Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hept B
Загружено:
Sury0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
58 просмотров9 страницHept B
Оригинальное название
hept B
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документHept B
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
58 просмотров9 страницHept B
Загружено:
SuryHept B
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 9
Hepatitis B vaccine
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is one of the most
common infectious diseases known to man.
• The World Health Organization (WHO)
estimates that there are as many as 285 million
chronic carriers of this virus worldwide. I
• Hepatitis B is 50 to 100 times more
infectious than AIDS.
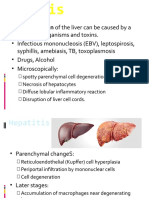
•Hepatitis B is irritation and swelling
(inflammation) of the liver due to infection
with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Other types
of viral hepatitis include: Hepatitis A,Hepatitis
C; Hepatitis D.
Hepatitis B Recombinant Vaccine
• It produces several chronic liver disorders such
as Fulminant chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and
primary liver cancer.
• It’s a novel and significant developed vaccine
which is produced from the antigenic proteins
of Hepatitis B virus by recombinant process
that duplicates the chemical messages and
secreted factors (Interleukin-2) for the
communication and activity of immune cells
A recent approach for Recombinant
Hepatitis B Vaccine production
• A special type of tropical monocot banana
under the genus Musa in the Musaceae
family, can be ideally engineered by genetic
mechanism process for the production of
hepatitis B vaccine--- it was suggested. With
this technology, the cost of vaccination could
be reduced.
General features of nucleic acid of
Hepatitis B Virus
• HB virus has been identified as a 42-nm
particle containing a double stranded circular
DNA molecule of about 3Kb size.
• DNA genome has a relative molecular mass of
approximately 2 X 106.
• DNA cloning. It’s an unusual feature among
other viruses.
General features of nucleic acid of
Hepatitis B Virus
• Plasma of human has been detected to have
varying amount of HB antigens. Three types of
viral coat proteins are recognized to be antigenic
• viral surface antigen (HBsAg)
• viral core antigen (HBcAg)
• the e-antigen (HBeAg)
General features of nucleic acid of
Hepatitis B Virus
• Suraface antigen HBsAG is found as 18-22 nm
spherical or tubular form particles. Recently
HBsAg gene or it’s subunits are used for the
production of recombinant Hepatitis B
vaccine.
General steps for Recombinant
Hepatitis B Vaccine production
• Production of these genes is needed in order to
get production of vaccines on a large scale. A
general procedure for the production of
recombinant Hepatitis B vaccines are
described here
HBs antigen producing gene is isolated from
the HB virus by normal isolation process (cell
lysis, protein denaturation, precipitation,
centrifugation and drying).
A plasmid DNA is extracted from a bacterium-
E.coli and is cut with restriction enzyme- Eco
RI forming the plasmid vector
The isolated HBs antigen producing gene is
located and inserted into the bacterial plasmid
vector on forming the recombinant DNA.
This recombinant DNA, containing the target
gene, is introduced into a yeast cell forming
the recombinant yeast cell.
The recombinant yeast cell multiplies in the
fermentation tank and produces the HBs
antigens.
After 48 hours, yeast cells are ruptured to free
HBsAg. The mixture is processed for
extraction.
The HBs antigens are purified.
HBsAg are combined with preserving agent
and other ingredients and bottled. Now it is
ready for vaccination in humans.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Lightworker's HandbookДокумент58 страницThe Lightworker's HandbookEvgeniq Marcenkova100% (9)
- Hepatitis Viruses ÍõÅà ÕДокумент85 страницHepatitis Viruses ÍõÅà Õrasool ghaffariОценок пока нет
- Viral Hepatitis (Virus Hepatitis)Документ75 страницViral Hepatitis (Virus Hepatitis)Ilmiah Bagus100% (1)
- 175 Mendoza V GomezДокумент2 страницы175 Mendoza V GomezAnonymous bOncqbp8yiОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis of Hepatitis B InfectionДокумент41 страницаDiagnosis of Hepatitis B Infectiontummalapalli venkateswara raoОценок пока нет
- PS2082 VleДокумент82 страницыPS2082 Vlebillymambo0% (1)
- Unit-V 5.1.0 Production of Recombinant ProteinsДокумент17 страницUnit-V 5.1.0 Production of Recombinant ProteinsBharathiОценок пока нет
- Completed Jen and Larry's Mini Case Study Working Papers Fall 2014Документ10 страницCompleted Jen and Larry's Mini Case Study Working Papers Fall 2014ZachLoving100% (1)
- Recombinant VaccinesДокумент22 страницыRecombinant VaccinesjugesmangangОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B & C & D VirusДокумент14 страницHepatitis B & C & D VirusAtheer AlabdyОценок пока нет
- Climate Change (B Ok - CC)Документ481 страницаClimate Change (B Ok - CC)Rashid LatiefОценок пока нет
- 1 Introduction Strategic Project Management (Compatibility Mode)Документ39 страниц1 Introduction Strategic Project Management (Compatibility Mode)Pratik TagwaleОценок пока нет
- Tan Vs PeopleДокумент1 страницаTan Vs PeopleGian Tristan MadridОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B VirusДокумент16 страницHepatitis B Virusbalaji KumaresanОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Strategies For Hepatitis B Virus Infection - Towards A CureДокумент18 страницTherapeutic Strategies For Hepatitis B Virus Infection - Towards A CureAdriana Villarreal FragaОценок пока нет
- Ant Vaccines WRF Hepatitis B FinalДокумент6 страницAnt Vaccines WRF Hepatitis B FinalRidhi MurarkaОценок пока нет
- NBVHJVДокумент20 страницNBVHJVThe BestОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis BДокумент31 страницаHepatitis Bodakam.harrisОценок пока нет
- L22 - Viral Carcinogenesis-Part 2-S23Документ23 страницыL22 - Viral Carcinogenesis-Part 2-S23waОценок пока нет
- Recombinant Vaccine: Neethu AsokanДокумент29 страницRecombinant Vaccine: Neethu AsokanShivraj JadhavОценок пока нет
- Hep B Group PresentationДокумент23 страницыHep B Group PresentationShemiza BalmacoonОценок пока нет
- Pemeriksaan Terkini Hepatitis Virus: Prof. Dr. Jusak Nugraha, DR, MS, SPPK (K) Lab Patologi Klinik FK UnairДокумент53 страницыPemeriksaan Terkini Hepatitis Virus: Prof. Dr. Jusak Nugraha, DR, MS, SPPK (K) Lab Patologi Klinik FK UnairMuh YunusОценок пока нет
- Liver International - 2018 - Schinazi - Towards HBV Curative TherapiesДокумент13 страницLiver International - 2018 - Schinazi - Towards HBV Curative Therapiesירדן לויןОценок пока нет
- RV AND AS AssignmentДокумент17 страницRV AND AS AssignmentADITYAROOP PATHAKОценок пока нет
- Immunology of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus InfectionДокумент16 страницImmunology of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus InfectionZineb RAISОценок пока нет
- Muhammad Asaad Maidin Departement Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin University, MakassarДокумент54 страницыMuhammad Asaad Maidin Departement Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin University, MakassarPratiwi PurnamaОценок пока нет
- Immunotherapy For Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: ReviewДокумент11 страницImmunotherapy For Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: ReviewShafa ShaviraОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis VirusДокумент83 страницыHepatitis VirusRudresh Shoorashetty ManoharОценок пока нет
- Dr. G. Thiruvenkadam Post Graduate Dept of Pediatric & Preventive DentistryДокумент31 страницаDr. G. Thiruvenkadam Post Graduate Dept of Pediatric & Preventive Dentistryதிருவேங்கடம் கோபாலன்Оценок пока нет
- Hepatitis: Sushil Paudyal Department of Community MedicineДокумент21 страницаHepatitis: Sushil Paudyal Department of Community MedicineSushil PaudyalОценок пока нет
- Modern Biotech Medical - Sem 1.2022.23Документ57 страницModern Biotech Medical - Sem 1.2022.23milyjonsin.25Оценок пока нет
- Hepatitis VirusesДокумент35 страницHepatitis Virusesm dawoodОценок пока нет
- HepatitisДокумент11 страницHepatitistorsedepointeОценок пока нет
- HEPATITISДокумент10 страницHEPATITISVanlal RemruatiОценок пока нет
- HEPADNAVIRIDAEДокумент14 страницHEPADNAVIRIDAEnur qistina humaira zulkarshamsiОценок пока нет
- Methodical Pointing For Students 23Документ10 страницMethodical Pointing For Students 23Bilind KhalilОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B VirusДокумент31 страницаHepatitis B VirusFriyoga SyahrilОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B Is An Infectious Illness Caused by Hepatitis B VirusДокумент5 страницHepatitis B Is An Infectious Illness Caused by Hepatitis B VirusCecilia de LeonОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B PDFДокумент15 страницHepatitis B PDFAvicenna_MSCОценок пока нет
- Recombivax HB®: Hepatitis B Vaccine (Recombinant)Документ13 страницRecombivax HB®: Hepatitis B Vaccine (Recombinant)Mimô SAОценок пока нет
- Chronic Hepatitis B: PreambleДокумент17 страницChronic Hepatitis B: PreambleEngr Hafiz Qasim AliОценок пока нет
- Oxygen 2222Документ75 страницOxygen 2222Salim AlmetewtyОценок пока нет
- Pharmaceuticals 14 00417 v2Документ27 страницPharmaceuticals 14 00417 v2Mida AdinaОценок пока нет
- Roadmap: A Roadmap For Serum Biomarkers For Hepatitis B Virus: Current Status and Future OutlookДокумент19 страницRoadmap: A Roadmap For Serum Biomarkers For Hepatitis B Virus: Current Status and Future Outlooksara ibrahemОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B Vaccine and Immunoglobulin: Key Concepts: Review ArticleДокумент7 страницHepatitis B Vaccine and Immunoglobulin: Key Concepts: Review ArticleMarcelitaTaliaDuwiriОценок пока нет
- Infectious Agent of Hepatitis B: Fbclid Iwar0Xvbd0Ebp7Zkt1Kclnzs65V3Azjwowjhwlp8Dseanahkma1Ycecebcs5KДокумент3 страницыInfectious Agent of Hepatitis B: Fbclid Iwar0Xvbd0Ebp7Zkt1Kclnzs65V3Azjwowjhwlp8Dseanahkma1Ycecebcs5Kangel mintsОценок пока нет
- HBV Easl 2017Документ57 страницHBV Easl 2017jessica100% (1)
- Recombinant VaccinesДокумент11 страницRecombinant VaccinesAshna JoshiОценок пока нет
- Hcca Rev Nri 2005Документ15 страницHcca Rev Nri 2005Patrick RamosОценок пока нет
- New Hepatitis B Vaccine Formulated With An Improved Adjuvant SystemДокумент8 страницNew Hepatitis B Vaccine Formulated With An Improved Adjuvant SystemJocel GómezОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis 1Документ40 страницHepatitis 1Noelle Grace Ulep BaromanОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B ActualizacionДокумент7 страницHepatitis B ActualizacionAbel Espinoza MedallaОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B: Prepared By: Mina Zana Nozhin Ahmed Hoshyar Omer Hawkar IsmailДокумент19 страницHepatitis B: Prepared By: Mina Zana Nozhin Ahmed Hoshyar Omer Hawkar Ismailraman saeedОценок пока нет
- RTHB 9 Recombinant Vaccines 27122023Документ30 страницRTHB 9 Recombinant Vaccines 27122023ayeshasattarsandhuОценок пока нет
- Recombivax PiДокумент13 страницRecombivax PiyigitilgazОценок пока нет
- Wands 1997Документ16 страницWands 1997LAURAОценок пока нет
- Research Paper On HBVДокумент7 страницResearch Paper On HBVhyz0tiwezif3100% (1)
- Background: Cirrhosis Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)Документ24 страницыBackground: Cirrhosis Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)Ignatius Rheza SetiawanОценок пока нет
- Immunology of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus InfectionДокумент15 страницImmunology of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus InfectionMark BowlerОценок пока нет
- Literature Review Hepatitis B VirusДокумент4 страницыLiterature Review Hepatitis B Virusafmztwoalwbteq100% (1)
- Jiaa668 PDFДокумент9 страницJiaa668 PDFhelen acostaОценок пока нет
- How To Achieve Functional Cure of HBV Stopping NUДокумент14 страницHow To Achieve Functional Cure of HBV Stopping NUCláudia SilvaОценок пока нет
- Viral HepatitisДокумент8 страницViral HepatitisPoka DineshОценок пока нет
- Hudu qHBePublished2018Документ7 страницHudu qHBePublished2018bread maniacОценок пока нет
- ICGEB 601 Seminar PRIYA 26.11.2018 PDFДокумент13 страницICGEB 601 Seminar PRIYA 26.11.2018 PDFHardik MehtaОценок пока нет
- Viral HepatitisДокумент58 страницViral HepatitisKathrine SiahaanОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B Virus and Liver DiseaseОт EverandHepatitis B Virus and Liver DiseaseJia-Horng KaoОценок пока нет
- HGHДокумент4 страницыHGHSury100% (1)
- Industrial Visit 2019 Mysore-Madikeri: 6 Semester BSC (BT) - Section AДокумент8 страницIndustrial Visit 2019 Mysore-Madikeri: 6 Semester BSC (BT) - Section ASuryОценок пока нет
- Building Services Iii FireДокумент14 страницBuilding Services Iii FireSuryОценок пока нет
- Fire Safety and Passive Fire ProtДокумент10 страницFire Safety and Passive Fire ProtSuryОценок пока нет
- CASE STUDY ChecklistДокумент2 страницыCASE STUDY ChecklistSuryОценок пока нет
- Uttam C Jain-1Документ6 страницUttam C Jain-1SuryОценок пока нет
- Greek Mythology ReviewerДокумент12 страницGreek Mythology ReviewerSyra JasmineОценок пока нет
- Final Test 1 Grade 10Документ4 страницыFinal Test 1 Grade 10Hường NgôОценок пока нет
- ACR Format Assisstant and ClerkДокумент3 страницыACR Format Assisstant and ClerkJalil badnasebОценок пока нет
- Botvinnik-Petrosian WCC Match (Moscow 1963)Документ9 страницBotvinnik-Petrosian WCC Match (Moscow 1963)navaro kastigiasОценок пока нет
- QBE 2022 Sustainability ReportДокумент44 страницыQBE 2022 Sustainability ReportVertika ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Allstate Car Application - Sign & ReturnДокумент6 страницAllstate Car Application - Sign & Return廖承钰Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 9 Government Programs and Suggestions in Addressing Social InequalitiesДокумент25 страницLesson 9 Government Programs and Suggestions in Addressing Social InequalitiesLeah Joy Valeriano-QuiñosОценок пока нет
- AGM Minutes 2009Документ3 страницыAGM Minutes 2009Prateek ChawlaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8: ETHICS: Mores Laws Morality and EthicsДокумент3 страницыChapter 8: ETHICS: Mores Laws Morality and EthicsJohn Rey BandongОценок пока нет
- A2 UNIT 2 Extra Grammar Practice RevisionДокумент1 страницаA2 UNIT 2 Extra Grammar Practice RevisionCarolinaОценок пока нет
- Reading Job Advertisements 4Документ2 страницыReading Job Advertisements 456. Trần Thị Thanh Tuyền100% (1)
- Richard Neutra - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент10 страницRichard Neutra - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNada PejicОценок пока нет
- Youtube/Ydsatak Tense Ders 1Документ9 страницYoutube/Ydsatak Tense Ders 1ArasIlgazОценок пока нет
- Chinese and Korean Art Before 1279 CeДокумент67 страницChinese and Korean Art Before 1279 Ceragunath palaniswamyОценок пока нет
- EA FRM HR 01 03 JobApplicationДокумент6 страницEA FRM HR 01 03 JobApplicationBatyОценок пока нет
- Nurlilis (Tgs. Bhs - Inggris. Chapter 4)Документ5 страницNurlilis (Tgs. Bhs - Inggris. Chapter 4)Latifa Hanafi100% (1)
- Corporate Social Responsibility in Bangladesh:: A Comparative Study of Commercial Banks of BangladeshДокумент12 страницCorporate Social Responsibility in Bangladesh:: A Comparative Study of Commercial Banks of BangladeshSaima Binte IkramОценок пока нет
- Sibayan, Patrick Jorge - Weekly Accomplishment (July 8-14, 2019)Документ2 страницыSibayan, Patrick Jorge - Weekly Accomplishment (July 8-14, 2019)Patrick Jorge SibayanОценок пока нет
- Conduct Disorder ChecklistДокумент1 страницаConduct Disorder Checklistiswarya vellaisamyОценок пока нет
- Bung Tomo InggrisДокумент4 страницыBung Tomo Inggrissyahruladiansyah43Оценок пока нет
- Marketing Chapter001Документ22 страницыMarketing Chapter001Reham MohamedОценок пока нет
- The New Rich in AsiaДокумент31 страницаThe New Rich in AsiaIrdinaОценок пока нет
- Leander Geisinger DissertationДокумент7 страницLeander Geisinger DissertationOrderPapersOnlineUK100% (1)