Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter Two: The Language of Business
Загружено:
guuleed0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров34 страницыFjdkdksjs
Оригинальное название
Chapter Two gh
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документFjdkdksjs
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров34 страницыChapter Two: The Language of Business
Загружено:
guuleedFjdkdksjs
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 34
Chapter two
The language of business
Con…
• Introduction:
• What is organization?
• Organization is a group of people, structured
in a specific way to achieve a series of shared
goals, vision and mission.
• Mission: the organizations reason for
existence
• Vision: the long dream of the organization
Management
• Management is the process of attaining
organizational goals in an effective and
efficient way thought functions of
management.
levels of management:
• three levels of management:
• Top management
• Middle management
• Lower management
Goals of the organization
• Goals of the organization
• Goal is a desired future state that the
organization attempts to realize
• Strategic goals: they pertain to the
organization as a whole rather than to specific
divisions or departments.
• Strategic goals are often called official goals
because of they are stated intentions of what
the organization wants to achieve.
Con….
• Tactical goals: these goals apply to a middle
managers and describes what major subunits
must do in order for the organization to
achieve its overall goals
• Operational goals: the specific results
expected from departments, work groups, and
individuals are operational goals within the
organization
Criteria for effective goals
• Specific and measurable: this occurs when
possible goals should be expressed in
quantitative terms, such as increasing profits by 2
percentage
• Cover key result areas: goal can’t be set for every
aspect of employee behavior or organizational
performance, if they were their pure number
would render them meaningless, instead of
managers should identify a few key result areas
Con….
• Challenging but realistic: goals should be challenging
but not unreasonable difficulties, for example one
newly hired manager discovered that his staff would
have to work 100 hours a week to accomplish
everything expected to them. When a goals are
unrealistic, they set employee up for failure and lead to
decreasing of employee morale and commitment.
• Defined time period: goals should specify the time
period over which they will be achieved. And a time
period is deadline starting the date on which goal
attainment will be measured
Con….
• Linked to reward: the ultimate impact of goals
depends on the extent to which salary
increase, promotions and a word are based on
goal achievement.
• That means people who attain goal should be
rewarded and failure of the goal attainment is
due to the factors outside the employee
control.
Organizing
• Organizing is the deployment/use of
organizational resources to achieve strategic
goals.
• Organizing is very important because of it
flows from strategy because it defines what to
do, while the organizing defines how to do it.
The organizing process:
• There are five important of organizing process
and they are as flows:
• Reflect on plans and organizational goals
• Establish a major tasks
• Divide the major tasks in to sub tasks
• Allocate the resources and directives for that
subtasks
• Evaluate the results of implemented ongoing
results
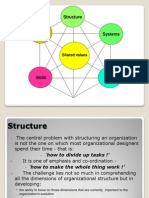
Purpose of organizational structure:
• The set of formal tasks assigned to individuals
and departments
• Formal reporting relations, including the lines
of authority, decision responsibilities, number
of hierarchical levels, and span of managers
control,
• The design of systems to ensure effective
coordination of employees across
departments.
Work simplification
• Work simplification sometimes called division
of labor is the degree to which organizational
tasks are subdivided in to
• For instance the separation of production
tasks in to bottling, quality control, and
maintenance, employees with each
department perform only the tasks relevant to
their specialized functions
Chain of Command:
• Chain of command is an unbroken line of
authority that links all persons in an organization
and shows who reports to whom. And it is
associated with two underling principles.
a) Unity of command that means each employee is
held accountable to only one supervisor.
b) Scalar principle means clearly defines lines of
authority in the organization that includes all
employees
Authority, Responsibility and
Delegation:
• Authority is vested in organizational position,
not people: mangers they have authority
because of the position they hold, and other
people in the same positions would have the
same authority. top to low
• Authority flows down the vertical hierarchy:
• Authority is accepted by subordinates:
Responsibility:
• Responsibility: is the duty to perform the
typically mangers are assigned authority equal
or appropriate with his/her responsibilities.
When the managers have responsibility for
task outcomes but little authority, the job is
possible but it is difficult
Accountability:
• Accountability: means that the people with
authority and responsibility are subject to
reporting and justifying tasks out comes to those
above them in the chain of command.
Subordinate must be aware of that they are
accountable for a task and accept the
responsibility and authority of performing it
• Delegation: is the process of managers use to
transfer authority and responsibility to
appositions below them in the organizational
hierarchy.
Span of management:
• Span of management: is the number of
employees reporting to supervisor, and
sometimes called span of control, this
characteristics of structure determines how
closely a supervisor can monitor subordinates.
Business Strategies
• strategy is a plan of action designed to achieve a long-
term or overall aim.
• Strategy is the art of planning and directing overall
military operations and movements in a war
• Objectives of strategy
• Product development strategies
• Market development strategies
• Direct investment.
• Organizational development ( manpower, financial and
material development)
Types of strategy
• Grand strategy: is the general plan of major
actions by which a firm intends to achieve its
long-term goals. And it falls into three general
categories and they are
• Growth: this is the way we can promoted
internally by investing in expansion or
externally by acquiring additional business
divisions, and internal can include
development of new or changed product
Con….
• Retrenchment: means that the organization
goes through a period of forced decline by
either shrinking current business units of
selling off to liquidating entire business
• Stability: same times are called pause strategy
and that means that the organization wants to
remain the same size or grow slowly.
Con….
Global strategy: in today’s global corporation,
senior executives they try to formulate logical
strategies to provide synergy among
worldwide operations full filing for common
purpose.
Globalization: is the way of the organization
standardized product design and advisement
strategies though the entire world.
Levels of strategy
• Corporate level strategy: the level of strategy
concerned with the question WHAT BUSINESS WE ARE?
And it pertain business as whole and the combination
of business units that make the corporate entity.
• Business-level strategy: the level of strategy concerned
with the question HOW DO WE COMPETE? And it
pertains to each business unit or product line within
the organization.
• Functional-level strategy: the level of strategy
concerned with question how do we support the
business level strategy ?and it pertains the all levels of
the organization and it is major departments.
Con….
• Competitive strategy
• Differentiation strategy: it is a type of competitive with
which the organization seeks to distinguish its products or
services form a competitors. And this method have very
strong marketing abilities and reward employee innovation
and corporate reputation quality or technological change
• Cost leadership: is the type of the competitive which the
organization aggressively, seeks efficient facilities, cuts cost
and employs cost control to be more efficient than
competitors.
• Focus strategy: is the type of Competitive that emphasizes
concentration on specific regional market or buyer group.
There are three forms of
Organizations
– Sole proprietorship,
– Partnership, and
– Corporation
Con…
• A Sole proprietorship is owned by one
individual. represents ownership by one
person.
– business firms, 70% are sole proprietorships.
– Advantages
• Ease in organizing
• Low cost of organizing
– Disadvantage : Limited source of financial
resources
Con…
• A partnership is owned by two or more
individuals
• Advantages
– More financial resources than a proprietorship.
– Additional management skills.
• Disadvantage
• Unlimited liability
• A corporation is owned by shareholder, who have
limited liability; legally, they can only lose their
investment in the company.
Con….
• A corporation is organized under state or
federal statutes as a separate legal entity.
• Advantage :The ability to obtain large
amounts of resources by issuing stocks.
• Disadvantage
• Double taxation
Types of Business
– Services Business
– merchandise Business
– Manufacturing Business
• Services Business : these Business provide services rather than
products to customers
• A service type of business provides intangible products (products
with no physical form). Service type firms offer professional skills,
expertise, advice, and other similar products
• They are known as "buy and sell" businesses.
• They make profit by selling the products at prices higher than their
purchase costs.
• A merchandising business sells a product without changing its form.
Value Chain of a Business
• A value chain is the way a business adds value
for its customers by processing inputs into
product or service
Business Products or Customer
Inputs Processes Services Value
Business Stakeholders
• A business stakeholder is a person or entity having an
interest in the economic performance of the business
Types of stakeholders
Internal and external stakeholders
• Identifying business opportunities
• Essentially, entrepreneurs recognize an opportunity
and turn it into a successful business.
• An opportunity is a favorable set of circumstances that
creates a need for a new product, service, or business
Observing Trends
• The first approach to identifying opportunities
is to observe trends and study how they
create opportunities for entrepreneurs to
pursue.
• The most important trends to follow are
economic trends, social trends, technological
advances, and political action and regulatory
changes
Con….
• Solving a Problem
• The second approach to identifying
opportunities is to recognize problems and
find ways to solve them.
• These problems can be recognized by
observing the challenges that people
encounter in their daily lives and through
more simple means, such as intuition,
serendipity, or chance
Вам также может понравиться
- Welcome Note!!!: You Have Now Completed This UnitДокумент37 страницWelcome Note!!!: You Have Now Completed This UnitShubh mangal100% (5)
- Human Aspects of Strategy ImplementationДокумент48 страницHuman Aspects of Strategy ImplementationDiksha Sinha100% (4)
- Oligopoly Market: Homogeneous Product Some Control Over PriceДокумент2 страницыOligopoly Market: Homogeneous Product Some Control Over PriceFerv r50% (2)
- Abaca Trading ProposalДокумент4 страницыAbaca Trading ProposalMILLER J. VILLAS100% (1)
- Marketing For Hospitality & TourismДокумент5 страницMarketing For Hospitality & Tourismislahu56Оценок пока нет
- Solved Rank The Absolute Values of The Price Elasticities of DemandДокумент1 страницаSolved Rank The Absolute Values of The Price Elasticities of DemandM Bilal SaleemОценок пока нет
- 18ES51 Module 2Документ43 страницы18ES51 Module 2satishsОценок пока нет
- StaffingДокумент35 страницStaffingmaduvatsОценок пока нет
- Management: Gestión EmpresarialДокумент80 страницManagement: Gestión EmpresarialCarlos SolísОценок пока нет
- Unit I Strategy and ProcessДокумент32 страницыUnit I Strategy and ProcessVickyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4. Marketing StrategyДокумент79 страницChapter 4. Marketing Strategyminale destaОценок пока нет
- Strategic IntentДокумент26 страницStrategic IntentVikasОценок пока нет
- Hbs 201 Management PrinciplesДокумент50 страницHbs 201 Management PrinciplesTawanda MahereОценок пока нет
- Management, Leadership, and Internal OrganizationДокумент28 страницManagement, Leadership, and Internal OrganizationShihan Salim شيهن سليمОценок пока нет
- Organ Is Ing FinalДокумент36 страницOrgan Is Ing FinalJohn HowardОценок пока нет
- Document 12Документ39 страницDocument 12misganabbbbbbbbbbОценок пока нет
- Business Strategy MODULE 1Документ39 страницBusiness Strategy MODULE 1DOLPHINОценок пока нет
- Strategy PPT Ch6Документ40 страницStrategy PPT Ch6Habtamu mamoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 Organisational StructureДокумент35 страницChapter 15 Organisational StructureShardulОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Concept and Nature of ObjectivesДокумент26 страницUnit 3 Concept and Nature of ObjectivesKunika JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Combined Notes Strategic Public Relations ManagementДокумент52 страницыCombined Notes Strategic Public Relations Managementabade vinОценок пока нет
- CH-1 Overview of MGMTДокумент33 страницыCH-1 Overview of MGMTyirgalemle ayeОценок пока нет
- The Nature of Organizing, Entrepreneuring, and ReengineeringДокумент4 страницыThe Nature of Organizing, Entrepreneuring, and ReengineeringJohnn MahalingamОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management and Business Policy Bba-Vi Semester Unit-IiДокумент25 страницStrategic Management and Business Policy Bba-Vi Semester Unit-IiAmit Srivastava100% (1)
- Management Control Systems: Authors: Anthony and Govindarajan 12 EditionДокумент31 страницаManagement Control Systems: Authors: Anthony and Govindarajan 12 EditionMohammad Sabbir Hossen SamimОценок пока нет
- Business 1.3Документ51 страницаBusiness 1.3samerОценок пока нет
- Bab 5Документ3 страницыBab 5andikaОценок пока нет
- Management Control SystemsДокумент70 страницManagement Control Systemsashi9812100% (3)
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementДокумент32 страницыStrategic Human Resource ManagementZehraAbdulAzizОценок пока нет
- Management FunctionsДокумент18 страницManagement Functionsjoshuajoshua3913Оценок пока нет
- Structure: Shared ValuesДокумент12 страницStructure: Shared ValuesPrem TiwariОценок пока нет
- Strategic Control and Corporate GovernanceДокумент18 страницStrategic Control and Corporate GovernanceDavid Ako100% (1)
- The Implementation ProcessДокумент12 страницThe Implementation Processjithin rajuОценок пока нет
- Foundations of Planning For Better ManagementДокумент44 страницыFoundations of Planning For Better ManagementBambi CulturaОценок пока нет
- Structure in An OrganisationДокумент26 страницStructure in An Organisationseagul_1183822Оценок пока нет
- Course Title: Introduction To Banking and Finance Week 2: The Financial Objectives of The FirmДокумент41 страницаCourse Title: Introduction To Banking and Finance Week 2: The Financial Objectives of The FirmGift AnosiОценок пока нет
- 4 - The Essential Manegerial FunctionsДокумент14 страниц4 - The Essential Manegerial Functionsjoey_lazarte0% (1)
- Pa 102 PP3 2022Документ27 страницPa 102 PP3 2022Pat SalasОценок пока нет
- CH 1 Strategic MGMT OveviewДокумент28 страницCH 1 Strategic MGMT Oveviewtemesgen yohannesОценок пока нет
- Goal Congruence: Dr. Aayat FatimaДокумент17 страницGoal Congruence: Dr. Aayat FatimaKashif TradingОценок пока нет
- Management Control System: Presented By: Ravish PrakashДокумент34 страницыManagement Control System: Presented By: Ravish PrakashAbhishek TripathiОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Nature and Purpose of OrganizingДокумент49 страницUnit 5 Nature and Purpose of OrganizingAnkit Patidar100% (1)
- Organizational PlanДокумент33 страницыOrganizational PlanBAsit khanОценок пока нет
- BS Unit 1Документ147 страницBS Unit 1KhushbuОценок пока нет
- PoM Module1 OrganizingДокумент56 страницPoM Module1 Organizingdeveloperamit4uОценок пока нет
- MGT 3010 Week 1Документ41 страницаMGT 3010 Week 1Herman BettОценок пока нет
- FUNDAMENTALS OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION DiscussionДокумент48 страницFUNDAMENTALS OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION Discussionalbagasan.auОценок пока нет
- Performance Measurement of Business Project: A Balanced Scorecard ApproachДокумент19 страницPerformance Measurement of Business Project: A Balanced Scorecard Approachharisankar.tpdОценок пока нет
- Planning PDFДокумент44 страницыPlanning PDFVISMAY PATELОценок пока нет
- Strategic Mangement 4Документ45 страницStrategic Mangement 4kritikachhapolia100% (1)
- Introduction To Management Part 3Документ50 страницIntroduction To Management Part 3Navruz KhakimovОценок пока нет
- Business Statagy and Policy Unit 1Документ13 страницBusiness Statagy and Policy Unit 1sai rocksОценок пока нет
- Business Notes CalcuДокумент11 страницBusiness Notes Calcunacho narroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Organizational Objectives - StudentsДокумент7 страницChapter 3 - Organizational Objectives - StudentsamjjjuОценок пока нет
- DrSaraKhan - 1511 - 16995 - 4 - SM 10Документ20 страницDrSaraKhan - 1511 - 16995 - 4 - SM 10MUHAMMAD ANAS BUKSHОценок пока нет
- Strategy ManagmentДокумент20 страницStrategy ManagmentTewodros SetargieОценок пока нет
- OrganisingДокумент25 страницOrganisingAnonymous 3ExxK2OОценок пока нет
- Chap 7Документ14 страницChap 7OsamaОценок пока нет
- What Is ManagementДокумент25 страницWhat Is ManagementHani ZaidiОценок пока нет
- Part2: Planning:: Chapter 3: Planning and Strategic ManagementДокумент7 страницPart2: Planning:: Chapter 3: Planning and Strategic ManagementyoussefkeskesОценок пока нет
- Business Organization: and ManagementДокумент21 страницаBusiness Organization: and ManagementChristian ZebuaОценок пока нет
- Mbo and StrategyДокумент38 страницMbo and StrategyAdarsh DashОценок пока нет
- IM & S Module 1Документ68 страницIM & S Module 1sindhuОценок пока нет
- Strategic Analysis of Internal Environment of a Business OrganisationОт EverandStrategic Analysis of Internal Environment of a Business OrganisationОценок пока нет
- 4784-A10-2 - Door ScheduleДокумент1 страница4784-A10-2 - Door ScheduleguuleedОценок пока нет
- Dooooors and WindoooowsДокумент27 страницDooooors and WindoooowsJayson Jedidiah UdangОценок пока нет
- Sample Drawings For Residential Additions PDFДокумент10 страницSample Drawings For Residential Additions PDFaiborlannnОценок пока нет
- SLAUGHTER SLABS For 3 DistrictsДокумент1 страницаSLAUGHTER SLABS For 3 DistrictsguuleedОценок пока нет
- Proposed Village Milk Centre Meat Stalls and Slaughter Slabs - Salaxley...... 2Документ36 страницProposed Village Milk Centre Meat Stalls and Slaughter Slabs - Salaxley...... 2guuleedОценок пока нет
- Proposed Village Milk Centre Meat Stalls and Slaughter Slabs - Salaxley...... 2Документ36 страницProposed Village Milk Centre Meat Stalls and Slaughter Slabs - Salaxley...... 2guuleedОценок пока нет
- 5 Unusual Facts About Kengo Kuma PDFДокумент9 страниц5 Unusual Facts About Kengo Kuma PDFguuleedОценок пока нет
- Arch ProgrammingДокумент30 страницArch ProgrammingMosha LittledogОценок пока нет
- Arch ProgrammingДокумент30 страницArch ProgrammingMosha LittledogОценок пока нет
- The Research Process VДокумент1 страницаThe Research Process VguuleedОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3aДокумент36 страницChapter 3aguuleedОценок пока нет
- ArchtectureeДокумент1 страницаArchtectureeguuleedОценок пока нет
- Case Study of The Gap, Inc.Документ6 страницCase Study of The Gap, Inc.nioriatti8924Оценок пока нет
- SH 2023 Q4 1 ICRA Logistics Road SectorДокумент8 страницSH 2023 Q4 1 ICRA Logistics Road Sectorpalak.jagetia1510Оценок пока нет
- 3.1 Quantitative Skills Practice QuestionsДокумент3 страницы3.1 Quantitative Skills Practice QuestionsRayan SibariОценок пока нет
- AIS Week 5 QuizДокумент2 страницыAIS Week 5 QuizMarvina Paula Vierneza LayuganОценок пока нет
- Car Scheme Policy: Proposed by Recommended by Approved by Approved byДокумент3 страницыCar Scheme Policy: Proposed by Recommended by Approved by Approved bySabbir Rahman JoyОценок пока нет
- Jose Antonio Herrero, Analysis of LMM Airport PrivatizationДокумент22 страницыJose Antonio Herrero, Analysis of LMM Airport PrivatizationdarwinbondgrahamОценок пока нет
- Coca Cola FinalДокумент12 страницCoca Cola FinalSamuel MosesОценок пока нет
- Bank MCQ & Written MATH ReviewДокумент5 страницBank MCQ & Written MATH ReviewNahidОценок пока нет
- 17c Formula Ebook - Diminished Value ClaimsДокумент20 страниц17c Formula Ebook - Diminished Value ClaimsDiminished Value of GeorgiaОценок пока нет
- Bioethanol HandbookДокумент187 страницBioethanol HandbookRaka Fajar NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Questions Chapter 10Документ25 страницQuestions Chapter 10abdul majid khawajaОценок пока нет
- RELEVANTCOSTING101Документ8 страницRELEVANTCOSTING101Ellie BonitaОценок пока нет
- FormulebladДокумент5 страницFormulebladwdqkj.nsd,ndsОценок пока нет
- Tutorial - Inventory TrackingДокумент11 страницTutorial - Inventory TrackingInformation should be FREEОценок пока нет
- Mckinsey-Model For Valuation of CompaniesДокумент56 страницMckinsey-Model For Valuation of CompaniesarjunrampalОценок пока нет
- Technical Analysis in Stock MarketДокумент24 страницыTechnical Analysis in Stock MarketSOURAV GOYAL67% (3)
- SuzlonДокумент23 страницыSuzlonPuneet GuptaОценок пока нет
- Demand Side PolicyДокумент15 страницDemand Side PolicyAnkit Shukla100% (1)
- Institutional Investor May 2006Документ6 страницInstitutional Investor May 2006Vikram Singh ChaudhryОценок пока нет
- NAS 17 LeasesДокумент16 страницNAS 17 LeasesbinuОценок пока нет
- 1.1. Introduction To Macroeconomics: Chapter OneДокумент118 страниц1.1. Introduction To Macroeconomics: Chapter OneBereketОценок пока нет
- Foreign Affairs May June 2021 IssueДокумент217 страницForeign Affairs May June 2021 IssueAbdul Haseeb100% (1)
- The Price of Land Sanjay ChakravortyДокумент4 страницыThe Price of Land Sanjay ChakravortyAadhya TrivediОценок пока нет
- Tea Industry AnalysisДокумент45 страницTea Industry AnalysisAnuruddha RajasuriyaОценок пока нет
- HomeworkДокумент3 страницыHomeworkMihaela Gavrilita50% (2)