The Cyclic Behaviour of RC StructuresSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- A Network Flow Model For The Vehicle Routing Problem With Time Windows and Multiple RoutesДокумент1 страницаA Network Flow Model For The Vehicle Routing Problem With Time Windows and Multiple RoutesSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Modeling of Wave Propagation in Soils Using The Finite Element MethodДокумент1 страницаModeling of Wave Propagation in Soils Using The Finite Element MethodSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- Methodologies For Safety Evaluation of Existing Timber StructuresДокумент1 страницаMethodologies For Safety Evaluation of Existing Timber StructuresSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Secretome Analysis of Ashbya GossypiiДокумент1 страницаSecretome Analysis of Ashbya GossypiiSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- The Economic Impact of Higher Education Institutions On Regional Development: The Case of The Polytechnic Institute of BragançaДокумент1 страницаThe Economic Impact of Higher Education Institutions On Regional Development: The Case of The Polytechnic Institute of BragançaSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Time-Slot Scheduling Algorithm For E-Health Wireless Sensor NetworksДокумент1 страницаA Time-Slot Scheduling Algorithm For E-Health Wireless Sensor NetworksSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Optimization of The Potential of Human Adult and Embryonic Stem Cells For Skin Tissue EngineeringДокумент1 страницаOptimization of The Potential of Human Adult and Embryonic Stem Cells For Skin Tissue EngineeringSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Reconstructing Genome-Scale Metabolic Models With MerlinДокумент1 страницаReconstructing Genome-Scale Metabolic Models With MerlinSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Wearable Photonic Bioelectric Monitoring DeviceДокумент1 страницаWearable Photonic Bioelectric Monitoring DeviceSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Brewing Fermentations More ProfitableДокумент1 страницаBrewing Fermentations More ProfitableSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Organizational Memory: A Proposal For Diagnose and InterventionДокумент1 страницаOrganizational Memory: A Proposal For Diagnose and InterventionSemana de Engenharia '2010Оценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- PDF Sensors Air Conditioning Automotive AN1Документ5 страницPDF Sensors Air Conditioning Automotive AN1Karthik RajaОценок пока нет
- Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesДокумент16 страницClass 10 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesKriish RatnaniОценок пока нет
- Just in Time AlgebraДокумент289 страницJust in Time AlgebraamaiscОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- GP 1 Module 3Документ46 страницGP 1 Module 3Raymund EspinoОценок пока нет
- BM2 24H+Installation+InstructionsДокумент7 страницBM2 24H+Installation+InstructionsremediospereiraОценок пока нет
- IT6602 SA Coaching Class QuestionsДокумент3 страницыIT6602 SA Coaching Class QuestionsvinothОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Chapter6b-Combinational Logic Design PracticesДокумент38 страницChapter6b-Combinational Logic Design PracticesZulkarnineОценок пока нет
- Genetic Variability and Correlation Studies in Okra (Abelmuschus Esculentus (L) Moench)Документ67 страницGenetic Variability and Correlation Studies in Okra (Abelmuschus Esculentus (L) Moench)rajsign5100% (3)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- DeskView Client 6 45 enДокумент166 страницDeskView Client 6 45 enRazvan22081997Оценок пока нет
- Tetzaveh Parsha GematriaДокумент1 страницаTetzaveh Parsha GematriaRabbi Benyomin HoffmanОценок пока нет
- 50TPD Soybean Oil Batch Type Solvent Extraction PlantДокумент4 страницы50TPD Soybean Oil Batch Type Solvent Extraction PlantKenan KardasОценок пока нет
- Solution: 4.5 Normal DistributionДокумент9 страницSolution: 4.5 Normal DistributionGladis Torres100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Subjects Revised Curriculum BS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGДокумент18 страницSubjects Revised Curriculum BS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGData StatsОценок пока нет
- Princom The Fundamentals of Electronics Module 2Документ9 страницPrincom The Fundamentals of Electronics Module 2melwin victoriaОценок пока нет
- I PartsДокумент18 страницI PartsAnilkumar KrОценок пока нет
- CS405PC JP Unit-3Документ44 страницыCS405PC JP Unit-3MEGHANA 3Оценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Complete Operator Training Manual PDFДокумент397 страницComplete Operator Training Manual PDFJacc jacc100% (2)
- Eaton Xeffect Industrial Switchgear Range Catalog Ca003002en en UsДокумент379 страницEaton Xeffect Industrial Switchgear Range Catalog Ca003002en en UsMAURIZIO MARINIОценок пока нет
- Nilfisk 2016Документ12 страницNilfisk 2016Ilham HamidОценок пока нет
- Ashikur Rahman 011172081 B: Name: IDДокумент13 страницAshikur Rahman 011172081 B: Name: IDAshikОценок пока нет
- Completation Inteligent RevistaДокумент9 страницCompletation Inteligent RevistaGabriel Castellon HinojosaОценок пока нет
- 3D-ICONS Guidelines PDFДокумент53 страницы3D-ICONS Guidelines PDFAna Paula Ribeiro de AraujoОценок пока нет
- TractionДокумент26 страницTractionYogesh GurjarОценок пока нет
- Ericsson Command LineДокумент39 страницEricsson Command LinejulescarrelОценок пока нет
- Proview TutorialДокумент12 страницProview TutorialManoel NascimentoОценок пока нет
- Exercise 2Документ4 страницыExercise 2Ir Fik TОценок пока нет
- Economics Solution Book PDFДокумент368 страницEconomics Solution Book PDFgoutam1235100% (3)
- Modal LogicДокумент14 страницModal LogicL'Homme RévoltéОценок пока нет
- MADNotes J2MEДокумент34 страницыMADNotes J2MEKanchana MorumpalliОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Damage and Fatigue Assessment of Dented Pipelines Using FeaДокумент10 страницMechanical Damage and Fatigue Assessment of Dented Pipelines Using FeaVitor lopesОценок пока нет