Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CH 16
Загружено:
Engr. Talha Riaz Persota0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров20 страницОригинальное название
ch 16.ppt
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров20 страницCH 16
Загружено:
Engr. Talha Riaz PersotaАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 20
Chapter 16
Network
Devices
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
16.1 Connecting Devices
Repeaters
Hubs
Bridges
Two-Layer Switches
Three-Layer Switches or Routers
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 16.1 Connecting devices
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 16.2 Repeater
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Note:
A repeater connects segments of a
LAN.
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Note:
A repeater forwards every frame; it
has no filtering capability.
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Note:
A repeater is a regenerator,
not an amplifier.
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 16.3 Function of a repeater
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 16.4 Hubs
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Note:
A bridge has a table used in filtering
decisions.
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 16.5 Bridge
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Note:
A bridge does not change the physical
(MAC) addresses in a frame.
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 16.6 Learning bridge
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Switches
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
19.3 Routing
Routing Techniques
Static Versus Dynamic Routing
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 19.28 Next-hop routing
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 19.29 Network-specific routing
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 19.30 Host-specific routing
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Figure 19.31 Default routing
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
THE END
McGraw-Hill ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004
Вам также может понравиться
- Ruckus ICX Implementer Exam GuideДокумент16 страницRuckus ICX Implementer Exam GuideCarmenОценок пока нет
- Ip Telephony CookbookДокумент228 страницIp Telephony CookbookMiranda WhiteОценок пока нет
- Spirent TestCenter Layer 2 Testing V3aДокумент52 страницыSpirent TestCenter Layer 2 Testing V3asumabangОценок пока нет
- Cisco MPLS Segment Routing - Introduction - v3Документ93 страницыCisco MPLS Segment Routing - Introduction - v3HatemОценок пока нет
- Network Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ20 страницNetwork Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Omer ArshadОценок пока нет
- Circuit SwitchingДокумент39 страницCircuit SwitchingETUDIANTS ETUDIANTSОценок пока нет
- ProtocolДокумент34 страницыProtocolapi-3703205Оценок пока нет
- CH 13Документ28 страницCH 13api-3703205Оценок пока нет
- CH 08Документ19 страницCH 08Nusrat ShameemaОценок пока нет
- Local Area Networks:: EthernetДокумент38 страницLocal Area Networks:: EthernetfaizanmasoodОценок пока нет
- Overview of Data Communications and Networking: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ25 страницOverview of Data Communications and Networking: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Tanveer SardarОценок пока нет
- CH 03Документ60 страницCH 03Mohammed Al-RadwanОценок пока нет
- Data Link Control and Protocols: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ43 страницыData Link Control and Protocols: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Carlos Lopez MejiaОценок пока нет
- Ch-11data Link Control and ProtocolsДокумент43 страницыCh-11data Link Control and ProtocolsSulphuric AcidОценок пока нет
- 12 Network Layer Ip AddressingДокумент100 страниц12 Network Layer Ip AddressingAzzaoui NadjetОценок пока нет
- Communication Systems - Chap12 To 13Документ55 страницCommunication Systems - Chap12 To 13Hansika RajapakshaОценок пока нет
- Congestion Control and Quality of Service: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ28 страницCongestion Control and Quality of Service: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004shiviasОценок пока нет
- Network Models: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ30 страницNetwork Models: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Andre MillerОценок пока нет
- Tcp/Ip: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ17 страницTcp/Ip: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Pavan KumarОценок пока нет
- Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ31 страницаTransmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Keyur MahantОценок пока нет
- Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ38 страницMcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001mnshraoОценок пока нет
- Communication Systems - Chap08 To 09Документ41 страницаCommunication Systems - Chap08 To 09Hansika RajapakshaОценок пока нет
- Networking and Internetworking Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ44 страницыNetworking and Internetworking Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Ani AnitaОценок пока нет
- Transmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ31 страницаTransmission Media: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Ralph Jayson SilangОценок пока нет
- Communication Systems - Chap10 To 11Документ44 страницыCommunication Systems - Chap10 To 11Hansika RajapakshaОценок пока нет
- Security Protocols in The Internet: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ26 страницSecurity Protocols in The Internet: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Anisa AnjumОценок пока нет
- Multiplexing: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ28 страницMultiplexing: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Krishnendu GuinОценок пока нет
- Local Area Networks: Gerd KeiserДокумент22 страницыLocal Area Networks: Gerd Keisereng2011techОценок пока нет
- Networking and Internetworking Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ44 страницыNetworking and Internetworking Devices: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001ramasamyОценок пока нет
- CH 16Документ44 страницыCH 16Rizqi FajrilОценок пока нет
- TCP/IP Chapter Explains Layers and ProtocolsДокумент15 страницTCP/IP Chapter Explains Layers and ProtocolsAni AnitaОценок пока нет
- The Osi Model and Tcp/Ip Protocol Suite: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000Документ36 страницThe Osi Model and Tcp/Ip Protocol Suite: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000lequocdoОценок пока нет
- CH 26Документ28 страницCH 26Rizqi FajrilОценок пока нет
- Analog and Digital - Aperiodic and Periodic SignalsДокумент77 страницAnalog and Digital - Aperiodic and Periodic SignalsvvvamsimohanОценок пока нет
- Bootp and DHCP: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000Документ11 страницBootp and DHCP: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000Rizqi FajrilОценок пока нет
- Multiplexing: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companie S, Inc., 2004Документ41 страницаMultiplexing: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companie S, Inc., 2004nargis79Оценок пока нет
- ch03 2Документ9 страницch03 2Umamaheswaran SОценок пока нет
- ch03 - 2-Continue AboveДокумент9 страницch03 - 2-Continue Aboveshivam dhawanОценок пока нет
- Underlying Technologies: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000Документ60 страницUnderlying Technologies: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000Rizqi FajrilОценок пока нет
- Tcp/Ip Protocol Suite: Part 2, Application Layer: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ38 страницTcp/Ip Protocol Suite: Part 2, Application Layer: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001AnilKarwankarОценок пока нет
- TrnsmsnmediaДокумент19 страницTrnsmsnmediaapi-3703205Оценок пока нет
- Data Link Control and Protocols: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Документ40 страницData Link Control and Protocols: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004PadmajaОценок пока нет
- TransportДокумент50 страницTransportapi-3703205Оценок пока нет
- SwitchingДокумент22 страницыSwitchingapi-3703205Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 Explains X.25 Packet Layer ProtocolДокумент13 страницChapter 16 Explains X.25 Packet Layer ProtocolAni AnitaОценок пока нет
- Forouzan Chp6Документ41 страницаForouzan Chp6Aniket MehtaОценок пока нет
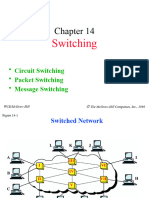
- Switching: - Circuit Switching - Packet Switching - Message SwitchingДокумент22 страницыSwitching: - Circuit Switching - Packet Switching - Message SwitchingArun KumarОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts: - Line Configuration - Topology - Transmission Mode - Categories of Networks - InternetworksДокумент13 страницBasic Concepts: - Line Configuration - Topology - Transmission Mode - Categories of Networks - InternetworksSwathi ChОценок пока нет
- Tcp/Ip Protocol Suite: Part 2, Application Layer: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ38 страницTcp/Ip Protocol Suite: Part 2, Application Layer: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Ayushi GuptaОценок пока нет
- ErrorДокумент10 страницErrorapi-3703205Оценок пока нет
- Forouzan chp7Документ31 страницаForouzan chp7Aniket MehtaОценок пока нет
- ch08 3Документ13 страницch08 3Ali AryanОценок пока нет
- Encoding: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ14 страницEncoding: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001mrutyunjaymaharanaОценок пока нет
- Wcb/Mcgraw-Hill The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 1998Документ9 страницWcb/Mcgraw-Hill The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 1998bandarisrinivasОценок пока нет
- Point-To-Point Protocol: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ12 страницPoint-To-Point Protocol: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001michaelnasiefОценок пока нет
- Analog TransmissionДокумент57 страницAnalog TransmissionMohamedNofalОценок пока нет
- Model Osi Dan Suite Protokol Tcp/Ip: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000Документ48 страницModel Osi Dan Suite Protokol Tcp/Ip: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000Heri RamadhanОценок пока нет
- Wcb/Mcgraw-Hill The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 1998Документ9 страницWcb/Mcgraw-Hill The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 1998Ali AryanОценок пока нет
- CH 13Документ13 страницCH 13mrutyunjaymaharanaОценок пока нет
- Error Detection and CorrectionДокумент10 страницError Detection and CorrectionKshitij GulatiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 22 - FTPДокумент42 страницыLecture 22 - FTPSenthamizh VaniОценок пока нет
- Ch14 SwitchingДокумент28 страницCh14 SwitchingtuhinОценок пока нет
- The Effects of Traffic Structure on Application and Network PerformanceОт EverandThe Effects of Traffic Structure on Application and Network PerformanceОценок пока нет
- English Composition & ComprehensionДокумент2 страницыEnglish Composition & ComprehensionEngr. Talha Riaz PersotaОценок пока нет
- Assignment Data CommunicationДокумент2 страницыAssignment Data CommunicationEngr. Talha Riaz PersotaОценок пока нет
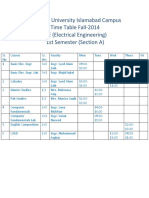
- Hamdard University Islamabad Campus Time Table Fall-2014 BE (Electrical Engineering) 1st Semester (Section A)Документ1 страницаHamdard University Islamabad Campus Time Table Fall-2014 BE (Electrical Engineering) 1st Semester (Section A)Engr. Talha Riaz PersotaОценок пока нет
- Business Letters ExampleДокумент1 страницаBusiness Letters ExampleTunggal Ika SaputraОценок пока нет
- BEE Course Outline PDFДокумент1 страницаBEE Course Outline PDFEngr. Talha Riaz PersotaОценок пока нет
- Assignment Data CommunicationДокумент2 страницыAssignment Data CommunicationEngr. Talha Riaz PersotaОценок пока нет
- CCNet AssigmentДокумент2 страницыCCNet AssigmentEngr. Talha Riaz PersotaОценок пока нет
- PresentationДокумент16 страницPresentationEngr. Talha Riaz PersotaОценок пока нет
- Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Routing AlgorithmsДокумент4 страницыMobile Ad Hoc Networks Routing AlgorithmsEngr. Talha Riaz PersotaОценок пока нет
- VXLAN Scaling Data Center DesignsДокумент7 страницVXLAN Scaling Data Center DesignsAlvaro PrietoОценок пока нет
- MPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP - Part 2 - WWW - IpciscoДокумент7 страницMPLS Label Distribution Protocol, LDP - Part 2 - WWW - IpciscoDAGNUXОценок пока нет
- EDS-G516E Series - Moxa-Eds-G516e-Series-Firmware-V6.3.rom - Software Release HistoryДокумент12 страницEDS-G516E Series - Moxa-Eds-G516e-Series-Firmware-V6.3.rom - Software Release HistoryHussainAlkwitiОценок пока нет
- NE40E V800R011C10 Configuration Guide - IP Routing 02 PDFДокумент1 436 страницNE40E V800R011C10 Configuration Guide - IP Routing 02 PDFbigdrsmithОценок пока нет
- Assignment CCNДокумент4 страницыAssignment CCNammad ahmadОценок пока нет
- Basement floor plan layoutДокумент1 страницаBasement floor plan layoutArun UdayabhanuОценок пока нет
- 4.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv6 ACLsДокумент7 страниц4.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv6 ACLskarenОценок пока нет
- OSPF Hub-And-Spoke Configuration ExamplesДокумент11 страницOSPF Hub-And-Spoke Configuration Examplesabdallah18Оценок пока нет
- 6.5.2.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Static Routes Instructions PDFДокумент2 страницы6.5.2.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Static Routes Instructions PDFaakash muthurama lingamОценок пока нет
- 2.2.4.10 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Switch Port Security InstructionsДокумент1 страница2.2.4.10 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Switch Port Security InstructionsAndrewОценок пока нет
- Ccent StudyДокумент175 страницCcent StudyChakravarthi Chittajallu0% (1)
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMДокумент3 страницы2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMElectronica EdwinОценок пока нет
- RARP and IP AddressingДокумент4 страницыRARP and IP AddressingTarun S VatsОценок пока нет
- Associate - Networking Version 1.0: Certification DescriptionДокумент4 страницыAssociate - Networking Version 1.0: Certification Descriptionson.600Оценок пока нет
- Laurent Ouakil, Guy Pujolle - Telephonie Sur IP - H.323, SIP, MGCP, QoS Et Securite, Filtrage, ToIP Sur Wi-Fi, PBX Asterisk, Skype Et Autres Softphones, VoIP, Offre Multi-Play Des FAI, ...Документ17 страницLaurent Ouakil, Guy Pujolle - Telephonie Sur IP - H.323, SIP, MGCP, QoS Et Securite, Filtrage, ToIP Sur Wi-Fi, PBX Asterisk, Skype Et Autres Softphones, VoIP, Offre Multi-Play Des FAI, ...Karima DjmОценок пока нет
- Ran74 - Ip Based Iub For Flexi Wcdma BtsДокумент9 страницRan74 - Ip Based Iub For Flexi Wcdma BtsgtspauldingОценок пока нет
- College of Computing and Information Sciences: Mid-Term Assessment Fall 2020 SemesterДокумент15 страницCollege of Computing and Information Sciences: Mid-Term Assessment Fall 2020 Semestertalha khanОценок пока нет
- TW DeployingMPLS TextДокумент146 страницTW DeployingMPLS TextKetan PatelОценок пока нет
- Nano IP Series - Ipn920.Документ2 страницыNano IP Series - Ipn920.PaMe LiTaОценок пока нет
- Configuring OSPFДокумент44 страницыConfiguring OSPFDenisОценок пока нет
- System and Network Administration (SNA) - Assignment: December 2017Документ99 страницSystem and Network Administration (SNA) - Assignment: December 2017Trees BОценок пока нет
- HostsДокумент3 482 страницыHostsjuan sierraОценок пока нет
- Fundamental of NetworkingДокумент4 страницыFundamental of Networkingendriasmit_469556062Оценок пока нет
- INAT OPC Server ManualДокумент54 страницыINAT OPC Server ManualTamas LorinczОценок пока нет
- Applies To:: How To Redirect HTTP Traffic To HTTPS On A BIG-IP F5 Load Balancer (Doc ID 889308.1)Документ3 страницыApplies To:: How To Redirect HTTP Traffic To HTTPS On A BIG-IP F5 Load Balancer (Doc ID 889308.1)mohisn963703Оценок пока нет
- MIB ReferenceДокумент97 страницMIB ReferenceDidier SepulvedaОценок пока нет