Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Installation
Загружено:
SAMMY PALAGANAS0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
20 просмотров11 страницtypes of installation
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документtypes of installation
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
20 просмотров11 страницInstallation
Загружено:
SAMMY PALAGANAStypes of installation
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 11
L.O 2 INSTALL O.
S AND DRIVERS FOR
PERIPHERALS / DEVICES
TYPES OF INSTALLATION
LECTURE ON HARDWARE
SUBJECT
• Objective: after the discussion the trainee/student MUST
able to
• Identify the different types of installation
• Determine the installation process
• Determine what installation will apply
Attended installation
• On Windows systems, this is the most common form of
installation. An installation process usually needs a user who
attends it to make choices, such as accepting or declining an
end-user license agreement (EULA), specifying preferences
such as the installation location, supplying passwords or
assisting in product activation. In graphical environments,
installers that offer a wizard-based interface are common.
Attended installers may ask users to help mitigate the errors.
For instance, if the disk in which the computer program is
being installed was full, the installer may ask the user to
specify another target path or clear enough space in the disk.
•Silent installation
•Installation that does not display messages or
windows during its progress. "Silent installation"
is not the same as "unattended installation" (see
below): All silent installations are unattended but
not all unattended installations are silent. The
reason behind a silent installation may be
convenience or subterfuge. Malware is almost
always installed silently.
• Unattended installation
• Installation that is performed without user interaction during its
progress or with no user present at all. One of the reasons to use
this approach is to automate the installation of a large number of
systems. An unattended installation either does not require the user
to supply anything or has received all necessary input prior to the
start of installation. Such input may be in the form of command line
switches or an answer file, a file that contains all the necessary
parameters. Windows XP and most Linux distributions are examples
of operating systems that can be installed with an answer file. In
unattended installation, it is assumed that there is no user to help
mitigate errors. For instance, if the installation medium was faulty,
the installer should fail the installation, as there is no user to fix the
fault or replace the medium. Unattended installers may record
errors in a computer log for later review.
•Headless installation
•Installation performed without using a computer
monitor connected. In attended forms of
headless installation, another machine connects
to the target machine (for instance, via a local
area network) and takes over the display output.
Since a headless installation does not need a
user at the location of the target computer,
unattended headless installers may be used to
install a program on multiple machines at the
same time.
• Scheduled or automated installation
• An installation process that runs on a preset time or when a
predefined condition transpires, as opposed to an installation
process that starts explicitly on a user's command. For
instance, a system administrator willing to install a later
version of a computer program that is being used can
schedule that installation to occur when that program is not
running. An operating system may automatically install a
device driver for a device that the user connects. (See plug
and play.) Malware may also be installed automatically. For
example, the infamous Conficker was installed when the user
plugged an infected device to their computer.
• Clean installation
• A clean installation is one that is done in the absence
of any interfering elements such as old versions of the
computer program being installed or leftovers from a
previous installation. In particular, the clean
installation of an operating system is an installation in
which the target disk partition is erased before
installation. Since the interfering elements are
absent, a clean installation may succeed where an
unclean installation may fail or may take significantly
longer.
• Network installation
• Not to be confused with network booting.
• Network installation, shortened netinstall, is an
installation of a program from a shared network
resource that may be done by installing a minimal
system before proceeding to download further
packages over the network. This may simply be a copy
of the original media but software publishers which
offer site licenses for institutional customers may
provide a version intended for installation over a
network.
QUIZ
Вам также может понравиться
- (Week 3) Ohs Policies and Procedures: Learning ObjectiveДокумент7 страниц(Week 3) Ohs Policies and Procedures: Learning ObjectiveSAMMY PALAGANASОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- CBLM Module NetworkingДокумент10 страницCBLM Module NetworkingSAMMY PALAGANASОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- CBLM Module HardwareДокумент20 страницCBLM Module HardwareSAMMY PALAGANASОценок пока нет
- Creating Bootable Flash DriveДокумент4 страницыCreating Bootable Flash DriveSAMMY PALAGANASОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Module 1 SIMPLE INTERESTДокумент15 страницModule 1 SIMPLE INTERESTElle Villanueva VlogОценок пока нет
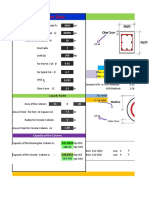
- Column Design With ExcelДокумент40 страницColumn Design With ExcelMatiur Rahman BasumОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Staircase Preliminary Design Based On NBC and IS CodeДокумент10 страницStaircase Preliminary Design Based On NBC and IS CodeEducation. HubОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Princom The Fundamentals of Electronics Module 2Документ9 страницPrincom The Fundamentals of Electronics Module 2melwin victoriaОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Partial Differential Equations (Pdes)Документ5 страницPartial Differential Equations (Pdes)uploadingpersonОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Astron: MFL Testing Procedure For Tank FloorДокумент16 страницAstron: MFL Testing Procedure For Tank FloorleonciomavarezОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Money ComponentsДокумент10 страницMoney ComponentsArifa AkterОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- 2 - EE - Intro - Electronics Pg. 28-41 Op Amp-Merged PDFДокумент402 страницы2 - EE - Intro - Electronics Pg. 28-41 Op Amp-Merged PDFAdelin IonutОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- FMC - Novolastic Subsea Thermal Insulation - LOW RESДокумент3 страницыFMC - Novolastic Subsea Thermal Insulation - LOW RESalphading50% (2)
- Estimation of Microbial GrowthДокумент25 страницEstimation of Microbial GrowthziaiitdОценок пока нет
- HKV-8 Valve Catalog SPLRДокумент128 страницHKV-8 Valve Catalog SPLRCabrera RodriguezОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Completation Inteligent RevistaДокумент9 страницCompletation Inteligent RevistaGabriel Castellon HinojosaОценок пока нет
- Unit 7 Motion Review Sheet AnswersДокумент3 страницыUnit 7 Motion Review Sheet AnswersFlorie Fe Rosario Ortega100% (1)
- Acoustical Materials 2.0Документ16 страницAcoustical Materials 2.0anuragОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Chapter 3.1 - Igneous RockДокумент64 страницыChapter 3.1 - Igneous Rockalvinllp83Оценок пока нет
- Part 01 - Review of EN ISO 9606-1Документ26 страницPart 01 - Review of EN ISO 9606-1Turbo Snail RОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Understanding The Relationship Between Human Behavior and Susceptibility To Cyber AttacksДокумент25 страницUnderstanding The Relationship Between Human Behavior and Susceptibility To Cyber AttacksVelibor SabanОценок пока нет
- Inv ItemДокумент127 страницInv Itemprabhu181Оценок пока нет
- Three-Dimensional Lithium-Ion Battery ModelДокумент35 страницThree-Dimensional Lithium-Ion Battery ModelmortezagashtiОценок пока нет
- Proview TutorialДокумент12 страницProview TutorialManoel NascimentoОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Subjects Revised Curriculum BS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGДокумент18 страницSubjects Revised Curriculum BS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGData StatsОценок пока нет
- Mazda 3Документ5 страницMazda 3Jhony GranadosОценок пока нет
- Cooling Unit SpecДокумент4 страницыCooling Unit Specmirali74Оценок пока нет
- Standarization of Volumetric SolutionsДокумент9 страницStandarization of Volumetric SolutionsZahid IqbalОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- List NotesДокумент27 страницList NotesMohit MauryaОценок пока нет
- Jaap's Puzzle PageДокумент1 страницаJaap's Puzzle PagePhilippe DenielОценок пока нет
- Aksa Ajd170Документ5 страницAksa Ajd170mhmmd14Оценок пока нет
- Bind Second Valve OverviewДокумент27 страницBind Second Valve OverviewNitin AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Computer Science: Chapter: 16 Relatonal DatabaseДокумент10 страницComputer Science: Chapter: 16 Relatonal DatabaseIshika RajputОценок пока нет
- MICOM P12x-TechnicalDataSheetДокумент28 страницMICOM P12x-TechnicalDataSheetSeba GonzálezОценок пока нет