Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Parts and Wholes Visual Presentation
Загружено:
jonniel caadan0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
56 просмотров39 страниц Here is a 100-word essay analyzing Picasso's painting "The Weeping Woman":
This painting depicts a woman's anguished face in blues and blacks. Picasso uses cubist techniques to break her down into geometric shapes and overlapping planes viewed from various angles, emphasizing her distress. The fragmented portrayal evokes how extreme emotion can fracture one's sense of self. The proximity of her features and overlapping lines create a sense of unease and psychological complexity. This style aligns with Gestalt principles of closure, where the eye fills in gaps to perceive a whole form, and figure-ground, with the negative space of her hair and clothing accentuating her weeping figure as the focal point. Picasso masterfully conveys inner
Исходное описание:
Gestalt Principles pptx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ Here is a 100-word essay analyzing Picasso's painting "The Weeping Woman":
This painting depicts a woman's anguished face in blues and blacks. Picasso uses cubist techniques to break her down into geometric shapes and overlapping planes viewed from various angles, emphasizing her distress. The fragmented portrayal evokes how extreme emotion can fracture one's sense of self. The proximity of her features and overlapping lines create a sense of unease and psychological complexity. This style aligns with Gestalt principles of closure, where the eye fills in gaps to perceive a whole form, and figure-ground, with the negative space of her hair and clothing accentuating her weeping figure as the focal point. Picasso masterfully conveys inner
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
56 просмотров39 страницParts and Wholes Visual Presentation
Загружено:
jonniel caadan Here is a 100-word essay analyzing Picasso's painting "The Weeping Woman":
This painting depicts a woman's anguished face in blues and blacks. Picasso uses cubist techniques to break her down into geometric shapes and overlapping planes viewed from various angles, emphasizing her distress. The fragmented portrayal evokes how extreme emotion can fracture one's sense of self. The proximity of her features and overlapping lines create a sense of unease and psychological complexity. This style aligns with Gestalt principles of closure, where the eye fills in gaps to perceive a whole form, and figure-ground, with the negative space of her hair and clothing accentuating her weeping figure as the focal point. Picasso masterfully conveys inner
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 39
• People use perception
which is a process that
involves interpretation,
use of knowledge, and
understanding.
PARTS AND
WHOLES
• Perception is not a passive procedure of just
accepting and decoding sensations like for
instance the visual scene that keeps changing
from time to time or the auditory senses of
listening to the humming, buzzling, and irritating
noises.
• The brain adjusts and bridges the gap to be able
to distinguish what people see, hear as well as
touch. (Berstein, Roy, Srull & Wickens, 1991)
Thus, perception and mereology are closely related.
• Mereology is a study of the wholes they form from its
parts
• Inquire (1994) notes that, each “part-part-whole schema
allows children to deal with problems more flexibly by
interpreting the semantic structures of different addition
and subtraction problems in terms of parts and wholes
• The words “whole” and “part” tell the segregating
relationship
• According to Gestalt (shape/form) theory, the world is a
functional logical whole, the events and experiences in
real life are arranged into significant components, and
the natural elements have their individual structure.
• Through perception Gestalt experts believe that the
brain enhances whole forms pertinent to visual
recognition from local to international figures such as
scrutinizing the lines, curves, points, and many other
shapes.
Your brain sees a dog walking, but it’s nothing more than a
series of moving dots.
“The unified whole is different from the sum of its parts.”
• Gestalt principles or laws are
rules that describe how the
human eye perceives visual
elements.
• These principles aim to show
how complex scenes can be
reduced to more simple shapes.
• They also aim to explain how
the eyes perceive the shapes as
a single, united form rather than
the separate simpler elements
involved.
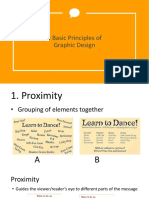
1.Proximity
“objects that are closer together
are perceived as more related
than objects that are further apart”
(Bradley, 2014).
This demonstrates that figures that
are closer to each other have the
tendency to cluster together since
the brain directly identifies object
that are familiar compared to
elements that are outside of the
category.
(2) Similarity
“Elements that share similar
characteristics are perceived
as more related than elements
that don’t share those
characteristics” (Bradley 2014).
This takes effect when objects
are grouped together and
perceptually they are similar to
the other through color,
texture, shape, shading, and
among other qualities.
(3) Common Regions
“Elements are perceived as
part of a group if they are
located within the same close
region” (Bradley 2014).
This principle portrays that
even related elements are
being enclosed yet outside the
boundary is consider a
separate entity
(4) Focal Points
“Elements with a points of
interest, emphasis or
difference will capture and
hold the viewer`s” (Bradley
2014).
This principle elaborates that
anything that is different in a
group of similar objects will
alert or provoke danger to the
viewers.
(5) Uniform Connectedness
“Elements that are visually
connected are perceived as
more related than elements with
no connection” (Bradley 2014).
This principle allows to connect
two set of uniform objects.
(6) Closure
“When seeing a complex
arrangement of elements, we
tend to look for a single
recognizable pattern” (Bradley
2014).
This indicates that people see
objects such as shapes, letters,
and pictures as wholes even
when these objects are not
complete because the brain has
the capacity to fill in the gaps
(7) Symmetry and Order
“People tend to perceive
objects as symmetrical
shapes that form around
their center ” (Bradley 2014).
This shows that the brain
sees objects as symmetrical
and creates a center even if
one part is missing allowing
the brain to immediately link
to form a shape.
(8) Continuation
“Elements arranged on a line
or curve are perceived as more
related than elements not on
the line or curve” (Bradley
2014).
This explains when objects are
clustered and incorporated
into perceptual wholes and
that they are aligned together
even if there is an intersection
between this objects.
(9) Figure or Ground
“Elements are perceived as
either figure (the element in
focus) or ground (the
background on which the
figure rests” (Bradley 2014).
This principles speaks of the
connection between positive
and negative spaces since the
eyes will divide whole objects
from backdrop to comprehend
the theme of the subject .
(10) Common Fate (Synchrony)
“Elements that move in the same
direction are perceived as more
related than elements that are
stationary or that move in
different direction” (Bradley
2014).
This illustrates when objects are
seen as lines moving in the same
direction, viewers will see them as
being related even if they are
different from each other.
(11) Parallelism
“Elements that are parallel to
each other are seen as more
related than elements not parallel
to each other” (Bradley 2014).
This parallelism principle applies
to lines that are moving or
pointing to the same destination
that will make these objects
related .
(12) Law of Pragnanz (Good
figure or law of simplicity)
“people will perceive and
interpret ambiguous or complex
images as the simplest form(s)
possible” (Bradley 2014).
This takes effect when objects
are grouped together and
perceptually they are similar to
the other through color, texture,
shape, shading, and among
other qualities.
(13) Past Experience
“Elements tend to be
perceived according to be
observer’s past experience”
(Bradley 2014).
This denotes that in some
situations visual stimuli are
grouped from past experience
such as street signs or traffic
lights.
Importance of the
GESTALT PRINCIPLE
• Enables individuals to
create an organized
whole.
• 90% is judged from the
brain and the remaining
10 % is from the eyes.
Importance of the
GESTALT PRINCIPLE
• These theories are used by the
designers and concept makers
to create a fad in the market.
• They also regulate these optical
illusions to create powerful
products and design giving
birth to artistry.
Importance of the GESTALT PRINCIPLE
• Gestalt even reduces the product
to have a plain design, logo or
slogan allowing many to save
space or aid communication.
• It is important to get a deeper
grasp of Gestalt Theories to
create a fad that will transform
into a trend and then later
provide branding from such
creation.
TASK: Picture Analysis
• You will see some paintings by
Pablo Picasso, a famous Spanish
painter known for his abstract
works and co-founder of the cubist.
• Select one painting and write a
100-word essay with the following
guide questions:
TASK: Picture Analysis
1. Describe the painting based from
your perception/interpretation.
2. What significance can you find in
the painting?
3. Associate the picture from any of
the 13 principles of the gestalt
theory.
Dora Maar Au Chat
Reading
The Weeping Woman
The Sculptor
Вам также может понравиться
- Self-Learning Module: Department of EducationДокумент15 страницSelf-Learning Module: Department of EducationLeny Ann Dela penaОценок пока нет
- Gestalt, The German Word Means Organised Whole' Is A Theory That About The Unification of Pattern, Form, StructureДокумент1 страницаGestalt, The German Word Means Organised Whole' Is A Theory That About The Unification of Pattern, Form, StructureDarleneОценок пока нет
- PerceptionДокумент58 страницPerceptionsayam jainОценок пока нет
- L-3 Parts and Whole 11 Gas, HumssДокумент26 страницL-3 Parts and Whole 11 Gas, HumssJessa NasalitaОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles in UI DesignДокумент53 страницыGestalt Principles in UI DesignRoshio Tsuyu TejidoОценок пока нет
- KRISLYN Trends Networks and Critical Thingking inДокумент8 страницKRISLYN Trends Networks and Critical Thingking inShianne Dancee CorpuzОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles 1Документ56 страницGestalt Principles 1Moiz AhmadОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles of PerceptionДокумент6 страницGestalt Principles of Perceptionapi-75736613100% (1)
- Gestalt PsychologyДокумент12 страницGestalt Psychologysiti hamdahОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles of Visual PerceptionДокумент4 страницыGestalt Principles of Visual PerceptionChinmay KaranОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles LinksДокумент21 страницаGestalt Principles LinksTeachJohnОценок пока нет
- VCTheory 02 2022Документ34 страницыVCTheory 02 2022Harsh DeppОценок пока нет
- VISUAL PERCEPTION AND ITS DEFICITSДокумент28 страницVISUAL PERCEPTION AND ITS DEFICITSSana NisarОценок пока нет
- Gestalt PrinciplesДокумент23 страницыGestalt PrinciplesKaushik BoseОценок пока нет
- GestaltДокумент16 страницGestaltYuni IsaОценок пока нет
- Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21st Century: Grade 12 Humss Learner'S Packet (Week 5)Документ8 страницTrends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21st Century: Grade 12 Humss Learner'S Packet (Week 5)Sir FelgerОценок пока нет
- Welcome To Course Title: Introduction To Psychology Lecture No: 8Документ26 страницWelcome To Course Title: Introduction To Psychology Lecture No: 8Sounds You WantОценок пока нет
- Theory of FCДокумент10 страницTheory of FCKenrick GraciasОценок пока нет
- Gestalt theories in designДокумент11 страницGestalt theories in designSaleem MokbelОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Laws and Perceptual ConstanciesДокумент27 страницGestalt Laws and Perceptual ConstanciesJia V JОценок пока нет
- Trends and Fads: Understanding the DifferenceДокумент11 страницTrends and Fads: Understanding the DifferenceMarcelo SakitingОценок пока нет
- Visual TheoriesboookДокумент47 страницVisual TheoriesboookBradley CzovОценок пока нет
- Psych 1XX3 Form Perception I Lecture NotesДокумент8 страницPsych 1XX3 Form Perception I Lecture NotesGurry Mann100% (1)
- Gestalt PrinciplesДокумент30 страницGestalt PrinciplesAFEEFA ZIAОценок пока нет
- 2.1. PerceptionДокумент24 страницы2.1. PerceptionCherry GuptaОценок пока нет
- PerceptionДокумент9 страницPerceptionSMN FTMAОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles ExplainedДокумент7 страницGestalt Principles ExplainedmanasvОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7 - DESIGN PRINCIPLESДокумент78 страницLecture 7 - DESIGN PRINCIPLESRosen AnthonyОценок пока нет
- Cognitive PerspectiveДокумент19 страницCognitive PerspectiveNAVARRO VIVIEN NATHANIELОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles: Sarvesh DobhalДокумент10 страницGestalt Principles: Sarvesh DobhalSarvesh DobhalОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Theory: Gestalt Theory Allows Communicators To Predict How Viewers Will Respond To Design ElementsДокумент37 страницGestalt Theory: Gestalt Theory Allows Communicators To Predict How Viewers Will Respond To Design ElementsAisyahZahraaОценок пока нет
- Laws of PragnanzДокумент21 страницаLaws of PragnanzJa Mi Lah100% (2)
- ReviewДокумент8 страницReviewMark Johnson Dela PeñaОценок пока нет
- 10 - Human Perception-66Документ66 страниц10 - Human Perception-66lovely personОценок пока нет
- SDE1201Документ47 страницSDE1201kochi.afdindiaОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Theory (Gestalt Psychology)Документ4 страницыGestalt Theory (Gestalt Psychology)CamilogsОценок пока нет
- Perception Functions ExplainedДокумент34 страницыPerception Functions ExplainedAmrit SahaniОценок пока нет
- First week Trends and Networks Modular ActivityДокумент4 страницыFirst week Trends and Networks Modular ActivityFELINOR ABELLANOZAОценок пока нет
- Theory of ArchitecureДокумент2 страницыTheory of ArchitecurePatricia Aira BenaidОценок пока нет
- Group 3 - Art and Psychology - Cornell NotesДокумент14 страницGroup 3 - Art and Psychology - Cornell NotesLory ReignОценок пока нет
- Ob IiДокумент20 страницOb IiHarsh GoelОценок пока нет
- I. Gestalt Principles LAW Example: HHHHHHHHHH QQQQQQQQQQ NNNNNNNNNN PPPPPPPPPPДокумент2 страницыI. Gestalt Principles LAW Example: HHHHHHHHHH QQQQQQQQQQ NNNNNNNNNN PPPPPPPPPPchone coralОценок пока нет
- Cognitive PerspectiveДокумент55 страницCognitive PerspectiveEmman Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- 3b Gestalt PsychologyДокумент34 страницы3b Gestalt PsychologyMichell Manisan CorpuzОценок пока нет
- 2d ConceptДокумент30 страниц2d ConceptSidra JavedОценок пока нет
- Perception Sem 2Документ30 страницPerception Sem 2sayam jainОценок пока нет
- A Feature Integration Theory of AttentionДокумент40 страницA Feature Integration Theory of AttentionAna Luisa SanchesОценок пока нет
- History and Use of Gestalt Principles in Contemporary Product Design and Interaction DesignДокумент5 страницHistory and Use of Gestalt Principles in Contemporary Product Design and Interaction DesignRohan JoyОценок пока нет
- Perception (OB)Документ18 страницPerception (OB)Vani GangilОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4-Visual and Perception-StudentДокумент37 страницLesson 4-Visual and Perception-StudentLarh Obese EmmanuelОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles and Gagne's TheoryДокумент7 страницGestalt Principles and Gagne's TheorySHENIVEL BANTEОценок пока нет
- Psychology Assignment (121813801012)Документ7 страницPsychology Assignment (121813801012)Rajiv BhatiaОценок пока нет
- Images and Models of ThoughtДокумент10 страницImages and Models of ThoughtLucas DelgadoОценок пока нет
- Gestalt theory in artДокумент4 страницыGestalt theory in artCholan PillaiОценок пока нет
- Three Forms of Meaning and The Management of Complexity: January 2013Документ48 страницThree Forms of Meaning and The Management of Complexity: January 2013Truman BlkОценок пока нет
- PerceptionДокумент44 страницыPerceptionKrislyEstillorePacalОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Principles Research PaperДокумент8 страницGestalt Principles Research PaperJules Hayward0% (1)
- Gestalt Final Na TalagaДокумент57 страницGestalt Final Na TalagaLovelyann BaytaОценок пока нет
- Visual Theory Notes-VCP AssignmentДокумент4 страницыVisual Theory Notes-VCP Assignmentsheilnandni kaushalОценок пока нет
- Las 3 Explicit and Implicit Claims in Written TextДокумент1 страницаLas 3 Explicit and Implicit Claims in Written Textjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Summative 2Документ1 страницаSummative 2jonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Types of Claims LAS Reading Activity SheetДокумент3 страницыTypes of Claims LAS Reading Activity Sheetjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- CW WHLPДокумент2 страницыCW WHLPjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Learning Competencies:: Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date QuarterДокумент3 страницыLearning Competencies:: Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date Quarterjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- WHLPДокумент2 страницыWHLPjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Weekly Home Learning PlanДокумент2 страницыWeekly Home Learning Planjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- WHLP March CulminatingДокумент3 страницыWHLP March Culminatingjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- WHLPДокумент2 страницыWHLPjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Work Immersion CGДокумент4 страницыWork Immersion CGαλβιν δε100% (16)
- Poetry Elements and GenresДокумент3 страницыPoetry Elements and Genresjonniel caadan100% (1)
- CrosswordДокумент1 страницаCrosswordjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Learning Competencies:: Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date QuarterДокумент3 страницыLearning Competencies:: Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date Quarterjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Learning Competencies:: Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date QuarterДокумент3 страницыLearning Competencies:: Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date Quarterjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Learning Competencies:: Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date QuarterДокумент3 страницыLearning Competencies:: Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date Quarterjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective TeensДокумент2 страницыThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective Teensjonniel caadanОценок пока нет
- Identifying Explicit and Implicit ClaimsДокумент3 страницыIdentifying Explicit and Implicit Claimsjonniel caadan78% (23)
- DLL ClaimsДокумент4 страницыDLL Claimsjonniel caadan100% (3)
- DLL Blank Weekly TemplateДокумент4 страницыDLL Blank Weekly TemplateYenyen Quirog-PalmesОценок пока нет
- Gagne's Nine Events of Instruction for Effective Course DesignДокумент4 страницыGagne's Nine Events of Instruction for Effective Course DesignEda Paje AdornadoОценок пока нет
- Parent Resource PacketДокумент4 страницыParent Resource PacketAya LagangОценок пока нет
- Educating the Emotional Mind for 21st Century SuccessДокумент6 страницEducating the Emotional Mind for 21st Century SuccesstitoОценок пока нет
- Chomsky's influential career in linguistics and politicsДокумент2 страницыChomsky's influential career in linguistics and politicsJaakuna HakaishaОценок пока нет
- The Directive Function of Speech in Development and Dissolution - A. R. LuriaДокумент13 страницThe Directive Function of Speech in Development and Dissolution - A. R. LuriaPamela CОценок пока нет
- Observation Inference-Notes PDFДокумент2 страницыObservation Inference-Notes PDFMery Jean Culanag SapatoseОценок пока нет
- The MYM Method ExplainedДокумент6 страницThe MYM Method ExplainedDanny JiminianОценок пока нет
- KINDERGARTEN-DLL Week 8 (July 22-26, 2019) AsfДокумент7 страницKINDERGARTEN-DLL Week 8 (July 22-26, 2019) AsfDonah FielОценок пока нет
- The Role of Input and Output in Second Language AcquisitionДокумент14 страницThe Role of Input and Output in Second Language AcquisitionAndrea BolañosОценок пока нет
- Solving Math Problems Step-by-StepДокумент7 страницSolving Math Problems Step-by-StepnopriansyahОценок пока нет
- Improving Reading Skills with JigsawДокумент8 страницImproving Reading Skills with JigsawNurhajah Tia SyarifahОценок пока нет
- Standard 8 Reading Comprehension RationaleДокумент2 страницыStandard 8 Reading Comprehension Rationaleapi-510119815Оценок пока нет
- ReadingДокумент5 страницReadingNguyễn Phạm Thảo NguyênОценок пока нет
- Skinner's Radical Behaviorism and Operant ConditioningДокумент10 страницSkinner's Radical Behaviorism and Operant ConditioningAlya YasmineОценок пока нет
- Communicative ApproachДокумент7 страницCommunicative ApproachAshe SoltanovaОценок пока нет
- TIP KitДокумент28 страницTIP KithpnadongОценок пока нет
- ColoursДокумент5 страницColoursPraveena KsОценок пока нет
- LET Reviewer 2019Документ10 страницLET Reviewer 2019shrek09081975100% (4)
- Unraveling Conscious, Subconscious & Unconscious Mind (Goodreads Article For General Reader)Документ3 страницыUnraveling Conscious, Subconscious & Unconscious Mind (Goodreads Article For General Reader)Jazmen folkОценок пока нет
- Development and Evaluation of A Contextualized Reference Material in Social StudiesДокумент13 страницDevelopment and Evaluation of A Contextualized Reference Material in Social StudiesAJHSSR JournalОценок пока нет
- Measurement, Assessment and Evaluation: in Outcome-Based EducationДокумент73 страницыMeasurement, Assessment and Evaluation: in Outcome-Based EducationJhade-Dy TorranoОценок пока нет
- Comparing learning theories and instructional design modelsДокумент26 страницComparing learning theories and instructional design modelsJemilyn PalangdaoОценок пока нет
- Week 4 Assignment Information Processing TheoryДокумент3 страницыWeek 4 Assignment Information Processing TheoryYvette Aguilar-CantuОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Considerations in An Inclusive EnvironmДокумент12 страницCurriculum Considerations in An Inclusive EnvironmRazelle Angiela AvorqueОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Learning Process in 40 CharactersДокумент4 страницыIntroduction to Learning Process in 40 CharactersAzraai AhmadОценок пока нет
- 72 Theories of LearningДокумент20 страниц72 Theories of LearningashleyОценок пока нет
- CW Week 6 Q2Документ3 страницыCW Week 6 Q2Marky LoveОценок пока нет
- Sensory Issues in AutismДокумент22 страницыSensory Issues in Autismapi-212056692100% (1)
- Stages of Development and Developmental Task - ActivityДокумент2 страницыStages of Development and Developmental Task - ActivityMary ann GatanОценок пока нет