Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biography Text
Загружено:
Nadya Salsabila100%(4)100% нашли этот документ полезным (4 голоса)
5K просмотров15 страницThe document provides an overview of what constitutes a biography and its typical structure and language features. It notes that a biography describes a person's life in detail and usually follows three parts: an orientation that introduces the subject, a series of chronological life events, and a reorientation conclusion. It also outlines the common language features of biographies, such as using specific names, past tense verbs, and words related to time. Finally, the document gives an example biography recount text to illustrate these points.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
BIOGRAPHY TEXT (1).pptx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document provides an overview of what constitutes a biography and its typical structure and language features. It notes that a biography describes a person's life in detail and usually follows three parts: an orientation that introduces the subject, a series of chronological life events, and a reorientation conclusion. It also outlines the common language features of biographies, such as using specific names, past tense verbs, and words related to time. Finally, the document gives an example biography recount text to illustrate these points.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(4)100% нашли этот документ полезным (4 голоса)
5K просмотров15 страницBiography Text
Загружено:
Nadya SalsabilaThe document provides an overview of what constitutes a biography and its typical structure and language features. It notes that a biography describes a person's life in detail and usually follows three parts: an orientation that introduces the subject, a series of chronological life events, and a reorientation conclusion. It also outlines the common language features of biographies, such as using specific names, past tense verbs, and words related to time. Finally, the document gives an example biography recount text to illustrate these points.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 15
As presented by: Nadya Salsabila Nanda Karuna and Nadiah Balquista Kaufua
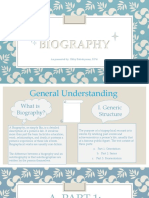
General Understanding
What is I. Generic
Biography? Structure
A Biography, or simply Bio, is a detailed
description of a person's life. It involves The purpose of a biographical recount is to
more than just the basic facts like education, inform by retelling past events and
work, relationships, and death; it portrays a achievements in a person’s life, usually that
person's experience of these life events. of a famous public figure. The text consist of
Biographical works are usually non-fiction. three parts:
a. Part 1: Orientation
The difference between a biography and an b. Part 2: Series
autobiography is that autobiographies are c. Part 3: Reorientation
written by the person themselves.
A. PART 1:
ORIENTATION
It gives the reader the background information as to why this person is noteworthy and
should have a biography written about them. The opening paragraph should answer the
questions: who, what, where, when, and how. This part usually contains an initial
description of the characters or actors in biographical texts.
B. PART 2:
SERIES
This part consists of series of events, most likely told in a chronological order. Here the writer
might refer to a certain time on line. Also contains events containing explanations that
occurred or was experienced by the characters, including the problems it faces in
achieving its goals and ideals. The interesting, memorable, amazing, and moving things
experienced by the characters are also described in the series section.
C. PART 3:
REORIENTATION
This part contains a type of conclusion with a comment on the contributions this person
has made or a summary and evaluation of the person’s achievement. This part might also
tell about the author’s view on the characters told. Reorientation is optional, it may exist,
but may also not exist depending on the author.
II. Language Features
Language features is the structure or arrangement of a paragraph (for example, sentence
structure, noun group/phrase, vocabulary, punctuation, grammar, etc.) Choices in language
features and text structures together define a type of text and shape its meaning. These choices
vary according to the purpose of a text, its subject matter, and audience.
A biography’s language features are none other than:
1. A biographical recount uses specific names of the people involved in the biography
2. It is mainly written in simple past tense (the final paragraph could also include present tense)
3. A biographical recount also uses words that have connections to do with a sense of time
4. A biographical recount describes events, so it uses many verb or action verbs.
THE CHARACTERISTICS OF
BIOGRAPHICAL RECOUNT TEXT
There are some characteristics of biographical recount text that you have to know, such as:
I. It is not written by the subject. It means that a biography is
written by someone else who wants to write about the
subject. It usually will be written based on the needs. Some
writer could write it in either short or long length.
2. It is always written in a third
person’s point of view
3. It is based on research, not on imagination, when
someone wants to make a biography, she or her must do
some researches. What kind of researches are they?
Reading all books related to the subject is one of the ways
of the research, besides reading, interviewing subject
relation (if it is possible) also can be as a research before
writing a biography.
4. Describing the subject’s
surroundings (where, when,
and how the person lived.)
5. Showing how the person
affected other people’s lives
through their behavior,
discoveries, social reform, etc.
6. Supplying details that
illustrate the person’s
individuality.
7. Using vivid language
to narrate the events
8. It is arranged
chronologically.
An example of Biography
Recount Text
Albert Einstein was born near the end of the
1800s in Ulf, Germany. He graduated from the
University of Zurich in Switzerland at age 26.
That was also when he did his famous work in
physics. Fourteen years later he won the Nobel
Prize for Physics.
For the next ten years he lived in Germany and
traveled a lot to talk to other scientists. Then in
the early 1930s he had to leave Germany
because of Hitler and the Nazi party. He moved
to the United States. From that time until his
death he lived in Princeton, New Jersey. He
died at the age of 74.
Вам также может понравиться
- LK Modul 4 English For EntertainmentДокумент7 страницLK Modul 4 English For EntertainmentSari FebriantiОценок пока нет
- Lkpd-Biography TextДокумент8 страницLkpd-Biography Textamy100% (1)
- Script Listening Kelas X Sem. GenapДокумент5 страницScript Listening Kelas X Sem. GenapZulfan Setiawan100% (2)
- Bahan Ajar Peminatan Bahasa Dan Sastra Inggris XДокумент34 страницыBahan Ajar Peminatan Bahasa Dan Sastra Inggris XCaecilia Kristanti71% (7)
- LKPD Bahasa Inggris Kelas XДокумент3 страницыLKPD Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xbenny syaputra75% (4)
- Latihan Soal Factual ReportДокумент6 страницLatihan Soal Factual ReportPutri AnggraeniОценок пока нет
- MATERI KD 3.15 BAHASA INGGRIS KELAS XI SEMESTER GANJIL-ARIF N Bagian 2 PDFДокумент13 страницMATERI KD 3.15 BAHASA INGGRIS KELAS XI SEMESTER GANJIL-ARIF N Bagian 2 PDFArif NurrahmanОценок пока нет
- Bahasa Inggris Kelas 10 Narrative TextДокумент10 страницBahasa Inggris Kelas 10 Narrative TextPenduduk Bumi Budiman75% (4)
- Materi Bahasa Inggris SMK Kelas XI Chapter II Opinion and ThoughtДокумент6 страницMateri Bahasa Inggris SMK Kelas XI Chapter II Opinion and ThoughtJaenal Abidin93% (15)
- News ItemДокумент22 страницыNews ItemSiti Shaliha100% (1)
- Modul Procedure Text Recipe Modul Atikah PgriДокумент24 страницыModul Procedure Text Recipe Modul Atikah Pgriatikah100% (1)
- Materi Bahasa Inggris Listening Speaking Reading Writing Kelas X SMA Semester GenapДокумент20 страницMateri Bahasa Inggris Listening Speaking Reading Writing Kelas X SMA Semester GenapGusti Idris100% (1)
- LKPD 3.3.1 Kelas XII PeminatanДокумент6 страницLKPD 3.3.1 Kelas XII PeminatanEndang Riadzt SupriadyОценок пока нет
- LKPD Asking and Giving SugesstionДокумент5 страницLKPD Asking and Giving SugesstionRM Burhanun Haq Ibad100% (1)
- LKPD Cause & EffectДокумент3 страницыLKPD Cause & EffectINSERI PAULINA WOMSIWOR100% (1)
- LKPD Narrative Text 1Документ2 страницыLKPD Narrative Text 1Burhan100% (6)
- Rubrik Penilaian - Membacakan Teks Dialog Dari Procedure TextДокумент3 страницыRubrik Penilaian - Membacakan Teks Dialog Dari Procedure Texttry elvia wahyuniОценок пока нет
- Writing Test Blue PrintДокумент17 страницWriting Test Blue PrintPutu Yanti KurniasihОценок пока нет
- ANNOUNCEMENTДокумент12 страницANNOUNCEMENTAinun Jariyati100% (1)
- RPP Adverbial ClauseДокумент6 страницRPP Adverbial ClauseLengga PradiptaОценок пока нет
- Soal Latihan Bahasa Inggris Asking and Giving OpinionДокумент2 страницыSoal Latihan Bahasa Inggris Asking and Giving OpinionIlma Adindra88% (56)
- Contoh RPP-Procedure TextДокумент17 страницContoh RPP-Procedure Textsuci widayati100% (1)
- LKPD Degree of ComparisonДокумент8 страницLKPD Degree of ComparisonNoviОценок пока нет
- LKPD 3.8Документ3 страницыLKPD 3.8Video Menarik100% (2)
- LKPD Narrative Text 1 PDFДокумент2 страницыLKPD Narrative Text 1 PDFRM Burhanun Haq Ibad67% (3)
- Soal Ulangan Harian Banner Poster PamphlДокумент12 страницSoal Ulangan Harian Banner Poster Pamphladi ruku100% (2)
- Narrative Text PowerPoint PresentationДокумент10 страницNarrative Text PowerPoint Presentationayu ningsih100% (1)
- REKAP SOAL & KUNCI JAWABAN UP Bhs Inggris KAT-1 THN 2022 OKEДокумент18 страницREKAP SOAL & KUNCI JAWABAN UP Bhs Inggris KAT-1 THN 2022 OKEDedep Defisa SantoriОценок пока нет
- LKPD 3.4 SMA Kelas 10 Reskianawidyaningsih WahidДокумент17 страницLKPD 3.4 SMA Kelas 10 Reskianawidyaningsih WahidKey Eleventh100% (1)
- Materi Ajar Memo, Menu, Schedule, SignДокумент5 страницMateri Ajar Memo, Menu, Schedule, SignAskme Azmy79% (62)
- Praktik LKPD Muhammad Mufti HarisДокумент5 страницPraktik LKPD Muhammad Mufti HarisMufti HarisОценок пока нет
- Latihan Soal Contrast Conjunction-1Документ3 страницыLatihan Soal Contrast Conjunction-1marvello gabriel100% (1)
- Format PPT Biography (Recount Text)Документ6 страницFormat PPT Biography (Recount Text)Diki Roy NirwansyahОценок пока нет
- LKPD SMK Analytical Exposition TextДокумент5 страницLKPD SMK Analytical Exposition Texthendra khoОценок пока нет
- Soal Congratulation and Compliment ExpressionДокумент4 страницыSoal Congratulation and Compliment ExpressionAdeRОценок пока нет
- Factual Report Text Exercise - EnglishДокумент1 страницаFactual Report Text Exercise - EnglishUbet ZubaidiОценок пока нет
- Nur Annisa MR - LK - 1.modul 1 Profesi - Bahasa InggrisДокумент4 страницыNur Annisa MR - LK - 1.modul 1 Profesi - Bahasa InggrisNur Annisa Mei RizkiОценок пока нет
- Naskah Soal Ulangan Umum Semester Ganjil - Bahasa Inggris XII IPA& IPSДокумент4 страницыNaskah Soal Ulangan Umum Semester Ganjil - Bahasa Inggris XII IPA& IPSElisa Isandhyta81% (16)
- Students Worksheet Suggestion and OffersДокумент2 страницыStudents Worksheet Suggestion and OffersJaenal Abidin100% (1)
- Kartu Soal Ujian B.InggrisДокумент11 страницKartu Soal Ujian B.InggrisMA_amiruddinОценок пока нет
- LKPD of Recount Text Kelas X: Name: ClassДокумент9 страницLKPD of Recount Text Kelas X: Name: ClassLisya Rivianti ZikraОценок пока нет
- Soal Filling FormДокумент2 страницыSoal Filling FormSoAlive89% (28)
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas XII SMKДокумент5 страницSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas XII SMKAlifudin Assidiq100% (1)
- Analytical Exposition Unit 4Документ9 страницAnalytical Exposition Unit 4Rauf YoungkingОценок пока нет
- RPP Short StoryДокумент8 страницRPP Short StoryRima Santika0% (2)
- Soal B. Inggris Kelas XIДокумент7 страницSoal B. Inggris Kelas XIZenZaad100% (1)
- Pembahasan Materi: You're Supposed To Turn Off The Light When You Are Not Working in The RoomДокумент2 страницыPembahasan Materi: You're Supposed To Turn Off The Light When You Are Not Working in The RoomsasОценок пока нет
- RPP Listening Report TextДокумент9 страницRPP Listening Report Textdian rahmaОценок пока нет
- Bahan Ajar Descriptive TextДокумент3 страницыBahan Ajar Descriptive Textica0% (1)
- LKPD SMA Kelas X Descriptive TextДокумент24 страницыLKPD SMA Kelas X Descriptive TextRafidha Fitri AnisaОценок пока нет
- Congratulating and Complimenting-2Документ15 страницCongratulating and Complimenting-2Andro Andre0% (1)
- LKPD X - RecountДокумент6 страницLKPD X - RecountRobik Ar RaffiОценок пока нет
- Modul English Club Level 1Документ10 страницModul English Club Level 1FMN UNAS100% (1)
- Biography TextДокумент15 страницBiography TextNur SyalsabillaОценок пока нет
- Biography Text 1Документ15 страницBiography Text 1okkyОценок пока нет
- Biography TextДокумент2 страницыBiography Textputri100% (7)
- Person's Life - The Texts Consist of Three PartsДокумент2 страницыPerson's Life - The Texts Consist of Three PartsikaОценок пока нет
- Literal Reading 1Документ14 страницLiteral Reading 1MiadchptryОценок пока нет
- BIOGRAPHYДокумент8 страницBIOGRAPHYalicia.ayubi01Оценок пока нет
- Literal Reading Book - Ready PublicationДокумент31 страницаLiteral Reading Book - Ready PublicationMiharu NishaОценок пока нет
- German Verbs in The Present TenseДокумент8 страницGerman Verbs in The Present TenseJasmina TepšaОценок пока нет
- ESP - GERUND 'N TO INFINITIVEДокумент46 страницESP - GERUND 'N TO INFINITIVELatifah AulannisaОценок пока нет
- Gold Advanced TestДокумент1 страницаGold Advanced Testjuliannna_bodor50% (6)
- Descriptions British English StudentДокумент9 страницDescriptions British English StudentSorana PaleuОценок пока нет
- Luger BookДокумент12 страницLuger Booksmillysam100% (1)
- Level 3: Skyrocket Scope and SequenceДокумент2 страницыLevel 3: Skyrocket Scope and SequenceMelinaEscuderoОценок пока нет
- Year 9 Pearson English - 20230613 - 0001Документ98 страницYear 9 Pearson English - 20230613 - 0001Alby FernandoОценок пока нет
- How To Learn A New Language QuicklyДокумент59 страницHow To Learn A New Language Quicklysamkamal01100% (2)
- German Grammar BookДокумент3 страницыGerman Grammar BookGenesis RosarioОценок пока нет
- Conjunction: Coordinating Conjunction Correlative ConjunctionДокумент21 страницаConjunction: Coordinating Conjunction Correlative ConjunctionWONG MEE KIEN MoeОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive VoiceДокумент7 страницActive and Passive Voiceazadali735323Оценок пока нет
- Relative Clause TestДокумент2 страницыRelative Clause TestArif İsmailОценок пока нет
- Current Studies in Spanish Linguistics (1992)Документ1 234 страницыCurrent Studies in Spanish Linguistics (1992)Djego RotésОценок пока нет
- Subject and Object Pronouns Possessive Adjectives - 93842Документ2 страницыSubject and Object Pronouns Possessive Adjectives - 93842Gigliane SouzaОценок пока нет
- JoanДокумент8 страницJoanAira Shaine PerezОценок пока нет
- Report of The 'Giving Instruction' PresentationДокумент19 страницReport of The 'Giving Instruction' Presentationvieyraa67% (3)
- English q2 Week 5Документ31 страницаEnglish q2 Week 5Nica Joy HernandezОценок пока нет
- Czech Phrasebook DictionaryДокумент10 страницCzech Phrasebook Dictionaryreiwj dsjОценок пока нет
- Viết - Tiếng Anh 3 - EN29.085Документ23 страницыViết - Tiếng Anh 3 - EN29.085davidlong1683Оценок пока нет
- Gramatical Category of Gender and Number EnglishДокумент8 страницGramatical Category of Gender and Number EnglishElena DavtyanОценок пока нет
- DLP 8 Q1mODULE 5Документ4 страницыDLP 8 Q1mODULE 5JOEVANNIE S. PAGAURAОценок пока нет
- BÀI TẬP PHỤ ĐẠO ĐẠI TỪ NHÂN XƯNGДокумент4 страницыBÀI TẬP PHỤ ĐẠO ĐẠI TỪ NHÂN XƯNGKim Loan Tran ThiОценок пока нет
- Plan de Lectie Booklet Clasa PregatitoareДокумент3 страницыPlan de Lectie Booklet Clasa PregatitoareAndreea SerbanОценок пока нет
- Maria Fernanda Cáceres Saavedra Ficha: 1693572 Grupo:200TgsodДокумент2 страницыMaria Fernanda Cáceres Saavedra Ficha: 1693572 Grupo:200TgsodMafe CaceresОценок пока нет
- Soal Passive VoiceДокумент5 страницSoal Passive VoiceDen RonggoОценок пока нет
- Phrasal Verb and Meanings RevisionДокумент13 страницPhrasal Verb and Meanings RevisionEkemini-AbasiОценок пока нет
- BEEC5 Apte V SH Students English Sanskrit Dictionary PDFДокумент484 страницыBEEC5 Apte V SH Students English Sanskrit Dictionary PDFserby108Оценок пока нет
- 4th Grade Mastery Club ChallengeДокумент4 страницы4th Grade Mastery Club Challengeapi-289674137Оценок пока нет
- Affix: - A Syllable Attached To The Root Word To Form New WordsДокумент17 страницAffix: - A Syllable Attached To The Root Word To Form New WordsRoberto NatividadОценок пока нет
- Computation and Cognition Toward A Foundation For Cognitive Science. (Zenon W. Pylyshyn) (Z-Library) - 69-108 - CAP3Документ40 страницComputation and Cognition Toward A Foundation For Cognitive Science. (Zenon W. Pylyshyn) (Z-Library) - 69-108 - CAP3Marcos Josue Costa DiasОценок пока нет
- How Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideОт EverandHow Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideОценок пока нет
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonОт EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.От EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (81)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisОт EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundОт Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (13)
- Spanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesОт EverandSpanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Abominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionОт EverandAbominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsОт EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsОценок пока нет
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllОт EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (83)
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageОт EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (429)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachОт EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (15)
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageОт EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (916)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachОт EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (81)
- Idioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsОт EverandIdioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (7)
- Learn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachОт EverandLearn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (151)
- How to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingОт EverandHow to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (26)
- Ruthless: How Donald Trump and Roy Cohn's Dark Symbiosis Changed AmericaОт EverandRuthless: How Donald Trump and Roy Cohn's Dark Symbiosis Changed AmericaРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (14)
- How to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneОт EverandHow to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (115)
- How To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessОт EverandHow To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (308)
- Essential Spanish in 2 hours with Paul Noble: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachОт EverandEssential Spanish in 2 hours with Paul Noble: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (49)