Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Terms Pain Man
Загружено:
Breeana MooreОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Terms Pain Man
Загружено:
Breeana MooreАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
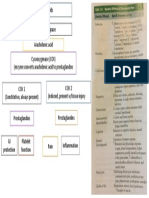
Pain Management pt.1 Unpleasant sensory or emotional experience assoc.
w/acute or potential
Addiction: Chronic neuro & biological disease include one or
tissue damage; exists when & whatever the pt says
more of following: impaired control over drug use, compulsive
use, continued use despite harm, craving opioids for other use
besides pain Intraspinal: within the spine; spaces around cord where
Opioid induced hyperalgesia (OIH): Phenomenon in
Adjuvant analgesic agent: Primary indication other than pain medication can be admin
which exposure to opioids induces increased sensitivity
but is an analgesic agent for some painful conditions; may be Lipophilic: Readily absorbed in fatty tissues
or a lower threshold, ‘flip side’ of tolerance’
referred to as a co-analgesic Metabolite: Product of biochemical reactions during drug
Opioid naïve: pt not taken enough opioid to become
Agonist-antagonist: Type of opioid (e.g. nalbuphine [nubain] metabolism
tolerant of effects
and butorphanol [stadol] that binds to the kappa opioid Mu agonist: Any opioid that binds to mu opioid receptor
Opioid tolerant: Tolerance to high doses, may include
receptor site reacting as an agonist (capable of producing subtype & produces analgesic effects (e.g morphine) used
sedation
analgesia) & simultaneously to the mu opioid receptor interchangeably with terms full agonist, pure agonist, and
Peripheral sensitization: Peripheral mechanism of
(reversing mu agonist effects morphine.
neuropathic pain that occurs when there is a change in
Allodynia: Pain due to stimulus that does not normally Neuropathic (pathophysiologic) pain: Pain sustained by
the number and location of ion channels, sodium
provoke pain, such as touch; typically in nerve injury areas, injury or dysfunction of the peripheral or central nervous
channels abnormally accumulate in injured nociceptors,
neuropathic pain syndromes. systems & distinctly different from nociceptive pain
producing lower nerve depolarization threshold, ectopic
Antagonist: Competes with agonist for receptor sites; can Neuroplasticity: Ability of peripheral & cns to change
discharges, increase response to stimuli
displace agonist inhibiting their action both structure & function as a result of noxious stimuli
Physical dependence: Bodies normal response if on
Breakthrough pain (BTP): transitory increase in pain that Neuropathic (physiologic) pain: Sustained by ongoing
opioid for if 2wks +, withdrawal may occur if stopped
occurs on a background of otherwise controlled persistent activation of sensory system conducts the perception of
abruptly or antagonist is admin
pain noxious stimuli; implies the existence of damage to
Placebo: Medication, procedure, surgery that produces
Ceiling effect: Analgesic dose above which further dose somatic/visceral tissues sufficient to activate nociceptive
an effect in a pt because of its intent not because of
increments produce no change in effect system
physical/chemical properties
Central sensitization: Mechanism of neuropathic pain, Nociceptor: Type of primary afferent neuron that has the
Preemptive analgesic agents: Pre-injury pain treatments
hyperexcitablity of central neurons in spinal cord, result of ability to respond to a noxious stimulus
(preop) to prevent pain
complex changes by incoming afferent barrages of nociceptors Nonopioid: Refers to analgesic agents that include
Refractory: Non responsive or resistant to therapeutic
Comfort-function goal: Pain rating above what the pt wants/ acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
interventions such as analgesic agents
interferes with activities Efficacy: Extend of which a (NSAIDs); term is used instead of ”nonnarcotic”
Self-report: Ability of an individual to give a report-pain,
treatment/med works & can produce ‘effect’ Opioid: Refers to codeine, morphine, and other natural,
intensity, most essential component of pain assessment
Half-life: Time it takes for plasma concen. (drug in body) to be semisynthetic & synthetic drugs that relieve pain by
Titration: Upward or downward adjustment of the
reduced by 50% - 4 to 5 half lives are required to approach a binding to multiple of opioid receptors; term narcotic
amount (dose) of an analgesic agent
steady-state level in the blood; after 4-5 half lives a drug that Opioid dose sparring effect: Occurs when nonopioid
Tolerance: Need to decrease or increase dependent on
has been discontinued generally is considered mostly adjuvant is added to an opioid, allowing the opioid dose
effects
eliminated from body to be lowered without diminishing analgesic effect
Hydrophilic: Readily absorbed in aqueous solution
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- PP On Enzyme PainДокумент1 страницаPP On Enzyme PainBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Risk For Injury T1 MSДокумент1 страницаRisk For Injury T1 MSBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Problems W:painДокумент1 страницаProblems W:painBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Pain 1 (Autosaved)Документ1 страницаPain 1 (Autosaved)Breeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Impaired Vision GlaucomaДокумент1 страницаImpaired Vision GlaucomaBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Med Surg 1 Exam 1Документ23 страницыMed Surg 1 Exam 1Breeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Depressive DisorderДокумент1 страницаDepressive DisorderBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hearing LossДокумент1 страницаHearing LossBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Dementia: Diagnosis Testing: CBC, Chemistry Profile, NM: Safe Environment, Watch For Sundowning, Risk For Falls, PromoteДокумент1 страницаDementia: Diagnosis Testing: CBC, Chemistry Profile, NM: Safe Environment, Watch For Sundowning, Risk For Falls, PromoteBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Delirium DepressionДокумент1 страницаDelirium DepressionBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Safety RestraintsДокумент1 страницаSafety RestraintsBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Nonpharm PainДокумент1 страницаNonpharm PainBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Routes of AdminДокумент1 страницаRoutes of AdminBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- OPIODSДокумент1 страницаOPIODSBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Safety: Falls: Impaired Mobility: Common Causes: Sensory Deficits, Parkinson, Diabetic NeuropathyДокумент1 страницаSafety: Falls: Impaired Mobility: Common Causes: Sensory Deficits, Parkinson, Diabetic NeuropathyBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Safety: Falls: Assessment: For Clients at Risk Repeat Risk Assessment Every 8hrs & Monitor More Freq. IdentifyДокумент1 страницаSafety: Falls: Assessment: For Clients at Risk Repeat Risk Assessment Every 8hrs & Monitor More Freq. IdentifyBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Elder Abuse & NeglectДокумент1 страницаElder Abuse & NeglectBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Neuropathic PainДокумент1 страницаNeuropathic PainBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- OPIODSДокумент1 страницаOPIODSBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- Seizure PrecautionДокумент1 страницаSeizure PrecautionBreeana MooreОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Introduction - WWT AzucareraДокумент7 страницIntroduction - WWT AzucareraSadieОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Training Our Minds in CFT - 1Документ5 страницTraining Our Minds in CFT - 1Anita CassОценок пока нет
- Acute Kidney Injury Prevention Detection and ManagementДокумент38 страницAcute Kidney Injury Prevention Detection and ManagementDobson Flores AparicioОценок пока нет
- Technical Information Librel FeLoДокумент4 страницыTechnical Information Librel FeLoRijalul AuthonОценок пока нет
- EBOT. Columna DegenerativaДокумент43 страницыEBOT. Columna DegenerativaAna GarridoОценок пока нет
- Guía de Diabetes y PsicosisДокумент5 страницGuía de Diabetes y PsicosiskarlunchoОценок пока нет
- Pub105961487 PDFДокумент164 страницыPub105961487 PDFTriandini SanusiОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Oral Chondroprotective Agents - Part IIДокумент5 страницOral Chondroprotective Agents - Part IItaner_soysurenОценок пока нет
- What Are Coping Mechanisms?Документ7 страницWhat Are Coping Mechanisms?Blaze QuibanОценок пока нет
- OsteoarthritisДокумент10 страницOsteoarthritisRehanОценок пока нет
- Girls and AutismДокумент2 страницыGirls and AutismMark Hayes100% (1)
- Full-Mouth Rehabilitation of A Patient With Severe Attrition Using The Hobo Twin-Stage ProcedureДокумент5 страницFull-Mouth Rehabilitation of A Patient With Severe Attrition Using The Hobo Twin-Stage ProcedureDentist HereОценок пока нет
- Epilepsy PDFДокумент15 страницEpilepsy PDFMohamedErrmaliОценок пока нет
- Mcinnes2005 Mutismo SelectivoДокумент10 страницMcinnes2005 Mutismo SelectivoCamila SiebzehnerОценок пока нет
- Documentation Assignments: Mental Health Case: George PaloДокумент3 страницыDocumentation Assignments: Mental Health Case: George PaloPattie100% (1)
- PBL Oral BiologyДокумент12 страницPBL Oral BiologyhusunasanОценок пока нет
- CystoclysisДокумент29 страницCystoclysisKate PedzОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Nursing ChecklistДокумент4 страницыPsychiatric Nursing ChecklistNevea CariñoОценок пока нет
- Ankylosing SpondylitisДокумент21 страницаAnkylosing SpondylitisPaul Kelner100% (2)
- Myotonic DiseaseДокумент11 страницMyotonic DiseaseOhlee TanОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Humanistic and Self Theory (Maslow and Rogers) : StructureДокумент19 страницUnit 4 Humanistic and Self Theory (Maslow and Rogers) : StructuremustafaОценок пока нет
- Fruit Enzymes LabДокумент10 страницFruit Enzymes Labapi-340117487Оценок пока нет
- 6.10.16 Gabrielle Lees Lecture PDFДокумент46 страниц6.10.16 Gabrielle Lees Lecture PDFRicardo LunaОценок пока нет
- 473 eДокумент9 страниц473 eAzmi FarhadiОценок пока нет
- Best Practices DWI CanadaДокумент109 страницBest Practices DWI CanadaninaanjaОценок пока нет
- Personal Notes While at McLeanДокумент12 страницPersonal Notes While at McLeanmcleanhospitalОценок пока нет
- Amoxicillin and Clavula NateДокумент4 страницыAmoxicillin and Clavula NateRoberto BenziОценок пока нет
- Kantar Article (2012) PsychopathologyДокумент3 страницыKantar Article (2012) PsychopathologyShelby Jones-StachnikОценок пока нет
- 6 Alcohol and Drug BooksДокумент6 страниц6 Alcohol and Drug BookswamadozОценок пока нет
- Pulpotomies For Primary Teeth July 2010Документ59 страницPulpotomies For Primary Teeth July 2010Raksmey PhanОценок пока нет