Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Rationale of Studying Sociology
Загружено:
Princess Rona Velasquez Alcantara0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров27 страницОригинальное название
2.-Rationale-of-Studying-Sociology.pptx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров27 страницRationale of Studying Sociology
Загружено:
Princess Rona Velasquez AlcantaraАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 27
Sociology
Sociology
• Who are the people
around you?
• What is their story?
• How do these stories
affect you?
Sociology
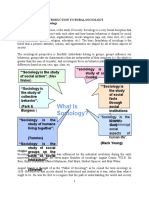
Etymological Definition
• “socius” (Latin) = “group / partners”
• “logos” (Greek) = “study”
• “sociology” – coined by August Comte
(French philosopher, 1798-1857)
Essential Definition
• Scientific study of
patterns of human
interaction that
deals with the study
of group life (Joseph
Fichter).
Sociology
• “scientific”
– Body of knowledge of
patterned structure
– Utilizes scientific methodology
– Investigates the social world
– Inquires how groups are
formed
– Determines how groups affect
the individual and vice versa
Sociology
• “Human interactions”
– Social relations
– Story of people
– Ways toward each other
– Social behavior
(and not of the individual)
– Changes taking place within society
Sociology
Sociology is the systematic
study of human society and
social interaction. It is based
on the idea that our relations
with other people create
opportunities for us to think
and act but also set limits on
our thoughts and action.
Sociology
• Howard Becker defined
sociology as the study of
people “doing things
together.”
Introduction to Sociology: What is 9
Sociology?
Sociology
• This reminds us that society
and the individual are
inherently connected, and
each depends on the other.
Introduction to Sociology: What is 10
Sociology?
Sociology
• Sociologists study this link:
how society affects the
individual and how the
individual affects society.
Introduction to Sociology: What is 11
Sociology?
A society is a large social grouping that shares the same
geographical territory and is subject to the same political
authority and dominant cultural expectations.
Society Is….
A society is a group of people who
share a culture and live more or less
together. They have a set of
institutions which provide what
they need to meet their physical,
social, and psychological needs
and which maintain order and the
values of the culture. 13
Social structures are
the more or less
stable patterns of
people’s interactions
and relationships.
14
Institutions are the
principal social
structures that organize,
direct, and execute the
essential tasks of
living.
15
Some institutions are:
Family,
Educational,
Economic,
Religion,
Law,
Political Systems
16
Cool Insights from Sociology
• Society makes us who we are by
structuring out interactions and
laying out an orderly world
before us
Introduction to Sociology: What is 17
Sociology?
Cool Insights from Sociology
• Society is a social construction, that is an
idea created by humans (i.e. doesn’t exist
in the biological world but only in the
social world) through social interaction
and given a reality through our
understanding of it and our collective
actions.
Introduction to Sociology: What is 18
Sociology?
What Does Society Look Like?
• While the idea of society is familiar, describing
it can be difficult. Ultimately society is made
up of many different components, such as
culture, race, family, education, social class,
and people’s interactions.
• People who share a culture and territory
Introduction to Sociology: What is 19
Sociology?
Meaning through Interaction
• People actively and collectively shape their
own lives, organizing their social interactions
and relationships into a meaningful world.
• Sociologists study this social behavior by
seeking out its patterns.
• Patterns are crucial to our understanding of
society
Introduction to Sociology: What is 20
Sociology?
Society
• Society is a group of people who
shape their lives in aggregated and
patterned ways that distinguish their
group from other groups.
Introduction to Sociology: What is 21
Sociology?
Areas of Sociology
1. Social organization
study of the various social
institutions, social groups,
social stratification, social
mobility, bureaucracy,
ethnic groups and
relations.
Areas of Sociology
2. Social Arts
3. Social Structures – arrangement
in the society
4. Social Processes – refers to the
recurrent and patterned
interactions or responses of
individuals to one another which
have attained stability
Areas of Sociology
5. Social Relationship
- Provide sociological
information that will help in
understanding society
objectively through the use
of scientific investigation
Areas
1.Physical 1. Social organization
anthropology 2. Social psychology
2. Cultural 3. Social change and social
anthropology disorganization
3. Archeology 4. Human ecology
5. Population and
4. Linguistics
demography
6. Sociological theory and
method
7. Applied sociology
SOCIOLOGY ANTHROPOLOGY
• Focuses on social • Focuses on culture
processes • Recent social science
• Recent social science • Understand way of life,
• Understand way of life, society culture
society culture • Complimented by
• Complimented by sociological researches
anthropological research • Originated from
• Originated from Western primitive groups (pre-
civilization (historical) historic)
• Method: particular • Method: generic
(sampling) (holistic)
Anthropology and Sociology
• Both sciences attempt to understand way of
life as manifested by the interdependence of
society and culture
• Sociology zooms in at social process,
whereas, Anthropology focuses on culture
• Anthropological studies are used by social
scientists and vice versa
• Thus, both sciences are intimately related to
each other—i.e., humanities.
Вам также может понравиться
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionДокумент21 страницаCell Membrane Structure and FunctionPrincess Rona Velasquez AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- The Rationale of Studying AnthropologyДокумент29 страницThe Rationale of Studying AnthropologyPrincess Rona Velasquez AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- How Individuals Learn Culture and Become Competent Members of SocietyДокумент72 страницыHow Individuals Learn Culture and Become Competent Members of SocietyPrincess Rona Velasquez Alcantara50% (2)
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsДокумент13 страницUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsPrincess Rona Velasquez AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionДокумент21 страницаCell Membrane Structure and FunctionPrincess Rona Velasquez AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsДокумент13 страницUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsPrincess Rona Velasquez AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Socio Cutural DimensionДокумент8 страницSocio Cutural DimensionAJ RicoОценок пока нет
- Soc CH 18Документ18 страницSoc CH 18Berktay AkyuzОценок пока нет
- Communication Technology and Society PDFДокумент2 страницыCommunication Technology and Society PDFAddisonОценок пока нет
- A Brief Introduction To Community ArchitectureДокумент12 страницA Brief Introduction To Community ArchitectureJust scribble me For funОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Lecture 5-6 - Making Research SociologicalДокумент31 страницаUnit 1 - Lecture 5-6 - Making Research SociologicalPradip Kumar YadavОценок пока нет
- Terminology Sociology PresentationДокумент53 страницыTerminology Sociology PresentationNeil DhitalОценок пока нет
- Business Ethics in Building A Good SocietyДокумент6 страницBusiness Ethics in Building A Good SocietyPeter Uka100% (4)
- Master TestДокумент8 страницMaster TestPaul EspinosaОценок пока нет
- Year 11 - Social InequalityДокумент143 страницыYear 11 - Social InequalityBrioОценок пока нет
- Sociology Assignment For Tutorial - BALLB 2nd SemesterДокумент9 страницSociology Assignment For Tutorial - BALLB 2nd SemesterHammad KhanОценок пока нет
- 2.-Topic-2-Culture (Autosaved)Документ88 страниц2.-Topic-2-Culture (Autosaved)maybel dela cruzОценок пока нет
- Rosicrucian Declaration of Human DutiesДокумент1 страницаRosicrucian Declaration of Human DutiesManjushree777Оценок пока нет
- CultureДокумент63 страницыCultureJj DestovОценок пока нет
- Brumfiel (1992) Lecture in Archeology: Breaking and Entering The Ecosystem - Gender, Class, and Faction Steal The ShowДокумент18 страницBrumfiel (1992) Lecture in Archeology: Breaking and Entering The Ecosystem - Gender, Class, and Faction Steal The ShowCatalina VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Performance Task On Introduction To PhilosophyДокумент1 страницаPerformance Task On Introduction To PhilosophyKristalyn Mary Dimas Diwayan - AlcagnoОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Map Matrix CollegeДокумент6 страницCurriculum Map Matrix CollegeEvelyn MagbarilОценок пока нет
- Proiect Engleza WordДокумент3 страницыProiect Engleza WordAlexander HopkinsОценок пока нет
- Culture Shift Risk Analysis For MulitnationalsДокумент24 страницыCulture Shift Risk Analysis For MulitnationalsAnchasIrОценок пока нет
- Sociology Solved Questions CSSДокумент20 страницSociology Solved Questions CSSMustafa AsifОценок пока нет
- Business and Society Relationship in 40 CharactersДокумент19 страницBusiness and Society Relationship in 40 CharactersBikki XetreeОценок пока нет
- Jurisprudence Sem 4Документ12 страницJurisprudence Sem 4Anurag PatelОценок пока нет
- Sociology of The Quran Part I - Ayatullah Murtada Mutahhari - XKPДокумент51 страницаSociology of The Quran Part I - Ayatullah Murtada Mutahhari - XKPIslamicMobilityОценок пока нет
- 2nd Sem UCSPДокумент1 страница2nd Sem UCSPElmer Oblino AbainzaОценок пока нет
- Dsoc202 Social Stratification English PDFДокумент315 страницDsoc202 Social Stratification English PDFAbrar DarОценок пока нет
- Bacchus and Civic Order The Culture of Drink in Early Modern Germany by B. Ann TlustyДокумент305 страницBacchus and Civic Order The Culture of Drink in Early Modern Germany by B. Ann TlustyAnonymous 9ep4UXzRxxОценок пока нет
- Socialization Lecture 6Документ38 страницSocialization Lecture 6TIED PKОценок пока нет
- Field Attachment Report: Field Station: Makutupora WardДокумент23 страницыField Attachment Report: Field Station: Makutupora WardYusuphally AllyОценок пока нет
- Rural Sociology (Repaired)Документ156 страницRural Sociology (Repaired)Jablack Angola Mugabe100% (2)
- CHAPTER4 FOLK ETHICS - ShodhgangaДокумент66 страницCHAPTER4 FOLK ETHICS - ShodhgangaDiego Brandeau100% (1)
- Final-Article-Role of Mathematics in The Development of Society-NCERДокумент14 страницFinal-Article-Role of Mathematics in The Development of Society-NCERMicol Sancho100% (1)